- State the importance of the following in a living organism
- Locomotion. (2marks)
- Respiration (1mark)
- Name the cell organelles which would be abundant in (2marks)
- Sperm cell
- Pancreas.
- State the functions of the following in the heart. (1mk )
- Sino Atrio Node (SAN)
- Interventricular septum
- Name two antigens that determine human blood groups. (2 marks)
-
- Explain why blood group O is a universal donor. (1 mark)
-
- Name the blood vessel that links arterioles to venules. (1 mark)
- What is the adaptive advantage of arteries having a narrower lumen? (1 mark)
-
- Name the tissues that transport water in plants. (1mk)
- State why the tissue above is said to be dead. (1mk)
- The diameter field of view of a light microscopic is 6.5mm. Plant cells lying across the diameter are 12.Determine the size of one cell in micrometers. (2 marks)
- State two adaptations of the phloem tissue. (2 marks)
- Name the process that results to formation of tissue fluid. (1mk)
- What is serum? (1mks)
- The diagram below shows a transverse section of a plant organ.
- Name the class to which the plant organ was obtained. (1mark)
- Give a reason for your answer in (a) above. (1mark)
-
- Which component of the blood gives the body immunity? (1 mark)
- Distinguish between natural and acquired immunity. (2 marks)
-
- Define the term excretion (1mk)
- In what state is water excreted in man? (1mks)
- Why do plants not excrete salts in their excretory products (1mk)
- Under what conditions does a green plant excrete oxygen? (1mks)
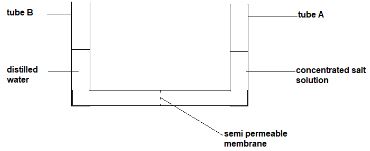
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follows
The experimental set up was left for 8 hours- Using your biological knowledge, show the level of fluids after 8 hours ( 2 marks)
- Which process was being investigated in the experiment? ( 1 mark)
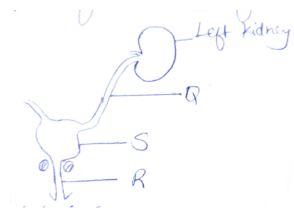
- Study the diagram of excretory system in man and answer the questions that follows
- Name parts labeled (2 marks)
- What is the function of the part labeled S ? (2 marks)
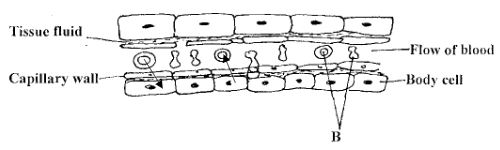
- The diagram below shows gaseous exchange in tissues.
- Name the gas that diffuses:
- To the body cells (1mk)
- From the body cells(1mk)
- name cell labeled B (1mk)
- Which compound dissociates to release the gas named in (a) (i) above?(1mk).
- Name the gas that diffuses:
- Other than carbon (IV)oxide, name other products of anaerobic respiration in plants(2mks)
-
- Name one structures for gaseous exchange in amphibians. (2mks)
- What is the effect of relaxation of diaphragm muscles during breathing in mammals. (3mks)
- State two ways in which respiratory surfaces adapted to their function? (2mks)
- Study the equation below and then answers the questions that follow.
C6 H12 O6 → L+ Energy- Name the process represented by the above equation (1mk)
- Identify substance L (1mk)
- Where in the cell does the above reaction take place? (1mk)
- Name the form in which energy is stored in the body of living organism. (1mk)
- The oxidation of a certain fat is represented by chemical equation shown below.
C57 H104 O6 + 80 O2 → 57CO2 +52H2O + Energy- Calculate the respiratory quotient (RQ) of the fat (2marks)
- What is the significance of RQ? (2marks)
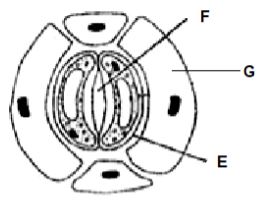
- The diagram below represents part of epidermis of a leaf
- Name the parts marked F and G (2 marks)
- State two aspects of cell E that are an adaptation to its function. (2 marks)
- Describe the changes that would take place in E if the cells were placed in concentrated sugar solution for a long period. (3 marks)
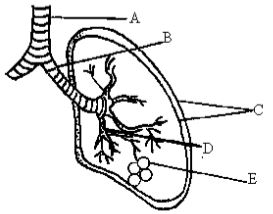
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow
- Name the parts labelled A, B and C (3 marks)
- State the function of the fluid found in between the parts marked C. (1mark)
- How is the part labelled E adapted to its function. (4 marks)
- State the significance of rings of cartilage found around the part marked A and B. (1mark)
- A student found a skull of an animal in the neighborhood of their school. The upper jaw had
4 incissors,2 canines, 6 premolars and 6 premolars and 6 molars- Using the information provided write down the dental formula of the animal (1 marks)
- Give two ways in which incisor differ from a premolar? (2 marks)
- Amylase is an enzyme in the alimentary canal. identify two juices that contains that enzyme (2 marks)
-
- Explain three ways in which a red blood cell is adapted to its functions. (3mks)
- In which form is carbon (IV) oxide transported? (2mks)
- How is the mammalian heart adapted to its functions? (20mks)
MARKING SCHEME
- State the importance of the following in a living organism
- Locomotion. (2marks)
- Acquire resources (food, water shelter);
- Escape from predators;
- to get mates;
- To escape harmful stimuli;
Any two (2mks)
- Respiration (1mark)
- To acquire energy for various activities;
- Locomotion. (2marks)
- Name the cell organelles which would be abundant in (2marks)
- Sperm cell
- Mitochondria
- Pancreas.
- Golgi bodies
- Sperm cell
- State the functions of the following in the heart. (1mk )
- Sino Atrio Node (SAN)
- Regulates the pace at which the heart beats; initiating and maintain contraction of the Heart;
(Any one)
- Regulates the pace at which the heart beats; initiating and maintain contraction of the Heart;
- Interventricular septum
- Prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood;
- Sino Atrio Node (SAN)
- Name two antigens that determine human blood groups. (2 marks)
- Antigen A;
- Antigen B;
- Rhesus factor / Antigen;
-
- Explain why blood group O is a universal donor. (1 mark)
- Lacks antigens to react with the recipient‘s antibodies (to cause agglutination);
-
- Name the blood vessel that links arterioles to venules. (1 mark)
- Capillaries;
- What is the adaptive advantage of arteries having a narrower lumen? (1 mark)
- To create/sustain higher blood pressure; (which moves the blood to all body parts from the heart)
- Name the blood vessel that links arterioles to venules. (1 mark)
- Explain why blood group O is a universal donor. (1 mark)
-
- Name the tissues that transport water in plants. (1mk)
- Xylem
- State why the tissue above is said to be dead. (1mk)
- Lacks cytoplasm and organelles;
- Name the tissues that transport water in plants. (1mk)
- The diameter field of view of a light microscopic is 6.5mm. Plant cells lying across the diameter are 12.Determine the size of one cell in micrometers. (2 marks)
Cell size = Diameter of field of view x 100
No of cells
= 6.5 x 1000
12
= 540μm - State two adaptations of the phloem tissue. (2 marks)
- Have cytoplasmic filaments along which food is translocated;
- sieve plate has pores for passage of organic material;
- Have companion cell which have numerous mitochondria to provide energy for tlanslocation;
- Presence of plasmodesmata to communicate between sieve tube elements and companion cells.
- Name the process that results to formation of tissue fluid. (1mk)
- Ultra filtration;
- What is serum? (1mks)
- Serum is blood whose plasma proteins have been removed.
- The diagram below shows a transverse section of a plant organ.
- Name the class to which the plant organ was obtained. (1mark)
- Monocotyledonae;
- Give a reason for your answer in (a) above. (1mark)
- Vascular bundles scattered/not arranged in a ring; absence of pith; absence of vascular cambium;
- Name the class to which the plant organ was obtained. (1mark)
-
- Which component of the blood gives the body immunity? (1 mark)
- White blood cells
- Distinguish between natural and acquired immunity. (2 marks)
- Natural immunity is inherited / transmitted from parents to off springs; Acquired immunity is acquired after suffering from a disease / through vaccination /vaccination through inoculation / through introducing antibodies. (Rej. Immunisation alone)
- Which component of the blood gives the body immunity? (1 mark)
-
- Define the term excretion (1mk)
- Process by which plants get rid of metabolic wastes.
- In what state is water excreted in man? (1mks)
- Liquid
- Water vapour any correct
- Why do plants not excrete salts in their excretory products (1mk)
- They absorb enough of what they require/ not in excess
- Define the term excretion (1mk)
- Under what conditions does a green plant excrete oxygen? (1mks)
- When the rate of photosynthesis is greater/ higher than the rate of respiration in plant leaves which utilize the oxygen release
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follows
The experimental set up was left for 8 hours- Using your biological knowledge, show the level of fluids after 8 hours ( 2 marks)
- The level of the fluid in delivery tub A should rise; while in the tube B it should be lower
( any level qualifies for a mark)
- The level of the fluid in delivery tub A should rise; while in the tube B it should be lower
- Which process was being investigated in the experiment? ( 1 mark)
- osmosis
- Using your biological knowledge, show the level of fluids after 8 hours ( 2 marks)
- Study the diagram of excretory system in man and answer the questions that follows
- Name parts labeled (2 marks)
- Q ureter
- R urethra
- What is the function of the part labeled S ? (2 marks)
- To collect urine from( both) kidneys ; and temporarily stores it ;( before it is excrete)
NB:Temporarity must be there to qualify for mark.
- To collect urine from( both) kidneys ; and temporarily stores it ;( before it is excrete)
- Name parts labeled (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows gaseous exchange in tissues.
- Name the gas that diffuses:
- To the body cells (1mk)
- Oxygen
- From the body cells(1mk)
- Carbon IVoxide
- To the body cells (1mk)
- name cell labeled B(1mk)
- red blood cell/erythrocytes
- Which compound dissociates to release the gas named in (a) (i) above?(1mk).
- Oxyhaemoglobin
- Name the gas that diffuses:
- Other than carbon (IV)oxide, name other products of anaerobic respiration in plants(2mks)
- Ethanol
- Energy / ATP/ 210kJ / heat;
Rej. atp, formula of alcohol.
- Name one structures for gaseous exchange in amphibians. (2mks)
- Skin ;Buccal cavity ; lungs; (any two)
- What is the effect of relaxation of diaphragm muscles during breathing in mammals. (3mks)
- It decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity; and increases the pressure inside; thus air is forced out of the lungs through the air passage into the atmosphere
- Name one structures for gaseous exchange in amphibians. (2mks)
- State two ways in which respiratory surfaces adapted to their function? (2mks)
- Has thin membrane to reduce distance over which gases diffuse;
- Moist to dissolve gases before they diffuse;
- Have large surface area to maximize gaseous exchange
- Are well ventilated to allow free movement of gases
- Are highly vascularized to transport the diffused gases
- Study the equation below and then answers the questions that follow.
C6 H12O6 L → L+ Energy- Name the process represented by the above equation (1mk)
- Anaerobic respiration in animals
- Identify substance L (1mk)
- Lactic acid
- Where in the cell does the above reaction take place? (1mk)
- cytoplasm
- Name the form in which energy is stored in the body of living organism. (1mk)
- Adenosine triphosphate
- Name the process represented by the above equation (1mk)
- The oxidation of a certain fat is represented by chemical equation shown below.
C57 H104 O6 + 80 O2 → 57CO2 +52H2O + Energy- Calculate the respiratory quotient (RQ) of the fat (2marks)
RQ = volume of carbon (IV)oxide released
Volume of oxygen released
57
80
= 0.7125 - What is the significance of RQ? (2marks)
- It gives the type of substrate undergoing respiration;
- It gives the type of respiration taking place;
- Calculate the respiratory quotient (RQ) of the fat (2marks)
- The diagram below represents epidermis of a leaf
- Name the parts marked F and G (2 marks)
- F – Stomatal opening/stoma;
- G – Epidermal cell;
- State two aspects of cell E that are an adaptation to its function. (2 marks)
- Thick inelastic inner wall; thin elastic outer wall;
- Has chloroplast for photosynthesis;
- Its bean shaped to create an aperture between two guard cells
- Describe the changes that would take place in E if the cells were placed in concentrated sugar solution for a long period.
(3 marks)- Water would leave vacuole and cytoplasm by osmosis; They shrunk and cell membrane draws away from the cell wall; the guard cell becomes plasmolysed; stoma is closed;
- Name the parts marked F and G (2 marks)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow
- Name the parts labelled A, B and C (3 marks)
- Trachea
- Bronchus; reject bronchi
- Pleural membranes; reject membrane
- State the function of the fluid found in between the parts marked C. (1mark)
- Reduce friction making the lungs to move freely in the chest cavity
- How is the part labelled E adapted to its function. (4 marks)
- Moist to dissolve respiratory gases
- Highly supplied with blood capillaries to transport
- Enclosed by thin membrane to reduce distance over which diffusion gases move.
- Numerous-large surface area to make gaseous exchange efficient increase the rate of gaseous exchange
- State the significance of rings of cartilage found around the part marked A and B. (1mark)
- Prevent it from collapsing during breathing
- Name the parts labelled A, B and C (3 marks)
- A student found a skull of an animal in the neighborhood of their school. The upper jaw had 4 incissors,2 canines, 6 premolars and 6 premolars and 6 molars
- Using the information provided write down the dental formula of the animal (1 marks)
- i2; c1; pm3; m3
2 1 3 3
- i2; c1; pm3; m3
- Give two ways in which incisor differ from a premolar? (2 marks)
- incisor has a sharp edge; its top is chisel shaped; it has one root
- Anylase is an enzyme in the alimentary canal. identify two juices that contains that enzyme (2 marks)
- Saliva
- Pancreatic juice
- Using the information provided write down the dental formula of the animal (1 marks)
- Explain three ways in which a red blood cell is adapted to its functions. (3mks)
- Have biconcave disc shape which increases the surface area for exchange of gases by diffusion;
- Have haemoglobin which has high affinity for oxygen; (hence faster transportation of oxygen).
- Lacks nucleus to provide more room for packaging of haemoglobin;
- Have thin plasma membrane that allows faster / rapid diffusion of gases;
- Have carbonic anhydrase which accelerates loading and off-loading of carbon (IV) oxide for faster offloading of carbon (IV) oxide transport. (any three)
- In which form is carbon (IV) oxide transported? (2mks)
- Carbamino hemoglobin;
- Carbonic acid;
- Explain three ways in which a red blood cell is adapted to its functions. (3mks)
ESSAY.
- How is the mammalian heart adapted to its functions?
- Heart is enclosed in a pericardial membrane/pericardium; that- produces a fluid; to lubricate it;
- the membrane also keeps the heart in position;
- Prevent heart from overstretching
- It is covered in a fatty layer; that acts as a shock absorber;
- made up of cardiac muscles; which are interconnected/intercalated hence contract and relax without fatigue or nervous stimulation/myogenic; for continuous pumping of blood throughout the lifespan of the animal;
- the muscles are supplied by nutrients and oxygen; by the coronary arteries; and the coronary veins take away wastes and carbon (IV) oxide;
- has interventricular septum; to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood;
- left ventricle has thicker muscles/more muscular; to generate high pressure to pump blood to all body tissues;
- heart has bicuspid; and tricuspid valves; to prevent back flow of blood to left auricle; and right auricle respectively;
- valves have tendinous cords/valve tendons; to prevent them from turning inside out;
- semi lunar valves located at the beginning of major arteries; prevent backflow of blood into the ventricles;
- has sino-artrio node located in the muscles of the right auricle; to initiate heart beat/contractions of heart muscles/cardiac muscles,
- rate of heart beat is controlled by nerves; vagus nerve; slows down heartbeat; while sympathetic nerve; speeds up the heartbeat;
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Questions and Answers - Form 2 End Term 2 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students