INSTRUCTIONS:
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided for each question.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- Mathematical tables and non-programmable electronic calculators may be used.
- Draw a diagram of the apparatus used to measure accurately 250cm3 of liquids or solutions. (1 mark)
- In the laboratory, there are two types of flames; with reasons, state which flame is used for:
- Heating……………(1 mark)
- Lighting……………(1 mark)
- Define the term drug abuse. (1 mark)
- Shanty accidentally mixed iron fillings, iron (III) chloride crystals and sulphur powder. Describe how she would obtain each of the substances separately. (3 marks)
- Classify the following as either chemical or physical changes. (5 marks)
Process Type of change Electrical conductivity by copper wire Rusting of an iron nail Sublimation of iodine Burning candle wax Attraction of iron filings by a magnet - Matter exists in three states. Describe how particles behave in each state according to kinetic theory of matter.
- Solid state: (2 marks)
- Liquid state: (2 marks)
- Gaseous state: (2 marks)
- Explain how acid rain can be formed. (2 marks)
- Solutions may be classified as strongly basic, weakly basic, neutral, weakly acid, or strongly acidic. The information below gives solutions and their pH values. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Classify the solutions in the table using the stated classifications. (2 Marks)Solution pH value Nature of solution B 0.5 C 6 - A farmer tested soil in his farm and found out that its pH was 5.5. This was below the recommended pH of 7.0. Suggest how the farmer could achieve the recommended pH of soil in his fam. (1 mark)
- Name three gaseous components of unpolluted air. (3 marks)
- Zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric (VI) acid to produce a colourless gas. Write an equation for the reaction. (1 mark)
- Describe a test for the colourless gas. (2 marks)
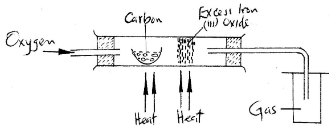
- The set – up below was used to obtain a sample of iron metal.
- Write two equations for the reactions which occur in the combustion tube. (2 marks)
Equation 1: .........................................................................................................................................................
Equation 2: ......................................................................................................................................................... - Name the gas collected in the gas jar. ...…………………………………… (1 mark)
- Give two uses of carbon (II) oxide that are also uses of hydrogen. (2 marks)
- Write two equations for the reactions which occur in the combustion tube. (2 marks)
-
- Name one natural source of water for a chemical industry. (1 mark)
- Kerosene is a hydrocarbon. Name the product of burning kerosene that is a liquid at room temperature. (1 mark)
- Metal Y can displace metal X from its oxide. Hydrogen can reduce the oxide of metal X. Metal X does not react with water, while metal Y reacts with water moderately. Metal Z reacts with explosively with water. Arrange the metals and hydrogen from the most reactive. (1 mark)
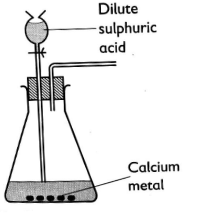
- The set-up below was used to prepare a gas Q.
- Complete the diagram to show how a dry sample of gas Q may be collected. (2 marks)
- Give a reason why calcium is not the most appropriate metal for use in this preparation. (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction for the formation of gas Q. (1 mark)
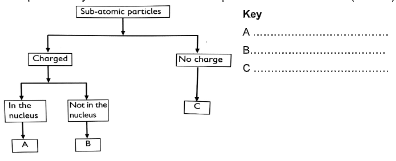
- Complete the key shown below for sub atomic particles. (3 marks)
- The relative atomic mass of element Y which consists of the isotopes 20Y and 22Y is 20.2. Calculate the percentage of the atoms in the isotopic mixture. (3 marks)
- The ionic radii of the ions of Q and R are given as follows: Q2+ = 2,8,8 and R- = 2,8.
- Complete the table below: (2 marks)
Element Group Period Q R - Write the formula of the product formed when Q and R react. (1 mark)
- Complete the table below: (2 marks)
- The halogens are a group of non-metals in Group VII of the Periodic Table.
- Describe an experiment which shows that chlorine is more reactive than iodine. Include an equation in your answer. (3 marks)
- State two observations made when warm sodium metal in a deflagrating spoon is lowered in a gas jar full of chlorine gas? (2 marks)
- Write an equation for the reaction in (b) above. (1 mark)
- The following table gives the number of protons in the nucleus of some elements. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of elements. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
Element E F G H I J K L Number of protons 3 12 6 17 10 19 14 35 - Which elements belong to the same group of the periodic table? (2 marks)
- How will the reactivity of element F compare with that of element K? Explain. (2 marks)
- The atomic numbers of elements X and W are 11 and 16 respectively.
- Write the electronic arrangements of the elements. (1 mark)
- Element X……………………………………
- Element W…………………………………
- Predict the type of bonding in the product formed if elements W and X were to be reacted. Give the formula of the resulting compound. (2 marks)
- Type of bond……………………………………
- Formula of compound ………………………
- Write the electronic arrangements of the elements. (1 mark)
- The table below show the physical properties of some substances. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
Substance Melting point (°C) Boiling point (°C) Electrical conductivity Solid Liquid U 1083 2595 Good Good V 801 1413 Poor Good W 6 80 Poor Poor X −114 −84 Poor Poor Y 3550 4287 Poor Poor - Which substance is likely to be; (1 mark)
- An element ……………………………
- A liquid at 22°C ………………………….
- Which substance is likely to have the following structures? (3 marks)
- Simple molecular structure …………………………………………………………….
- Giant ionic structure ………………………………………………………………………
- Giant atomic structure ……………………………………………………………………
- Which substance is likely to be; (1 mark)
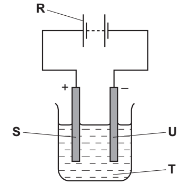
- The diagram below shows the apparatus used for the electrolysis of molten sodium bromide.
- What does the term electrolysis mean? (1 mark)
- Which letter R, S, T or U on the diagram represents the cathode? (1 mark)
- State the observation made at the anode. (1 mark)
- Which condition is missing in the set-up? …………………………………… (1 mark)
- Write the half equation for the reaction at: (2 marks)
- Cathode: …………………………………………………………………………………….
- Anode: ……………………………………………………………………………………….
- State Graham’s Law of diffusion. (1 mark)
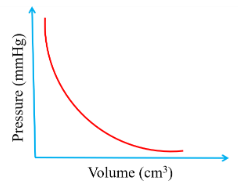
- Sketch a curve to illustrate the relationship between the volume of a fixed mass of a gas and its pressure at constant temperature. (1 mark)
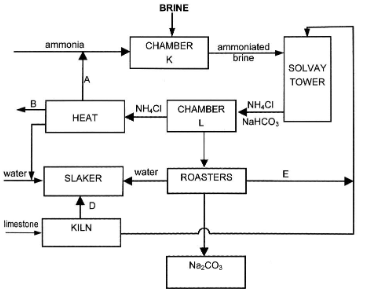
- Study the flow chart below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the substances labelled A, B, D and E. (2 marks)
- Cold water is made to circulate around chamber K. Suggest a reason for this. (1 mark)
- Give one reason for recycling in this process. (1 mark)
- Write down the equations for the reactions taking place in:
- The kiln (1 mark)
- Solvay tower (overall equation) (1 mark)
- Give two uses of substance B. (1 mark)
- Describe an experiment that can be used to prepare a solid sample of sodium hydrogen carbonate in the laboratory starting with sodium metal. (3 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
- Draw a diagram of the apparatus used to measure accurately 250cm3 of liquids or solutions. (1 mark)
- In the laboratory, there are two types of flames; with reasons, state which flame is used for:
- Heating……nonluminous flame because it is very hot (1 mark)
- Lighting……… luminous flame because it produces a lot of light (1 mark)
- Define the term drug abuse. (1 mark)
- The use of a drug for purposes other than the intended purposes or overdose or underdose of a drug.
- Shanty accidentally mixed iron fillings, iron (III) chloride crystals and sulphur powder. Describe how she would obtain each of the substances separately. (3 marks)
- Spread the mixture on a flat surface. Pass a magnet repeatedly over the mixture to attract iron filings. Heat the remaining mixture, iron (III) chloride sublimes and it is collected on a cool surface leaving behind sulphur.
- Classify the following as either chemical or physical changes. (5 marks)
Process Type of change Electrical conductivity by copper wire physical Rusting of an iron nail chemical Sublimation of iodine physical Burning candle wax chemical Attraction of iron filings by a magnet physical - Matter exists in three states. Describe how particles behave in each state according to kinetic theory of matter.
- Solid state: (2 marks)
- The particles vibrate in fixed positions due to strong forces of attraction between the particles.
- Liquid state: (2 marks)
- The particles move within the liquid due to moderate forces of attraction between the particles.
- Gaseous state: (2 marks)
- The particles move in all directions randomly because there are very weak forces of attraction between the particles.
- Solid state: (2 marks)
- Explain how acid rain can be formed. (2 marks)
- Industrial gases such as sulphur (IV) oxide and nitrogen (IV) oxide are acidic. When they are released into the atmosphere, they react with rain water which falls down as acid rain.
- Solutions may be classified as strongly basic, weakly basic, neutral, weakly acid, or strongly acidic. The information below gives solutions and their pH values. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Classify the solutions in the table using the stated classifications. (2 Marks)Solution pH value Nature of solution B 0.5 Strongly acidic C 6 Weakly acidic - A farmer tested soil in his farm and found out that its pH was 5.5. This was below the recommended pH of 7.0. Suggest how the farmer could achieve the recommended pH of soil in his fam. (1 mark)
- Add lime/ CaO /Ca(OH)2 to the soil to neutralize acidity
- Name three gaseous components of unpolluted air. (3 marks)
- Oxygen, dust, nitrogen, noble gases, water vapour.
-
- Zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric (VI) acid to produce a colourless gas. Write an equation for the reaction. (1 mark)
Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g) - Describe a test for the colourless gas. (2 marks)
- Place a burning splint at the mouth of a gas jar with the colourless gas. It extinguishes the burning splint with a pop sound.
- Zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric (VI) acid to produce a colourless gas. Write an equation for the reaction. (1 mark)
- The set – up below was used to obtain a sample of iron metal.
- Write two equations for the reactions which occur in the combustion tube. (2 marks)
- Equation 1: C(s) + O2(g) → CO(g)
- Equation 2: Fe2O3(s) + 3CO(g) → 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g)
- Name the gas collected in the gas jar. (1 mark)
- carbon (IV) oxide
- Give two uses of carbon (II) oxide that are also uses of hydrogen. (2 marks)
- Used as a fuel
- Used as a reducing agent
- Write two equations for the reactions which occur in the combustion tube. (2 marks)
-
- Name one natural source of water for a chemical industry. (1 mark)
- Rivers, lakes, oceans, boreholes, springs
- Kerosene is a hydrocarbon. Name the product of burning kerosene that is a liquid at room temperature. (1 mark)
- water
- Metal Y can displace metal X from its oxide. Hydrogen can reduce the oxide of metal X. Metal X does not react with water, while metal Y reacts with water moderately. Metal Z reacts with explosively with water. Arrange the metals and hydrogen from the most reactive. (1 mark)
- Z>Y>X
- Name one natural source of water for a chemical industry. (1 mark)
- The set-up below was used to prepare a gas Q.
- Complete the diagram to show how a dry sample of gas Q may be collected. (2 marks)
- Give a reason why calcium is not the most appropriate metal for use in this preparation. (1 mark)
- Calcium metal reacts with dilute sulphuric (VI) acid to form insoluble calcium sulphate which coats the metal preventing further reaction.
- Write an equation for the reaction for the formation of gas Q. (1 mark)
Ca(s) + H2SO4(aq) → CaSO4(s) + H2(g)
- Complete the diagram to show how a dry sample of gas Q may be collected. (2 marks)
- Complete the key shown below for sub atomic particles. (3 marks)
Key- A - protons
- B- electrons
- C - neutrons
- The relative atomic mass of element Y which consists of the isotopes 20Y and 22Y is 20.2. Calculate the percentage of the atoms in the isotopic mixture. (3 marks)
(20 × x) + (22 × (100 − x) = 20.2
100
20x + 2200 − 22x = 2020
−2x = − 180
x = 90
100 − x = 10
∴ 90% for 20Y
10% for 22Y - The ionic radii of the ions of Q and R are given as follows: Q2+ = 2,8,8 and R- = 2,8.
- Complete the table below: (2 marks)
Element Group Period Q Group II Period 4 R Group IV Period 2 - Write the formula of the product formed when Q and R react. (1 mark)
- QR
- Complete the table below: (2 marks)
- The halogens are a group of non-metals in Group VII of the Periodic Table.
- Describe an experiment which shows that chlorine is more reactive than iodine. Include an equation in your answer. (3 marks)
- Bubble chlorine through a solution of potassium iodide. A brown solution is formed
- State two observations made when warm sodium metal in a deflagrating spoon is lowered in a gas jar full of chlorine gas? (2 marks)
- Sodium burns with a bright yellow flame.
- A white solid is formed
- Write an equation for the reaction in (b) above. (1 mark)
2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s)
- Describe an experiment which shows that chlorine is more reactive than iodine. Include an equation in your answer. (3 marks)
- The following table gives the number of protons in the nucleus of some elements. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of elements. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Which elements belong to the same group of the periodic table? (2 marks)
- E , I and G or F, H, J and K
- How will the reactivity of element F compare with that of element K? Explain. (2 marks)
- Element F us more reactive than element K because element F can easily lose electrons than element K.
- Which elements belong to the same group of the periodic table? (2 marks)
- The atomic numbers of elements X and W are 11 and 16 respectively.
- Write the electronic arrangements of the elements. (1 mark)
- Element X – 2.8.1
- Element W- 2.8.6
- Predict the type of bonding in the product formed if elements W and X were to be reacted. Give the formula of the resulting compound. (2 marks)
- Type of bond – ionic bond
- Formula of compound - X2W
- Write the electronic arrangements of the elements. (1 mark)
- The table below show the physical properties of some substances. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Which substance is likely to be; (1 mark)
- An element - W, X, U or Y
- A liquid at 22°C - W
- Which substance is likely to have the following structures? (3 marks)
- Simple molecular structure - X
- Giant ionic structure - V
- Giant atomic structure - Y
- Which substance is likely to be; (1 mark)
- The diagram below shows the apparatus used for the electrolysis of molten sodium bromide.
- What does the term electrolysis mean? (1 mark)
- The decomposition of a substance by use of electricity.
- Which letter R, S, T or U on the diagram represents the cathode? (1 mark)
- U
- State the observation made at the anode. (1 mark)
- A brown gas is formed
- Which condition is missing in the set-up? - heat (1 mark)
- Write the half equation for the reaction at: (2 marks)
- Cathode: 2Na+(l) → 2Na(s) + 2e-
- Anode: Br-(l) + 2e- → Br2(g)
- What does the term electrolysis mean? (1 mark)
- State Graham’s Law of diffusion. (1 mark)
- The rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its density as long as temperature and pressure are kept constant.
- Sketch a curve to illustrate the relationship between the volume of a fixed mass of a gas and its pressure at constant temperature. (1 mark)
- Study the flow chart below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the substances labelled A, B, D and E. (2 marks)
- A – ammonia
- B – Calcium chloride
- D – Calcium oxide
- E – Carbon (IV) oxide
- Cold water is made to circulate around chamber K. Suggest a reason for this. (1 mark)
- To cool it since the reactions in chamber K are exothermic
- To crystallize sodium hydrogen carbonate
- Give one reason for recycling in this process. (1 mark)
- To minimize cost of production
- To prevent pollution
- Write down the equations for the reactions taking place in:
- The kiln (1 mark)
CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g) - Solvay tower (overall equation) (1 mark)
NH3(g) + H2O(l) + CO2(l) + NaCl(aq) → NaHCO3(s) + NH4Cl(aq)
- The kiln (1 mark)
- Give two uses of substance B. (1 mark)
- Used in deicing roads in the temperate regions in winter
- Used as a drying agent
- Used to prevent dust from rising in mine floors
- Used in road surfacing
- Used in the extraction of sodium from molten rock salt.
- Name the substances labelled A, B, D and E. (2 marks)
- Describe an experiment that can be used to prepare a solid sample of sodium hydrogen carbonate in the laboratory starting with sodium metal. (3 marks)
- Add small pieces of sodium metal to water one at a time to form a solution of sodium hydroxide. Bubble excess carbon (IV) oxide into the sodium hydroxide solution to form sodium hydrogen carbonate solution. Gently heat the solution to saturation and allow it to cool to form crystals. Pour out the mother liquor and dry the crystals between filter papers.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Questions and Answers - Form 2 End Term 3 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students