INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- THIS PAPER CONSISTS OF THREE SECTIONS A, B AND C
- ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A AND B
- ANSWER ANY TWO QUESTIONS IN SECTION C IN THE ATTACHED FOOLSCAPS
SECTION A (30MKS)
Answer all questions from this section.
- Name two tools used in castration of livestock. (1mk)
- Name four methods used in the farm to restrain animals. (2mks)
- List four precautions that should be taken when using farm tools and equipment. (2mks)
- Give two distinguishing features between the following breeds of rabbits. Kenya white and California white. (1mk)
- Name four dairy goat breeds reared in Kenya. (2mks)
- Give two functions of calcium in dairy cows. (1mk)
- Give two measures a poultry farmer can use to control fleas in poultry. (1mk)
- Name the compartment of the ruminant digestive system where microbial digestion takes place. (1mk)
- State four ways of minimizing disowning of lambs by ewes. (2mks)
- Give the gestation period of the following animals. (2mks)
- Cow
- Sow
- Ewe
- Doe
- Differentiate between pen lambing and drift lambing. (1mk)
- State four reasons why castration is done in livestock. (2mks)
- State two ways that shows how good feeding help to control livestock diseases. (1mk)
- Explain four factors which are considered when siting a fishpond. (2mks)
- Name four notifiable diseases in livestock. (2mks)
- Name two causes of ruminal tympany in ruminant animals. (1mk)
- List four tools used in laying concrete blocks in construction of a wall. (2 marks)
- Differentiate between notifiable disease and zoonotic disease. (2 marks)
- State four factors that determine nutritional requirements in dairy goats. (2 marks)
- State four properties of concrete that make it suitable for constructing farm buildings. (2marks)
SECTION B (20MKS)
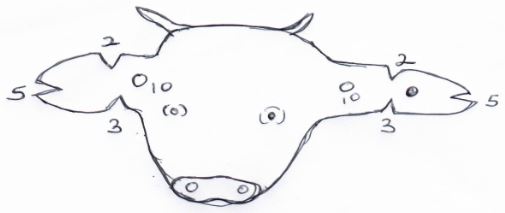
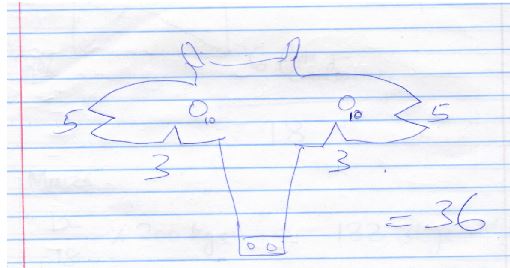
Answer all questions. - The diagram below illustrates a method of identification in livestock production. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the type of identification illustrated above. (1mk)
- Give the identification number of the animal illustrated in the diagram above. (1mk)
- Using diagrams illustrate how you can identify animals number 24 and 36 using the above method. (2mks)
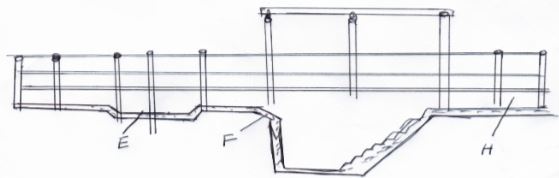
- The illustration below shows a cross section of a cattle dip.
- Name the parts labelled E and G.
E: ……………………………………(1mk)
G: ……………………………………(1mk) - State one use of each of the parts labelled E, F, H. (3mks)
E:
F:
H:
- Name the parts labelled E and G.
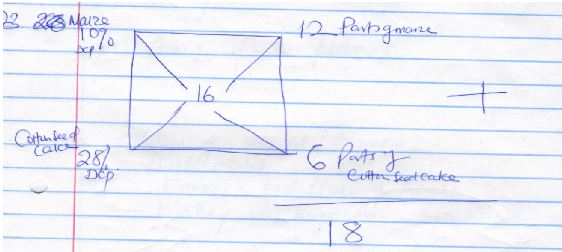
- A farmer wanted to prepare a 200kg of pig’s ratio containing 16% DCP. Using the Pearson’s square method calculate the amount of maize containing 10% DCP and cotton seed containing 28% DCP the farmer would need to prepare the ration. Show your working. (4mks)
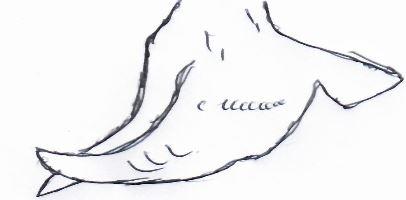
- The diagram below illustrates a hoof of a sheep. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the routine management practice that should be carried out on the hoof illustrated above. (1mk)
- State two reasons for carrying out the management practice in (a) above. (2mks)
- The diagram below illustrates a symptom of a disease in poultry. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Identify the disease. (1mk)
- Identify the causal organism. (1mk)
- Apart from the lesions, state two other symptoms of the disease. (2mks)
- State one control measure of the disease. (1mk)
SECTION C (40MKS)
Answer any two questions from this section.
-
-
- Describe contagious abortion (Brucellosis) disease under the following sub-headings.
- Causal organisms. (1mk)
- Animals affected (2mks)
- Symptoms (4mks)
- Control measures (6mks)
- Describe the structural features of a calf pen. (7mks)
- Describe contagious abortion (Brucellosis) disease under the following sub-headings.
-
- Give the reasons why embryo transfer use should be encouraged in dairy cattle breeding. (10mks)
- Explain five factors that a farmer should consider when siting a bee hive to prevent swarming of bees. (10mks)
-
- What are predisposing factors of a disease? (1 mark)
- Describe mastitis under the following sub– headings
- Causal organism. (1 mark)
- Predisposing factors (4 marks)
- Symptoms. (4 marks)
- Describe factors that may necessitate culling in livestock production. (10 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
-
- Burdizzo
- Rubber ring and elastrator
- Scalpel/sharp knife (2 x ½ Reject Rubber ring or elector alone)
-
- Using crush
- Rope
- Bull ring and leadstick/Nose ring & Lead stick (Reject bull ring or lead stick alone)
- Yoke
- Halters
- Casting (4x ½)
-
- Use tools for the correct purpose
- Keep tools safely after use
- Handle tools correctly during use
- Use of safety devices/protective clothes
- Maintain them in good working conditions (4 x ½)
-
- Kenya white is white all over the body while California white is white with black nose and ears.
- Kenya white has pink eyes while California white has black/brown eyes. (mark any as a whole) 1x1
-
- British Alpine
- Saanen
- Toggen burg
- Anglo Nubian
- Jamna pari (4x ½)
-
- Milk synthesis
- Formation of strong bones
- Improves vision
- Disease resistance/ immunity
- Improves vigour/proper growth (2 x ½)
-
- Proper hygiene
- Dusting using appropriate pesticide
- Covering affected parts with petroleum jelly to suffocate stick fast fleas. (2 x ½)
- Rumen/paunch (1x1)
-
- Steaming up of ewes to have sufficient milk for the lamb
- Use of lambing pens
- Ewes to be made to recognize lambs after lambing down
- Blind folding ewes to activate maternal instinct
- Treat mastitis/inflamed udder (4x ½)
-
Animal Gestation period Cow 270-285 days Sow 112 – 118 days/ 3 months, 3weeks, 3days Ewe 150 days Doe 28-32 days - In drift lambing all pregnant ewes are put together in one paddock and then separated as they lamb down whereas pen lambing is where ewes are only separated from one another after showing signs of lambing. (Mark as whole) 2x ½
-
- Make the animal docile
- Improve meat quality
- Control breeding diseases
- Control breeding/inbreeding/hereditary defects
- Improve growth rate (4 x ½)
-
- Control deficiency diseases
- Impart resistance to diseases
- Good physical appearance (2 x ½)
-
- Clean water – free from pollutants
- Slope of the land /topography – Gentle slope to ensure water flows by gravity
- Type of soil – clay soil which has high water holding capacity
- Reliable source of water – water available the year round
- Security – secure from thieves & predators (4 x ½)
-
- Anthrax
- Rinder pest
- Foot & mouth
- Rift valley fever
- New castle
- Fowl pox
- Fowl typhoid
- Gumboro (4x ½)
-
- Obstructing of oesophagus due to bulky food
- Abnormal pressure exerted on oesophagus by swelling in the wall of chest
- Indigestion due to eating poisonous substances or soft young grain forage/lush pasture (2 x ½)
-
- Mason’s trowel (reject trowel)
- Wood float.
- Plumb bob and line.
- Mason’s square.
- Mason’s chisel.
- Mason’s line.
- Tape measure (4 × ½ = 2 marks)
- Notifiable disease - Disease that spreads very fast and where outbreak must be reported to government authority e.g. Anthrax, Newcastle. Zoonotic disease - disease that can be passed from livestock to human beings. e.g. anthrax, brucellosis. mark as a whole (2 × 1 = 2 mark)
-
- Body size
- Level of milk production.
- age of animal.
- physiological status.
- environmental temperature. (4 × ½ = 2 marks)
-
- Fire proof.
- High durability.
- Easy to clean
- Easy to mould into various shapes.
- its strong.
- not attacked by vermins. (4 × ½ = 2 marks)
SECTION B
-
- Ear notching
- 40
-
-
-
- E- Foot path
- G- Dip tank
-
- E - Clean hooves/control footrot
- F - Forces animal to slide into the dip wash
- H - Allow dipwash to drip from the animal and flow back to the dip tank
-
-
Maize
12 x 200kgs = 133.3kgs Maize
18
Cotton seedcake
6 x 200kgs = 66.7kgs cotton seed cake
18 -
- Hoof trimming
-
- Control foot rot
- Prevent ram from injury ewe during tupping
- Allow proper movement
- Prevent sheep from injuring themselves
-
-
- Fowl pox
- Avian fox/virus
-
- Loss of appetite/anorexia
- Dullness
- Emaciation/loss of weight
- Water discharge from eyes and nose
-
- Vaccination
- Removing and killing affected birds
SECTION C
-
-
-
- Brucella abortus/suis/maliceasis/Bacterium
- Cattle, pigs, goats, sheep
-
- Spontaneous abortion/premature birth
- Retained after birth/placenta
- Inflamed testis/orchitis in bulls
- Low libido in bulls
- Yellow, brown, slimmy, odourless discharge from vulva
- Infertility in female cattle/cows
-
- Artificial insemination/embryo transplant
- Cutting and slaughtering and disposing affected animals
- Vaccination
- Avoid contact with aborted foetus
- Blood test to detect infected animals
- Cleanliness
-
- Concrete floor/slatted raised floor – easy cleaning
- Proper drainage – Avoid dampness
- Single housing – Avoid hair ball formation and diseases and parasite transmission
- Proper lighting – sunlight to allow getting of vitamin D
- Draught free – Diseases e.g Pneumonia
- Leak proof- Avoid wet ness
- Adequate space – Allow room for exercise feeding and watering equipment
-
-
-
- Calf born in the local surrounding hence minimizing effects of climatic change
- Embryos can be stored for a long time awaiting a recipient female
- Allows faster multiplication of a superior animal/breed
- Stimulate production of milk in females which were not ready or able to produce milk
- Saves cost of production in rearing bulls
- Embryos are cheaper than animals of equal value
- Easy and cheap to transport in test tubes compound to live animals
- High yielding embryo can be implanted into less valuable females to improve production
- Easy to plan
- Prevent injury of cows by heavy bulls
-
- Availability of water
- Availability of flowers
- Sheltered place
- Free from noise and other disturbances
- Away from human beings and livestock
-
-
- Predisposing factors - are those conditions inside or outside the body of an animal which lead to an animal contracting a disease or injury.
-
- Causal organism - bacterium / streptococcus spp / staphylococcus spp.
- Predisposing factors
- Old age
- Beginning and end of lactation/ stage of lactation.
- loosely hanging udders.
- incomplete milking.
- mechanical injuries on teats and udder.
- poor sanitation.
- poor milking techniques
- Symptoms.
- Milk contains pus, blood, thick clots or turns watery.
- Animals reject suckling or milking and kick due to pain on udder and teat.
- death of infected quarter may occur.
- milk has salty taste.
- Factors that may necessitate culling in livestock production.
- old age.
- low level of production.
- physical defects / deformities i.e. mono-eyed, limping, irregular number of teats, scrotal hernia, defective and weak backline.
- poor health / ill health.
- poor body conformation.
- bad temperament / undesirable behaviour like cannibalism in poultry, kicking in dairy
Download Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 3 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students