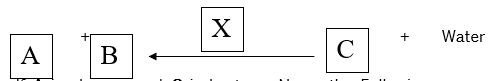INSTRUCTIONS
- Write your answers correctly and clearly in the spaces provided
- Be keen on Spelling of Technical Terms
- Name the branch of Biology that deals with the study of the following:
- Classification of living organisms (1mk)
- Internal structure of an organism (1mk)
- Explain why an insect needs to undertake gaseous exchange (2mks)
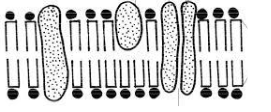
- Identify and state the function of each of the following apparatus (4mks)
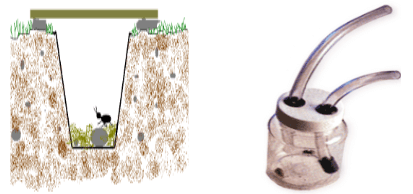
-
- Write down the formula for calculating magnification when using a light microscope to observe specimen (1mk)
- Sam drew the rear leg of a grasshopper which measured 45mm on the insect. If he used a magnification of X0.5, calculate the length of the leg drawn in centimeters. (3mks)
- Use the diagram shown to answer the questions that follow
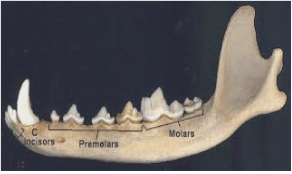
- Name the mode of feeding for the animal whose lower jaw is shown above (1mk)
- Give TWO reasons for your answer in a) above (2mks)
- Account for the following observations
- A mountain climber has more red blood cells than a person of the same size, age and gender living in low lands (2mks)
- A baby has higher energy requirement than an adult (2mks)
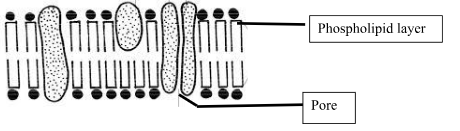
- The diagram shown below is of a structure found in cells
- Label the following parts: Phospholipid layer; a pore (2mks)
- State TWO properties of the structure above (2mks)
-
- Define the term ‘active transport’ (1mk)
- Give TWO ways in which active transport and diffusion are different .(2mks)
- State the economic importance of the following excretory products from plants (3mks)
- Papain: ……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Quinine: ……………………………………………………………………………………………………...
- Colchicine: ………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- The following diagram is a cross section of a dicot plant
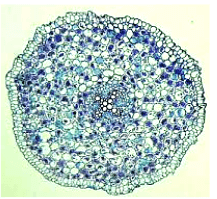
- From which organ of the plant was the cross section above obtained? (1mk)
- Give a reason for your answer in a) above (1mk)
-
- How is large surface area achieved in red blood cells in order to enable them be efficient at their function. (2mks)
- Give TWO advantages of Carbon (IV) Oxide transportation by the red blood cells (2mks)
- Distinguish between the following terms:
- Allograft and isografts (2mks
- Guttation and Transpiration (2mks
-
- Explain how the following antibodies defend the body against pathogens
- Lysins……………………(1mk)
- Agglutinins………………(1mk)
- Which other way do White Blood Cells defend the body against pathogens in addition to use of antibodies? 1mk
- Explain how the following antibodies defend the body against pathogens
-
- What is the role of proximal convoluted tubule in the kidney? (1mk
- Give TWO adaptations of proximal convoluted tubule to its function (2mks
- Name the organelles that form the following: (2mks
- Ribosomes …………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Lysosomes: …………………………………………………………………………………………..
- State THREE structural differences between arteries and veins (3mks
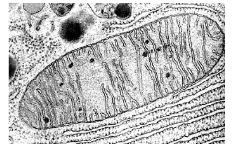
- Study the diagram shown below
- State the adaptation of the organelle shown above to its function .(1mk
- Name TWO products from the process that takes place in the organelle shown above which are useful in the physiological process that occurs in the chloroplast of plant cells (2mks
- Why do Red Blood Cells lack the organelle shown above? (1mk
-
- What is an enzyme? (1mk
- Give THREE factors that increase rate of enzymatic reactions (3mks
- The table below shows the number of various teeth in the jaws of an animal
Canines Molars Incisors Premolars Lower Jaw 2 6 4 4 Upper Jaw 2 6 0 4 - Determine the total number of teeth the animal has (1mk
- Write down the dental formula of the animal whose teeth are shown on the table above (1mk
- With a reason, determine the mode of feeding of the animal represented above (2mks
- Mode of Feeding…………………………………………………………………………………………
- Reason……………………………………………………………………………………………………
-
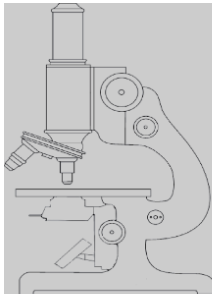
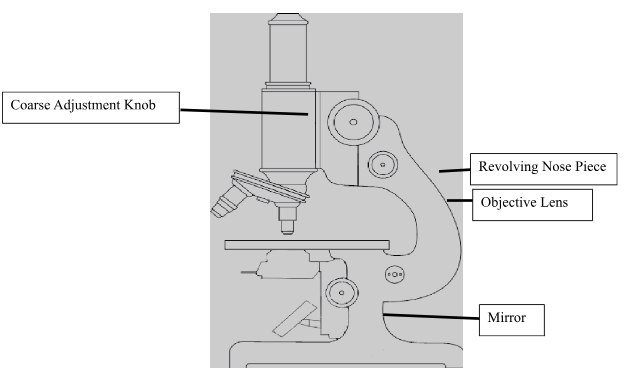
- Label the following parts of the light microscope on the diagram shown below (4mks
Coarse Adjustment Knob; Revolving Nose Piece; Mirror; Objective lens - State TWO precautions observed before storage of the light microscope (2mks
- Label the following parts of the light microscope on the diagram shown below (4mks
- Consider the following experimental set up used to investigate a physiological process
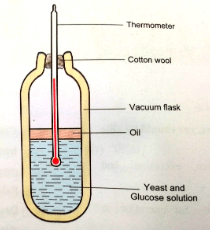
- What was the aim of the experiment? (1mk
- Account for the change that will take place in the thermometer (2mks
- Suggest a control for the experiment shown above (1mk
- Consider the following equation of a chemical equation
If A is glucose and C is Lactose, Name the Following- Enzyme X ………………………………………..….(1mk
- Compound B …………………………………………(1mk
- The following diagram shows onions cells captured in a field of view of a light microscope.
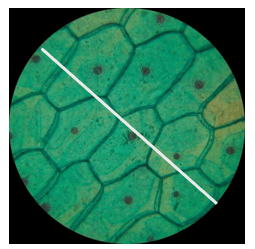
- Measure the length of the white line to determine the diameter of the field of view in millimeters (1mk
- How many cells are found along the diameter represented by the white line? (1mk
- Determine the actual diameter of one cell if a magnification of X1000 was used to observe the cells above (3mks
- State a weakness of the process above of estimating cell size (1mk)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Taxonomy;
- Anatomy;
- Supply Oxygen needed for Respiration/Oxidation of food; Expel Carbon (IV) Oxide (whose accumulation in the body will be toxic);
-
- Pitfall Trap; Trap small crawling animals;
- Pooter; Suck small animals on tree barks/rocks;
-
- = Eye Piece Lens Magnification X Objective Lens Magnification;
REJ if the word ‘Magnification’ is omitted - Magnification = (object length/Image length)
Image length = Object length/Magnification)
= 45mm/0.5;
= 90mm
But 10mm = 1cm
Thus 90mm = (90mm X 1cm)/10mm; NB: Deny Mark if Units not shown here
Image length = 9cm; NB: Deny Mark if Units not shown here
- = Eye Piece Lens Magnification X Objective Lens Magnification;
-
- Carnivorous;
- Long curved canine; Has Carnassial tooth;
-
- Increase Surface area to capture Oxygen molecules; Since higher altitudes have lower Oxygen Concentration;
- More Physically Active than an adult; Still Undergoing rapid growth/cell division; Larger surface area thus loses more heat energy per unit area, thus needs more to compensate for the lost one;
-
-
- Semi-permeable/selectively permeable; polarized/has negative and positive charges; sensitive to changes in temperature/ Denatured by temperature beyond 40°C;
-
-
- Movement of particles against concentration gradient by use of energy;
-
Active Transport Diffusion Molecules Move against Concentration gradient/ Molecules Move along the Concentration Gradient; Requires Energy/Is an Active Process Energy Not Required/Is Passive; Uses Carrier Molecules Carrier Molecules Not Required;
-
- Papain-Meat Tenderizer;
- Quinine-Treatment of Malaria;
- Colchicine-Anti-cancer therapy; Genetic Research;
-
- Root;
- Star-shaped Xylem; Xylem is central;
-
- Are Numerous; Biconcave Shape;
- pH of blood not altered; faster/efficient (due to action of enzyme carbonic anhydrase);
-
-
- Allograft-Graft/Organs from persons who are not genetically identical;
- Isografts-Grafts from genetically identical twins; NB: Award at each point
-
- Guttation: Loss of Water in Liquid form/: Loss of Water in Liquid form through hydathodes
- Transpiration: Loss of water vapour/Loss of water vapour via Stomata/Lenticels/Pneumatophore; NB: Award at each point
-
-
-
- Lysins: Digest Cell membranes or Cell wall of pathogens;
- Agglutinins: Clump pathogens together thus stops them from multiplication/ ease ingestion of pathogens by phagocytes;
- Phagocytosis/Being Ingested/Engulfed (by Granulocytes/Monocytes);
-
-
- Selective reabsorption of nutrients;
- Long to increase surface area for reabsorption of nutrients; Highly coiled to slow down movement of renal fluids for efficient reabsorption; Numerous micro-villi to increase surface area for reabsorption of nutrients; Numerous mitochondria to supply enough energy for reabsorption of nutrients; thin inner lining to a offer a shorter distance for faster diffusion of nutrients into the blood stream; Mark 1st TWO
-
- Nucleolus;
- Golgi apparatus/Golgi bodies;
-
ARTERY VEIN Narrow Lumen Wider Lumen; Thick Muscular and Elastic Wall Thin Less Muscular and inelastic Wall; Lack Valves along its length Have Veins along its length; -
- Highly folded inner membrane/Has cristae to increase surface area for attachment of more respiratory enzymes;
- Energy/Adenosine Triphosphate; Carbon (IV) Oxide;
- Prevent Oxygen utilization thus increase efficiency in Oxygen transport;
-
- It is a Bio-catalyst/Catalyzes/Increases rate of metabolic reactions;
- Optimum temperature; Optimum pH; Higher Enzyme Concentration; Higher Concentration of Enzyme co-factors/co-enzymes; Lack of/Lower concentration of Inhibitors; Lower Concentration of Substrate; Mark 1st 3
-
- Total Number of Teeth = (2+2+6+6+4+4+4) = 28;
- i 0 c 1 pm 2 m 3 ; REJ: Capital letters; Lack of Fractions
2 1 2 3 - Herbivorous; Lack incisors in the upper jaw; REJ: Has Horny pad;
-
-
- Clean lenses with a soft lens tissue; Clean other parts using a soft cloth/tissue paper; Click the Low Power Objective Lens into Position; Store in a cabinet away from dust; Mark 1st 2
-
-
- To find out if heat energy is released during respiration;
- Increase in temperature recorded by the thermometer; since yeast beaks glucose through respiration to release heat;
- Same set up but without yeast;
-
- Lactase;
- Galactose;
-
- 62mm;
- 6 (cells);
- Observed Diameter of Cell = Diameter of Field of View/Number of cells
= 62mm/6cells
= 10.33mm; NB: Deny Mark if Units not shown here
Actual Diameter of 1 cell = Diameter of Observed cell/Total Magnification
= 10.33mm/1000; NB: Deny Mark if Units not shown here
= 0.0103mm; NB: Deny Mark if Units not shown here - Cells are not linearly/uniformly arranged along the diameter of field of vies; Cells are of different Size; Cells are of different Shapes;
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Questions and Answers - Form 2 End Term 3 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students