QUESTIONS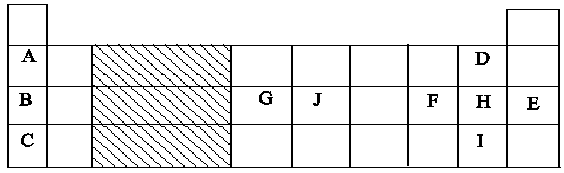
- The figure below represents a section of the periodic table. Study it and answer questions (a) to (h). Note that the letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
- Consider elements D. H and I
- Give the chemical family of these elements. (1 mk)
- How do their ionic size compare. (1mk)
- Compare and explain the reactivity of the three elements. (2mks)
- Write the electronic configuration of;
- Element H (1mk)
- The ion of element G. (1mk)
- A molecule of one of the elements is shown below. (2mks)
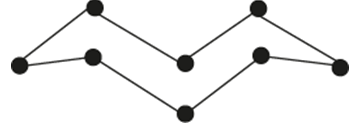
- Identify this element from the section of the periodic table and give its actual symbol and name. (2mks)
- Explain why this element has a higher boiling point compared to that of oxygen. (2mks)
- Write an equation to show the reaction between the element named above with oxygen. (1mk)
- Predict the pH of the oxide of the above element when in water. Explain. (2mks)
- Consider elements D. H and I
- The flow chart below shows some reactions starting with copper (II) nitrate. Study it and answer questions that follow.
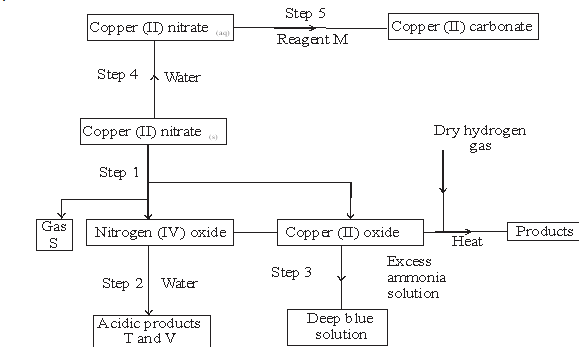
- State the condition necessary in step 1.(1mk)
- Identify: (4mks)
Reagent M ___________
Gas S ___________
Acidic products T____________
V__________ - Write the formula of the complex ion formed in step 3. (1mk)
- Write the equations for the reaction in (2 marks)
Step 1
Step 2
-
- The diagram below shows a set up that was used to prepare oxygen gas and passing it over a burning candle. The experiment was allowed to run for some time.
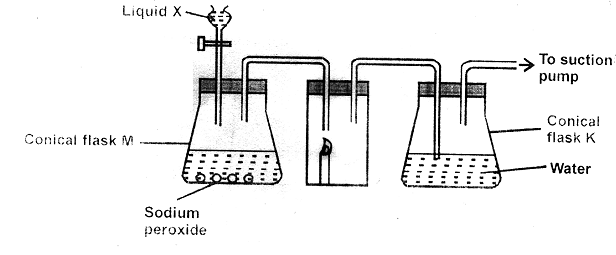
- Name liquid X (1mk)
- Suggest the pH of the solution in conical flask K. Explain (2mks)
- Write an equation for the reaction taking place in the conical flask M. (1mk)
- State and explain the two observations made when hydrogen sulphide is bubbled into the solution containing iron (III) chloride. (2mks)
-
- Describe a simple chemical test that can be used to distinguish between carbon (IV) oxide and carbon (II) oxide gases. (3mks)
- Give one use of carbon (II) oxide. (1mk)
- A form two student inverted a gas jar full of carbon (IV) oxide over water and sodium hydroxide solution as shown below.
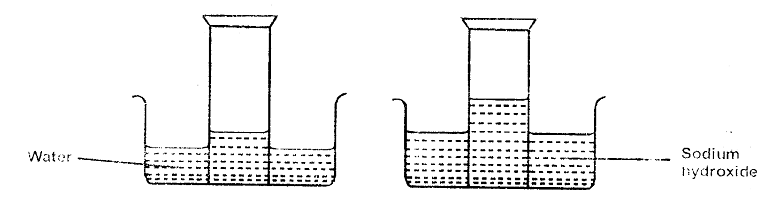 Explain the observations made. (2mks)
Explain the observations made. (2mks)
- The diagram below shows a set up that was used to prepare oxygen gas and passing it over a burning candle. The experiment was allowed to run for some time.
-
- Name the two crystalline forms of sulphur (1 Mark)
- The scheme below represents the steps followed in the contact process. Study it and answer the questions that follow:-
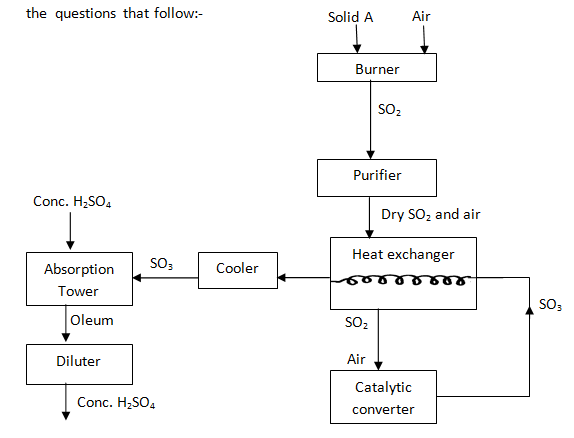
- Name one impurity removed by the purifier. (1 mark)
- Why is it necessary to remove impurities? (1 mark)
- Write down the equation of the reaction taking place in the converter (1 mark)
- Name the two catalysts that can be used in the converter (2 marks)
- What is the function of heat exchanger? (1 mark)
- Sulphuric (VI) Oxide is not dissolved directly into water? Explain (1 mark)
-
- Name the main pollutant in the contact process. (1 mark)
- How can the pollution in (g) (I) above be controlled? (1 mark)
- Give one use of sulphuric (VI) acid (1 mark)
- The flow chart below shows industrial manufacture of sodium carbonate.
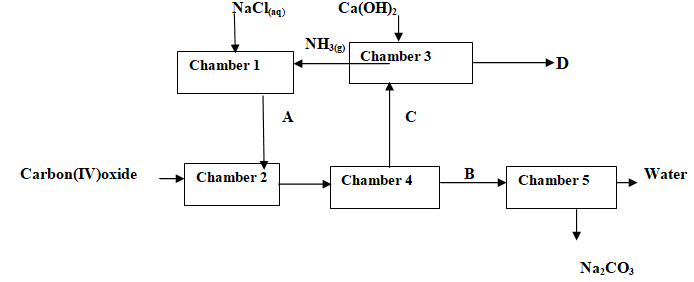 Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Study it and answer the questions that follow.- Name substances A, B, C and D. (4mks)
- Write equation for the reactions taking place in chamber 3 and 5. (2mks)
Chamber 3
Chamber 5 - Name the physical process in chamber 4 and 5. (2mks)
Chamber 4
Chamber 5 - Name one source of cheap carbon (IV) oxide for Solvay process. (1mk)
-
- A student set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram below to prepare and collect dry ammonia gas.
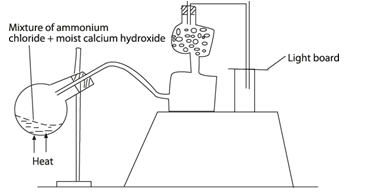
- Identify three mistakes in the set up and give a reason why each is mistake. (3mks)
- Name a suitable drying agent for ammonia. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction that occurred when a mixture of ammonium chloride and calcium hydroxide was heated. (1mk)
- Describe one chemical test for ammonia gas. (1mk)
- Ammonia gas is used to manufacture nitric (V) acid as shown below.
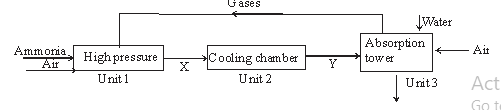
- This process requires the use of a catalyst. In which unit is the catalyst used? (1mk)
- Identify compound X and Y. (2mks)
- Ammonia reacts with nitric (v) acid to form ammonium nitrate fertilizer. Calculate the percentage composition of nitrogen in ammonium nitrate. (N = 14, O = 16, H = 1) (3 marks)
- A student set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram below to prepare and collect dry ammonia gas.
-
- State Graham’s Law. (2mks)
- The table below shows the relationship between the pressure and volume of a fixed mass of ozone gas.
Pressure (K pa) 1 4 8 16 20 160 Volume (cm3) 140 40 20 10 8 1 Inverse of volume 1/v (cm-3) - Complete the table by filling the inverse of volume. (3mks)
- Draw a graph of pressure against the reciprocal (inverse) of volume. (4mks)
- Using the graph, determine the volume of ozone if pressure is 12Kpa. (3mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- Halogens
- Ionic radius increases from D to I this is due to increase in number of energy.
- Reactivity reduces from D to I due to increase in atomic radius down the group which leads to a decrease in the strength of nuclear force of attraction.
-
- 2.8.7
- 2.8
-
- F – S – Sulphur
- A molecule of sulphur is made of packed ring of 8 atoms joined by strong covalent bonds while a molecule of oxygen has weak van der wall forces hence higher B.P of sulphur than oxygen.
- S(s) + O2(g) →SO2(g)
- Below 7 because SO2 dissolves in water to form acidic solution of sulphurous acid.
-
-
- Heating
- M – sodium carbonate/ potassium carbonate
S – oxygen
T – nitric (v) acid
V – nitric (III) acid - [Cu(NH3)4]2+
-
- 2Cu(NO3)2(s)→ 2CuO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2
- NO2(g) + H2O(l) →HNO2(aq) + HNO3(aq)
-
-
- Water
- Any pH between 4 - 7 – due to presence of carbonic acid
- 2Na2O2(aq) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + O2(g)
- Brown solution change to pale green solution. This is due to F3+ reduced to Fe2+ by H2S
-
- When CO2 is bubbled in lime water white precipitate is formed while NO2 white precipitate formed with CO.
- Extraction of metals, used as fuel
- CO2 is highly soluble in sodium hydroxide to form Na2CO3 while is slightly soluble in water.
-
-
- Rhombic sulphur (½ mk)
Monoclinic sulphur (½ mk) - Dust or Arsenic compounds (½ mk)
- Avoid poisoning of the catalyst (Avoid destruction of catalytic properties by impurities
- 25O2(g) + O2(g)→2SO3(g)
-
- Vanadinim (V) Oxide ( ½ mk)
- Heat incoming air (SO2 & Air)
Cools the SO3 - The reaction between SO2 and water is highly exothermic which makes the solution boil to form a mist of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid which pollutes the environment
-
- SO2
- Un reacted SO2 is recycled
Absorbed by Ca(OH)2 in tall chimneys
Passed over hot carbon (IV) Oxide and sulphur which is recycled and Carbon (IV) Oxide released to the environment
- Manufacture of fertilizers
- Rhombic sulphur (½ mk)
-
-
- Ammoniacal brine/ammoniate brine
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate/NaHCO3
- Ammonium chloride/NH4Cl
- Calcium chloride/CaCl2
- 2NH4Cl (aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq)→CaCl2 (aq) +2H22O (l) + 2NH3(g)
NaHCO3(s)→heat→Na2CO3(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) -
- Filtration
- Decomposition
- Limestone/Calcium carbonate
-
-
-
- Wrong method of collection.(3mks)
ammonia is less denser than air. -
- Flask should be slanting downwards left to right
- Water produced may run back & break the flask
- Moist reactants should not be used
- ammonia gas dissolves in water
- Anhydrous calcium oxide
- 2NH4Cl(s) + Ca(OH)2(s)→ 2NH3(g) + 2H2O(l) + CaCl2(s)
- Deep a glass rod in conc. HCl and bring it into contact with ammonia in a test tube. White fumes formed.
- Wrong method of collection.(3mks)
-
- Unit 1
- X – nitrogen (II) oxide (NO)
Y – nitrogen (IV) oxide (NO2) - NH4NO3
N = 28
H = 4
O = 48
80
28 x 100 = 35.0%
80
-
-
- The volume of a fixed mass of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at constant temperature. (1mk)
-
Pressure (K pa) 1 4 8 16 20 160 Volume (cm3) 140 40 20 10 8 1 Inverse of volume 1/v (cm-3) 0.006 0.025 0.05 0.1 0.125 1.000 - axes- ½mk, scale- ½mk, line-1mk, plotting-1mk
- Reading from the graph (student graph)(1mk)
Evaluation on the reciprocal of volume.(1mk)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 2 Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

