Musya
Types of Songs - Music CBC Grade 6 Notes
Types Of Songs
- Religious songs
- Patriotic songs
- Topical songs
- Popular songs
- Action song
- Western art sons
- African art songs
NB: An art song is a traditional song that has been rearranged for solo or choral performance.
They are usually accompanied by musical instruments.
Western Art Songs
- Is a European or western folk song which has been arranged for solo or choral performance.
- Are simply art song based on the western/European style of performance.
- Art songs are written in verses.
- Western art songs are based on stories and talk about the beauty of nature.
- When performing western art songs ensure that you bring out the correct mood.
- The mood can be shown through facial expressions, gestures observing performance directions and observing correct tempo or speed.
- Different art songs convey different messages.
- Example of western art song:
Lyrics: The Path to the Moon
Eric H. Thiman l ChoirI long to sail on a path to the moon
On a de-ep blue night
when the wind is cool
A glist'ning Path that runs out to sea
Silver the sails to carry me
To ca--rry
Ca--rry
Ca--rry me over the sea
So will I sail on a stary night
on the path to the moon, a sea bird's flight!
Skimming the waves where the fishes play
Traveling on for many a day
Silver the sails to carry me,
to ca--rry
ca--rry
ca--rry me over the sea!
African Art Song
- African folk songs or African songs which have been rearranged for solo or choral performances.
- They can also be accompanied by African musical instruments or western musical instruments
- African art songs are written and performed in an African style.
- The songs use African rhythm and language
- African art songs are based on traditions of Africa.
- Example of African art song
WIMBO WA HISTORIA
Wimbo huu ni wimbo wa historia watu wote mnaombwa msikize kwa makini
Ilikuwa oktoba 1952 watu wote tulisikia kenyatta ameshikwa
Hakushikwa kenyatta pekee yake lakini alishikwa na mabingwa wa uhuru
Oooooh ooohh ooohhh
Ilikua kilio nchini kenya watu wote tuliona huzuni mwingi sana
Wakina baba kina mama na watoto wote walilia machozi wakisema wooooi wooooiiii woi tunataka
Kenyatta aachiliwe
Baba (wa) taifa alipotoka gerezani aliwakuta wajumbe wetu wametengana vibaya sana
Kishayake baba taifa alikata shauri moja kujiunga na chama chetu Kanu
Aliongoza wajumbe pa kaula ya kufika huko alipigwa na mayai yaliyooza
Baba taifa hakujali alishinda na kurudi na katibaya nchi yetu hapa Kenya
Ilipofika Disemba kumi na mbili sitini na tatu mzee wetu alinyakua uhuru kenya
Kisha yake Disemba sitini na nne mzee wetu alipandisha bendera jamuhuri
Mzee wetu alituomba tusahau yaliyopita badala yake tuijenge nchi yetu
Alisema Harambee tuungane na hivi sasa tumejua harambee ni umoja
Asante baba wetu kweli we asante baba wetu
Patriotic Songs
- They are sung in praise of a county and its leaders.
- They emphasize on patriotism, ,peace, unity love, pride of our country and social cohesion among citizen.
- The words in patriotic songs may talk about history, people, resources, sceneries and values of a nation.
- Examples of patriotic songs
- Kenya, Kenya Taifa Leo
- Tunajivuniakenyanchiyetu,
- Tushangiliekenya.
Religious / Sacred Songs
- They are songs performed by different for religious groups e.g. Christianity, Islam and Hinduism
- Are specifically sung for the purpose of worship and praise a divine or prayer.
- Example of a religious song
This is the day
This is the day (x2)
That the Lord has made (x2)
Let us rejoice (x2)
And be glad in it (x2)
This is the day that the Lord has made
Let us rejoice and be glad in it
This is the day (x2)
That the Lord has made
Come unto Me (x2)
O My people come (x2)
Sing praise to Him (x2)
I will make you one (x2)
Come unto Me, O My people come
Sing praise to Him, I will make you one
This is the day (x2)
That the Lord has made
Sing and be glad (x2)
For the Lord is good (x2)
He’s done great things (x2)
As He said He would (x2)
Sing and be glad, for the Lord is good
He’s done great things, as He said He would
This is the day (x2)
That the Lord has made
Topical Songs
- Are songs that talk about issues affecting the society.
- They are used to convey special message on pertinent and contemporary issue.
- Some of the issues that affect society include:
- Safety
- personal hygiene
- health and nutrition,
- importance of education
- environmental conservation
- drought/famine
- disease
- water and sanitation
- Children’s right
- Topical songs offer advice on how the society can address the various issues.
Example of topical songs.- Corona ni hatari
- Wash your hands
- Njoo twende shule
Culture and Social Organisation In Eastern Africa - Social Studies CBC Grade 6 Notes
Culture
- Culture is people way of living.
- The culture of people includes:
- The language they speak
- The food they eat
- The clothes they wear
- The way they worship
- The games and sports they play.
Age Groups And Age Sets In African Traditional Society
- An age set is a social group of people of similar age with a shared identity.
- Members of an age set maintain set class ties over a long period of time
- An age group is a social group of people born during a particular period of time
Functions of a clan in society
The Clan System
- A clan is a group of people who have a common ancestor or forefather
- Clan members are related by blood
- Clans were founded by males
- Communities trace their origin through the male ancestor
- Agikuyu clans bear the names ot the nine daughters of gikuyu and mumbi.
- A group of clans make an ethnic group or community
- Members of the same clan are not allowed to marry each other
Functions Of A Clan
- Clan elders settled disputes among clan members
- Clan owned land on behalf of its members
- Giving a sense of belonging e.g. identity
- Setting rules to govern its members
- Planning and conducting important ceremonies
- Negotiating and paying dowry
- Educating the youth
- Providing comfort to members during hard times
- Safeguarding the values of the clan
- Determining religious practises and beliefs of the clan
- Protecting its members from external attacks
Aspects Of African Traditional Culture And Ought To Be Preserved.
- Some aspects of African traditional culture include traditional food
- Worship ceremonies
- Festivals
- Music
- Dances
- Language
- Games and sports
- Dressing
School And Community
- A school is a place where pupils go to be taught or to learn
- Is an educational institution designed to provide learning to learners with the support of teachers
- A school mainly equips learners with knowledge and skills
- A school trains individuals to be responsible or useful members of the society
- We have government and private schools
Ways In Which School Collaborates With The Community
- School allows the community to use school facilities during weekends an school holidays.
Movement, Settlement And Population In Eastern Africa - Social Studies CBC Grade 6 Notes
- Effects Of The Migration And Settlements Of Selected Language Groups In Eastern Africa
- Unity Of Language Groups In Eastern Africa
- Population Distribution In Eastern Africa
Effects Of The Migration And Settlements Of Selected Language Groups In Eastern Africa
- Displacement of smaller communities
- Agikuyu displaced gumba and athi in central kenya
- Abagusii displaced by luo and kalenjins
- Bantu displaced by galla from shungwaya
- Conflicts between communities
- Abagusii and the luo
- Galla and bantu
- Ngoni and the people of southern Tanzania
- Population increase
- Intermarriage between communities
- Adoption of economic practises among communities
e.g.bantu learnt cattle keeping from nilotes and cushites learnt cultivation from the Bantus - Introduction of new items of trade
- Borrowing of different words led to development of new languages
- Borrowing of cultural practises
- Bantu borrowed circumcision from the cushites
- Bantus borrowed age-set systems from the cushites
Unity Of Language Groups In Eastern Africa
- Intermarriage
- Trade activities
- Education for all
- Cultural interaction
- Living peacefully
Population Distribution In Eastern Africa
- Population refers to the number of people living in a given place
- Population distribution refers to how people are spread over in an area
- Population of eastern Africa is not evenly distributed
- Some areas are;
- Sparsely populated
- Medium/moderately populated
- Densely populated
Factors That Influence Population Distribution In Eastern Africa
- Climate i.e. rainfall and temperature
- Soils
- Relief
- Drainage
- Economic activities
- Vegetation
- Government policy
- Pests and diseases
- Political factors(security)
Population Density In Eastern Africa
Population density is the number of people living in a square km
Densely Populated Areas Of Eastern Africa
- The highlands region
- The lake basin
- Major towns and cities
- Coastal areas of Kenya and Tanzania
- Rwanda
- Mining areas
Sparsely Populated Areas Of Eastern Africa
- North Eastern Uganda
- Central and Northern Tanzania
- Southern and Western Ethiopia
- Large parts of Eritrea
- North Eastern Kenya
- Most of Somalia
- Mountain tops
- Flood plains
- Northern Sudan
Effects Of High Population Density In Eastern Africa
There is high population density in most towns of eastern Africa.
Negative Effects
- Food shortage
- Low standards of living and growth of slums
- Inadequate social amenities
- Land fragmentation
Positive Effects
- Attracts investments
- Increase tax collection collected by the government
- Big markets for products
- Cheap labour
Language Groups In Eastern Africa - Social Studies CBC Grade 6 Notes
Language Groups In Eastern Africa
- Language group refers to people or communities who speak the same language or related languages.
- People of eastern Africa belong to different language group
- The Bantu
- The Nilotes
- The Cushites
- The Semites
Classification Of Communities In Eastern Africa According To Language Groups
Bantus
- Are the largest language group in eastern Africa
- Originally homeland was DRC, Cameroon, Zaire
- Are mainly found in Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Rwanda and Burundi
- Tanzania has the largest number of Bantu.
Kenya Abaluhya,abagusii,abakuria,agikuyu,ameru,aembu,akamba,ambeere,taita,mijikenda,
pokomoTanzania Chagga,sukuma,gogo,hehe,ngoni,yao,nyamwezi,vinza,ha,zaramo,pare,fipa Uganda Baganda,banyore,basoga,bagishu, batoro,banyoro Rwanda Hutu,tutsi Burundi Hutu
Cushites
- They are pastoralists
- Migrated into eastern Africa from Saudi Arabia
- Main reason for migration was to search for water and pasture for their animals
- They are divided into;
- Eastern cushites
- Southern cushites
- Eastern Cushites
Kenya Somali, orma, boran, burji, gabbra, rendille, galla, boni Ethiopia Rendille, afar, sindamo, galla, danakil, oromo, ogaden Somalia Boran, somali, rendille, oromo, ogaden, hawiyah, gurreh, danakil. - Southern Cushites
Mostly lives in central Tanzania and lower Tana River regions of Kenya
Kenya Sanye, Dahalo Tanzania Hawa iraqw, mbugu, burugu, avamanik, sandawe, hadza, makogodi
Nilotes
- Is the second largest group in eastern Africa
- Originated from Nile valley, bhar-el-ghezal in south Sudan
- They were pastoralists
- Mainly migrated in search of pasture and water
- They also practised fishing along the rivers
- Are divided into three sub groups namely
- River-lake nilotes
- Highland nilotes
- Plain nilotes
- River-lake nilotes
Kenya Luo Uganda Acholi, labwar, japadhola, langi, alur, lughbava Tanzania Luo s.sudan Shilluk, anuk, nuer, dinka - Highland nilotes
kenya Kipsigis, nandi, tugen, keiyo, pokot, marakwet, sabaot, ogiek ,dorobo. uganda Sebei, sabiny tanzania Datoga - Plain nilotes
kenya Samburu, maasai, turkana, njemps, iteso, el-molo-suk uganda Karamanjong, jie, iteso tanzania Maasai sudan Yoposa ethiopia Baria, gumuz
The Semites
- Migrated from south Arabia Asia into the horn of Africa
- They crossed into Africa through the red sea
- Others came through the Indian ocean
- Mainly migrated looking for trade items and trading opportunity
- They are found in Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea and Sudan
Kenya Nubians Sudan Nubians, arabs, amharas, Ethiopia Falasha, arabs, tigreans, amharas, baggara Eritrea Tigreans, amharas Somalia Arabs
Reasons For The Migration Of Selected Language Groups Into Eastern Africa
- Migration of people from one place to settle in another place
- People migrate from one place to another because of various reasons
Reasons For The Migration Of The Bantus
- They wanted fertile farming land to grow groups
- Escape from hostile neighbours
- Population pressure
- Running away from Outbreak of pests and diseases
- Running away from Drought and famine
- Internal disputes and conflicts
- Their population had increased and so they were looking for space to settle
Reasons For The Migration Of The Nilotes
- Need for pasture and water
- Running away from Epidaemic (outbreak of diseases)
- Running away Hostile neighbours i.e. external attacks
- Internal conflicts/disputes
- Overpopulation
- Running away from Drought and famine
Reasons For The Migration Of The Cushites
- Need for pasture and water
- Outbreak of diseases epidemics
- Moving from Drought and hunger
- Hostile neighbours
- Running away from Internal conflicts among clan members
- Overpopulation hence need to settle away
- Spirit of adventure
Reasons For The Migration Of The Semites
- Need for better trading opportunities
- Search for trade goods
- Overpopulation
- Family and clan disputes
- Spirit of adventure
- Outbreak of human and animal diseases
- Spread their culture
- Wanted to spread Islam
Historic Environments In Eastern Africa - Social Studies CBC Grade 6 Notes
- Historic Built Environments In Eastern Africa
- The Main Historic Built Environments In Eastern Africa
- Importance of the main historic built environment in Eastern Africa
Historic Built Environments In Eastern Africa
- Historic built environment refers to features made by people
- These features have a historic value
- They include
- Museums
- Monuments
- Historical buildings
- Cultural centers
The Main Historic Built Environments In Eastern Africa
| Name of the built environment | country | historic environment | |
| 1 | Kigali genocide memorial | Rwanda | museum |
| 2 | Fort Jesus | Kenya | |
| 3 | Namugongo shrine | Uganda | |
|
4 |
Independence monument | Burundi | monument |
| 5 | John Garang mausoleum | South Sudan | |
| 6 | Black hawk down Crush Site | Somalia | |
| 7 | The peoples palace | Djibouti | |
| 8 | Askari Monument | Tanzania | monument |
| 9 | Victory Monument | Ethiopia | Monument |
| 10 | Bomas of Kenya | Kenya | Cultural centre |
| 11 | Hyrax museum | Kenya | museum |
Importance Of The Main Historic Built Environment In Eastern Africa
- They create a sense of belonging
- They serve as resources learning centres
- Attracts tourist and earn as foreign exchange
- They enable social interactions with friends, family and community
- Many people are employed to work in historical buildings, museums and take care of monuments
Vegetation In Eastern Africa - Social Studies CBC Grade 6 Notes
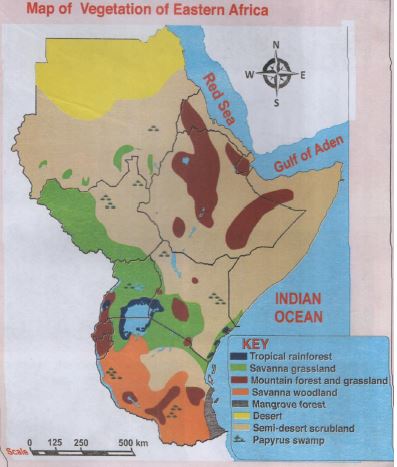
- Map Of Eastern African Showing The Main Types Of Vegetation
- Characteristics Of The Main Types Of Vegetation In Eastern Africa
Vegetation
- Vegetation refers to plants that grow in a place.
- It consists of trees, bushes, grass and shrubs.
- The vegetation that grows on its own is called natural vegetation
- The vegetation that is planted is called planted vegetation
- Types of vegetation in eastern Africa
- Tropical rainforest vegetation
- Savannah woodland
- Savannah grassland
- Mountain vegetation
- Swamp vegetation
- Desert vegetation
- Semi-desert
- Mangrove vegetation
Map Of Eastern African Showing The Main Types Of Vegetation
Characteristics Of The Main Types Of Vegetation In Eastern Africa
Tropical Rainforest Vegetation
- Also called equatorial vegetation
- Found in equatorial climatic region
Characteristics Tropical Rainforest Vegetation
- Tall trees that form canopies
- Vegetation is evergreen
- Trees have straight trunks
- Trees have broad leaves
- Trees have buttress roots
- Forests are thick and dense
- Trees are mainly hardwoode.g.oak, teak, mvule, mahogany, ebony, camphor,obeche, iroko, heartwood, ironwood, rosewood, sapele, limba, okoune
Savannah Woodland Vegetation
- Comes immediately after tropical rainforests
- Mainly consist of trees
Characteristics Savannah Woodland Vegetation
- Trees are of medium height
- Trees are widely spaced ( scattered)
- Trees are deciduous
- Tall grass between the trees
- Tree tops are umbrella shaped
- Common trees are acacia and baobab
- Trees are deep rooted and have thick barks
Savannah Grassland Vegetation
- Mainly consist of grass and few scattered trees
Characteristics Savannah Grassland Vegetation
- Drought resistant vegetation
- Grass may grow upto 2m
- Tall elephant grass
- Few scattered trees
- Trees have thick barks
- Trees have thorny leaves
- Main trees are baobab, acacia, cacti, euphorbia
Swamp Vegetation
- Common in swampy regions, along rivers and shores of small lakes
- Mainly grows in poorly drained areas.
- Main vegetation are; Papyrus reeds, Water lilies
- Found in South sudan bahr-el-ghazal-sudd swamp, kyoga in Uganda, malagarasi swamp in Tanzania, amboseli swamp in Kenya
Mangrove Vegetation
- Grows in the muddy salty waters along shores of Indian ocean
- The mangrove trees they have breathing roots (aerial roots)
- Trees are mainly hardwood ever green and medium height
- Is found along the shores of Indian ocean and mouths of r.ruvuma, r.juba
Mountain Vegetation
- Grows on the slopes of mountains
- Is widespread on the windward sides of the mountains
- Vegetation changes as altitude increases
- Vegetation is mainly influenced by the altitude
- Is also called alpine or montane vegetation from top to bottom the vegetation ranges from bare rocks, health and moorland , bamboo, rain forest and savannah.
Semi-desert Vegetation
- Found in areas with rainfall between 250mm-500mm
Characteristics Semi-desert Vegetation
- Short scanty thorny bushes
- Short tough and scattered patches of grass
- Vegetation is drought resistant with modified for thorns
- Common plants cactus, baobab and euphorbia
Desert Vegetation
- Found in areas with rainfall less than 250mm
Characteristics Desert vegetation
- Stunted plants
- Plants have thorny or needle-like leaves ( catus is the most common plant)
- Large section of Ground is bare
- Plants have thick fleshy stems
- Plants are deep rooted
- Spiky scanty grass
- Found in true deserts e.g. Kaisut and chalbi and taru deserts
Climatic Regions In Eastern Africa - Social Studies CBC Grade 6 Notes
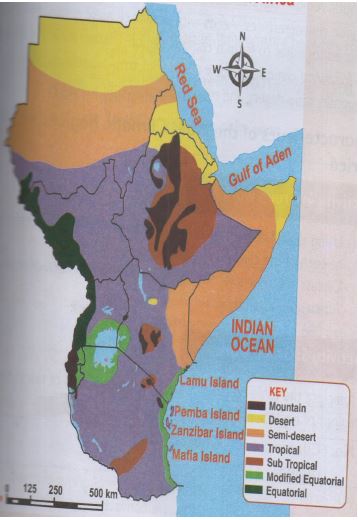
- Main Climatic Regions In African
- Characteristics Of The Main Climatic Regions Of Eastern Africa
- Characteristics Of Modified Equatorial
- Characteristics Topical Climatic Region
- Characteristics Mountain Climatic Region
- Sub Tropical Climatic Region
- Characteristics Of Semi Arid Climatic Region
- Characteristics Of Desert Climatic Region
- Characteristics Of Semi Arid Climatic Region
- Influence Of Climatic Regions On Human Activities In Eastern Africa
Main Climatic Regions In African
- Climate is the average weather condition of a given place for a very long period of time.
- Climatic regions refer to continuous geographic area with similar climatic characteristics.
- Areas with similar climatic characteristics conditions are grouped together to form a climatic region
- Climatic regions in Eastern Africa include
- Equatorial
- Tropical
- Sub tropical
- Desert
- Mountain
- Semi desert
- Modified equatorial
Characteristics Of The Main Climatic Regions Of Eastern Africa
- Characteristics of equatorial region
- High rainfall throughout the year above 1500mm
- Receives convectional rainfall
- Rainfall is well distributed throughout the year
- High temperatures throughout the year
- Annual average temperatures of about 26 ̊ C
- High humidity throughout the year
- Two rainfall peaks between April - May and November - December
- Small range of temperatures
- No distinct dry season
Characteristics Of Modified Equatorial
- High rainfall between 1000m-2000mm per year
- Moderate temperature of about 22ºC (due to low altitude
- Convectional rainfall due to nearness to large water bodies
- High humidity throughout the year due to high rate of evaporation
- it has two main seasons wet and dry
- Long rains between march-may
- Short rains between October – December.
Characteristics Topical Climatic Region
- Has hot wet seasons and cool dry seasons
- Cooler seasons have no rainfall hence remains dry
- Hotter seasons receives a lot of rainfall hence they are wet
- Rainfall is between 750mm – 1200mm
- Has two distinct rainy seasons
- Long rains between march-may
- Short rains between September – October.
- Temperature average is 21 ̊ c – 32 ̊ c
Characteristics Mountain Climatic Region
- High relief rainfall between 1100mm – 2500mm
- Cool/low temperatures due to high altitude (at the peak of the mountain
- Leeward sides are cool and dry
- Peaks of high mountains are permanently covered by snow
Sub Tropical Climatic Region
- Cool or moderate temperature between 18c and 23 c
- High rainfall between 1100mm and 2500mm per year
- Rainfall is throughout the year
Characteristics Of Desert Climatic Region
- Low/unreliable rainfall below 250mm per year
- Rainfall is irregular
- High temperatures of up to 40 ̊
- Clear/cloudless skies throughout the year
- Very high diurnal range of temperatures
- Hot and dry most of the months of the year
- Prolonged drought
Characteristics Of Semi Arid Climatic Region
- Long dry season
- High throughout the year.
- Rainfall range between 250mm- 680mm per year
- In arid and semi arid areas, pastoralism is the main economic activity. The areas receives low rainfall that cannot support crop farming
- In tropical areas where rainfall is reliable crop farming is practised as the main economic activities
- Too much rain leads to flooding ad destruction of crops and property
- Drought leads to famine and loss of livestock
- Appreciating the climatic regions of Eastern Africa
Influence Of Climatic Regions On Human Activities In Eastern Africa
- In arid and semi arid areas, pastoralism is the main economic activity. The areas receives low rainfall that cannot support crop farming
- In tropical areas where rainfall is reliable crop farming is practised as the main economic activities
- Too much rain leads to flooding ad destruction of crops and property
- Drought leads to famine and loss of livestock
Main Physical Features in Eastern Africa - Social Studies CBC Grade 6 Notes
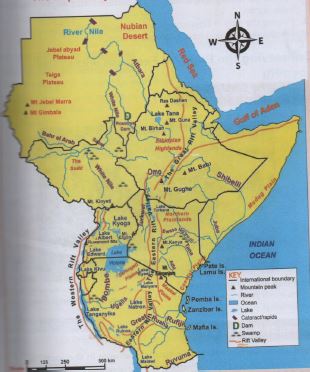
- The Main Physical Features In Kenya
- Map Of Eastern African Showing Main Physical Features
- Conserving The Physical Features Within The Locality
- Physical features are naturally things found on the surface of the earth
- They include:
- Mountains
- Valleys
- Plateaus
- Ocean
- Seas
- Gorges
- Plains
- Lakes
- Rivers
- Swamps
- Hills, rangers
The Main Physical Features In Kenya
- Mountains
- Are masses of very high land.
- They are the highest physical features on the earth.
- Major mountains in Eastern Africa
KENYA TANZANIA UGANDA SUDAN ETHIOPIA Mt.kenya Mt.kilimanjaro Ruwenzori Jabel-marra Ras dashan Mt.longonot Mt.meru Nubadarfur Guna Mt.marsabit Pare mts Kissu Danakil alps Mt .kulal Ngorongoro crater Menengai crater Lool molasin
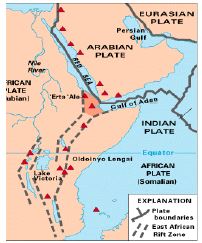
- Rift valley
- A valley is a low lying are with steep slopes.
- In Eastern African the rift valley has 2 branches that stretch across several countries
- The two branches are the eastern rift valley and the western rift valley
- Lakes
- A lake is a water body that is surrounded by land
- A hollow/depression filled with water
- We have
- Fresh water lakes
- sailty water lakes
- Main lakes in eastern Africa are
KENYA UGANDA TANZANIA ETHIOPIA RWANDA Turkana
Baringo
Bogoria
Nakuru
Elementaita
Naivasha
Magadi
Jipe
ChalaAlbert
Edward
Bunyonyi
Bisini
George
Kyoga
Kivu
mutandaNatron
Manyara
eyasi
Rukwa
Malawi
tanganyikaChamo
Abaya
Steffanie
Shala
tanaruhondo
kivu
- Plains
- Are low lying areas of almost flat land.
- Examples
KENYA UGANDA TANZANIA SOMALIA Lotikipi, awara, kano, Luwero Serengeti Bilesha Kaputei, loita, Nakasongola maasai Sarar Budalangi,kapiti Haded bilesha
Formation Of Main Physical Features Of Eastern Africa
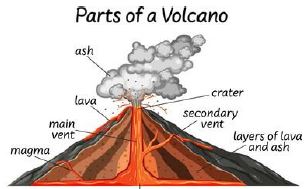
Formation Of Volcanic Mountains
- They are also called volcanoes
- They are formed through the process of volcanicity/eruption.
- Eruption is when the hot molten material underground is forced out by great pressure
- The hot molten material is called magma
- When magma gets to the surface is called lava
- The magma gets out through a main pipe called vent
- The opening at the top of a volcanic mountain is called a crater
- Most mountains in eastern africa are volcaning mountains
KENYA TANZANIA RWANDA Kenya
Elgon
Longonot
Menengai crater
Marsabit
Suswa
KulalMt meru
Mt Kilimanjaro
Ngorongoro
Lool malsinMt karisimbi
Nyiragongo
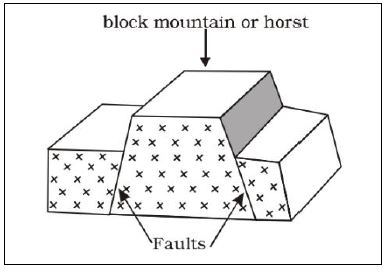
Formation of Block Mountains
- They are also called horst mountains
- They were formed through faulting and uplifting process
- Faults are lines of weakness
- Faults were developed as a result of forces acting on the layers of the earth
- The forces involved are tensional and compressional forces
- The middle block was pushed upward by underground forces
- The underground forces called up thrust force
- Examples
ETHIOPIA UGANDA TANZANIA Danakali alps ruwenzori Pare
usambara
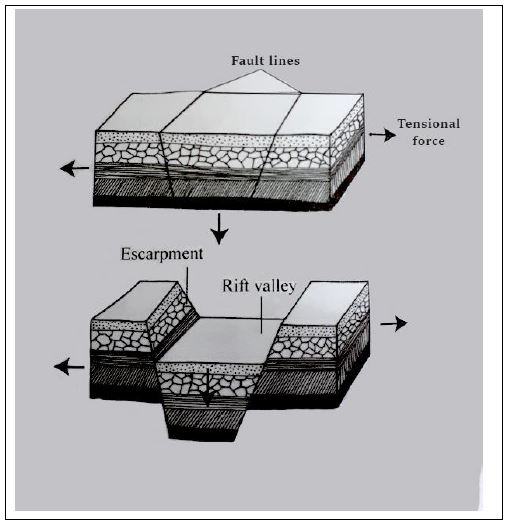
Formation Of The Rift Valley
- The rift valley was formed when two cracks or fault line formed within the crustal rocks
- The land between the two faults sunk forming a valley
- Was formed through the faulting process
- Formed by either tensional or compressional forces
- When two parallel faults developed the tensional forces pulls the rocks apart
- The middle block between the faults sink
- The steep sides of a rift valley are called escarpments
Formation Of Lakes
- The major lakes in eastern African were formed as a result of
- Faulting
- River deposition
- Down warping
- Volcanicity
Rift Valley Lakes
- During the formation of the rift valley, some parts of the land sunk deeper than others forming depressions.
- The depressions were filled with water to form lakes
- Example – lake Tanganyika in TZ
Lakes Formed As A Result Of Down Warping
- Down warping is a process by which the earth sinks inwards due to pressure forming a big basin.
- Water fills this basin to form a lake.
Example: lake Victoria in Kenya
Lakes Formed As A Result Of Volcanicity
- Lava dammed
- Lava dammed lakes are formed when lava flow on the surface of the earth and comes int contact with a river, blocking it
- This leads to the formation of a lake
Example: lake kivu in Rwanda
- Crater lakes
- When volcanic eruption occurs, the top of the mountain may be blown of forming a hallow depression called crater.
- Water fills the hallow depression forming a crater lake.
- Example; Lake paradaise in Kenya, Ngozi in Tanzania and Shalla in Ethiopia.
Formation Of Plains
- Plains are wide low lying areas of flat land.
- Plains are formed as a result of erosion and deposition of the eroded materials.
Map Of Eastern African Showing Main Physical Features
Conserving The Physical Features Within The Locality
We should protect and conserve physical features found in our locality
- Prevent overuse and deforestation of forest.
- Avoid pollution of water bodies.
- Educate people on importance of physical features.
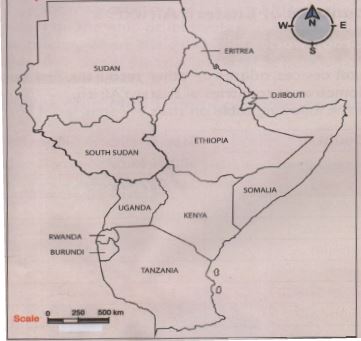
Countries in Eastern Africa - Social Studies CBC Grade 6 Notes
Position and Size of Countries in Eastern Africa
Countries in Eastern Africa
- Eastern Africa is the region located in the eastern region of Africa.
- It is made up of eleven independent countries namely:
- Sudan
- Ethiopia
- Tanzania
- Somalia
- South Sudan
- Kenya
- Uganda
- Eritrea
- Burundi
- Rwanda
- Djibouti
NB
- Sudan is the largest country in eastern Africa
- South Sudan became independent in JULY 2011
- Djibouti is the smallest country in eastern Africa
- Countries without a coastline are called landlocked e.g. Burundi, Uganda, Rwanda,
- Ethiopia and South Sudan.
Position Of Countries Of Eastern African
- Using a compass you can locate position of a country in relation to her neighbours.
- Kenya lies to the -:
- North east of Tanzania
- South of Ethiopia
- South east of South Sudan,
- East of Uganda
- West of Somalia
- Immediate neighbours of Kenya are Tanzania, Uganda, South Sudan, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
Size Of The Countries Of Eastern Africa
| COUNTRY | SIZE in square kilometres (km2) |
| Sudan | 1.886 million km2 |
| Tanzania | 945,087 km2 |
| Somalia | 637,655 km2 |
| South Sudan | 644,329 km2 |
| Kenya | 580,367 km2 |
| Uganda | 241,037km2 |
| Eritrea | 117, 598 km2 |
| Burundi | 27,834 km2 |
| Rwanda | 26, 338 km2 |
| Djibouti | 23,200 km2 |
| Ethiopia | 1.104 million km2 |
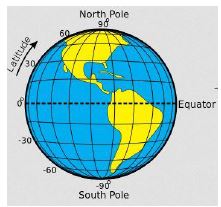
Locating Places On A Map Using Latitudes And Longitudes
- Eastern Africa lies within latitudes 22 ̊N AND 12 ̊S and between longitudes 22 ̊E and 51 ̊E/52 ̊E.
Latitudes
- These are imaginary lines that runs from west to east
- They are also called parallels
- The main line of latitude is equator at 0 ̊
- Equator divides the earth into two equal halves called hemisphere.
Characteristics Of Latitudes
- They are parallel
- They are of different lengths
- They affect climate
- They are measured in degrees from the equator
- They are 180 lines of latitudes in total
- Latitudes lines are;
- Equator at 00
- The tropic of cancer 23 ½º N
- The arctic circle 66 ½ ̊N
- The tropic of Capricorn 23 ½º S
- The Antarctic circle 66 ½º S
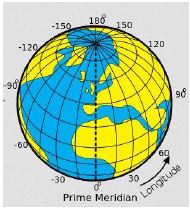
Longitudes
- These are imaginary lines that run from North Pole to south pole of the earth
- They are also called meridians or horizontals
- Main line of longitude is Greenwich meridian at 0 ̊
- Greenwich meridian is also called prime meridian
- Prime meridian passes through the Greenwich town in London and Accra in Ghana
Characteristics Of Longitudes
- They run from north to south
- They are not parallel
- They meet at the poles they affect time
- They are of the same length
- They are measured in degrees east por west of prime meridian
- They are 360 ̊ lines of longitudes in total.
| Town | Location | |
| 1 | Nairobi | 1.3º S, 36.8ºE |
| 2 | Dodoma | 6.5738 S, 6.2631º E |
| 3 | Kampala | 0.3634º N, 32.6051º E |
| 4 | Mogadishu | 2.0º N, 45.3º E |
| 5 | Kigali | 1.9441º S, 30.06º E |
| 6 | Bujumbura | 3.36º S , 29.3599º E |
| 7 | Asmara | 15.3381º N, 39.9318º S |
| 8 | Khartoum | 15.30º N, 32.31º E |
| 9 | Djibouti | 11.8251º N, 42.5903º E |
| 10 | Juba | 0.2240º N, 41.6012º E |
| 11 | Addis ababa | 8.9806º N, 7578º E |
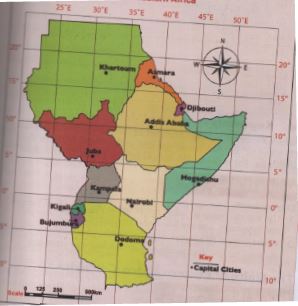
Unity among eastern African countries can be promote through trade
Indigenous Kenyan Craft - Art and Craft CBC Grade 6 Notes
- Basketry
- Coil And Stitch Technique
- Samples Of Coil And Stitch Items
- Selecting Materials For Coil And Stitch Technique
- Preparing Selected Materials For Coil And Stitch Technique
- Methods Of Preparing Selected Materials For Coil And Stitch Technique
- What to consider when coiling and stitching an item.
- Making a floor mat using coil and stitch technique using man-made materials or natural materials.
- Leatherwork
- Coil And Stitch Technique
Basketry
Basketry is the art of making containers and other items using flexible fibres.
Coil And Stitch Technique
- It is the art of coiling materials and sticking them together using a needle and thread to make an item.
Samples Of Coil And Stitch Items
- There are two types of coils
- Plaited coils – are made by braiding two or more strands of a material to make a pattern.
- Roiled coils – are made by roiling strands of materials together
- Items made using the coil and stitch technique are made using any suitable materials that can be rolled e.g. banana fibres, palm leaves
- In weaving, the materials used are interlaced vertically and horizontally on a loom to form an item.
- The vertical threads are called warps and the horizontal threads are the wefts orfillings.
- In basketry, one does not use a loom.
- In the coil and stitch technique, the materials are rolled in a circular form and stitched together using a needle and a string.
Selecting Materials For Coil And Stitch Technique
- Coil and stitch materials can be sourced from
- natural materials or
- man-made materials
- Natural materials are those that can be found in the environment
- Man-made materials include synthetic.
| Man-made materials | Natural materials |
| Nylon Carbon fibre Polyester Yarn Acrylic yarn |
Raffia Wool Silk Reeds Cane Banana fibres sisal |
- Materials used in coil and stitch technique should be flexible and easy to roil to form the coils needed.
- When selecting materials to make a door mat using the coil and stitch technique, consider whether they are
- Durable
- easy to clean and
- non slippery.
- Always use non slippery materials to avoid slip and fall accidents
Preparing Selected Materials For Coil And Stitch Technique
- There are different ways fo preparing materials to be used to make an item using the coil and stitch technique.
- They include
- Dyeing
- Plaiting
- Tearing
Methods Of Preparing Selected Materials For Coil And Stitch Technique
- Tearing methods
- Involves splitting materials such as banana fibres into thin strips for easier use.
- This can be done using your hands or a fibre stripper.
- Dyeing
- Is the process of changing the original colour of materials used to make an item to different colour.
- Plaiting
- Is a technique whereby strands of suitable materials such as rope or silk are braided together to make a single string of fibre.
- Stripping method
- Collected the suggested tools- Fibre stripper/basin/cutting tools/sisal/water
- Spilt the sisal stem into thin strips that can fit in the fibre stripper.
- Place the sisal strips in the middle of the fibre stripper and pull them through to get sisal fibre.
- Wash the fibre using clean water
- Dry the washed sisal fibre in the open sun.
What to consider when coiling and stitching an item.
- Uniformity of coils
- Consistent tension
- Craftsmanship
- Materials
Making a floor mat using coil and stitch technique using man-made materials or natural materials.
- Collect the suggested materials and tools.
Needle/scissors/thread/man-made materials - Prepare the strand by rolling the length of the strand you need
- Use nylon paper or sellotape to wrap and cover the beginning end of the strand.
- Coil the wrapped end of the strand to form a small circle. Using a thread and needle, stitch the wrapped end of the strand by inserting and pulling the needle through the strand. Start stitching from the center as you move outwards.
- Fasten the loop after the first round by passing the needle from right towards the left onto the back of the strand.
- Continue to coil and stitch the strand to make a mat. Add more rope until you get your desired size of the floor mat.
- Finish the floor mat by fastening the end of the strand using stitches
- Display your floor mat
Leatherwork
- Leather work involves using different types of leather materials to make items.
- Leather materials is produced from skin hides of animals.