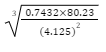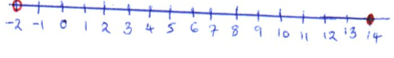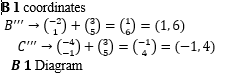INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consists of two sections; Section I and Section II.
- Answer ALL the questions in Section I and ONLY FIVE questions in Section II.
- Show all the steps in your calculations, giving your answer at each stage in the space provided below each question.
- Marks may be given for correct working even if the answer is wrong.
- Non programmable silent electronic calculators and KNEC mathematical tables may be used except where stated otherwise.
SECTION I (50 Marks)
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- Without using tables or a calculator evaluate; (3 marks)
−24 ÷ −8 × 5 −(−30)
−16 × 4 ÷ 2 + (−8) - Factorize completely 3x2 − 2xy − y2 (2 marks)
- A Kenyan bank buys and sells foreign currencies as shown below.
A tourist arrived in Kenya with 100 500 Hong Kong Dollars and changed the whole amount to Kenyan shillings. While in Kenya he spent Ksh. 430 897 and changed the balance to Japanese yen before leaving for Tokyo. Calculate the amount in Japanese Yen that he received. (3 marks)Currency Buying (Ksh) Selling (Ksh) 1 Hong Kong dollar
100 Japanese yen9.84
76.089.87
76.12 - Use logarithm tables to evaluate (4 marks)
- The sides of a triangle were measured to 1 decimal as 6.5cm, 7.4cm and 8.2cm respectively. Calculate the percentage error in its perimeter
(4 marks) - Line L1 passes through points A(2,−4) and B(6, −8). Find the equation of the line L2, the perpendicular bisector of AB leaving your answer in the form ax + by + c = 0 . (3 marks)
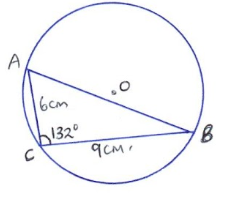
- In the figure below, O is the centre of the circle. AC = 6 cm, BC = 9 cm and ∠ACB = 132°
- Calculate length AB correct to 2 decimal places. (2 marks)
- Calculate the area of the circle. (2 marks)
- Evalute, without using mathematical tables or the calculator, the expression. (3 marks)
2 log105 − ½log1016 + 2log1040 - Rationalize the denominator and leave your answer in surd form. (3 marks)
3
2√5 + √2 - Solve the quadratic equation 6a2 = 5a + 4 using completing the square method. (3 marks)
- The hire purchase terms of a cupboard is a deposit of Ksh 4,400 and six monthly installments of Ksh 900 each. The hire purchase price is 175% of the cost price while the cash price is 25% more than the cost price .Calculate the cash price of the cupboard. (3 marks)
- Construct triangle PQR in which PQ=QR=5 cm and ∠ PRQ=35°. Measure PR. (3 marks)
- A and B are two matrices. If A =
find B given that A2 = A + B. (3 marks)
- Make n the subject of the formulae in A = P(1 + r/100)n (3 marks)
- Solve the following inequality and show your solution on a number line. (3 marks)
4x − 3 ≤ ½(x + 8) < x + 5 - The sixth term of an arithmetic progression is 27 and the tenth term is 43. Find the 16th term. (3 marks)
SECTION II (50 Marks)
Answer ONLY five the questions in the spaces provided.
- Mr. Omwega is employed. His basic salary is Kshs. 21, 750 and is entitled to a house allowance of Kshs 15, 000 and a travelling allowance of Kshs 8, 000 per month. He also claims a family monthly relief of Kshs 1, 056 per month. Other deductions are;
- Union dues Kshs 200 and
- Co-operative shares Kshs 4, 500 per month.
The table below shows the tax rates for the year.
Calculate;Income (Kshs per annum) Tax rates 1 - 116,600
116,161 - 225, 600
225, 601 - 335, 040
335,041 - 444, 480
Over 444, 48010%
15%
20%
25%
30%- Mr. Omwega’s annual taxable income. (2 marks)
- The tax paid by Mr. Omwega in the year. (6 marks)
- Mr. Omwega’s net income per month. (2 marks)
-
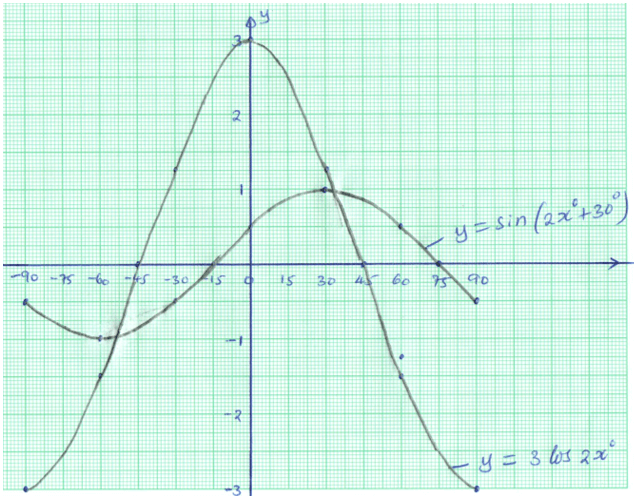
- Complete the table below giving your values correct to 2 decimal places. (2 marks)
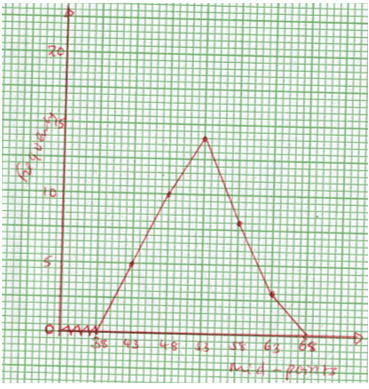
x° −90 −75 −60 −45 −30 −15 0 15 30 45 60 75 90 3 cos 2x° −3 −2.6 0 1.5 3 2.6 0 −1.5 −3 Sin (2x + 30)° −0.5 −1 −0.87 0 0.5 1 0.5 0 −0.5 - On the grid provided, draw on the same axes the graph of y=3cos 2x° and y=sin 2x+30° for interval -90°≤x≤90°. Take the scale 1 cm represent 15° on x – axis and 2 cm represent 1 unit on the y – axis. (4 marks)
- Use the graph in (b) above to solve the equation;
- 3cos 2x° =sin 2x+30° (2 marks)
- 6cos 2x° +5=0 (2 marks)
- Complete the table below giving your values correct to 2 decimal places. (2 marks)
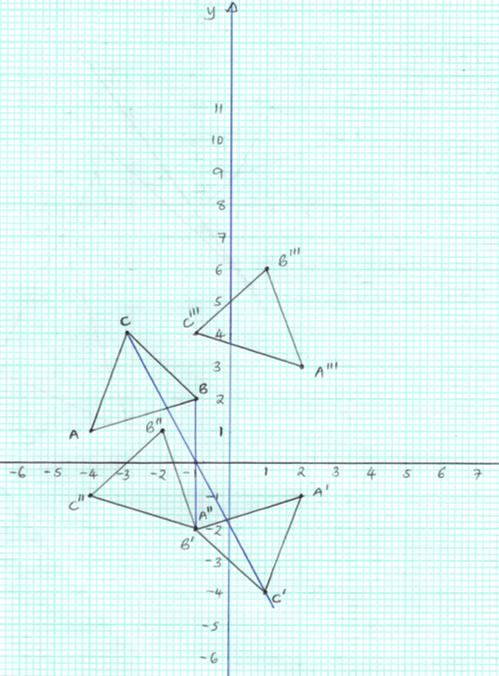
- Triangle ABC has coordinates A (−4,1, B (−1,2) and C (−3,4).
- On the grid provided, draw triangle ABC. (1 mark)
- Triangle A'B'C' is the image of triangle ABC under an enlargement with scale factor -1 about the origin. On the same grid draw triangle A'B'C' and state its coordinates. (3 marks)
- Triangle A''B''C'' is the image of triangle A'B'C' under a rotation of −90° about the origin. On the same grid draw triangle A''B''C'' and state its coordinates. (3 marks)
- Under a certain translation T, the image of points A''B''C'' are mapped onto triangle A'''B'''C''' such that point A'' is mapped onto A'''2, 3.
- Find the translation T. (1 mark)
- Find the coordinates of the image points B''' and C''' and plot triangle A'''B'''C''' on the same grid. (2 marks)
- A parent has two children whose age difference is 5 years. Twice the sum of the ages of the two children is equal to the age of the parent.
- Taking x to be the age of the elder child, write an expression for
- The age of the younger child. (1 mark)
- The age of the parent (1 mark)
- In twenty years’ time, the product of the children’s age will be 15 times the age of their parent
- Form an equation in x and hence determine the present possible ages of the older child. (4 marks)
- Find the present possible ages of the parent. (2 marks)
- Determine the possible ages of the younger child in twenty years’ time. (2 marks)
- Taking x to be the age of the elder child, write an expression for
- The masses of 40 students were measured to the nearest kilogram and recorded as shown below.
52 58 54 51 59 53 56 51
43 41 53 58 54 65 58 59
49 63 49 49 47 45 46 52
52 55 52 55 49 57 53 63
42 45 46 48 60 49 48 53- Use this data to complete the table below. (4 marks)
Mass in Kg Class mid point x Frequency f fx 41 - 45 46 - 50 48 10 480 51 - 55 56 - 60 61 - 65 63 3 189 Σf = 40 Σfx = - Calculate ;
- The mean mass. (2 marks)
- The median mass (2 marks)
- Draw a frequency polygon for the distribution. (2 marks)
- Use this data to complete the table below. (4 marks)
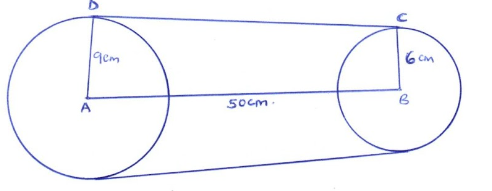
- The figure below shows two pulleys with centres A and B of radii 9 cm and 6 cm respectively. C and D are contact points of the belt with the pulleys. The distance between the centres of the two pulleys is 50 cm. a belt is tied around the two pulleys as shown.
Calculate,- Length DC (2 marks)
- The length of arc DE (3 marks)
- The length of arc CF (3 marks)
- The total length of the belt. (2 marks)
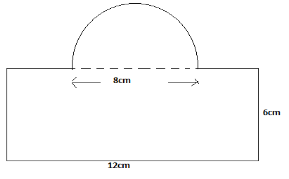
- The figure below shows a rectangle attached to a semi-circle
- Calculate;
- the area of the figure (3marks)
- the perimeter of the figure (3 marks)
- If the figure represents a cross-section of a steel girder of length 9m, determine the volume of the steel girder in cubic centimetres (2 marks)
- If the mass of the steel girder is 306kg, calculate its density in g/cm3. (2 marks)
- Calculate;
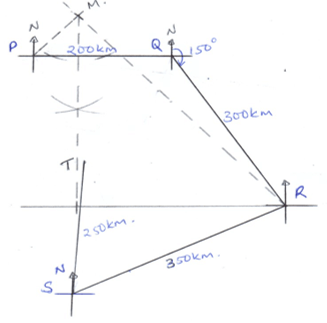
- Five towns P,Q, R S and T are situated such that Q is 200 km east of P. R is 300 km from Q on a bearing of 150° from Q. S is 350 km on a bearing of 240° from R. T is 250 km from S and its bearing from P is 160°.
- Using a scale of 1 cm to represent 50 km, draw a diagram representing the position of the towns. (5 marks)
- From the diagram, determine:
- The distance in km from P to T. (1 mark)
- The bearing of S from Q. (1 mark)
- A plane heading to town R takes off from town P and flies upward at a constant angle which is less than 90°. After flying a distance of 100 km in the air, it sees a town R at angle of depression of 50°. By scale drawing, find the horizontal distance of the plane from R at this point.
(3 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
| NO | WORKING | MARKS | REMARKS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | Numerator −24÷−8×5+30 3×5+30 15+30=45 Denominator −16×4÷2+(−8) −16×2−8 −32−8=−40 Num = 45 = −11/8 Den −40 |
M1 M1 A1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | 3x2 − 3xy + xy − y2 3xx − y + yx − y (x−y)(3x+y) |
M1 M1 A1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3. | 100 500 dollars to shillings = 9.84×100 500 = sh. 988 920 Balance after expenses = Sh. 988 920-430 897 = Sh. 558 023 Amount received in Japanese Yen = 558 023 ×100 75.12 = 742 842 Yen |
M1 M1 A1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4. | 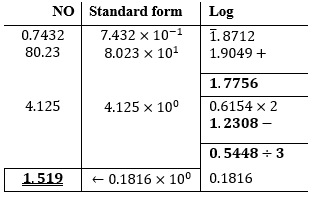 |
B1 B1 B1
A1 |
All logarithms Addition and subtraction Cube root Correct answer |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5. | Absolute error = 0.05 Actual Perimeter = 6.5 + 7.4 + 8.2 = 22.1cm Max perimeter = 6.55 + 7.45 + 8.25 = 22.25cm % error =½(22.25 − 21.95) × 100% |
B1 M1 A1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6. | Mid-point of AB = (2+6,−4 + (−8)) = (4, −6) 2 2 Equation of L2 ⇒ 1/1 = y −(−6) |
M1 M1 A1 |
Correct coordinates of mid-point Gradient of line L2 Equation of L2 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7. |
|
M1 A1 M1 A1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8. | log1025 − log104 + log101600 log10 (25 × 1600) 4 log10 10 000 = 4 |
M1 A1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9. | 3(2√ 5 − 2√ (2√5 + √2) (2√5 − √2) 6√5 − 3√ 2 20 − 2√10 + 2√10 − 2 6√5 − 3√2 20−2 6√5 − 3√2 ⇒ 1/3√5 − 1/6√2 18 |
M1 M1 A1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10. | 6a2 − 5a = 4 a2 − 5/6a = 23 a2 − 5/6a + 25/144 = 2/3 + 25/144 (a − 5/12)2 = 0.8403 a − 5/12 = 0.8403 = ±0.9167 a = 0.9167 + 5/12 OR − 0.9167 + 5/12 a = 1.333 OR −0.5 |
M1 M1 A1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11. | HP = 41400 + (900×6) = 9800/ = Cost price 100/175 × 9800 = 5600 / = ∴ Cash price = 125/100 × 5600 = 7000 /= |
M1 M1 A1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12. | 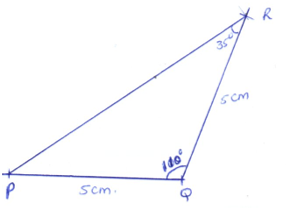 PR = 8.3 ± 0.1cm |
B1 B1 B1 |
Lines PQ = QR = 5cm ∠ R = 35°, ∠Q = 110° and complete triangle |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | 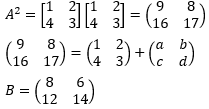 |
B1 M1 A1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14. | (1 + r/100)n = A/P n log (1 + r/100)n = Log A/P n = log A/P log(1+r/100) |
M1 M1 A1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15. |
4x − 3 ≤ 0.5x + 8 |
M1 A1 B1 |
Both inequalities solved Compound inequality Number line |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16. |
a + 5d = 27 |
B1
M1 A1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17. |
|
M1 A1 M1 M1 M1 A1 M1 A1 M1 A1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20. |
|
B1 B1 B1 M1 M1 A1 M1 A1 M1 A1 |
Correct equation solving | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 21. |
a). The completed table is show below.
b) (i)Mean mass x̄ = ∑f x (ii) Median = 50.5 + (20 – 15) × 5 c) Frequency polygon on the attached graph. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 |
|
M1 A1 B1 M1A1 B1 M1A1 A1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23. |
|
M1 M1 A1 M1 M1 A1 M1 A1 M1 A1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24. |
|
B1 B1 |
Download Mathematics Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 3 Mid Term 3 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students