- This paper consists of three sections; A, B and C
- Answer ALL the questions in sections A and B
- Answer any TWO questions in section C
- All answers to be written in English
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- Name causal agent of anaplasmosis disease in cattle (½mk)
- State four reasons for castration in pigs (2 mks)
- State four characteristics of roughage livestock feeds (2 mks)
- State four roles of worker bee in a colony (2 mks)
- State one function for each of the following
- Shovel (½mk)
- Strip cup (½ mk)
- Give three ways in which infectious diseases can spread from one livestock to another within a farm. (1 ½ mk)
- Name three methods that are used in selection of breeding stock in livestock production. (1 ½ mk)
- Name one livestock disease that is transmitted by each of the following parasites
- Blue ticks (½ mk)
- Brown ear ticks (½ mk)
- Tsetse flies (½ mk)
- State four methods of controlling round worms (Ascaris sp) in livestock (2 mks)
- Apart from hides, name the raw materials obtained from each of the following livestock for the textile industry.
- Goat (½ mk)
- Sheep (½ mk)
- Rabbit (½ mk)
- Name two nutritional diseases of cattle (1 mk)
- State four signs of infestation by external parasites in goats (2 mks)
- Give four disadvantages of inbreeding in livestock. (2 mks)
- Name four parts of a farm building that can be reinforced using concrete (2 mks)
- State four advantages of fish farming in Kenya (2 mks)
- State four disadvantages of using plunge dips in tick control (2 mks)
- Name the complementary tool for each of the following tools named below.
- Trochar (½mk)
- Hand – drill (½ mk)
- Hypodermic needle (½ mk)
-
- Name two livestock diseases controlled through embryo transplant (1 mk)
- Give the meaning of the following terms as used in livestock breeding
- Close breeding (½mk)
- Line breeding (½mk)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- Below is a diagram illustrating the reproductive system of a bull. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
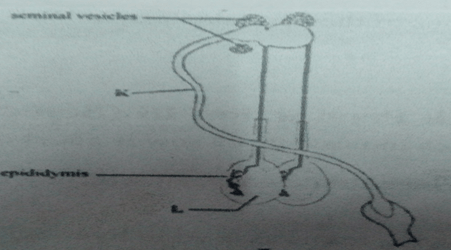
- Identify the parts labelled
- K (1 mk)
- L (1 mk)
- State the functions of the part labelled
- Epididymis (1 mk)
- Seminal vesicles (1 mk)
- Name the tool used to collect semen from the livestock (1 mk)
- Identify the parts labelled
- The illustration below shows a cross section of a cattle dip.
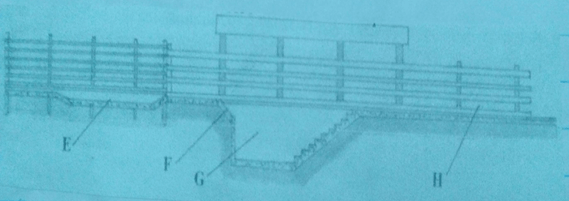
- Name the parts labelled E and G (2 mks)
- State one use for each of the parts labelled E, F and H (3 mks)
- The diagram below represents farm tools and equipment. Study them and answer the questions that follow.
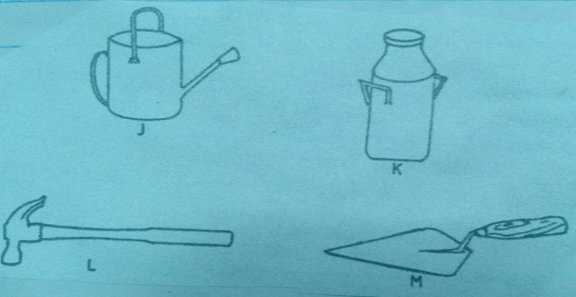
- Identify the tool/equipment labelled M and J (2 mks)
- State one use for each of the tool/ equipment labelled K and L. (2 mks)
- Give two maintenance practices for the equipment labelled K (1 mk)
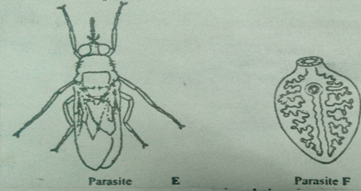
- The diagram below represents livestock parasites
- Identify parasite E (½ mk)
- State three symptoms that may be observed in an animal that has been attacked by parasite F. (3 mks)
- Name the intermediate host for parasite F. (½ mk)
- Give one control measure of each parasite. (1 mk)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any two questions from this section in the spaces provided after question 25.
-
- Describe the uses of fences on the farm (10 mks)
- Explain the factors considered when culling livestock. (5 mks)
- Give five harmful effects of liver flukes in sheep rearing. (5 mks)
-
- Giving a relevant example in each case, describe the role of the various components of a balanced diet in livestock nutrition. (10 mks)
- Outline the general characteristics of indigenous cattle (5 mks)
- Explain hoe physiological factors are used as a sign of ill or good health. (5 mks)
-
- Describe East Coast Fever under the following sub – headings.
- Livestock affected (1 mk)
- Vector and causal organisms (2 mks)
- Signs of attack (5 mks)
- Control measures (2 mks)
- Outline the procedure followed when hand spraying cattle to ensure effective use of acaricides to control ticks. (10 mks)
- Describe East Coast Fever under the following sub – headings.

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- Name causal agent of anaplasmosis disease in cattle (1/2 mk)
- Protozoa/ anaplasma marginate/ anaplasma spp.
- State four reasons for castration in pigs (2 mks)
- Prevent uncontrolled mating
- Improve the quality of meat
- Promote faster growth/ facilitate weight gain
- Make them docile
- Control breeding diseases
- Control inbreeding. (4 X 1//2 = 2 mks)
- State four characteristics of roughage livestock feeds (2 mks)
- Bulky
- High fibre content
- Low nutrient content
- Low digestibility
- Mainly plant origin (4 X 1//2 = 2 mks)
- State four roles of worker bee in a colony (2 mks)
- Kills the drone after mating the queen
- Scouting for new home
- Collect nectar/water/gum/propolis/pollen
- Make honey combs
- Protect the colony
- Clean the hive
- Make honey and bees wax
- Seal the cracks and crevices (4 X 1//2 = 2 mks)
- State one function for each of the following
- Shovel
- mixing mortal/manure (1/2 mk)
- Lifting soil/manure
- Strip cup (1/2 mk)
- detect mastitis infection in milk.
- Shovel
- Give three ways in which infectious diseases can spread from one livestock to another within a farm. (1 ½ mk)
- Through vectors
- Through ingestion of contaminated food and water/ through food and water
- Through contact
- Through inhalation of contaminated air/through air. (3X 1//2 = 1 ½ mks)
- Name three methods that are used in selection of breeding stock in livestock production. (1 ½ mk)
- Progeny testing
- Mass selection
- Contemporary comparison (3X 1//2 = 1 ½ mks)
- Name one livestock disease that is transmitted by each of the following parasites
- Blue ticks - Anaplasmiosis/ gall sickness/Red water/ babeosis (1/2 mk)
- Brown ear ticks - ECF / corridor disease/ Nrb sheep disease (1/2 mk)
- Tsetse flies – Trypanosomiasis/ nagana (1/2 mk)
- State four methods of controlling round worms (Ascaris sp) in livestock (2 mks)
- Use of antihelmintics/deworming
- Proper disposal of feaces/hygiene
- Burning of infected pasture
- Rotational grazing
- Ploughing (4 X 1/2 = 2 mks)
- Apart from hides, name the raw materials obtained from each of the following livestock for the textile industry.
- Goat - mohair (1/2 mk)
- Sheep - wool (1/2 mk)
- Rabbit - fur (1/2 mk)
- Name two nutritional diseases of cattle (1 mk)
- Milk fever/parturient puresis
- Bloat
- Calf tetany / tetany / grass staggers/ grass tenany (2 X ½ = 1 mk)
- State four signs of infestation by external parasites in goats (2 mks)
- Anorexia/loss of appetite under heavy digestion
- Stiff dry coat/starring coat
- Dehydration and pale mucosa
- Eggs and adults are seen in feaces
- General emaciation
- Anaemic condition when infestation is heavy
- Pot – bellies especially in young animals
- Coughing (4 X 1//2 = 2 mks)
- Give four disadvantages of inbreeding in livestock. (2 mks)
- Reduction of vigour in animals/ loss of hybrid vigour / heterosis
- Quality of products is lowered
- Reduction in disease resistance ability
- Appearance of undesirable hereditary defects
- Increase in abortion/embryonic mortality
- Decline in fertility
- Reduced production. (4 X 1//2 = 2 mks)
- Name four parts of a farm building that can be reinforced using concrete (2 mks
- Foundation of the building
- Floor slab/ floor
- Lintel
- Pillars
- Walls (4 X 1//2 = 2 mks)
- State four advantages of fish farming in Kenya (2 mks)
- Cheap source of protein for the family
- Require little land and is possible where land is limiting
- Quick source of income for the farmer
- Make fish to be available with the locality (4 X 1//2 = 2 mks)
- State four disadvantages of using plunge dips in tick control (2 mks)
- High initial construction cost/ high capital
- Dangerous for young and pregnant, sick animals/heavy
- Requires a lot of water
- Poisoning by swallowing dip wash (4 X 1//2 = 2 mks)
- Name the complementary tool for each of the following tools named below.
- Trochar – canula (1/2 mk)
- Hand – drill – drill bit/twist drill (1/2 mk)
- Hypodermic needle – syringe (1/2 mk)
-
- Name two livestock diseases controlled through embryo transplant (1 mk)
- Brucellosis / contagious abortion / Bang’s disease
- Vaginitis e.g. Borine trichomoniasis
- Vibriosis ( Borine genital campylo bacteriosis ) (2 X ½ = 1 mk)
- Give the meaning of the following terms as used in livestock breeding
- Close breeding – mating of closely related animals (1/2 mk)
- Line breeding – mating of distantly related animals that share a common ancestry. (1/2 mk)
- Name two livestock diseases controlled through embryo transplant (1 mk)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- Below is a diagram illustrating the reproductive system of a bull. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the parts labelled
- K - Urethra (1 mk)
- L - Testes / testis (1 mk)
- State the functions of the part labelled
- Epididymis – stores sperms (1 mk)
- Seminal vesicles – secrete seminal fluid/ semen in which sperms move (1 mk)
- Name the tool used to collect semen from the livestock (1 mk)
- Artificial vagina
- Identify the parts labelled
- The illustration below shows a cross section of a cattle dip.
- Name the parts labelled E and G
- E – footbath (1 mk)
- G – dip tank (1 mk)
- State one use for each of the parts labelled E, F and H
- E – cleans hooves/ controls foot rot (1 mk)
- F – forces the animal to slide and plunge in to the dip wash (1 mk)
- H – Allows the dip wash to drip from the animal and flow back to the dip tank (1 mk)
- Name the parts labelled E and G
- The diagram below represents farm tools and equipment. Study them and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the tool/equipment labelled M and J
- M – Masons trowel (1 mk)
- J – watering can (1 mk)
- State one use for each of the tool/ equipment labelled K and L.
- K – temporary storage of milk/ holding milk during transportation (1 mk)
- L - driving nails in to wood/removing nails from wood (1 mk)
- Give two maintenance practices for the equipment labelled K (1 mk)
- Cleaning after use
- Painting with aluminum paint to prevent rusting
- Repair / replace broken/worn out parts
- Sterilizing the equipment (2 X ½ = 1 mk)
- Identify the tool/equipment labelled M and J
- The diagram below represents livestock parasites
- Identify parasite E
- Tsetse fly (1/2 mk)
- State three symptoms that may be observed in an animal that has been attacked by parasite F. (3 mks)
- Loss of weight and emaciation
- Pot – bellied condition
- Suffer indigestion
- Damage to the liver tissue and hemorrhage
- Anemic condition
- Swollen and painful abdomen
- Dullness and appearing depressed
- Recumbence precedes death (3 X 1 = 3 mks)
- Name the intermediate host for parasite F. (1/2 mk)
- Fresh water snail / mud snail (1 X ½ = ½ mk)
- Give one control measure of each parasite. (1 mk_
- Parasite E
- Bush clearing
- Spraying suitable chemicals / insecticides
- Use of impregnated nets/ fly traps
- Use of sterilizing agents e.g. radio isotopes male flies (1 X ½ = ½ mk)
- Parasite F
- Spraying chemicals to stagnant water
- Physical killing fresh water snail
- Draining stagnant water / swampy areas
- Burning infested pastures during dry seasons
- Not grazing animals near marshy areas by fencing (1 X ½ = ½ mk)
- Parasite E
- Identify parasite E
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any two questions from this section in the spaces provided after question 25.
-
- Describe the uses of fences on the farm (10 mks)
- Provide security from thieves, predators
- Enable pad docking/ rotational grazing/mixed farming
- Control parasites and disease by keeping away foreign animals
- Show boundaries between farms
- Hedges act as wind breakers
- Have an aesthetic value / beauty
- Hedges help to conserve soil and water
- Provides privacy
- Enable isolation of animals for different purpose
- Help avoid boundary disputes
- Controls movement of animals and people - preventing formation of unnecessary paths in the farm (10 X 1 = 10 mks)
- Explain the factors considered when culling livestock. (5 mks)
- Poor health
- Physical deformities
- Infertility
- Poor quality products
- Bad temperamental
- Old age
- Hereditary defects
- Poor mothering ability
- Low production
- To avoid inbreeding (5 X 1 = 5 mks)
- Give five harmful effects of liver flukes in sheep rearing. (5 mks)
- Digestive upsets due to blocking of bile
- Emaciation/ recumbency leading to death
- Anaemia due to destruction due to sucking blood
- Swollen low jaw / oedema in the jaws
- Swollen abdomen
- Destruction of liver tissues / hemorrhage (5 X 1 = 5 mks)
- Describe the uses of fences on the farm (10 mks)
-
- Giving a relevant example in each case, describe the role of the various components of a balanced diet in livestock nutrition. (10 mks)
- Carbohydrates – main source of energy/ respired to release energy e.g. cereals, root crops, tubers, grass pastures
- Fats and oils are respired to produce energy e.g. oil seeds, animal by- products, foliage
- Proteins cause growth, repair, and production of antibodies, enzymes, hormones and products. E.g. seed cake, leguminous foliage, animal by-products, young green grass
- Vitamins for protection against infection, promote growth, bone formation, muscular activity and organic catalysts. E.g. green feeds, sunlight, milk, whole grains
- Minerals for strong bone formation, milk synthesis, formation of hard – shelled eggs, prevent mineral deficiency diseases and promote growth. E.g. cereal grains, green vegetables, fish meal, liver meal, salt licks
- Water for biochemical body excretion, cooling effect, transport of food nutrients and components of body fluids, parts of body excretion and products. E.g. metabolic water, bound water, free water.
- Component 5X 1 = 5mks
- Function 5 X ½ = 2 ½ mks
- Source 5 X ½ = 2 ½ mks
- Outline the general characteristics of indigenous cattle (5 mks)
- They have humps
- Tolerant to tropical diseases
- Slow growth rate
- Low produce of milk and meat
- Walk long distances in search of food and water
- Have calving interval of more than one year
- Survive in high temperatures ( any 5 X 1= 5 mks)
- Explain how physiological factors are used as a sign of ill or good health. (5 mks)
- Respiration rate: healthy animals breathe in and out with ease while sick animals breathe with difficulties, irregular and forced breath
- Body temperature: each livestock species has a normal range of temperature, deviation from range is a sign of ill health
- Level of production: good health is characterized by steady production while ill health is indicated by sudden drop in production
- Appetite: health animals eat regularly and enough while diseased have very appetite or anorexia
- Feacal matter: health animals produce feaces that are of right consistence, colour, texture and smell, while animals produce hard, dry, and too watery or with blood spots. ( any 5 X 1= 5 mks)
- Giving a relevant example in each case, describe the role of the various components of a balanced diet in livestock nutrition. (10 mks)
-
- Describe East Coast Fever under the following sub – headings.
- Livestock affected (1 mk)
- Cattle (1 X 1 = 1 mk)
- Vector and causal organisms (2 mks)
- Brown ear tick/Rhipicephalus
- Protozoa / appendiculatus theileria parra (2 X 1 = 2 mks)
- Signs of attack (5 mks)
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Profuse salivation
- Fever
- Lachrymation
- Labored breathing
- Reduced appetite
- Impaired vision
- Coughing
- Hemorrhage in vulva and mouth (5 X 1 = 5 mks)
- Control measures (2 mks)
- Tick control
- Treated using appropriate drugs
- Vaccination (2 X 1 = 2 mks)
- Livestock affected (1 mk)
- Outline the procedure followed when hand spraying cattle to ensure effective use of acaricides to control ticks. (10 mks)
- Restrain the animal in a crush
- A stir up pump or knapsack sprayer is used to put the acaricide
- Spray the entire backline from the shoulder to the tail head.
- Spray the sides in a zigzag motion to trap and retain the wash from the backline.
- Spray the belly with the nozzle facing upwards
- Spray the scrotum/udder and the hide flanks carefully
- Spray both hind legs upto and including the heels
- Spray the udder, the tail head and around the anus/vulva
- Hold the tail switch on the rump and spray it thoroughly to ensure complete wetting
- Spray the neck and the fore legs from the flanks to the heels
- Spray the head and the face making sure the bases of the horns are thoroughly wetted
- Spray the inside of the ears
- Release the animal after drying of the animal (10 X 1 = 10 mks)
- Describe East Coast Fever under the following sub – headings.
Download Agriculture Questions and Answers - Form 4 Mid Term 1 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students