- This paper consists of three sections; A, B and C
- Answer ALL the questions in sections A and B
- Answer any TWO questions in section C
- All answers to be written in English
SECTION A (30 Mks)
Answer all questions in the spaces provided
-
- Name three forms of horticulture practiced in Kenya. (1 ½ mks)
- State three ways in which ranching can be improved. (1 ½ mks)
-
- State three factors that determine the depth of cultivation. (1 ½ mks)
- Name three implements that can be used to carry out sub – soiling (1 ½ mks)
- Name four reasons for treating water before use. (2 mks)
- State four limitations of sprinkler irrigation (2 mks )
- Give the use of the following in the preparation of compost manure. (2 mks)
- Calcium Ammonium Nitrate
- Top soil
- Well decomposed manure
- Wood ash
- Give four uses of farm records. (2mks)
- State four roles of calcium in plants. (2 mks)
- Give four problems associated with use of vegetative planting materials (2 mks)
- State four importances of grafting and budding in crop production. (2 mks)
- State four limitations of land – lordism and tenancy. (2 mks)
- Giving examples, state two ways in which weeds can be classified according to plant morphology. (2 mks)
- Name four legumes grown in high altitude areas (2 mks)
- State four factors to consider when drawing a farm plan. (2 mks)
- Name four books of accounts . (2 mks)
SECTION B (30 MARKS)
ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED
- The diagram below shows a section of a plant from which the planting material illustrated was obtained.
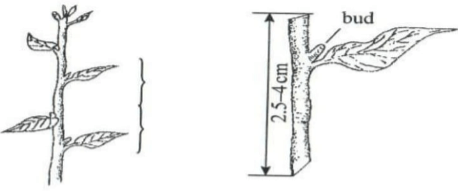
- Identify the planting material illustrated (1 mk)
- Give two reasons why only the middle part of the plant was used to prepare the planting material (2 mks)
- Apart from using the middle part, explain two precautions that should be observed when preparing the illustrated materials
(2 mks)
- The diagram below illustrates water storage structures.
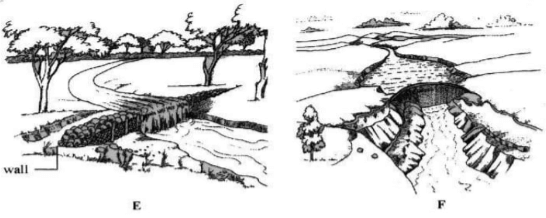
- Identify the structure labeled E (1 mk)
- Give two reasons why farmers prefer structure F to E. (2 mks)
- State two maintenance practices for the structure labeled F (2mks)
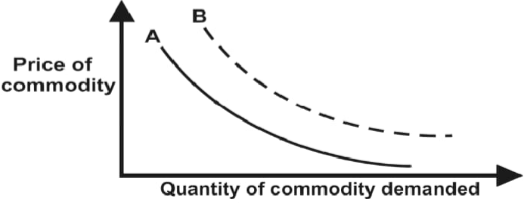
- The diagram below illustrates the law of demand in agricultural marketing. Study it answer the questions that follow.
- Give a reason for the shape of the circle labeled A (1 mk)
- if the price of the commodity remains constant, explain four factors that can cause the curve to shift from A to B.
- Below is a diagram showing a crop disease
- Identify the crop disease (1 mk)
- State three control measures for the crop disease. (3 mks)
- Name the category in which the crop disease is classified. (1 mk)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
ANSWER ANY TWO QUESTIONS FROM THIS SECTION IN THE SPACES PROVIDED
-
- Explain how each of the properties of rainfall and light influence crop rotation.
- Rainfall (8 mks
- Light
- Explain four environmental factors that influence effectiveness of herbicides (8 mks)
- Explain how each of the properties of rainfall and light influence crop rotation.
-
- Discuss cabbage production under the following sub – headings.
- Varieties (2 mks)
- Field management (3 mks)
- Harvesting and marketing
- Explain five problems associated with agricultural credit (5 mks)
-
- Describe the procedure of harvesting pyrethrum (4 mks)
- Explain the precautions that should be observed during the harvesting of pyrethrum (4 mks)
- Discuss cabbage production under the following sub – headings.
-
- Explain five advantages of mulching in crop production (5 mks)
- Explain the three stages in propagation of plants by tissue culture in crop production (7 mks)
- Stage 1 –
- Stage 2 –
- Stage 3 – .
-
- State five roles of trees in soil and water conservation. (5 mks)
- Explain three care and management required of agro forestry trees (3 mks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (30 Mks)
Answer All questions in the spaces provided
-
- Name three forms of horticulture practiced in Kenya. (1 ½ mks)
- floriculture
- olericuture
- pomoculture (3X ½ = 1 ½ mks)
- State three ways in which ranching can be improved. (1 ½ mks)
- Provision of watering points to the pastoral communities
- Providing mineral concentrate supplements especially in times of drought
- Adopting breeding programs that improve the genetic makeup, improving productivity. (3X ½ = 1 ½ mks)
- Name three forms of horticulture practiced in Kenya. (1 ½ mks)
-
- State three factors that determine the depth of cultivation. (1 ½ mks)
- Type of crop to be planted
- Implements used/available
- Type of soil (3X ½ = 1 ½ mks)
- Name three implements that can be used to carry out sub – soiling (1 ½ mks)
- Subsoilers
- Chisel plough
- Cultivators (3X ½ = 1 ½ mks)
- State three factors that determine the depth of cultivation. (1 ½ mks)
- Name four reasons for treating water before use. (2 mks)
- Remove excess chemicals
- Kill disease causing micro – organisms
- Remove solid sediments
- Remove bad taste and smell (4 X ½ = 2 mks)
- State four limitations of sprinkler irrigation (2 mks )
- Expensive installations are required
- Encourages fungal diseases
- Causes soil erosion
- May require the establishment of wind break
- Maintenance requires a lot of skill and it’s expensive. (4 X ½ = 2 mks)
- Give the use of the following in the preparation of compost manure. (2 mks)
- Calcium Ammonium Nitrate
- To raise the level of Nitrogen in the resulting manure
- Top soil
- To introduce micro – organisms responsible for decomposition
- Well decomposed manure
- To provide food and shelter for micro – organisms
- Wood ash
- To raise the level of phosphorus and potassium in the resulting manure (4X ½ = 2 mks)
- Calcium Ammonium Nitrate
- Give four uses of farm records. (2mks)
- Compare performance of different enterprises
- Show history of the farm
- Guide in planning and budgeting
- Detect losses or theft
- Assessment of income tax
- Determine value of the farm (assets and liabilities)\
- Easy to share profits and losses
- Settling disputes among heirs
- Show whether its making profit or losses and obtain credit
- Supporting insurance claims
- Provide labour information, i.e. NSSF
- Helps in selling assets, i.e. animals and machinery. (4 X ½ = 2 mks)
- State four roles of calcium in plants. (2 mks)
- Promotes formation of aggregates
- Increases bacterial activities i.e. Nitrogen fixation
- Raises pH (pH5 to pH 6-7) making P and K available
- Strengthens plant cell walls
- Necessary in protein synthesis (4 X ½ = 2 mks)
- Give four problems associated with use of vegetative planting materials (2 mks)
- Does not result in new crop variety
- Keeping the material free of disease is difficult
- Materials cannot be stored for long
- Materials are bulky, thus difficult to store and transport. (4 X ½ = 2 mks)
- State four importances of grafting and budding in crop production. (2 mks)
- Plants with desirable root characteristics but with undesirable products may be utilized
- Facilitates the changing of the top from undesirable to desirable
- Possible to grow more than one type of fruit or flower on same plant
- Propagate clones
- Repair broken trees
- Shorten the maturity age. (4 X ½ = 2 mks)
- State four limitations of land – lordism and tenancy. (2 mks)
- If tenants have no written agreement, they will have no incentive on the land
- Where lease period is short, no incentives to make long term investments
- Land rates are not fixed, may lead to overexploitation of tenants
- Where lease is short, consideration is profit maximization, not concerned with land improvement. (4 X ½ = 2 mks)
- Giving examples, state two ways in which weeds can be classified according to plant morphology. (2 mks)
- Narrow – leaved weeds e.g. couch grass
- Broad - leaved weeds e.g. black jack
- Name four legumes grown in high altitude areas (2 mks)
- Kenya white clovers
- Lonsiana white clovers
- Subterranean clovers
- Lucerne (4 X ½ = 2 mks)
- State four factors to consider when drawing a farm plan. (2 mks)
- Size of the farm
- Environmental factors
- Current trends in labour markets
- Farmer’s objectives and preferences
- Possible production enterprises
- Existing market conditions and price trends
- Availability and cost of farm inputs
- Security
- Communication and transport facilities
- Government policy (4 X ½ = 2 mks)
- Name four books of accounts . (2 mks)
- Ledger
- Inventory
- Cash book
- Journal (4 X ½ = 2 mks)
SECTION B (30 MARKS)
ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED
- The diagram below shows a section of a plant from which the planting material illustrated was obtained.
- Identify the planting material illustrated (1 mk)
- Stem cutting
- Give two reasons why only the middle part of the plant was used to prepare the planting material (2 mks)
- Top part tend to rot when planted
- Bottom part takes longer to root
- Apart from using the middle part, explain two precautions that should be observed when preparing the illustrated materials
(2 mks)- Place it in water until it is planted to prevent dehydration
- Each cutting should have a leaf and a bud for photosynthesis and establishment respectively
- Use a sharp knife or blade to prevent breaking of the cutting
- Make slanting cuts to prevent accumulation of moisture.
- Identify the planting material illustrated (1 mk)
- The diagram below illustrates water storage structures.
- Identify the structure labeled E (1 mk)
- Weir
- Give two reasons why farmers prefer structure F to E. (2 mks)
- Water levels is regulated
- Can be used to generate HEP
- Stores large volume of water
- State two maintenance practices for the structure labeled F (2 mks)
- Disilting/dredging
- Remove trees and bushes from wall to prevent cracks and water seepage
- Repairing broken/ worn out parts
- Identify the structure labeled E (1 mk)
- The diagram below illustrates the law of demand in agricultural marketing. Study it answer the questions that follow.
- Give a reason for the shape of the circle labeled A (1 mk)
- As the price of commodity increases the quantity demand decreases and vice versa.
- if the price of the commodity remains constant,explain four factors that can cause the curve to shift from A to B.
- If there is increase in the income of consumers.
- Affective advertisement / sales promotion.
- Increase in the price of a related / substitute.
- If there is an increase in population.
- Taste and preference.
- If the quality of the commodity goes up.
- Give a reason for the shape of the circle labeled A (1 mk)
- Below is a diagram showing a crop disease
- Identify the crop disease (1 mk)
- Maize smut
- State three control measures for the crop disease. (3 mks)
- Ensure field hygiene
- Use of certified seeds
- Use of resistant varieties
- Rogueing
- Crop rotation
- Name the category in which the crop disease is classified. (1 mk)
- Fungal disease
- Identify the crop disease (1 mk)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
ANSWER ANY TWO QUESTIONS FROM THIS SECTION IN THE SPACES PROVIDED
-
- Explain how each of the properties of rainfall and light influence crop rotation.
- Rainfall (8 mks
- Reliability – determines the timing of land preparation and planting
- Amount – determines the type of crop to grow
- Distribution – influences the type and variety of crops to grow in an area.
- Intensity – high rainfall intensity damages crops and causes soil erosion
NB// property 4X1 = 4mks
Explanation 4X1 = 4 mks
- Light
- Intensity – the rate of photosynthesis increases with increase in light intensity
- Duration – determines the flowering and types of crops to grow i.e. short – day, long – day / day neutral plants.
- Wavelength – plants absorb light of specific wavelength making natural light more suitable for photosynthesis
NB// property 4X1 = 4mks
Explanation 4X1 = 4 mks
- Rainfall (8 mks
- Explain four environmental factors that influence effectiveness of herbicides (8 mks)
- Wind – deflects herbicides to unwanted areas
- Rain – may wash away the herbicides to have pro – longed effects on weeds
- Soil – should be moist to soak the herbicides to have pro – longed effects on weeds.
- Light – should be of high intensity to optimum to ensure that the weeds are physiological active / minimizes loss of herbicides by evaporation
- Explain how each of the properties of rainfall and light influence crop rotation.
-
- Discuss cabbage production under the following sub – headings.
- Varieties (2 mks)
- Early maturing varieties i.e. sugar loaf, mukuki, golden acres, Gloria hybrid, and Copenhagen market.
- Late maturing varieties, i.e. Early drum head, savoy, prize drum – head, perfection surc – head.
- Field management (3 mks)
- Top – dressing. Top dress at 20 – 25 cm, one teaspoonful of SA or CAN and repeat 3 – 4 weeks after.
- Weeding – ensure field is weed – free, hand weeding.
- Pest control – i.e. aphids, cutworms
- Disease control – i.e. dumping off, black rot, dowing middew.
- Harvesting and marketing
- Takes 3 – 4 months after transplanting
- Heads are cut when solid and compact.
- Sold in wholesale or single in urban or rural areas
- Varieties (2 mks)
- Explain five problems associated with agricultural credit (5 mks)
- Lack of collaterals
- Diversion of loans to other uses
- High interest rates
- Assets used as collateral may be auctioned for non – repayment
- Lack of knowledge / skills to manage finances
- Lack of proper record keeping
-
- Describe the procedure of harvesting pyrethrum (4 mks)
- Pick flowers selectively / pick flowers with horizontal petals
- Use forefingers and the thumb
- Pick by twisting the heads so that no stem is left attached
- Put the picked flowers in woven basket
- Explain the precautions that should be observed during the harvesting of pyrethrum (4 mks)
- Picking starts 3 – 4 months after planting to maintain quality
- Picked flowers are put in woven baskets to allow ventilation and avoid fermentation of flowers
- Wet flowers should not be picked because they heat up and ferment
- Picked flowers should not be compacted to avoid heating up and fermenting
- A suitable picking interval 14 – 21 days is maintained to avoid harvesting over blown flowers
- Break the flower stalk to maintain quality
- Avoid picking an open flower.
- Describe the procedure of harvesting pyrethrum (4 mks)
- Discuss cabbage production under the following sub – headings.
-
- Explain five advantages of mulching in crop production (5 mks)
- Prevents water evaporation, maintaining moisture in the soil for crop use
- Acts as an insulator, modifies or regulate the soil temperature
- Controls soil erosion by reducing the speed of running water, intercepting rain drops increasing rate of infiltration.
- Controls the weeds by suppressing their growth
- Organic materials are decomposed by soil micro – organisms resulting in to humus, improving soil structure and water holding capacity.
- Organic materials improve soil fertility by releasing nutrients after decomposition.
- Explain the three stages in propagation of plants by tissue culture in crop production (7 mks)
- Stage 1 – establishing the aseptic culture
- Developing the propagule by enhancing cell division and enlargement (2X1 = 2mks)
- Stage 2 – sub culturing to rapidly multiply the propagules through somatic development of embryos to produce auxiliary buds and adventitious roots. (1X1=1mk)
- Stage 3 – preparation of the propagule for the establishment in the soil through
- Rooting of the regenerated plantlets
- Hardening the plantlets
- Converting the plantlets from heterotrophic to autotrophic mode of nutrition. (4X1=4mks)
- Stage 1 – establishing the aseptic culture
-
- State five roles of trees in soil and water conservation. (5 mks)
- Protect the soil below from raindrop erosion by reducing the force with which it falls on to the ground
- Provides shade and reduce loss of moisture through evaporation
- Acts as wind breakers
- The roots of trees bind soil particles together.
- Reduces speed of running water thus reducing its erosive power
- The leaves decay to supply humus which improves soil structure and increases water infiltration into the soil
- Explain three care and management required of agro forestry trees (3 mks)
- Protection
- Pruning and training
- Grafting old trees.
- State five roles of trees in soil and water conservation. (5 mks)
- Explain five advantages of mulching in crop production (5 mks)
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Term 3 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students