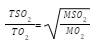INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES: -
- Answer all the questions
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
- Name the process which takes place when: (3mks)
- Solid Carbon (Iv) Oxide (dry ice) changes directly into gas
- A red litmus paper turns white when dropped into chlorine water
- Propene gas molecules are converted into a giant molecule
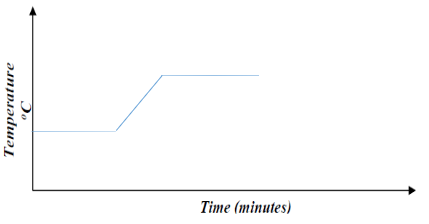
- Substance Q has a melting point of 15°C and boiling point of 70°C.
- On the same axes, draw the melting point and boiling point graph for Q. (2mks)
- State the physical state of substance Q at room temperature (room temperature =25°C) (1mk)
- On the same axes, draw the melting point and boiling point graph for Q. (2mks)
- The table below shows solutions A, B and C are tested and observations records as shown:
Solution Observations on indicator A Methyl orange turns yellow B Phenolphthalein turns colourless C Litmus turns purple - Using the table above, name an acid (1mk)
- How does the pH value of 1M potassium hydroxide solution compare with that of 1M aqueous ammonia? Explain (2mks)
-
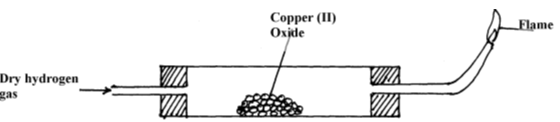
- The set-up below is used to investigate the properties of hydrogen.
- On the diagram, indicate what should be done for the reaction to occur. (1mk)
- Name another gas that can be used instead of hydrogen gas. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction that occurs in the combustion tube. (1mk)
- Explain the observation made in the combustion tube (2mk)
- The set-up below is used to investigate the properties of hydrogen.
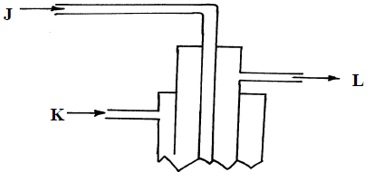
- Sulphur is extracted from underground deposits by a process in which three concentric pipes are sunk down to the deposits as shown below
- Name the process represented above (1mk)
- What is passed down through pipe J? (1mk)
- Name the two allotropes of Sulphur (1mk)
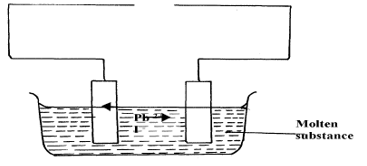
- The set-up below was used to investigate electrolysis of a certain molten compound;-
- Complete the circuit by drawing the cell in the gap left in the diagram. (1mk)
- Write half-cell equation to show what happens at the cathode (1mk)
- Using an arrow show the direction of electron flow in the diagram above (1mk)
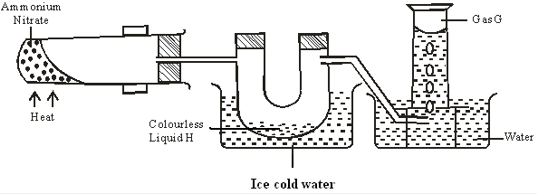
- Ammonium nitrate was gently heated and the products collected as shown in the diagram.
- Identify:
- Colourless liquid H (1mk)
- Gas G (1mk)
- Describe one physical and one chemical test that can be used to identify gas G. (2mk)
- Identify:
- Name the following substances.
- CH2 CH CH2 CH3 (1mk)
- CH3 CH CH CH2 CH3 (1mk)
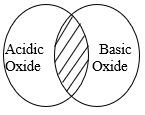
- The diagram below shows the acidic and basic oxides fit into the general family of oxides.
- State the name given to the type of oxide that would be placed in the shaded area. (1mk)
- Give the name of any oxide that would be placed in the shaded area. (1mk)
- Laboratory results showed the composition of a compound to be 58.81% barium, 13.72%, sulphur and 27.47% Oxygen. Calculate the empirical formula of the compound. (Ba=137, S = 32, O = 16). (3mks)
-
- What is meant by the term allotrophy? (1mark)
- Graphite is one of the allotropes of carbon. Explain in terms of structure and bonding why graphite is soft with greasy feeling. (2marks)
- A hydrocarbon Q was found to decolourise acidified potassium manganate (vii) solution. When two moles of Q were burnt completely six moles of carbon (iv) oxide and six moles of water were formed.
- Write the molecular and structural formula of Q. (2mark)
- Name the homologous series to which Q belongs (1mark)
- State Charles’ law. (1mk)
- A gas occupies 4dm3 at −23°C and 152 mmHg. At what pressure will its volume be halved, if the temperature then is 227°C.? (2marks)
- Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
Substance Solubility in water Electrical Conductivity Solid Molten X Insoluble Good Good Y Soluble Poor Good Z Insoluble Poor Poor - Which of the substances is highly likely to be potassium chloride? Explain (2marks)
- What type of bond exists in substance X? (1mark)
- State a possible structure in substance Z? (1mark)
- 200cm3 of oxygen gas took 60 seconds to diffuse through a porous plug. Determine the time taken by 300cm3 of sulphur (IV) oxide to diffuse through the same plug under the same conditions. (O=16, S = 32) (3mks)
- Dilute sulphuric acid was added to a compound X, of magnesium. The solid reacted with the acid to form a colourless solution Y and a colourless gas Z which formed a white precipitate when bubbled through lime water.
Name:-- Compound X (1mark)
- Solution Y (1mark)
- Colourless gas Z (1mark)
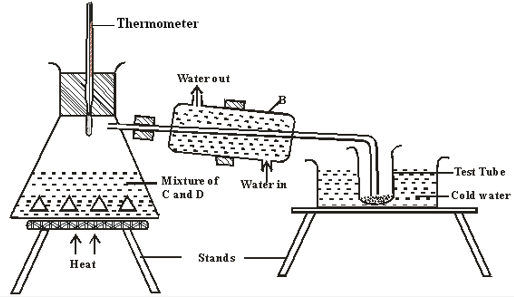
- The set up below represents the apparatus that may be used to separate a mixture of two miscible liquids C and D whose boiling points are 80°C and 110°C.
- Name B (1mark)
- What is the purpose of the thermometer (1mark)
- Which liquid was collected in the test tube? (1mark)
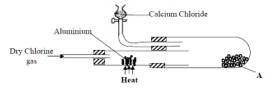
- In an experiment, dry chlorine gas was reacted with aluminium as shown in the diagram below
- Name substance A (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place in the combustion tube (1mk)
- State the function of the calcium chlorine in the set-up above (1mk)
- Differentiate between the bleaching action of chlorine and sulphur (IV) oxide gas. (1mk)
- The grid given below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. (The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements)
- What name is given to the group of elements to which C and F belong? (1 marks)
- Which letter represents the element that is the least reactive? (1 marks)
- What type of bond is formed when B and react? (1 marks)
- Write the formula of the compound formed when element D and oxygen gas react (1 marks)
- On the grid indicate with a tick the position of element G which is in the third period of the periodic table and forms G3− ions. (1 marks)
- In the manufacture of Sulphuric (VI) acid by contact process sulphur (IV) oxide is made to react with air to form sulphur (VI) oxide as shown:-
2SO2(g) + O2(g)2SO3(g) ΔH = −196KJ
- Name the catalyst in this reaction (1mk)
- State and explain the effect of the following changes on the yield of sulphur (VI) oxide
- Increasing the pressure (1mk)
- Using a catalyst (1mk)
- Explain why sulphur (VI) oxide gas is absorbed in concentrated sulphur (VI) acid before dilution (1mk)
- Give the name of each of the processes described below which takes place when the salt are exposed to air for some time.
- Anhydrous Copper (II) Sulphate becomes blue. (1mk)
- Calcium chloride forms an aqueous solution. (1mk)
- Fresh crystals of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3: 10H2O become covered with a white powder of formula Na2CO3: H2O. (1mk)
- The table below gives the solubilities of potassium bromide and potassium sulphate at 0°C and 40°C.
When aqueous mixture containing 60g of potassium bromide and 27g of potassium sulphate in 100g of water at 80°C was cooled to 40°C, some crystals were formed.Substances Solubilities in g/100g of water Potassium bromide 0° 40° 55 75 Potassium sulphate 10 12 - Identity the crystals. (1mk)
- Determine the mass of crystals formed. (1mk)
- Name the method used to obtain the crystals. (1mk)
- Suggest one industrial application of the method named in (c) (iii) above (1mk)
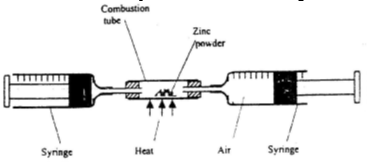
- In an experiment a certain volume of air was passed repeatedly from one syringe to the other over heated excess zinc powder as shown in the diagram below
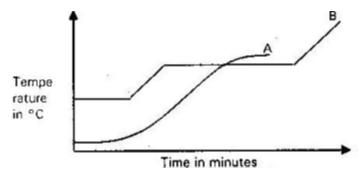
The experiment was repeated using excess magnesium powder. In which of the experiments was the change in volume of air greatest? Give reasons. (3mks) - The graph below shows the changes that occur when a pure and an impure substance are heated.
- Which curve represents pure substance? Explain. (2mks)
- Name one factor which affects the melting point of a solid and state effects. (2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
- Name the process which takes place when: (3mks)
- Solid Carbon (Iv) Oxide (dry ice) changes directly into gas
- Sublimation
- A red litmus paper turns white when dropped into chlorine water
- Bleaching
- Propene gas molecules are converted into a giant molecule
- Self addition/ polymerization
- Solid Carbon (Iv) Oxide (dry ice) changes directly into gas
- Substance Q has a melting point of 15oC and boiling point of 70oC.
- On the same axes, draw the melting point and boiling point graph for Q. (2mks)
- State the physical state of substance Q at room temperature (room temperature =25oC) (1mk)
- Liquid
- On the same axes, draw the melting point and boiling point graph for Q. (2mks)
- The table below shows solutions A, B and C are tested and observations records as shown:
- Using the table above, name an acid (1mk)
- B
- How does the pH value of 1M potassium hydroxide solution compare with that of 1M aqueous ammonia? Explain (2mks)
- 1M potassium hydroxide being a strong base has a higher pH value than 1M aqueous ammonia which is a weak base.
- Using the table above, name an acid (1mk)
-
- The set-up below is used to investigate the properties of hydrogen.
- On the diagram, indicate what should be done for the reaction to occur. (1mk)
- Heat
- Name another gas that can be used instead of hydrogen gas. (1mk)
- Ammonia gas, carbon(ii) oxide
- Write an equation for the reaction that occurs in the combustion tube. (1mk)
CuO (s) + H2(g) → Cu (s) + H2O (l) - Explain the observation made in the combustion tube (2mk)
- Black copper(ii)oxide turns brown. Copper(ii)oxide is reduced to copper metal.
- On the diagram, indicate what should be done for the reaction to occur. (1mk)
- The set-up below is used to investigate the properties of hydrogen.
- Sulphur is extracted from underground deposits by a process in which three concentric pipes are sunk down to the deposits as shown below
- Name the process represented above (1mk)
- What is passed down through pipe J? (1mk)
- Hot compressed air
- Name the two allotropes of Sulphur (1mk)
- Monoclinic and Rhombic Sulphur
- The set-up below was used to investigate electrolysis of a certain molten compound;-
- Complete the circuit by drawing the cell in the gap left in the diagram. (1mk)
- Left is +ve Right is -ve
- Write half-cell equation to show what happens at the cathode (1mk)
Pb2+(l) + 2e → Pb(s) - Using an arrow show the direction of electron flow in the diagram above (1mk)
- From left to right
- Complete the circuit by drawing the cell in the gap left in the diagram. (1mk)
- Ammonium nitrate was gently heated and the products collected as shown in the diagram.
- Identify:
- Colourless liquid H (1mk)
- Water
- Gas G (1mk)
- Nitrogen(i) oxide/N2O
- Colourless liquid H (1mk)
- Describe one physical and one chemical test that can be used to identify gas G. (2mk)
- Physical – Has a pleasant smell
- Chemical- relights a glowing splint
- Identify:
- Name the following substances.
- CH2 CH CH2 CH3 (1mk)
- But-1-ene
- CH3 CH CH CH2 CH3 (1mk)
- Pent-2-ene
- CH2 CH CH2 CH3 (1mk)
- The diagram below shows the acidic and basic oxides fit into the general family of oxides.
- State the name given to the type of oxide that would be placed in the shaded area.(1mk)
- Amphoteric
- Give the name of any oxide that would be placed in the shaded area. (1mk)
- Zinc oxide/ Aluminium oxide/ Lead (ii) oxide
- State the name given to the type of oxide that would be placed in the shaded area.(1mk)
- Laboratory results showed the composition of a compound to be 58.81% barium, 13.72%, sulphur and 27.47% Oxygen. Calculate the empirical formula of the compound. (Ba=137, S = 32, O = 16). (3mks)
BaSO4Ba S O 58.81
137
0.4293
0.42875
113.72
32
0.42875
0.42875
127.47
16
1.716875
0.42875
4 -
- What is meant by the term allotropy? (1mark)
- It’s the existence of an element in more than one form in the same physical state
- Graphite is one of the allotropes of carbon. Explain in terms of structure and bonding why graphite is soft with greasy feeling.(2marks)
- Has weak der waals forces of attraction between its hexagonal layers that make them slide over each other
- What is meant by the term allotropy? (1mark)
- A hydrocarbon Q was found to decolorize acidified potassium manganate (vii) solution. When two moles of Q were burnt completely six moles of carbon (iv) oxide and six moles of water were formed.
- Write the molecular and structural formula of Q. (2mark)
- C6H12
- Name the homologous series to which Q belongs (1mark)
- Alkenes
- State Charles’ law. (1mk)
- The volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature at constant pressure
- Write the molecular and structural formula of Q. (2mark)
- A gas occupies 4dm3 at -23°C and 152 mmHg. At what pressure will its volume be halved, if the temperature then is 227°C.? (2marks)
V = 153 x 4 x 500
250 x 2
= 608mmmHg - Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
- Which of the substances is highly likely to be potassium chloride? Explain (2marks)
- Y. Being ionic it conducts electric current only in molten form when ions are mobile
- What type of bond exists in substance X? (1mark)
- Metallic
- State a possible structure in substance Z? (1mark)
- Molecular structure
- Which of the substances is highly likely to be potassium chloride? Explain (2marks)
- 200cm3 of oxygen gas took 60 seconds to diffuse through a porous plug. Determine the time taken by 300cm3 of sulphur (IV) oxide to diffuse through the same plug under the same conditions. (O=16, S = 32) (3mks)
200cm3 O2 =60s
300cm3 O2=90s
300cm3 SO2=??
SO2 = 127.279 seconds - Dilute sulphuric acid was added to a compound X, of magnesium. The solid reacted with the acid to form a colourless solution Y and a colourless gas Z which formed a white precipitate when bubbled through lime water.
Name:-- Compound X (1mark)
- Magnesium carbonate / MgCO3
- Solution Y (1mark)
- Magnesium suphate /MgSO4
- Colourless gas Z (1mark)
- Carbon (iv) oxide / CO2
- Compound X (1mark)
- The set up below represents the apparatus that may be used to separate a mixture of two miscible liquids C and D whose boiling points are 80°C and 110°C.
- Name B (1mark)
- Liebig condenser
- What is the purpose of the thermometer (1mark)
- To indicate when various fraction are distilling out
- Which liquid was collected in the test tube? (1mark)
- C
- Name B (1mark)
- In an experiment, dry chlorine gas was reacted with aluminium as shown in the diagram below
- Name substance A (1mk)
- Aluminium chloride
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place in the combustion tube (1mk)
2Al (s) + 3Cl2 (g) → 2AlCl3 (s) - State the function of the calcium chloride in the set-up above (1mk)
- prevents water vapour from getting in hence protecting the salt formed from hydrolyzing.
- Name substance A (1mk)
- Differentiate between the bleaching action of chloride and sulphur (IV) oxide gas. (1mk)
- Chlorine gas bleaches by oxidation while Sulphur (iv) oxide bleaches by reduction
- The grid given below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. (The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements)
- What name is given to the group of elements to which C and F belong? (1 marks)
- Alkaline earth metals
- Which letter represents the element that is the least reactive? (1 marks)
- A
- What type of bond is formed when B and reacts? (1 marks)
- covalent
- Write the formula of the compound formed when element D and oxygen gas react (1 marks)
D2O3 or Al2O3 - On the grid indicate with a tick the position of element G which is in the third period of the periodic table and forms G3- ions. (1 marks)
- Left of E in the same raw
- What name is given to the group of elements to which C and F belong? (1 marks)
- In the manufacture of Sulphuric (VI) acid by contact process sulphur (IV) oxide is made to react with air to form sulphur (VI) oxide as shown:-
2SO2(g) + O2(g)2SO3(g) ΔH = -196KJ
- Name the catalyst in this reaction (1mk)
- Vanadium (v) oxide or platinum
- State and explain the effect of the following changes on the yield of sulphur (VI) oxide
- Increasing the pressure (1mk)
- Increases the yield of SO3. Low pressure favours forward reaction
- Using a catalyst (1mk)
- No effect
- Increasing the pressure (1mk)
- Explain why sulphur (VI) oxide gas is absorbed in concentrated sulphur (VI) acid before dilution (1mk)
- The reaction is highly exothermic thus forms a mist of acid droplets of sulphuric acid in the air.
- Name the catalyst in this reaction (1mk)
-
- Give the name of each of the processes described below which takes place when the salt are exposed to air for some time.
- Anhydrous Copper (II) Sulphate becomes blue. (1mk)
- Hygroscopy
- Calcium chloride forms an aqueous solution. (1mk)
- Deliquescence
- Fresh crystals of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3: 10H2O become covered with a white powder of formula Na2CO3: H2O. (1mk)
- Efflorescence
- Anhydrous Copper (II) Sulphate becomes blue. (1mk)
- Give the name of each of the processes described below which takes place when the salt are exposed to air for some time.
- The table below gives the solubilities of potassium bromide and potassium sulphate at 0°C and 40°C.
When aqueous mixture containing 60g of potassium bromide and 27g of potassium sulphate in 100g of water at 80°C was cooled to 40°C, some crystals were formed.- Identity the crystals. (1mk)
- Potassium sulphate
- Determine the mass of crystals formed. (1mk)
27 − 12 = 15g - Name the method used to obtain the crystals. (1mk)
- fractional crystallisation
- Suggest one industrial application of the method named in (c) (iii) above (1mk)
- Obtaining/separating sodium chloride from trona in lake magadi
- Identity the crystals. (1mk)
- In an experiment a certain volume of air was passed repeatedly from one syringe to the other over heated excess zinc powder as shown in the diagram below.
The experiment was repeated using excess magnesium powder. In which of the experiments was the change in volume of air greatest? Give reasons. (3mks)- Magnesium. Its more reactive than zinc hence reacts with both oxygen and nitrogen gas forming magnesium oxide and magnesium nitride while zinc reacts with oxygen only forming zinc oxide.
- The graph below shows the changes that occur when a pure and an impure substances are heated.
- Which curve represents pure substance? Explain. (2mks)
- B . Has a sharp / constant m.p/ b.p
- Name one factor which affects the melting point of a solid and state effects. (2mks)
- Impurities. Lowers the m.p
- Which curve represents pure substance? Explain. (2mks)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Term 3 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students