INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper consists to three sections A, B and C.
- Answer all questions in sections A and B.
- Answer any two questions in section C in the attached foolscaps.
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section.
- Differentiate between pork and bacon. (1 mark)
- What is a capon in agriculture? (1 mark)
- Name one appropriate equipment used to administer liquid dewormer to calves. (1 mark)
- State two features of indigenous cattle (Bos indicus) that make them more adaptable to tropical climates. (2 marks)
- Name two dairy goat breeds reared in Kenya. (2 marks)
- Give the distinguishing features in each case between the following.
- Kenya white and Californian white. (1 mark)
- Large white and land race. (1 mark)
- Give two examples of one host ticks. (1 mark)
- List two types of concentrates. (1 mark)
- Give four products obtained from rabbits. (2 marks)
- Explain the term “production ration” as used in livestock feeding. (1 mark)
- Give four functions of calcium in dairy cow. (2 marks)
- Differentiate between the following words used to refer to livestock. (2 marks)
- Bullock and steer.
- Gilt and sow
-
- Explain the meaning of the term “digestibility” as used in livestock production. (1 mark)
- State two factors affecting digestibility. (2 marks)
- State two methods of selection in livestock. (2 marks)
- State four signs of heat in cows. (2 marks)
- Name two methods of acaricide application onto cattle.
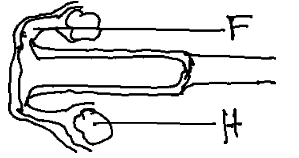
- The diagram below shows the reproductive system of cow. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the parts labelled F and H. (1 mark)
- Give two functions of the part labelled G. (1 mark)
- Give the role of the part labelled J. (1 mark)
- Give two ways used to improve production in indigenous cattle. (1 mark)
SECTION B (20 MARKS )
Answer all the questions in this section.
- A farmer intends to prepare 400kg of feed containing 20% DCP for chicks using feedstuff A, 12% DCP and feedstuff B 38% DCP. Using the Pearson’s square method, calculate how much of each feedstuff he would require. (5 marks)
-
- Label the diagram of a ruminant’ s stomach below fully. (2 marks)
- State one function for each of the parts labelled. (4 marks)
- Label the diagram of a ruminant’ s stomach below fully. (2 marks)
- The illustration below shows a livestock parasite.
- Identify the parasite. (1 mark)
- Name two species of livestock the parasite infects. (2 marks)
- How is the parasite passed from livestock to human beings? (1 mark)
- Give two forms in which the parasite is found in livestock. (2 marks)
- State three control measures of this parasite. (4 marks)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any two questions in this section.
-
- Describe the life cycle of a three-host tick. (8 marks)
- Discuss tick control methods. (9 marks)
- State three harmful effects of ticks in livestock. (3 marks)
- Describe ten commonly used masonry tools and equipment in construction of farm structures stating their use. (20 marks)
-
- Discuss the importance of the following nutrients, minerals and vitamins in livestock nutrition.
- minerals (4 marks)
- Vitamins (8 marks)
- Give the differences between ruminants and non-ruminants. (8 marks)
- Discuss the importance of the following nutrients, minerals and vitamins in livestock nutrition.
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section.
- Differentiate between pork and bacon. (1 mark)
- The meat from a pig, in its raw state, is called pork. In its cured state pork becomes bacon
- What is a capon in agriculture? (1 mark)
- A capon is a surgically unsexed male chicken, usually less than eight months old.
- Name one appropriate equipment used to administer liquid de-wormer to calves. (1 mark)
- Drenching gun
- State two features of indigenous cattle (Bos indicus) that make them more adaptable to tropical climates. (2 marks)
- Resistance to tropical diseases
- Well adapted to the tropical climate
- Name two dairy goat breeds reared in Kenya. (2 marks)
- Saanen
- Toggenburg
- British alpine
- Anglo Nubian
- Jamnapari
- Give the distinguishing features in each case between the following.
- Kenya white and Californian white. (1 mark)
- California white is white in colour with one or more of the following parts being black:ears, nose and tails Kenya white is white and has red eyes.
- Large white and land race. (1 mark)
- Large white the snout is broad and slightly dished and ears are upright
- The landrace is white in colour, it has a straight snout and long ears drooping over the face
- Kenya white and Californian white. (1 mark)
- Give two examples of one host ticks. (1 mark)
- The blue tick
- The cattle tick
- The tropical horse tick
- List two types of concentrates. (1 mark)
- Energy concentrates
- Protein concentrates
- Give four products obtained from rabbits. (2 marks)
- rabbit production includes wool (fur)
- and skins or pelts
- bi product including ballet shoes, glue, gloves, toy
- Explain the team “production ration” as used in livestock feeding. (1 mark)
- Production Ration: The amount of feed mixture which is given to a growing, working or producing animal over and above its maintenance need
- Give four functions of calcium in dairy cow. (2 marks)
- Adequate calcium is important for colostrum and milk synthesis, muscle and nerve function, immunity, resistance to diseases
promotes fast blood clotting in wounds
- Adequate calcium is important for colostrum and milk synthesis, muscle and nerve function, immunity, resistance to diseases
- Differentiate between the following words used to refer to livestock. (2 marks)
- Bullock and steer.
- A castrated male is called a steer; older steers are often called bullocks
- Gilt and sow
- gilt can be a young female pig, at or nearing the age of first breeding sow is a female pig.
- Bullock and steer.
-
- Explain the meaning of the term “digestibility” as used in livestock production. (1 mark)
- Digestibility refers to the amount of nutrient absorbed by the individual and is generally calculated as the amount of nutrient consumed minus the amount of nutrient retained in the feces.
Or - Digestibility is defined as the fraction of a nutrient ingested that is digested and absorbed by the animal
- Digestibility refers to the amount of nutrient absorbed by the individual and is generally calculated as the amount of nutrient consumed minus the amount of nutrient retained in the feces.
- State two factors affecting digestibility. (2 marks)
- The form in which the food is given to the animal
- The species of animal
- Explain the meaning of the term “digestibility” as used in livestock production. (1 mark)
- State two methods of selection in livestock. (2 marks)
- Mass selection
- Progeny testing
- Contemporary comparison
- State four signs of heat in cows. (2 marks)
- Restlessness or frequent movement
- Mounting others and when mounted it stands
- Mucus discharge from the vulva
- Decline in milk production
- Frequent bellowing
- Name two methods of acaricide application onto cattle. (1mark)
- Using a knapsack sprayer
- Dipping in a plunge dip
- Use of spray race
- The diagram below shows the reproductive system of cow. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the parts labelled F and H. (1 mark)
- F- fallopian tube
- H- ovary
- Give two functions of the part labelled G. (1 mark)
- G is the cervix
- Prevent entry of micro- organisms to the uterus
- Opens during birth to allow the foetus out
- G is the cervix
- Give the role of the part labelled J. (1 mark)
- J is the uterus walls, offers site for implantation of the zygote
- Give two ways used to improve production in indigenous cattle. (1 mark)
- improving the quality of feeds.
- regular treatment of animals through deworming and prevention against other diseases.
- Name the parts labelled F and H. (1 mark)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section.
- A farmer intends to prepare 400kg of feed containing 20% DCP for chicks using feedstuff A, 12% DCP and feedstuff B 38% DCP. Using the Pearson’s square method, calculate how much of each feedstuff he would require. (5 marks)
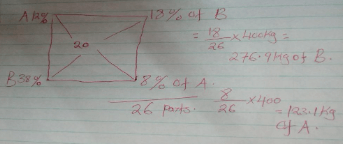
-
- Label the diagram of a ruminant’ s stomach below fully. (2 marks)
- A - the rumen,
- B - the reticulum,
- C- the omasum
- D - the abomasum
- State one function for each of the parts labelled. (4 marks)
- A- Rumen microbes ferment feed and produce volatile fatty acids, which is the cow’s main energy source. Rumen microbes also produce B vitamins, vitamin K and amino acids.
- B - the reticulum is attached to the rumen with only a thin tissue divider. This component holds heavy or dense objects — such as metal pieces and rocks — and trap large feed particles that are not small enough to be digested. The reticulum facilitates regurgitation
- C - omasum is nicknamed “manyplies” because of its internal structure. It is lined with large leaves and folds of tissue that resemble the pages of a book. These folds absorb water and nutrients from feed that passes through after its second round of chewing
- D - ABOMASUM has glands release hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes to help the abomasum further break down feed and plant material.
- Label the diagram of a ruminant’ s stomach below fully. (2 marks)
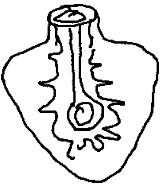
- The illustration below shows a livestock parasite.
- Identify the parasite. (1 mark)
- liverfluke
- Name two species of livestock the parasite infects. (2 marks)
- Two are the most common ones ie
- Fasciola heptica (sheep)
- Fasciola gigantica (cattle)
- How is the parasite passed from livestock to human beings? (1 mark)
- Once swallowed by the host, cercaria penetrates walls of the intestine and hatch into adults.
- Adults migrate to the liver where they grow, mature, mate and produce eggs.
- Give two forms in which the parasite is found in livestock. (2 marks)
- Adult flukes are found in the bile duct of the liver of the host animal.
- Here they produce eggs, which are passed into the alimentary canal through the bile duct
- State four control measures of this parasite. (4 marks)
- Chemically by use of CuSO4 Sodium pentachlorophenate etc which is added to stagnant water to kill the snails.
- Draining swampy areas/leveling any depression that may hold water in the pastures.
- Burning of the pastures during the dry seasons to kill cercaria
- Not grazing animals near marshy or waterlogged areas.
- Routine drenching using antihelminthes e.g. NaSO4, hexachloroethane drugs.
- Identify the parasite. (1 mark)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any two questions in this section.
-
- Describe the life cycle of a three-host tick. (8 marks)
- These ticks require three different hosts to enable them to complete their lifecycle.
- Eggs hatch on the ground into larvae.
- Larvae attaches itself to the first host, feed on blood, become engorged and drop off to the ground and moults into nymphs.
- The nymphs look for a second host, feed on blood, become engorged and drop off to the ground and moult into adults.
- Adults seek for the third host, climb, feed become engorged and mate.
- Females drop off to the ground to lay eggs.
- Discuss tick control methods. (9 marks)
- Natural/ Biological method.
- This is the use of the tick’s natural enemies, which predate on the ticks. E.g. using predators such as birds to control ticks.
N/B Only a small number of ticks is controlled using this method.
- This is the use of the tick’s natural enemies, which predate on the ticks. E.g. using predators such as birds to control ticks.
- Mechanical method
- Burning the infected pastures.
- Burning destroys eggs, larvae, nymphs and adults.
- Interfering with the ticks environment
This is achieved by:-- Ploughing pasture land.The eggs are exposed to the sun heat or are deeply buried.
- By top dressing pasture using lime or dressing using acaricides.
- Fencing off the pasture and farm.
- Hand picking the ticks (deticking)
- Starving the ticks to death
- This is achieved by practicing rotational grazing.
- It interrupts the lifecycle of the ticks.
- Burning the infected pastures.
- Chemical control method.
This is done by application of acaricide.
Methods of acaricide application- Spraying regularly with the acaricide.
- Dipping animals in plugs dips containing the acaricide.
- Hand dressing using pyegrease.
- Natural/ Biological method.
- State three harmful effects of ticks in livestock. (3 marks)
- Depriving the host of its food.
- Sucking blood.
- Damaging the organs of the host.
- Cause irritation on the skin of the host.
- Destruction of hides and skins.
- Transmission of diseases.
- Describe the life cycle of a three-host tick. (8 marks)
- Describe ten commonly used masonry tools and equipment in construction of farm structures stating their use. (20 marks)
- A cold chisel has a wide, flat head that is perfectly designed for slicing bricks or veneer stone in half with a blow from a hammer.
- A brick hammer has a blunt side for tasks like chopping bricks or stones in half with a quick, decisive blow.
- Squares are used when constructing and measuring right angles and for corner layouts. They are usually made of metal for durability.
- A mason’s level is used when establishing vertical or plumb lines and horizontal or level lines.
- Tooth chisel is also used for fine dressing. It is a handheld tool of metal consisting of a long shaft, with a toothed cutting edge at one end.
- Hand Saw It is used to cut soft stones. It is a saw with a wide crosscut toothed steel blade and wooden/plastic handle at one end. It is used in one hand.
- Basic masonry trowel is made up of stainless steel with a plastic/ wooden handle. The ends of trowel may be bull nosed or pointed. This is used to lift and spread mortar in joints during masonry construction
- Spade they are used to mix mortar and also used to place cement, mortar, concrete in head pan. Spade is also used to dig the soil for foundation trenches
- Mortar pan is commonly used in construction sites and is made of iron or plastic. It is a vessel made of rigid plastic or steel used to hold or carry sand, cement, mortar and concrete.
-
- Discuss the importance of the following nutrients, minerals and vitamins in livestock nutrition.
- Minerals (4 marks)
- Minerals play a key role in the maintenance of osmotic pressure,
- Regulate the exchange of water and solutes within the animal body.
- Minerals serve as structural constituents of soft tissues.
- Minerals are essential for the transmission of nerve impulses and muscle contraction.
- Vitamins (8 marks)
- Vitamins aid an animal by helping to regulate body functions,
- keeping the body healthy,
- promoting resistance to diseases.
- In the body, vitamin A plays a role in several distinct functions, including vision, bone growth, reproduction
- maintenance of epithelial cells, which cover the body surface (e.g., skin) and mucous membranes of body cavities
- The role of vitamin A in night vision is well established
- Proper vitamin nutrition can also decrease stress levels in broilers headed for the slaughterhouse and improve the quality of the animal’s meat. The presence of the right vitamins contributes to better nutritional quality in meat, longer shelf life, and better transfer of essential vitamins to human
- Vitamins A, B6 and E – can help improve gut and intestine health, and therefore feed conversion, in the absence of antibiotics.
- Minerals (4 marks)
- Give the differences between ruminants and non-ruminants. (8 marks 4x 2=8 marks)
2 = 8 marksRuminant Non-ruminant 1. Polygastric Monogastric 2. Chew and regurgitate food Does not chew and regurgitate food 3. Digest cellulose in the rumen by micro-organisms Cellulose digested in the caecum. 4. No ptyalin in saliva Ptyalin in saliva 5. Most digestion and absorption takes place in the rumen Most digestion and absorption takes place in the small intestines 6. Has alkaline saliva Has neutral saliva.
- Discuss the importance of the following nutrients, minerals and vitamins in livestock nutrition.
Download Agriculture Questions and Answers - Form 2 End Term 3 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students