- The paper consists of three sections A B and C
- Answer all the questions in Section A and B
- Answer any two questions in section C
- Answer all the questions in English
SECTION A (30MKS)
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided
- Name the routine field practice done by;
- Remove of extra suckers in banana stool. (½ mk)
- Removal of old stems down to level of top foliage in pyrethrum (½ mk)
- Removal of suckers from coffee bushes (½ mk)
- State three characteristic of phosphate fertilizers. (1½ mks)
- State two physical properties of soil that influence crop production (1 mk)
- Outline four ways by which crop pests are classified (2 mks)
- State three use of labour records in Agricultural (1½ mk)
- Give four advantages of overhead irrigation in crop production (2 mks)
- List three basic concepts in agricultural economics. (1½ mk)
- Give four varieties of tomatoes grown for processing (2 mks)
- State four pasture management practices done to enhance per unit area. (2 mks)
- Name two macro-nutrients which are classified as;
- Fertilized elements (1mk)
- Liming elements (1mk)
- Give three ways by which pruning helps to control disease in crops. (1½ mk)
- State four ways in which weeds are exceedingly adapted to the environment (2 mks)
- State four factors that determine the time at which a crop is planted. (2 mks)
- Give four factors that affect the effectiveness of a pesticide. (2 mks)
- State four reasons for staking tomatoes in crop production. (2 mks)
- State three cultural methods of soil and water conservation (1½ mk)
- State four benefits of having a land tittle deed to a farmer (2mks)
SECTION B (20MKS)
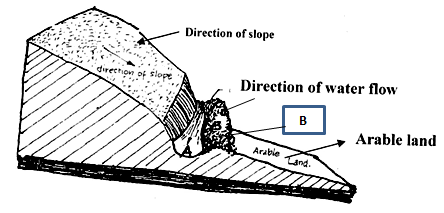
- The illustration below shows a newly constructed cut-off drain. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
-
- How can part of the structure labeled B be stabilized after it has been constructed? (1mk)
- Identify the part of the cut-off drain labeled A. (1mk)
- Describe the procedure of constructing a cut-off drain. (2mks)
-
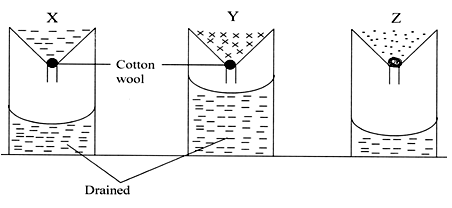
- The experiment below was set to compare the porosity and water holding capacity of three different types of soils.
- Identify the soils in each of the following funnels labeled X, Y and Z. (1½mks)
- Which of the types of soil can be said to have the highest porosity rate? (½mk)
- Give reasons for your answers in (ii) above. (2mks)
- Which type of soil would be suitable for planting paddy rice? (1mk)
- Explain your answer in (iv) above. (1mk)
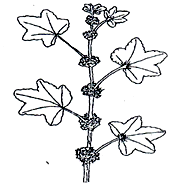
- Below is a diagram of a Common East African Weed.
- Identify the weed illustrated above. (1mk)
- Give one harmful effect of the weed illustrated above to livestock. (1mk)
- State two methods of controlling the weed illustrated above. (1mk)
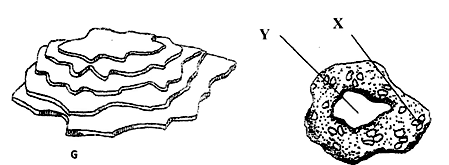
- The diagrams below illustrate some soil structures. Study them and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the soil structures F and G. (1mk)
- Name the part labeled X and Y in diagram F. (1mk)
- Describe two ways through which structure G influence crop production. (2mks)
- The diagrams labeled D and E below are illustrations of coffee established using two different formative pruning systems. Study them and answer the questions that follow.

- Name the system of pruning illustrated in diagram D above. ( 1mk)
- Describe how the pruning system illustrated in diagram E is carried out. (2mks)
SECTION C (20MKS)
Answer any two questions in section C
-
- Explain factors affecting rooting of cutting (5mks)
- State and explain the factors that determine the spacing of crops when planting (10mks)
- Give five ways in which government policy influence agriculture (5mks)
-
- State and explain the cultural methods used in control of crop pests (8mks)
- Describe the procedure of silage making (7mks)
- State the observable indicators of economic development of a nation (5mks)
-
- Outline five advantages of adding organic manure into the soil (5mks)
- Describe the precautions taken when harvesting tea (3mks)
- Study the following information which was extracted from Mr. Mulong’os farm record on 31.2.12.2020 and answer the questions that follow.
Loan payable to bank – shs. 300,000
Five milking cows - shs. 250,000
400 layers - shs. 80,000
20 goats - shs. 30,000
Debt payable to coo-p society - shs. 20,000
Building and structures - shs. 600,000
Bonus payable to workers - shs 19,000
Cattle feeds - shs. 10,000
Animal drugs in store - shs. 4,000
Debt receivable - shs. 18,000
Breakages to repair - shs. 30,000
Cash to at hand - shs.20,000
Cash in bank - shs 30,000
Spray equipment - shs. 12,000- Prepare a balance sheet for Mr. Mulang’os farm using the information above (6mks)
- Was Mr. Mulango farm business solvent or insolvent? (1mk)
- Describe post-harvest practices carried out on maize (5mks)

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (30MKS)
-
- Removal of extra banana suckers stool
- Banana of stool management (½ mk)
- Removal of old stems pyrethrum
- Cutting back pyrethrum (½ mk)
- Removal of suckers in coffee
- De-suckering in coffee
- Accept pruning (½ mk)
- Removal of extra banana suckers stool
- Three properties of phosphate fertilizers
- Sparingly soluble in water
- Have a residual effect in the soil
- Not liable to leaching
- Have a slight scorching effect (3 x ½=1½mks)
- Two physical properties of soil on crops
- Soil texture
- Soil profile/depth
- Soil structure (2 x ½ = 1mk)
- Four ways of classifying crop pests
- Mode of feeding
- Crops attached
- Stage of development of the pest
- Stage of growth of crop
- Scientific classification
- Level of damage
- Habitat of where there are found (4 x 1/2 = 2mks)
- Three uses of labor records
- Help in payment of wages
- Used in calculations of operation costs
- Use in assessment of income tax.
- Used in calculating profits or losses (3 x 1/2 = 11/2mk)
- Four advantages of overhead irrigation
- Water is evenly distributed over the required area
- Less wastage of water than furrow irrigation
- Can be practiced on sloppy grounds
- Foliar fertilizers can be applied with irrigation water. (4x 1/2 = 2mks)
- Basic economic concepts
- Scarcity
- Preference and choice
- Opportunity cost (3 x 1/2 = 11/2mk)
- Four varieties for processing tomatoes
- Primabel
- San merzanno
- Cal J
- Kenya beauty
- Slein Z
- Rutjer S
- 10 x hybrid (4 x 1/2 = 2mk)
- Four pasture management to enhance yields
- Weed control
- Top dressing
- Topping re-seeding
- Pest control
- Controlled grazing
- Irrigation (4 x 1/2 = 2mks)
-
- Fertilizer elements
- Nitrogen
- Phosphorus
- Potassium (2 x 1/2 = 1mk)
- Liming elements
- Calcium
- Sulphur
- Magnesium (2 x 1/2 = 1mk)
- Fertilizer elements
- Three ways in which pruning control diseases
- Enhance penetrating of spray to kill vectors
- Remove infected branches
- Remove micro-climate that to discovering pest and diseases
- Maintains field hygiene to reduce infections (3 x ½ = 1½mks)
- Four ways of weeds adaptation to the environment
- Elaborate /extension root system
- Ability to survive in poor soils
- Have short life cycle
- Some propagate vegetatively e.g. wandering jew
- Prolonged seed dormancy
- Wide range of ecological condition (4 x 1/2 =2mks)
- Four factors that determine time of planting
- Rainfall patterns/water availability
- Growth habit of the crop
- Purpose of the crop
- Prevalence of pests and diseases
- Market demand (4 x 1/2 = 2mk)
- Four factors that affect effectiveness of a pesticide
- Concentration of pesticide
- Weather conditions
- Persistence of pesticides
- Formulation
- Mode of action (4 x 1/2 = 2mks)
- Reasons for staking in tomatoes
- Production of clean fruits
- Prevent infestation by soil borne diseases
- Facilitate spraying and harvesting of the crop
- Controls incidence of disease outbreaks e.g. light (4 x 1/2 = 2mks)
- Cultural methods of soil and water conservation
- Mulching
- Cover cropping strips/filter strips
- Grassed water ways
- Planting agroforestry trees
- Contour farming (3 x 1/2 = 11/2mks)
- Four benefits of land tittle deed
- Can be used as security to get a loan/credit
- Minimize land disputes
- A farmer can sell part or whole land (3 x 1/2 = 1/2mks)
SECTION B (20 MKS)
-
-
- By planting grass/suitable vegetation (1 x 1 = 1mk)
- A – channel/trench (1 x 1 = 1mk)
-
- Measure √ and mark √ the layout of the drain
- Dig and remove √ soil from the channel and heap it on the lower √ side of the drain (4 x 1/2 = 2mks)
-
-
-
- X = loam
- Y = sand
- X = clay (3 x 1/2 = 11/2 mks)
- Soils Y (sand ) (½ mk)
- It has drained the highest amount of water as opposed to others. (1 x 1 = 1mk)
- Soil Z/clay soil (1 x 1 = 1mk)
- It is not easily drained/ does not loose water easily when flooded (1 x 1 = 1mk)
-
-
- Mallow weed (1 x 1 = 1mk)
- Poisonous/toxic to livestock (1 x 1 = 1mk)
-
- Uprooting (1 x 1 = 1mk)
- Use of appropriate herbicides Rej chemicals
Rej legislative (2 x 1/2 = 1mk)
-
-
- F – Granular structure (½ mk)
- G – Platy structure (½ mk)
-
- X – Humus with clay (½ mk)
- Y – Air Space (½ mk)
-
- It prevents drainage/water infiltration (2 x 1 = 2mks)
- Prevent root penetration
- Influences soil aeration
-
-
- D – Single stem pruning (1 x = 1mk)
-
- The main stem is capped at 38 cm above the ground to encourage more suckers to grow
- Select two strong and healthy suckers and remove the others
- The selected suckers should form a U-shape to avoid splitting (2 x 1 = 2mk)
SECTION C
-
- Factors affecting rooting of cuttings
- Temperature, warm temperatures are required for rooting
- Relative humidity, high humidity is required for proper rooting of cuttings
- Light intensity, hardwood cutting root well in dark while soft wood cuttings root well in high light intensity
- Leaf area hard wood cuttings root well without leaves while soft wood require leaves to root
- Chemical treatment – use of rooting hormones promotes rooting of cuttings (5 x 1 = 5mks)
- Factors influencing spacing
- Growth habit of the crop, spreading or tillering crops require wider spacing that that do not
- Purpose of the crop /intended use maize for silage is planted at a closer spacing than those for grain production
- Type of machinery to use for field practices
- Spacing adopted should allow free passage of machines for yield operations like weeding,
- Number of seeds per hole where more than one seed per hole is to be planted, wider spacing is used.
- Soil fertility, a fertile soil allows closer spacing compared to poor soils
- Moisture content of the soil /amount of rainfall in an area - High moisture content/rainfall may allow closer spacing but low rainfall necessities wider spacing
- Pest and diseases control; properly spaced crops make it difficult for pests to move from one crop to the other. Stating 1 mk each 5x 1 = 5mks
Explanation 1 mk each 5 x 1 = 5mks total 10mks.
- Ways in which government policy influences agriculture
- Provides subsidy on farm input to reduce cost of production done by reducing tax on inputs to make them cheaper
- Heavy taxation of imported goods to make them more expensive than local goods thus protecting local goods from adverse competition
- Quality control by setting up laws to ensure production of high quality goods which can compete locally and internationally
- Conservation of natural resources to make them sustain agriculture
- Stepping up control measures of diseases, parasite and pests. (5 x 1 = 5mks)
- Factors affecting rooting of cuttings
-
- Cultural methods of pest’s control
- Crop rotation; a crop attacked by a certain pest is alternated with crop that is not attacked by starving the pest to death.
- Timely planting make plants to escape attack by pest.
- Proper tillage proper cultivation exposes pests to be scorched by the sun to death or to the eaten by predators
- Good field hygiene’s; involves keeping the field free from plant materials that harbor pest
- Use of clean planting material prevents introduction and spreading of pests
- Close season; a certain crop is not grown in order to break the life cycle of pest
- Use of certified seeds; these seeds are free from pests thus reduce introduction and spread of pests.
- Use of pest resistant in varieties e.g. goose – necked variety of sorghum is resistant to attack by birds
- Use of trap crop, trap crop attracts pests from the main crop and is then uprooted and destroyed
- Destroy alternative hosts, weeds that harbor pests are removed and destroyed and this starves the pests to death
- Proper spacing makes it difficult for pests to move from crop to the other,
- Pruning creates unsuitable habit for pests any (any 8 x 1= (8mks)
- Procedure for silage making
- Prepare silo before harvesting the crops
- Harvest the crop at appropriate size of storage
- Wilt the crop for 6-12 hours
- Fill the silo with crop compacting every 10-12 layer
- Check the temperature regularly to ensure correct ensling temperature
- Cover the ensiled material with polythene paper
- Cover the silo with thick layer of the soil to maintain a ridge/hump to prevent rain water from entering the silo.
- Dig a trench around the silo to drain water away (7 x 1 = 7mks)
- Observable indicates of economic development of a ration
- Development of better infrastructure
- Better housing for citizens
- Better and more recreation/facilities
- High teacher more student ratio
- Improved level of technology
- Less number of persons per doctor
- High number of people owning radios, tvs and motor vehicles
- High employment rates
- Amount of food per capita available (5 x 1 = 5mks)
- Cultural methods of pest’s control
-
- Advantages of adding against manure into the soil
- Improves soil fertility when it decays too release nutrients
- Encourages microbial activities in the soil
- Improves water infiltration and retention capacity
- Improves soil drainage and aeration
- Reduces toxicity of the soil
- Prevents toxicity of nutrients
- Moderates /buffers the soil pit by preventing rapid chemical changes
- Regulates the soil temperature (Any 5 x1 = 5mks)
- Precaution taken when harvesting tea.
- Leaves should not be compressed in the baskets as it would cause heating up and lowering of availability
- Plucked tea must be kept cool and shaded
- Plucked tea should be taken to the factory for processing the same day it is harvested
- Plucked tea leaves should be pit in woven baskets for ventilation
- Discard dormant tea shoots/central leaves which are not opened as they are hard due to unfavorable conditions (Any 3 x 1 = 3mks)
- Mr. Mulongo’s farm balance sheet as at 31.12.2020
-
(6mks)Liabilities Assets Amount Short term liabilities Amount Current assets Cattle feeds in storeAnimal drugs in storeDebts receivableCash at handCash in bankSubtotalShs Cts Shs. Cts. 10,000
4,000
18,000
20,000
30,000
82,00000
00
00
00
00
00Debts payable to coo-p sec Bonus payable to workersBreakages to repairSub-total20,000
19,000
30,000
69,00000
00
00
00Long Term liabilties Fixed assests Loan payable to bank
300,000
00 Building and structures 600,000 00 00 5 milking cows 25,000 00 Subtotal 300,000 00 400 layers 80,000 00 20 goats 30,000 00 Spray equipment 12,000 00 Subtotal 972,000 00 Total liabilties 369,000 00 Total assests 1,054,000 00 Net worth 685,000 00 Total 1,054,000 Total 1,054,000 00 - Mr. Mulong’s business was solvent. (1mk)
-
- Post-harvest practices carried out maize
- Shelling to remove grains from the cobs
- Drying to the correct moisture content
- Cleaning – to remove foreign materials from the yield
- Dusting – applying insecticides to prevent attack by storage pests
- Starting and grading according to the quality
- Processing e.g. milking into flour
- Packing - e.g. into 90kg bags for sale (Any 5 x1 = 5mks)
- Advantages of adding against manure into the soil
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 4 End Term 2 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students