- Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided.
- All workings must be clearly shown where necessary.
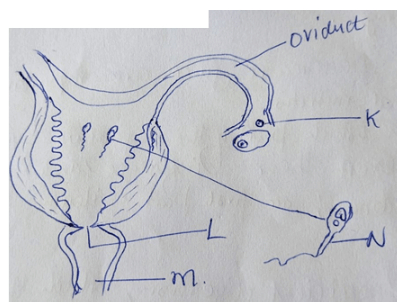
- Study the diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow
-
- Label parts labelled (2mks)
- K –
- L -
- M-
- Through which process is structure labeled K in (a) (i) above produced? (1mk)
- Label parts labelled (2mks)
- How is the cell labeled N adapted to perform its functions. (3mks)
- Name the hormone that stimulates the production of cell labeled K.at puberty. (1mk)
-
- Bile and pancreatic juice are important secretions in animal nutrition.
- In which part of the digestive system do they exert their influence? (1mk)
-
- For efficient digestion, which of the two secretions should be mixed with the chyme first? (1mk
- Explain your answer (4mks)
- Explain why an adult does not need to eat too much protein in a meal/diet. (2mks)
- The table below shows the approximate distribution of blood groups in a sample of 100 people in a population.
Blood group Frequency Rhesus +ve Rhesus −ve A 26 22 4 B 20 18 2 AB 4 3 1 O 50 42 8 - Calculate the percentage of Rhesus negative (Rh-ve) individuals in the population? (1mk)
- Account for
- The large number of blood group O individuals in a population. (2mks)
- The small number of individuals with blood group AB. (2mks)
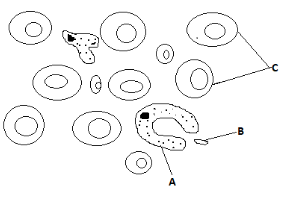
- The diagram below represents a blood smear on a glass slide.
- State the importance of structure C being large numbers in the blood smear. (1mk)
- Give a reason why structure C would be found in large numbers in high altitude than in low altitude. (1mk)
- Name the process by which structure A would engulf structure B. (1mk)
-
- Identify organs B and D in photograph T2 and state the class of organism from which they were obtained. (4mks)
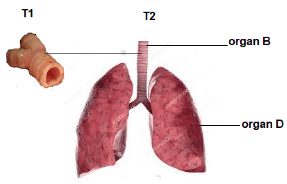
- State the common function of the organs identified in (a) above. (1mk)
- Name the parts of the body where B and D in photograph T2 are found. (2mks)
- List the adaptations of D to its functions. (3mks)
- Using observable features only, state how B is adapted to its function (2mks)
- Identify organs B and D in photograph T2 and state the class of organism from which they were obtained. (4mks)
- The set apparatus was assembled by a group of students to investigate some physiological process. Glucose solution was boiled and oil added on top of it. The glucose solution was then allowed to cool before yeast was added.
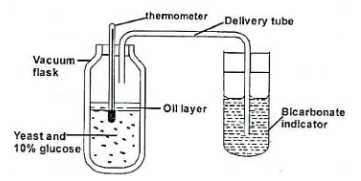
-
- Give ONE aim of the experiment. (1mk)
- Explain observations expected after 24hrs. (2mks)
-
- Why was the glucose solution boiled before adding the yeast suspension? (1mk)
- What was the importance of cooling the glucose solution before adding the yeast? ( 1mk)
- In another investigation, a bird was found to use 10 litres of oxygen to give a respiratory quotient of 0.7 during period of flight.
- Name the type of food that was being respired by the bird ( 1mk)
- Determine the amount of carbon (IV) oxide produced during the same flight. (2mk)
-
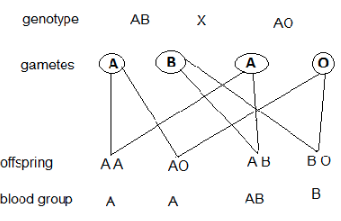
- Mr. Juma has sued Serenity Hospital on grounds that their child was wrongly identified such that they got the wrong one. The child is blood group O. Mr. Juma is blood group AB while Mrs. Juma is heterozygous blood group A.
- Work out the possible blood group of their offsprings. (4 marks)
- Is Mr. Juma justified in his claims? Explain. (2 mark)
- State two blood disorders in humans that result from mutation. (2 marks)
SECTION B:
Answer question 7 (Compulsory) and either question 8 or 9 in the spaces provided after question 8.
- A Farmer wished to plant certain species of Erythrina trees on his farm. However, their seeds normally take time to germinate after sowing. To overcome this problem, he put the seeds in hot water maintained at 50°C.
Batches of 20 seeds were removed at one minute intervals and then planted in trays containing moist soil. After 15 days, the number of seeds that germinated in each tray was counted.
The results obtained were as shown in the table below.
Batch order Time intervals(minutes) Germinated seeds Percentage of seeds that Germinated. 1st 0 3 2nd 1 3 3rd 2 8 4th 3 15 5th 4 18 6th 5 13 7th 6 10 8th 7 6 9th 8 2 10th 9 0 11th 10 0 - Calculate the percentage germination rate for each batch and fill in the table. (5mks)
- Use your results to plot a graph showing percentage germination against the duration in which the seeds were soaked in hot water. (6mks)
- From the graph derive the expected number of seeds that would germinate if soaked for 4.5 minutes. (1mk)
- Using the graph briefly explain the effect of hot water treatment on seed germination of Erythrina. (5mks)
- Explain why there was no germination of seeds soaked in hot water for nine to ten minutes. (1mks)
- Besides hot water treatment, suggest two other methods that can be used to speed up germination in Erythrina. (2mks)
- Explain the adaptations of parts of the ear in the outer and middle ear. (20 mks)
- Describe how the kidney Nephron functions. (20 mks)
MARKING SCHEME
- Study the diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow
-
- Label parts labelled (2mks)
- K – egg/ovum rej. ova
- L - Cervix
- M- vagina/vaginal canal
- Through which process is structure labeled K in (a) (i) above produced? (1mk)
- Ovulation
- Label parts labelled (2mks)
- How is the cell labeled N adapted to perform its functions. (3mks)
- Long tail to propel /propulsion towards egg
- has numerous mitochrondris – to provide energy for propulsion;
- has acrosome that has lytic enzymes to digest part of ovum wall to allow sperms to penetration
- has habloid mucles tofuse with ovum nuclears to maintain chiploidy in zygote;
- Name the hormone that stimulates the production of cell labeled K.at puberty. (1mk)
- oestrogen
-
- Bile and pancreatic juice are important secretions in animal nutrition.
- In which part of the digestive system do they exert their influence? (1mk)
- Duodenum; acc first part of ileum
-
- For efficient digestion, which of the two secretions should be mixed with the chyme first? (1mk
- Bile juice;
- Explain your answer (4mks)
- The salts in it ( sodium tanrocholate/sodium glycocholate) neutralize the acidity in chyme; and create alkaline medium; suitable for pancreatic enzymes( ie pancreatic amylase, lipase);
- It emulsifies fat/oil ( to create large surface area for lipase enzyme);
- For efficient digestion, which of the two secretions should be mixed with the chyme first? (1mk
- Explain why an adult does not need to eat too much protein in a meal/diet. (2mks)
- Excess protein are not stored in the body; they are deaminated to produce urea/some coverted to fats
- In which part of the digestive system do they exert their influence? (1mk)
- The table below shows the approximate distribution of blood groups in a sample of 100 people in a population.
- Calculate the percentage of Rhesus negative (Rh-ve) individuals in the population? (1mk)
15 x 100 = 15%
100 - Account for
- The large number of blood group O individuals in a population. (2mks)
- The allele O appears in many blood groups/Allele O appears in blood group A, B and O; therefore higher chances of being inherited in a population;
- The small number of individuals with blood group AB. (2mks)
- Allele A and B are co-dominant; hence express themselves only in blood group AB;
- The large number of blood group O individuals in a population. (2mks)
- The diagram below represents a blood smear on a glass slide.
- State the importance of structure C being large numbers in the blood smear. (1mk)
- To increase the surface area for efficient transport/increase efficiency of delivery of oxygen; (to tissue)
- Give a reason why structure C would be found in large numbers in high altitude than in low altitude. (1mk)
- At high altitude air is less dense/partial pressure of oxygen is low/there is low concentration of oxygen, hence the number of red blood cells/structure C increases to increase oxygen carrying capacity of blood;
- Name the process by which structure A would engulf structure B. (1mk)
- Phagocytosis;
- State the importance of structure C being large numbers in the blood smear. (1mk)
- Calculate the percentage of Rhesus negative (Rh-ve) individuals in the population? (1mk)
-
- Identify organs B and D in photograph T2 and state the class of organism from which they were obtained. (4mks)
ORGAN IDENTITY CLASS B Trachea/windpipe; mammalia D lungs: mammalia - State the common function of the organs identified in (a) above. (1mk)
- Gaseous exchange.
- Name the parts of the body where B and D in photograph T2 are found. (2mks)
- B - Neck region and the thoracic cavity;
- D - Thoracic cavity/chest cavity/thorax;
- List the adaptations of D to its functions. (3mks)
- Have a large surface area to ensure diffusion of larger volume of gases;
- Highly vascularized to transport the diffusing gases; hence maintain a steep concentration gradient;
- have a thin epithelium to reduce the diffusion distance of gases;
- Using observable features only, state how B is adapted to its function (2mks)
- Have rings of cartilage that prevent it from collapsing; and
- keeps the lumen fully open even when the neck bends;
- Identify organs B and D in photograph T2 and state the class of organism from which they were obtained. (4mks)
- The set apparatus was assembled by a group of students to investigate some physiological process. Glucose solution was boiled and oil added on top of it. The glucose solution was then allowed to cool before yeast was added.
-
- Give ONE aim of the experiment. (1mk)
- To show that energy is released in anaerobic respiration;/
- To show that carbon (IV) oxide is produced in anaerobic respiration;
- Explain observations expected after 24hrs. (2mks)
- Increase in temperature/ tthermometer reading since energy/heat is released;
- Colour of indicator changed to yellow due to acidity/carbon (IV) oxide released changed indicator to yellow;
- Give ONE aim of the experiment. (1mk)
-
- Why was the glucose solution boiled before adding the yeast suspension? (1mk)
- Expel dissolved oxygen;
- What was the importance of cooling the glucose solution before adding the yeast? ( 1mk)
- Prevent entry of air/oxygen into glucose solution; (any one)
- Why was the glucose solution boiled before adding the yeast suspension? (1mk)
- In another investigation, a bird was found to use 10 litres of oxygen to give a respiratory quotient of 0.7 during period of flight.
- Name the type of food that was being respired by the bird ( 1mk)
- Fat
- Determine the amount of carbon (IV) oxide produced during the same flight. (2mk)
RQ = vol of CO2 produced /vol of O2 used
0.7 = X/10
X = 7 litres
- Name the type of food that was being respired by the bird ( 1mk)
-
- Mr. Juma has sued Serenity Hospital on grounds that their child was wrongly identified such that they got the wrong one. The child is blood group O. Mr. Juma is blood group AB while Mrs. Juma is heterozygous blood group A.
- Work out the possible blood group of their offsprings. (4 marks)
- Is Mr. Juma justified in his claims? Explain. (2 mark)
- Yes;
No possibility of the couple’s child to have blood group O
- Yes;
- State two blood disorders in humans that result from mutation. (2 marks)
- Haemophilia; sickle cell anaemia;
- Work out the possible blood group of their offsprings. (4 marks)
SECTION B:
Answer question 7 (Compulsory) and either question 8 or 9 in the spaces provided after question 8.
- A Farmer wished to plant certain species of Erythrina trees on his farm. However, their seeds normally take time to germinate after sowing. To overcome this problem, he put the seeds in hot water maintained at 50oC.
Batches of 20 seeds were removed at one minute intervals and then planted in trays containing moist soil. After 15 days, the number of seeds that germinated in each tray was counted.
The results obtained were as shown in the table below.- Calculate the percentage germination rate for each batch and fill in the table. (5mks)
Batch order Time intervals(minutes) Germinated seeds Percentage of seeds that Germinated. 1st 0 3 15 2nd 1 3 15 3rd 2 8 40 4th 3 15 75 5th 4 18 90 6th 5 13 65 7th 6 10 50 8th 7 6 30 9th 8 2 10 10th 9 0 0 11th 10 0 0 - Use your results to plot a graph showing percentage germination against the duration in which the seeds were soaked in hot water. (6mks)
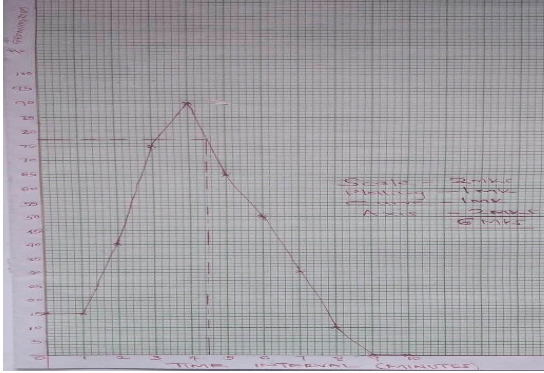
- From the graph derive the expected number of seeds that would germinate if soaked for 4.5 minutes. (1mk)
- 76.5% ± 0.1;
- Using the graph briefly explain the effect of hot water treatment on seed germination of Erythrina. (5mks)
- Increase in exposure of the seed to hot water increased number of seeds that germinated up to optimum; more exposure beyond optimum reduced number of seeds that germinated;
- Water softened the hard seed coat; and activated germination enzymes; up to optimum where more exposure denature the enzymes lowering germination;
- Explain why there was no germination of seeds soaked in hot water for nine to ten minutes. (1mks)
- All the enzymes were denatured;
- Besides hot water treatment, suggest two other methods that can be used to speed up germination in Erythrina. (2mks)
- Scarification;
- Roasting;
- Calculate the percentage germination rate for each batch and fill in the table. (5mks)
- Explain the adaptations of parts of the ear in the outer and middle ear. (20 mks)
- The pinna: contains cartilage which keeps it erect and open; /funnel shaped; to collect and direct sound waves to the external auditory meatus/canal;
- External auditory meatus/canal; is a hollow tube that connects concentrate and directs sound waves to the tympanum/ear drum; its glandular; to secrete a waxy substance; which is an insect repellant/ and traps dust/maintains the flexibility of the ear drum/tympanic membrane; it has hairs; tha trap solid particles/dust/push excess wax outwards.
- Tympanic membrane / ear drum; is a pliable membrane that easily vibrates; on impinging sound waves into vibrations; and transmits them to the ear ossicles /maleus and stapes;
- The ear ossicles/maleus and stapes are loosely suspended to act as lever system; within the middle ear; which allow them to vibrate/amplify sound vibrations; and transmit them to oval window/fenestra ovalis;
- Eustachian tube; a hollow tube that connects idle ear to the back of the throat/pharynx; it equalizes the air pressure on both sides of the tympanum/in the middle ear with the atmospheric pressure.
Total 22 marks; max 20 marks
- Describe how the kidney Nephron functions . (20 mks)
- The afferent arteriole/vessel supplies blood to glomerulus;
- Afferent arteriole has a wider diameter than efferent arteriole;
- This difference in the diameter of the afferent and efferent arterioles causes high pressure; leading to ultra filtration;
- (The walls of blood capillaries are one cell thick) hence all the glucose, amino acids, salts, urea and water; filter into the Bowman ’s capsule; to form glomerular filtrate; white blood cells/ red blood cells/(plasma) proteins (such as globulin/platelets) are too large to pass through the capillary wall/ hence remain in blood capillary; the filtrate flows into the proximal convoluted tubule; where all glucose, amino acids (and vitamins) are selectively reabsorbed; back into the blood stream;
- Many mitochondria provide energy for reabsorption of the substances against concentration gradient/active transport;
- The filtrate flow into the loop of henle where water in the descending loop moves by osmosis into the blood capillary; sodium chloride is actively pumped from ascending arm into the blood capillary;
- The filtrate flows into distal convoluted tubule; water is reabsorbed; salts reabsorbed from distal convoluted tubule (into blood capillary);
- The glomerular filtrate flows into collecting tubule/duct; where more water is reabsorbed (into the blood stream);
- Antiduretic hormone (ADH)/vasopressin influences the amount of water reabsorbed (depending on osmotic pressure of blood);
- The filtrate flows down the collecting ducts now referred to as urine; is emptied into pelvis; and then into ureter;
NB// Award = reabsorbed into blood once.
Max 20 marks
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 4 End Term 2 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students