QUESTIONS
- Matter exists in three states which can be related as shown in the diagram below.
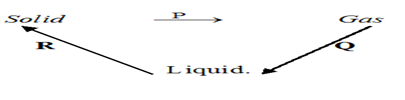
Name processes: P: ………………………………………… (1mk)
R: ………………………………………………….. (1mk) -
- Give one reason some of the laboratory apparatus are made of ceramics. (1 mark)
- Name two apparatus that can be used to measure approximately 75 cm of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid. (2 marks)
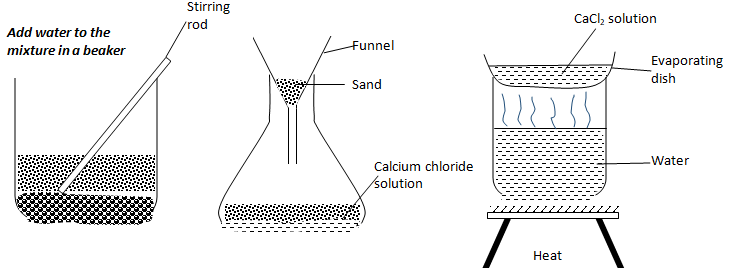
- Draw the procedural set-ups that can be used to separate a mixture of sand and calcium chloride to obtain crystals of calcium chloride. (3 marks)
- State two applications of chromatography. (2 marks)
- The above set-up was used to determine the chemical properties of carbon (II) oxide.
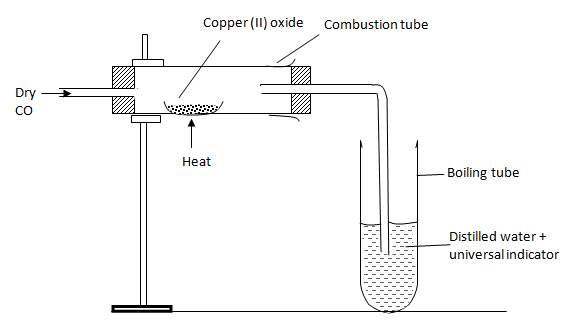
- Write the chemical equation for the reaction taking place in the combustion tube.(1 mark)
- State and explain the observation made in the boiling tube. (2 marks)
- A student placed some hydrogen peroxide in a test tube then added a small amount of Solutions can be classified as acids, bases or neutral. The table below shows solutions and their pH values
Solution pH – values K 1.5 L 7.0 M 14.0 - Select any pair that would react to form a solution of pH 7 (1 Mark)
- Identify two solutions that would react with aluminium hydroxide. Explain (2 Marks)
- 9.12g of a gaseous compound contains 8g of silicon while the rest is hydrogen. Determine the empirical formula of the compound. (H = 1, Si = 28) (3 Marks)
- Study the set-up below and answer the questions that follow.
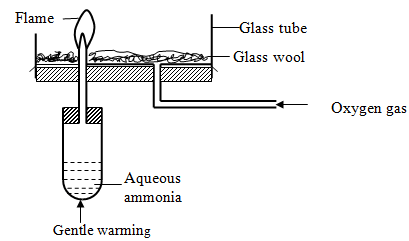
- Why is aqueous ammonia warmed gently? (1 Mark)
- What is the colour of the flame? (1 Mark)
- Write the chemical equation for the reaction that takes place (1Mark)
- Chlorine can be prepared in the laboratory by using the following reagents and chemicals.
Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid, water, manganese (IV) oxide, concentrated hydrochloric acid.- State the role of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid. (1 mark)
- Write the equation for formation of chlorine. (1 mark)
- What is the role of manganese (IV) oxide? (1 mark)
-
- State Boyle’s law. (1 mark)
- A gas occupies 270cm3 at a pressure of 660mmHg at 37ºC. What is the new volume if pressure is changed to 810 mmHg at 63ºC? (2 marks)
- An organic compound contain s 24.24% carbon, 4.04% hydrogen and the rest chlorine. If its relative molecular mass is 99, what is its molecular formula? (3 marks)
(C = 12, H = 1, Cl = 35.5) - A given mass of sodium nitrate was heated completely and 320 cm3 of the gas was produced at s.t.p. Determine the mass of the sodium nitrate heated.
(Na = 23. N = 14, O = 16, molar gas volume = 22.4L) (3 marks) -
- Give one advantage of using methyl orange over phenolphthalein as an indicator. (1 mark)
- Three drops of litmus solution was added to 20 cm3 of 2M hydrochloric acid in a beaker followed by 20 cm3 of 2M ammonium hydroxide. State and explain the observation made. (2 marks)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
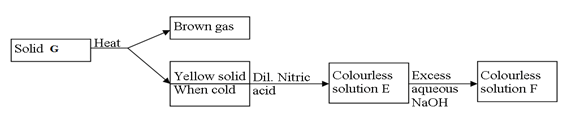
- Identify solid G(1mk)
- Write a balanced chemical equation between the yellow solid and dilute nitric acid. (1mk)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
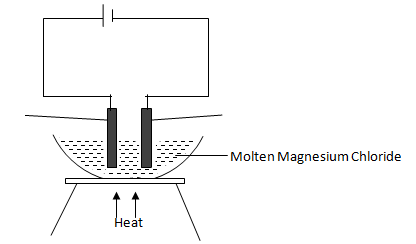
- Define the term electrolysis. (1 mark)
- On the diagram, label the Anode and Cathode. (2 marks)
- Write the equation at the anode. (1 mark)
- In order to find the proportion by volume of gases in air, a sample of air was passed through two wash bottles, the first containing sodium hydroxide solution and the second containing concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid. The remaining gas was then collected in a syringe.
- Why was the air passed through;
- sodium hydroxide solution? (1 mark)
- concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid? (1 mark)
- Name is the major gas collected in the syringe. (1 mark)
- Why was the air passed through;
- During the manufacture of sodium carbonate in the industry.
- Give the name of the process to manufacture sodium carbonate. (1 mark)
- Write the final equation to form sodium carbonate during the process. (1 mark)
- Give one use of sodium carbonate. (1 mark)
- Describe how to prepare crystal of magnesium sulphate starting with magnesium powder.(3mks)
-
- Complete the diagram below to show how dry sample of hydrogen gas is prepared in the laboratory. (2 marks)
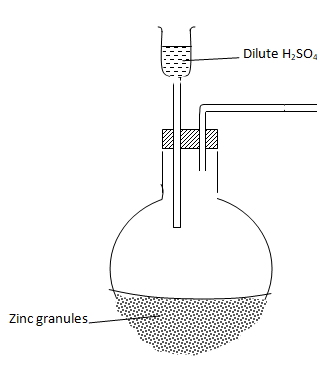
- Name the catalyst which could be used to increase the reaction rate of production of hydrogen gas in the set up drawn above. (1 mark)
- Complete the diagram below to show how dry sample of hydrogen gas is prepared in the laboratory. (2 marks)
- An element consists of two isotopes with atomic masses 59 and 61 in the ratio of 3 : 2 respectively.
- What are isotopes? (1 mark)
- Calculate the relative atomic mass of the element. (2 marks)
- An element 2412R :
- To which chemical family does it belong? (1 mark)
- Write the electron arrangement of the atom. (1 mark)
- Draw the structure of its ion. (1 mark)
- If 25cm3 of 0.1M H2SO4 solution neutralized a solution contain 1.06g of sodium carbonate in 250cm3 of solution, calculate the morality and volume of sodium carbonate solution.
(Na = 23, O = 16, C = 12) (3 Marks) - 50cm3 of oxygen gas diffused through a porous plug in 80 seconds. How long will it take 100cm3 of sulphur (IV) oxide to diffuse through the same plug? (S = 32, o = 16) (3 Marks)
-
- State the role of the following parts during fractional distillation of a mixture of water and ethanol
- Glass beads in the fractionating column (1 Mark)
- Fractionating column (1 Mark)
- State any one application of fractional distillation (1 Mark)
- State the role of the following parts during fractional distillation of a mixture of water and ethanol
-
- State what is observed when sodium hydroxide pellets are left in air overnight.(1 mark)
- What name is given the process shown by the salt in (a) above? (1 mark)
- Given;
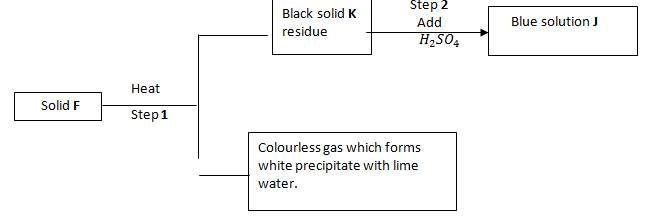
- Identify;
Solid F - …………………………………………………………………………. (1 mark)
Solid J - …………………………………………………………………………… (1 mark) - Write equation for step 1. (1 mark)
- Identify;
- Use dot (•) and cross (X) to show the bonding in Lithium oxide. (2 mark)
- Excess magnesium ribbon was burnt in air to form a white solid mixture. Write two equations to show the formation of the white solid mixture. (2 marks)
- The set-up below shows how gas A was prepared and reacted with heated magnesium
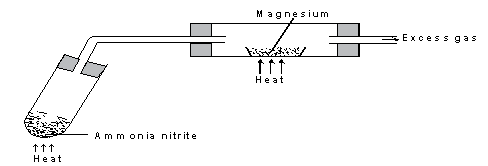
- Give a reason why it is not advisable to heat magnesium before heating ammonium nitrite. (1mk)
-
- Identify gas A (1mk)
- Write a chemical equation for the reaction between gas A and magnesium (1mk)
- Study the set-up below and answer questions that follow.
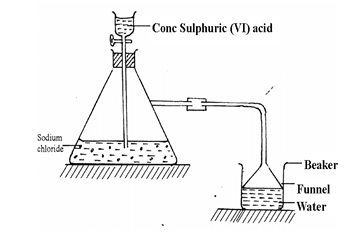
- Name the gas that is produced when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid reacts with the sodium chloride (1 mark)
- Why is it necessary to use a funnel in the beaker? (1 mark)
- How does the gas affect the PH of the water in the beaker? (1 mark)

MARKING SCHEME
- Matter exists in three states which can be related as shown in the diagram below.
Name processes: P: Sublimation (1mk)
R: Condensation (1mk) -
- Give one reason some of the laboratory apparatus are made of ceramics. (1 mark)
Does not break easily hence can withstand strong heating. - Name two apparatus that can be used to measure approximately 75 cm of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid. (2 marks)
- 100cm3 measuring cylinder.
- Graduated 100cm3 beaker.
- Give one reason some of the laboratory apparatus are made of ceramics. (1 mark)
- Draw the procedural set-ups that can be used to separate a mixture of sand and calcium chloride to obtain crystals of calcium chloride. (3 marks)
- State two applications of chromatography. (2 marks)
- In sports to identify banned substances.
- To test purity of drugs in pharmacy.
- Identify contaminants in food and drinks.
- Identify harmful substances in cosmetics.
- The above set-up was used to determine the chemical properties of carbon (II) oxide.
- Write the chemical equation for the reaction taking place in the combustion tube. (1 mark)
CO(g) + CuO(s) → Cu(s) + CO2(g) - State and explain the observation made in the boiling tube. (2 marks)
The solution turns red, CO2 formed dissolves to form an acidic solution.
- Write the chemical equation for the reaction taking place in the combustion tube. (1 mark)
- A student placed some hydrogen peroxide in a test tube then added a small amount ofSolutions can be classified as acids, bases or neutral. The table below shows solutions and their pH values
- Select any pair that would react to form a solution of pH 7 (1 Mark)
K and M - Identify two solutions that would react with aluminium hydroxide. Explain (2 Marks)
K and M . This is because K is acidic and M is basic and aluminium hydroxide being amphoteric would react with both.
- Select any pair that would react to form a solution of pH 7 (1 Mark)
- 9.12g of a gaseous compound contains 8g of silicon while the rest is hydrogen. Determine the empirical formula of the compound. (H = 1, Si = 28) (3 Marks)
Element Si H
Mass (g) 8 1.12g (9.12 – 8.0)
No. of moles 8/28 = 0.286 1.12/1 = 1.12
Mole ratio0.286/0.286) = 1 1.12/0.286 = 4
Empirical formula is SiH4 - Study the set-up below and answer the questions that follow.
- Why is aqueous ammonia warmed gently? (1 Mark)
To liberate ammonia gas rapidly - What is the colour of the flame? (1 Mark)
Green-yellow - Write the chemical equation for the reaction that takes place (1Mark)
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g)→4NO(g) + 6H2O (i)
UB eqn = zero mk
Penalise ½ mk for wrong or missing S.S.
- Why is aqueous ammonia warmed gently? (1 Mark)
- Chlorine can be prepared in the laboratory by using the following reagents and chemicals.
Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid, water, manganese (IV) oxide, concentrated hydrochloric acid.- State the role of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid. (1 mark)
To dry chlorine - Write the equation for formation of chlorine. (1 mark)
MnO2(s) +4HCl(aq) →MnCl2(aq) +Cl2(g)+ 2H2O(l) - What is the role of manganese (IV) oxide? (1 mark)
OxidizesHCl to chlorine
- State the role of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid. (1 mark)
-
- State Boyle’s law. (1 mark)
The volume a fixed mass of a gas, is inversely proportional to the pressure at constant temperature. - A gas occupies 270cm3 at a pressure of 660mmHg at 37ºC. What is the new volumeif pressure is changed to 810 mmHg at 63º C? (2 marks)
P1V1 = P2V2
T1 T2
P1=660 P2=810
V1=270 V2= ?
T1=37+273=310ºK T2=336
V2= P1V1T2 = 660×270×336
P2T1 810×310
=338.4516cm3
- State Boyle’s law. (1 mark)
- An organic compound contain s 24.24% carbon, 4.04% hydrogen and the rest chlorine. If its relative molecular mass is 99, what is its molecular formula? (3 marks)
(C = 12, H = 1, Cl = 35.5)
Ef= CH2ClElement C H Cl %Mass 24.24 4.04 71.72 RAM 12 1 35.5 Moles 24.24/12 4.04/1 71.72/35.5 2.02/2.02=1 4.04/2.02=2 2.02/2.02=1 Mole ratio 1 2 1
MF= (EF)η
=R.M.M/EFM = 99⁄49.5=2
MF = (CH2Cl)2
C2H4Cl2 - A given mass of sodium nitrate was heated completely and 320 cm3 of the gas was produced at s.t.p. Determine the mass of the sodium nitrate heated.
(Na = 23. N = 14, O = 16, molar gas volume = 22.4L) (3 marks)
2NaNa3(s) → 2NaNO2(s)+O2(g)
Moles of O2 produed
If 1 mole evolve 22400cm3
320cm3
320 × 1= 0.0143 moles
22400
From r.r. of 1 : 2
Moles of NaNO3=2×0.0143=0.0286moles
RFM NaNO3=23+14+(16)3=85
If 1 mole→85g
0.0286→?
0.0286/1×85 =2.431g -
- Give one advantage of using methyl orange over phenolphthalein as an indicator.(1 mark)
Shows distinct colours is acids, bases and neutral solutions unlike phenolphthalein which cannot differentiate between acids and neutral solutions. - Three drops of litmus solution was added to 20 cm3 of 2M hydrochloric acid in a beaker followed by 20 cm3 of 2M ammonium hydroxide. State and explain the observation made. (2 marks)
The colour changed from red to colourless.
The acid was neutralized completely by the ammonium hydroxide.
- Give one advantage of using methyl orange over phenolphthalein as an indicator.(1 mark)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify solid G (1mk)
Pb(NO3)2 - Write a balanced chemical equation between the yellow solid and dilute nitric acid.(1mk)
PbO(s) + 2H(NO3)2(aq) → Pb(NO3)2 + H2O(l)
- Identify solid G (1mk)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
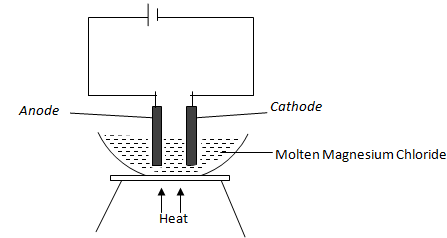
- Define the term electrolysis. (1 mark)
Process by which an electrolyte gets decomposed when an electric current is passed through it. - On the diagram, label the Anode and Cathode. (2 marks)
- Write the equation at the anode. (1 mark)
2C(l) C2(g)+2e
- Define the term electrolysis. (1 mark)
- In order to find the proportion by volume of gases in air, a sample of air was passed through two wash bottles, the first containing sodium hydroxide solution and the second containing concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid. The remaining gas was then collected in a syringe.
- Why was the air passed through;
- sodium hydroxide solution? (1 mark)
To absorb CO2 - concentratedsulphuric (VI) acid? (1 mark)
To absorb water vapour
- sodium hydroxide solution? (1 mark)
- Name is the major gas collected in the syringe. (1 mark)
Nitrogen
- Why was the air passed through;
- During the manufacture of sodium carbonate in the industry.
- Give the name of the process to manufacture sodium carbonate. (1 mark)
Solvay process - Write the final equation to form sodium carbonate during the process. (1 mark)
2NaHCO3(s) → Na2CO3(s)+CO2(g)+H2O(l) - Give one use of sodium carbonate. (1 mark)
- Manufacture glass
- softening hard water
- Give the name of the process to manufacture sodium carbonate. (1 mark)
- Describe how to prepare crystal of magnesium sulphatestarting with magnesium powder.(3mks)
To some amount of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid in beaker- Add magnesium powder as you stir till in excess.
- Filter to obtain magnesium sulphate as filtrate.
- Heat the filtrate to concentrate.
- Cool in order to form crystals.
- Dry between filter papers.
-
- Complete the diagram below to show how dry sample of hydrogen gas is prepared in the laboratory. (2 marks)
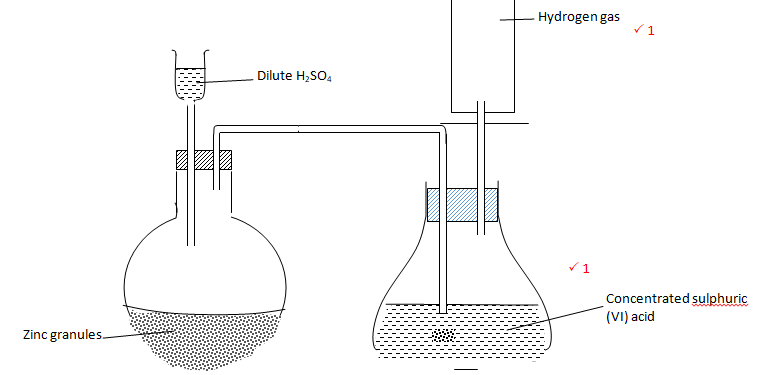
- Name the catalyst which could be used to increase the reaction rate of production of hydrogen gas in the set up drawn above. (1 mark)
Crystals of copper (II) sulphate
- Complete the diagram below to show how dry sample of hydrogen gas is prepared in the laboratory. (2 marks)
- An element consists of two isotopes with atomic masses 59 and 61 in the ratio of 3 : 2 respectively.
- What are isotopes? (1 mark)
Atoms of the same element with same atomic number but different mass number due to difference in the number of neutrons. - Calculate the relative atomic mass of the element. (2 marks)
R.A.M = (59 × 3)+(61 × 2)
5
= 177 + 122
5
= 299
5
= 59.8
- What are isotopes? (1 mark)
- An element:2412R
- To which chemical family does it belong? (1 mark)
Alkaline earth metals - Write the electron arrangement of the atom. (1 mark)
2.8.2 - Draw the structure of its ion. (1 mark)
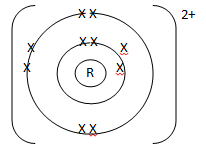
- To which chemical family does it belong? (1 mark)
- If 25cm3 of 0.1M H2SO4 solution neutralized a solution contain 1.06g of sodium carbonate in 250cm3 of solution, calculate the morality and volume of sodium carbonate solution.
(Na = 23, O = 16, C = 12) (3 Marks)
No. of moles of NaCO3 = 1.06/106 = 0.01 moles
0.01 moles contained in 250cm3
? moles contained in 1000cm3
= 0.01 x 1000 = 0.04M
250
NaCO3(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → NaSO4(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
Reacting mole ration Na2CO3: H2SO4
1 : 1
Moles of Na2CO3 = Moles of H2SO4
Moles of H2SO4 = 0.1/1000 = 0.0025 moles = Moles of Na2CO3
0.04 moles – 1000cm3
0.0025 - ?
0.0025 x 1000
0.04
= 62.5cm3 - 50cm3 of oxygen gas diffused through a porous plug in 80 seconds. How long will it take 100cm3 of sulphur (IV) oxide to diffuse through the same plug? (S = 32, o = 16) (3 Marks)
50cm3 of O2(g) take sec
100cm3 of O2(g) take sec ?
80sec x 100 = 160secs
50
M/mass of 02 = 32
SO2 = 32 + 32 = 64
√MSO2= TSO2
MO2 TO2
√64/32 = TSO2/160sec
(2√64/32)= TSO2
1602
64/32 = TSO2
25600
TSO2= 25,600 x 64
32
TSO2 = 226.27 sec -
- State the role of the following parts during fractional distillation of a mixture of water and ethanol
- Glass beads in the fractionating column (1 Mark)
Increases the surface area for condensation process. - Fractionating column (1 Mark)
It allows water vapour to condense into liquid and flow back into the flask before the boiling point of water is reached.
- Glass beads in the fractionating column (1 Mark)
- State any one application of fractional distillation (1 Mark)
During oil refinery, crude oil is separated into a number of fractions
- State the role of the following parts during fractional distillation of a mixture of water and ethanol
-
- State what is observed when sodium hydroxide pellets are left in air overnight.(1 mark)
It forms a solution. - What name is given the process shown by the salt in (a) above? (1 mark)
Deliquescence
- State what is observed when sodium hydroxide pellets are left in air overnight.(1 mark)
- Given;
- Identify;
Solid F -CuCO3 (1 mark)
SolidJ -CuSO4 (1 mark) - Write equation for step 1. (1 mark)
CuCO3(s) →CuO(s) + CO2(g)
- Identify;
- Use dot (•) and cross (X) to show the bonding in Lithium oxide. (2 mark)
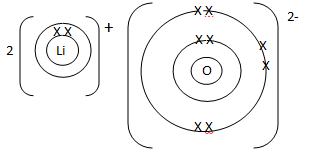
- Excess magnesium ribbon was burnt in air to form a white solid mixture. Write two equations to show the formation of the white solid mixture. (2 marks)
2Mg(s)+O2(g) → 2MgO(s)
3Mg(s)+N2(g)→ Mg3N2 - The set-up below shows how gas A was prepared and reacted with heated magnesium
- Give a reason why it is not advisable to heat magnesium before heating ammonium nitrite. (1mk)
Magnesium would react with air in the combustion tube since nitrogen gas has not yet been produced. -
- Identify gas A (1mk)
Nitrogen gas - Write a chemical equation for the reaction between gas A and magnesium (1mk)
3Mg(s)+N2(g)→ Mg3N2(s)
- Identify gas A (1mk)
- Give a reason why it is not advisable to heat magnesium before heating ammonium nitrite. (1mk)
- Study the set-up below and answer questions that follow.
- Name the gas that is produced when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid reacts with the sodium chloride (1 mark)
Hydrogenchloride - Why is it necessary to use a funnel in the beaker? (1 mark)
It prevents sucking back/increases surface area for dissolving - How does the gas affect the PH of the water in the beaker? (1 mark)
The pH of the water drops
- Name the gas that is produced when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid reacts with the sodium chloride (1 mark)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 2 Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

