Musya
Athletics: Field Events - Physical Health Education CBC Grade 6 Revision Notes
Field Events
- Are categorised into
- Jumps – high jump, pole vault, long jump and triple jump
- throws – discuss, javelin, short put, and hammer.
High Jump
- It is a field event in which competitors must jump unaided over a horizontal bar placed at measured heights without dislodging it.
- 2 main consideration is Lift and clearance
Safety Instruction
- Ensure proper spacing during drills and practise
- Wear appropriate PHE attire during activity.
- Follow teacher’s instructions during practise
- Ensure the runway is free from obstacles
- Use a flat ground
- Jump one learner at a time.
- Perform warm up adequately before participating in an activity
Warm Up Activities
- Jumping jacks
- Stand with your legs shoulder width knees slightly bent and hands on the sides
- Jump and open the arms and legs out to the sides. Arms come above the head and legs wider than shoulder width.
- Close your arms and legs back to your sides, returning to the start.
- Repeat several times.
- Skip and skip
- Move while stepping from one foot to the other with a hop
- Raise your arm opposite the moving foot alternatively.
- Press ups
- Place hands on the ground face down
- Extend your legs back and balance on your hands and toes.
- Keep the body straight
- Bend your elbows and lower yourself until your elbows are at an angle of 90 degrees.
- Push backup through your hands to the start position.
- Place hands on the ground face down
- Extend your legs back and balance on your hands and toes
- Keep the body straight
- Bend over your elbows and lower yourself until your elbows are at an angle of 90 degrees
- Push backup through your hands to the start position.
- Wind Break
- Pretend to be in a windstorm, with wind blowing arms as branches..
- Start while the wind is strong and finish as the wind calms.
Facility And Equipment In High Jump
- facility used in high jump is a space where a runway is marked.
- There is a landing area where suitable material for landing is placed.
- For example, sah'ust, landing maaress
- Equipment include crossbar, uprights, tape measure
Rules Followed In High Jump As You Practise
- Do not touch the ground beyond the plane of the upright and the landing area before the cross bar.
- take off should be on one foot
- Do not dislodge the bar to master the take off points.
Styles Of High Jump
- The scissors
- straddle
- Fosbury flop
- Western roll
Scissor Technique In High Jump
- This is a method of clearing the bar in high jump.
- It involves the legs making a crossing action over the crossbar during fight.
- The crisscrossing is what gives the technique its name scissors
Safety Instruction
- Ensure proper spacing during drills and practise
- Wear appropriate PHE attire during activity.
- Follow teacher’s instructions during practise
- Ensure the runway is free from obstacles
- Use a flat ground
- Jump one learner at a time.
- Perform warm up adequately before participating in an activity
Warm Up Activities
- Jumping jacks
- Stand with your legs shoulder width knees slightly bent and hands on the sides
- Jump and open the arms and legs out to the sides. Arms come above the head and legs wider than shoulder width.
- Close your arms and legs back to your sides, returning to the start.
- Repeat several times
- Side shuffle
- Stand with your feet hip distance apart.
- Bend forward at the hips, knees bent, looking forward and chest Liftted.
- Hold your hands in loose fists in front of your chest.
- Move right using small quick shufe steps for 15 minutes
- Repeat movement to the left side. continue shuffling right and left.
- Lunges
- Start by standing up tall.
- Step forward with one foot until your leg reaches a 90 degree angle
- Lift your front lunging leg to return to the starting position.
- Repeat 5 times on one leg then change to the other.
Cool Down Activity
- Stretch and spell
- Use body stretch to spell the word scissor one letter at a time
- Wait for seconds before spelling a different letter.
- learning points on the scissor technique
- the approach – approach the bar at a comfortable speed.
- the take off - hold your shoulders high and fex the take off leg to launch you into the air
- the fight – hold the leg nearer the bar straight and Swing it into the air to clear the bar
- Once your lead leg is over the bar, kick the other foot to clear the bar.
- Landing- land on your feet to complete the jump
Safety Measures To Observe When Participating In High Jump
- Perform warm up actvites before participation
- Attempt jumps, one learner at a time.
- Use the run way when it is clear
- Ensure the material used on the landing area is in place before Attemptng a jump.
- When the bar is dislodged, pick and place it on the upright before an Attempt is made.
Standing javelin
Equipment And Sector In Standing Javelin
- Javelin throw is a field event where the javelin, a spear about 2.5min length is thrown.
- A javelin is a spear shape implement.
- The javelin has several parts
- Metal head – it is the part that has metal tip
- Metal tip – it is made of metal and determines the outcome of the exact measurement once the javelin has landed
- chord grip – this covers a section of the shaft and it is the part that is held by the thrower.
- The tail – this is the part of the javelin that trails it as the implement is thrown.
- The shaft – it makes the largest part of javelin. The chord grip is within the shaft.
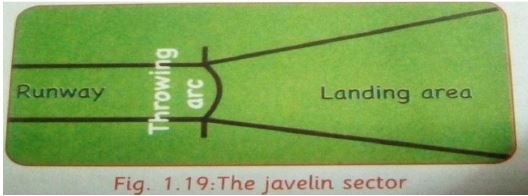
Javelin Sector
- The javelin throw facility includes a runway, a throwing arc and a landing sector.
Safety Instruction
- Ensure proper spacing during drills and practise
- Wear appropriate PHE attire during activity.
- Follow teacher’s instructions during practise
- Do not stand in the way of javelin or where it is landing
- Carry the implements back after a throw.
- Perform warm up adequately before participating in an activity
Warm Up Activities
- Jumping jacks
- Stand with your legs shoulder width knees slightly bent and hands on the sides
- Jump and open the arms and legs out to the sides. Arms come above the head and legs wider than shoulder width.
- Close your arms and legs back to your sides, returning to the start.
- Repeat several times
- Ankle circles
- Stand with feet hip width apart and your arms to the sides.
- Shift your height to the right leg and point your toes down into the ground.
- Start rotating your left foot making small circles with your ankles.
- Repeat the exercise with your right foot
- Shoulder rotation
- Stand tall with your arms by your sides
- Swing your arms forward until they are high as you can go, do not raise your shoulders.
- Return your arms to the starting positions and repeat the action
Cool Down activity
- climb the stair case
- Pretend to be climbing a stair case. Stretch your knees and arms the
Throw In Standing Javelin
- Proper technique requires the athlete to hold the javelin with only one hand on the chord grip.
- The javelin must be thrown with an over the shoulder motion.
- The competitor can’t turn his back to the throwing area until the javelin is airborne
Skills In Standing Javelin
- The stance
- Grip
- Release
- Recovery technique
If Using The Real Implement
- Always carry the javelin vertically with the point down
- Be aware that the tail is as potentally dangerous as the tip.
- Never run to collect a javelin
- Take care when removing the javelin from the ground. Check that the area around is clear before doing so.
- When the javelins are not in use, they should be firmly stuck into the ground in a vertical position.
Warm Up Activities
- Body weight squats
- Stand with your hands on the back of your head and your feet shoulder width apart.
- Turn your feet out slightly to open the hip joint. Loher your body until your thighs are parallel to the foor
- Pause, then return to the starting position.
- Arm swings
- hold your arms straight out to the side
- Swing them and cross them in front of your chest
- Hip circles
- Stand tall with your feet at hip width
- Keeping your hands in front of your stomach, pull your right knee up until it is parallel with the foor, then pull the knee out, opening up the hip.
- Return to the start position and repea on the other side
Cool Down Activity
- Heel and toe
- Walk in circles on heels for 20 seconds
- Walk in circles on tip toes for 20 seconds
Phases In The Standing Javelin
(the learning points)
- The stance
- Stand with Feet fexed, the foot opposite the throwing hand slightly forward.
- Toes of the feet to point direction of the throw.
- The grip
- Grip the javelin such that it lies along the palm of the hand which is turned upwards.
- Old it firmly in a relaxed way without applying tension in the forearm.
- Grip the javelin by bringing thumb and the frst tho joints of the index finger are behind the chord
- The index finger supports the shaft
- The finish grip
- It is a methold of gripping the javelin where the middle finger rest closer to
the top of the chord and index finger hraps higher along the shaft.
- It is a methold of gripping the javelin where the middle finger rest closer to
- Recovery
- Athlete hill try to balance to avoi' falling.
Measuring The Distance
Measure The Distance By
- starting from where the tip of the javelin frst strikes the ground
- The zero tape measure goes out to where the javelin tip strikes the ground
Shot Put
- The shot put is a a field event. The action of throwing the shot is called putting
- It involves putting of a heighted ball for distance.
- The athlete compete for distance thrown
- The implement is made of solid iron or bass
- The short is put with one hand. It is held next to the neck.
- It may not drop below or behind shoulder level at any time
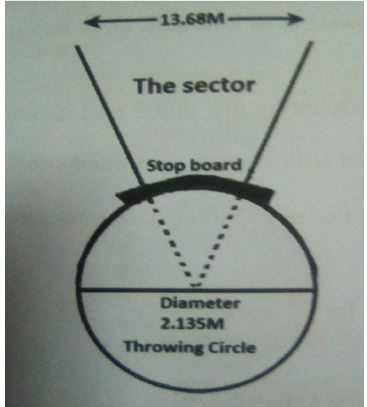
The Shot Put Sector
- A shot put sector features throwing circle, from which an athlete puts the shot and throwing sector which is triangle in shape.
- The circle has a diameter of 2.1 5 meters.
- The throwing sector measures 1 .68 at its hidest and 20 metres
Throwing style
- Standing style
- Obrien style
Standing Shot Put
Safety Instruction
- Do not throw the shot until the teacher gives you permission to do so
- Do not retrieve the shot until the teacher gives you permission to do so
- Wear appropriate attire
Warm Up Activity
- Mountain climbers
- Put both hands and knees on the foor
- Place your right foot near your right hand and extend your left leg behind you
- In one smooth motion, shitch your legs , keeping your arms in the same position
- Side reach
- Stand with feet wider than shoulder width apart
- Lean your body to the right side and bend your right knee slightly
- Stretch your left arm upwards in line with your body
- Repeat on the opposite
- Arm circles
- Stand with your fet shoulder width apart and extend your arms parallel to your foor
- Circle your arms forward using small controlled motions, gradually make the circles bigger
- Reverse the direction of the circles afer about 10 second
Cool Down Activity
- Heel and toe
- Walk in circles on heels for 20 seconds
- Walk in circles tip toes for 20 seconds
Obrien Shot Put
Safety Instruction
- Ensure proper spacing during drills and practise
- Wear appropriate PHE attire during activity.
- Follow teacher’s instructions during practise
- Putt the shot towards one end
- Do not stand on the side where the shot is landing
- Carry the implement back
- Perform warm up adequately before participating in an activity
Warm Up Activities
- Back pedalling
- Run backwards with short, quick pumping your arms and landing on the balls of your feet
- Keep your chest up and take as many steps as possible
- Plank walk out
- Start in a standing position
- Bend forward until you touch the ground with your hands
- Slowly walk your hands forward as far as you can
- Pause then walk your hands back towards your feet
- Repeat several times
- Arm swings
- Hold your arms out to the side
- Swing them and cross them in front of your chest
Cool Down Activity
- Slowly walk within the marked area
Learning Points
- Stance and grip
- Stance
- Stand with the feet shoulder width apart parallel to the target holding the shot
- Stand with the feet shoulder width apart parallel to the target holding the shot
- Grip
- Hold the shot with the base of the fingers
- Spread the fingers slightly apart and the thumb sed for support
- The hand be bent back in a cocked position holding the shot
- The elbow is held up to the side, away from the body
- The thumbs should be pointsng down the palms facing outwards and the fingers behind the shot( elbows up, thumbs down, palms out position)
- Release and recovery
- Stand with the feet parallel to the target
- Place the shot under the jaw and against the neck
- Extend the non putting arm towards the target
- Release the shot
- Recovery
- Extend the wrist to flick the shot off the fingers as it leaves the hand for recovery
- Stance
| IMPLEMENT | U13 | U15 | U17 | Junior men | Senior men | U13 | U15 | U17 | Junior women | Senior women |
| Shot put | 3kg | 4kg | 5kg | 6kg | 7.26 kg | 2.72 kg | 3kg | 3kg | 4kg | 4kg |
| Discuss | ||||||||||
| Hammer | ||||||||||
| Javelin | 400g | 600g | 700g | 800g | 800g | 400g | 500g | 500g | 600g | 600g |
Athletics: Track Events - Physical Health Education CBC Grade 6 Revision Notes
- Bunch Start
- Drop Finish Technique
- Shoulder Shrug Technique
- Non Visual Baton Exchange Down Sweep Method In Relays
Track Events
Bunch Start
- Also known as the bullet start.
- In this start the knee of the rear leg is opposite the toe of the leading leg.
- The hands are placed shoulder width apart behind the starting line.
Safety Instructions
- Use your lane and stick to it
- Wear appropriate PHE attire during activity.
- Follow teacher’s instructions
- Warm up adequately before participating in an activity
Warm Up Activities
- Running on the spot
- Learning points for running on the spot
- Lift your right arm and left foot at the same time
- Raise your knee
- At the same time, move your right arm and your left arm forward and up
- Switch to the opposite foot quickly
- Start slowly as you increase speed
- Continue the these movements
- Rabbit hops
- Stand with feet shoulder width apart
- Keep your hands held at the chest
- Take off with both feet and land with both feet.
Cool Down Activities
- Slow match
- Stand feet shoulder width apart
- Arms bent at the elbows
- Bing your right elbow forward at the same time as you bring your left knee up.
- Repeat on the opposite side and keep alternating sides until there is rhythm.
- Perform the activity very slowly.
Learning Points For The Bunch Start
- On your command, On your marks, Go to the starting line on crouch position.
- Place the legs such that the toes of the rear foot are approximately in line the heel of the front foot.
- Place both feet behind the starting line
- Place the arms straight shoulders width apart with fingers spread behind the line and thumb turned away.
- Keep the head in line with the body, eyes focused ahead down on the lane.
- On the set command, go in ready position with the whole body and raise the hips just above the shoulders.
- On the command go, press hard against the ground for a forward push as you accelerate down the lane.
Drop Finish Technique
- It is a method of finishing.
- The athlete bends, pushes both arms backwards and steps to the finishing line.
- They touch the tape with chest
- Approach the finishing line at full speed.
- Focus ahead.
- On finishing a step to the finishing line, bend and push both arms backwards and touch the finishing line with your chest first.
Safety Instructions
- Ensure proper spacing during drills and practise
- Wear appropriate PHE attire during activity.
- Follow teacher’s instructions during practise
- Warm up adequately before participating in an activity
Warm Up Activities
- Plucking partners tall
- Each person tucks a tail into the back of their short or trousers
- Run afer a partner and try to pluck their tail while keeping yours safe.
- Play a game for one minute and change partners.
- Squat jumps
- Start in squat positon with your arms by your side
- Swing your arms towards the sky and jump.
- Land gently on the balls of the feet into a squat positon and repeat the activity
- Perform the activity for one minute
- Latteral rabbit jumps
- Make small jumps side by side like you are jumping over something.
- Keep your legs as close as possible
- Swing your arms to help you jump.
Cool Down Activities
- Curling and stretching
- Lie on the right side of the body.
- Fold your leg and pull them towards the chest.
- slowly stretch your hands and feet.
- Repeat the activity times.
- Slow dance
- Stand freely.
- Dance in a slow motion for 0 seconds
- Rest for 5 seconds and repeat
Learning Points To Perform The Drop Finish Technique
- Approach the finishing line at full speed.
- Focus ahead.
- On reaching a step to the finishing line, bend and push both arms backwards and touch the finishing line with your chest frst.
Shoulder Shrug Technique
- It is a method of finishing a race.
- The athlete in his last stride bends one shoulder so that his chest is turned sideways as it touches the tape or crosses the finish line.
Safety Instructions
- Ensure proper spacing during drills and practise
- Wear appropriate PHE attire during activity.
- Follow teacher’s instructions during practise
- Warm up adequately before participating in an activity
Warm Up Activities
- High knees
- Jog in place, bringing your knees high up as you can
- Arm rotation
- Stretch out both arms to the shoulder level. Rotate them in forward and backward.
- Cross Jacks
- Stand with the feet shoulder width apart.
- extend out the arms straight on either sides with palms facing down.
- Jump and cross the right arm over the lef arm and foot over lef.
- Jump with the legs to the sides and open your arms, then cross with theopposite arm and foot.
Cool Down Activities
- Copy me
- Take turns to demonstrate your favourite stretch
- The others to copy the demonstration. Do it slowly.
- Slow skip
- Skip for a distance of 2 metres
- reduce the skipping distance and skipping speed slowly untl uou are in one place. Start marching slowly at the point and then stop
Learning Points To Perform The Shoulder Shrug Technique
- Approach the finishing line at full speed.
- Focus ahead
- On your last stride to the finishing line, bend one shoulder so that the chest is turned sideways as it touches the tape or as it crosses the finishing line.
Non Visual Baton Exchange Down Sweep Method In Relays
The Non Visual Baton Exchange Method
- This is where the outgoing runner receives the baton without seeing it being placed onto the hand.
- The hand that receives that baton carries it without bringing it to other hand.
Learning Point For The Non Visual Baton Exchange Method
The Incoming Runner
- Run at a speed within your lane
- Reach the runner hho is receiving the baton at full speed.
- extend the hand carrying the baton and pass it onto the hand of the receiver in a downward movement
The Outgoing Runner
- extend the receiving hand behind, at the hip level, while focusing head and accelerating down the lane.
- The palm faces up and a hide angle is formed betheen the thumb and the rest of the fingers.
- After the baton is placed on the receiving hand, hold it tight.
Safety Instructions
- Ensure proper spacing during drills and practise
- Wear appropriate PHE attire during activity.
- Follow teacher’s instructions during practise
- Do not throw the baton to one another.
- Warm up adequately before participating in an activity
Warm Up Activities
- Pluck partners tail
- In pairs take turns to run afer each other aaemptng to pluck a tail tied at the back.
- walking knees hugs
- Make steps and raise the knee up holding it with both arms and pulling towards your chest.
- Cycling in the air
- Lie on your back. Raise your legs and more them as if riding a bicycle
Cool Down Activities
- toe touch
- Reach up and touch down the sky for 20 seconds. Change and reach down to touch the toes for 20 seconds.
- clumb the stair case
- Pretend to be climbing a stair case. Stretch your knees and arms.
Forestry - Class 8 Social Studies Revision Notes
Forestry
- This is the planting and taking care of forests.
- A forest is a group of trees growing together.
- N/B 3% only of kenyan land is under forest.
Types Of Forest
- Natural forest
- Planted forest
Natural forest
- Grows on its own
- Hardwood trees are grown
- They take long time to mature
- Trees are of different species
- Hardwood trees are also called indegenous trees
- Obeche
- Meru oak
- Camphor
- Rosewood
- Ebony
- Mahogany
- Greenheart
- Iroko
Categories Of Natural Forest
- Coastal tropical forest
- Mountain highland forest
- Mangrove forest
- Tropical rainforest
Highland Forest
- Also called mountain forest
- Found in areas with high rainfall
- Found on slopes of mountains ,example:
- Mt. Kenya Forest
- Mt. Elgon Forest
- Aberdare Ranges Forest
- Kipkelion
- Mau Forest
- Kaoyagat Forest
- Malava
- Ngong Hills
Mangrove Forest
- Found along the salty water in the coast
Coastal Tropical Forest
- Also called lowland rainforest, examples:
- Arabuko Sokoke
- Boni
- Witu
Tropical Rainforest
- covered with tall trees
- a good example is Kakamega Forest and Nandi Hills Forest.
Planted Forest
- Cultivated and developed by man
- Softwood trees are grown
- Softwood are also kwown as exotic trees
- Trees are of the same species
- They mature fast
- Grown in straight rows
- Softwood make papers
- Softwood trees
- Cedar
- Cypress
- Eucalyptus
- Pine
- Wattle tree
- Gravillea
- Spruce
Planted Forest Locations
- Ainamioi - Kericho County
- Turbo - Uasin Gishu County
- Molo - Nakuru County
- Kaptagat - Nakuru County
- Timboroa - Uasin Gishu
- Londiani - Kericho
- Kinale - Kiambu
Problems Facing Forests
- Pests and diseases
- Defforestation
- Drought
- Forest fire
- Over exploitation by human being
- Government policy of degazettment of forests
- Mismanagement of forests
- Illegal logging
- Damage of wildlife
- NB the main problem facing forestry is clearing for agriculture and settlement.
- Main reason why we preserve natural forests is to protect the rare/indegenous trees.
- Main reason why we presreve forest is to protect water catchment areas.
Defforestation
- This is the illegal cutting down of trees without replacing
- It is the main problem facing forests
- Leads to desertification
- Destruction of water catchment areas
- It interferes with the carbon cycle
- Interferes with water cycle
- Leads to soil erosion
- Soil erosion leads to dam siltation
- Dam siltation affects the hep production
- Species of trees become extinct or rare
- Leads to shortage of rainfall
Soil Conservation Measures
- these are ways of protecting,preserving and managing forests.
- Afforestation
- Reafforestation
- Agroforestry
- Educating people on the importance of forests
- Using alternative source of energy
- Gazzetment of forests reserves
- Putting up electric fence around the forest
- Providing tree seedlings
- Discourage the use charcoal
- Use of energy saving jikos
- Public awareness campaigns to conserve forests
Mining - Class 8 Social Studies Revision Notes
- Limestone
- Flourspar
- Diatomite
- Salt
- Marbles
- Gemstone
- Distribution Of Minerals In Kenya
- Contribution Of Minerals To The Economic Of Kenya
- Effects Of Mining On The Environment
Mining
- This is the extraction of minerals from the ground
- Major minerals in Kenya
- soda ash
- limestone
- flourspar
- diatomite
- marbles gemstone
- salt
Limestone
- found in areas with sedimentary soil/rocks
Mining Areas
- Bamburi- Mombasa County
- Athi River- Machakos County
- Homa Hills- Homa Bay
- Sultan Hamud- Makueni County
- Koru- Kisumu County
mining methods used is open cast method
Uses Of Limestone
- Making cement
Making fertilizer
Manufacturing paints
Treating water
Used in road construction
Flourspar
- mined at kimwarer in kerio valle,elgeyo marakwet county.
- Method used is open cast mining method
Uses Of Flourspar
- Making toothpaste
- Making sulphuric acid
- Making cement
- Making cans
- Strengthening iron, steel and alluminium
- Used in oil refineries
Diatomite
- Mined at Kariandusi near Gilgil in Nakuru County
- Mining method is open cast method
Uses Of Diatomite
- Making paintspreserving fertilizer
- Making water filters
- Making heat insultors
- Used in dry cleaning industries
- Used to make plasters
- Making soaps
Salt
- Mined at Magadi-kajiado County, Ngomeni and Fundisa In Kilifi County
Uses Of Salt
- Flavouring food
- Preserving food
- Making soap
- Making dyes
- Flavouring animal feeds
- Manufacturing papers
- Making chemicals
- Making drugs
Marbles
- Marble is a hard smooth stone
- Has white and dark colours
Mining Methods
- Quarrying or open cast
Mining Areas
- Athi River- Machakos
- Kerio Valley- Marakwet County
Uses
- Making ornaments- rings, necklaces, bangles, earring
- Making statues
Gemstone
- Also called precious stone.
Types Of Gemstone
- rubies
- garnets
- tourmalines
Mined in Voi and Mwatate in Taita Taveta County
Uses
- Making bangles
- Making earings
- Making necklaces
Distribution Of Minerals In Kenya
Contribution Of Minerals To The Economic Of Kenya
- Create employment
- Earns foreign exchange
- It is a source of income
- Has led to urbanization
- The government earns revenue
- Has promoted trade
- Has improved people’s living standards
Effects Of Mining On The Environment
- Noise pollution
- Air pollution
- Ugliness of the landdestruction of vegetation
- Pits left can result to death of people and animals
- Pits become breeding areas for snails and mosquitoes
Agriculture - Class 8 Social Studies Revision Notes
- Settlers Farming
- Settlement Schemes
- Irrigation Schemes
- Horticultural Farming
- Fish Farming
- Fish Farming In Kenya
- Fish Farming In Japan
- Comparison Of Fish Farming In Kenya And Japan
Agriculture
- This is the growing of crops and the keeping of animals
Settlers Farming
- Settlers are the Europeans who came and grabbed fertile land for farming
White Highlands
- Also known as crown land
- These are fertile areas that were grabbed from africa ns
African Native Reserves
- These were the infertile lands
- Africans were congested in reserves
- They were agriculturaly less productive
- Africans provided cheap forced labour in the settlers farm
Settlers Farming Areas
- Eastern highlands
- Nyeri
- Murang’a
- Embu
- Kiambu
- Meru
- Thika
- Nanyuki
- Nyandarua
- Laikipia
- Western Highlands(Rift Valley)
- Kericho
- Uasin gishu
- Trans nzoia
- Sotik
- Nakuru
- Bomet
- Coastal Region
- Taita taveta
- Kilifi
- Voi
- Malindi
Features/characteristics Of Settlers Farming
- Obtained cheap labour from the africans
- Introduced commercial farming i.e.cash crop farming
- Introduced new crop farming
- Practised farming in the cool and wet highlands i.e.the white highlands
- Practised mixed farming
- Kept beef cattle in ranches in dry areas
- Grew sisal and cotton in dry areas.
- Introduced plantation farming
- Used machines and fertilizers
- Practised crop rotation
- Irrigation farming was done in drier areas.
- Effects of settlers farming
Positive effects
- Introduced cash crop/commercial crops e.g.coffee,tea,pyrthrum,etc
- Introduced mechanised farming
- Introduced the use of farm inputs e.g.fertilizers and chemicals.
- Introduced exotic breed cattle
- Introduced plantation or large scale farming
- Led to industrialzation
- Led to development of infrastructure i.e.roads and railways.
- Led to urbanization e.g kitale and eldoret
- Introduced cross breeding
- Led to formation of cooperatives
Negative Effects
- Africans lost thier land i.e. became squatters
- Creation of african native reserves
- Led to forced labour
- Disrupted the communal land ownership i.e. land tenure system.
- Africans were over exploited
- Led to increased racism/racial discrimination
- Development of the wtite highlands only
- Introduced payment of taxes to africans
Exotic Breed Cattle
- Jersey
- Fresians
- Guernsey
- Aryshire
Exotic Beef Cattle
- Aberdeen angus
- Hereford
- Chalorais
Exotic Dual Cattle
- Sahiwal
- Indegenous cattle
- Zebu
- Boran
Settlement Schemes
- These were areas set aside by the government tothe landless.
- Ways of acquiring the settlement schemes
- Buying land from settlers
- Reclamation of hostile areas i.e.
- Spraying areas infested with tsetse flies
- Irrigating arid and semi-arid areas
- Draining swamps
- Forest excision i.e clearing the forest to settle the squatters.
- Formation of land buying companies.
Reasons For Establishment Of Settlement Schemes
- To settle the squatters
- To boost food production
- To reduce population pressure
- To ease congestion
- To improve peoples’ living standards
Distribution Of Settlement Schemes
- Mwea Irrigation Schemes
- Ol Kalou Salient Schemes
- Jomo Kenyatta At Mpeketoni Lamu
- Bura-galolo Settlement Schemes
- Island Farms In Central
- Muguga jet Schemes - Central
- Ahero - nyanza
- Lambwe Valley - Nyanza
- Matunda Settlement
- Ravine/ Sabatia
Benefits Of Settlement Schemes
- Landless people have been settled
- Waste land have been put into use
- Have created employment
- Have boosted food production
- Have united people in the country
- Have led to development
- Agricultural export from schemes earn foreign exchange
- Have reduced population pressure
Problems Facing Settlement Schemes
- Soil erosion
- Population pressure
- Poor means of transport
- Lack of social amenities
- Lack of title deeds
- Sometimes there is ethnic hatred in the schemes
- Lack of modern equipment
- Sometimes farmers are unable to repay loans
- Mismanagement of schemes
Irrigation Schemes
- Irrigation is growing of crops using water
- They include;
- Mwea irrigation schemes
- Perkerra irrigation schemes
- Ahero irrigation schemes
Mwea Irrigation Schemes
- It is in Kirinyaga County
- It is the oldest in the country
- It was established in 1954
- The main reason for establishment was to settle the landless
- It has black cotton soil
- This region slopes gently to support flow of water by gravity.
- Source of water - Water comes from river Thiba and Nyamindi which are tributaries of River Tana
- Main crop grown
- Rice (paddy)
- Water melon
- Sukumawiki
- Maize
- French beans
- Canal irrigation method
- Canals direct water into the rice field called basins
- Water flows by gravity
Perkerra irrigation scheme
- Located in Baringo County
- Was established in 1954
- The main reason for establishment was to bring more land under cultivation
- Water for irrigation comes from River Perkerra
- Seed maize (main crop)
- Chillies
- Tomatoes
- Onions
- Watermelons
- Pawpaws
- Uses furrow irrigation method
- Involves construction of furrows and ridges
- Crops grown on the ridges
- Water directed to the furrows
- NB; the main reason why irrigation schemes were established was to boost food production.
Contribution Of Irrigation Schemes To The Economy Of Kenya
- Create employment
- Source of income
- Have led to indutrialization
- Have improved people’s living standards
- Have led to development of roads
- Earn Kenya foreign exchange
- Unproductive land have been put into use
- Have led to urbanization
- They are sources of livelihood
Problems Facing Irrigation Schemes
- Pest and diseases
- Mismanagement of irrigation schemes
- Long distances to the market
- Silting of canals
- Water shortages
- High cost of farm inputs e.g.seeds and fertilizers
- Delayed payment
- Lack of agricultural extension officers
- Exhaustion of soil
Horticultural Farming
- This is the growth of fruits, flowers, and vegetable
- Viticulture - This is the growth of fruits only
- Floriculture -This is the growth of vegetable only.it is also called market gardening
Features/characteristics Of Horticulture
- Practised in areas with fertile soil
- It is capital intensive
- It is labour intensive
- The farms are intensively cultivated
- Crops are grown in green houses
- Practised in both small and large scale
- High quality seeds and fertilizers are used
- Mainly done for sale
- Regular spraying is done
Crops Grown In Horticultural Farming
- Vegetable
- Spinach
- Kales
- French beans
- Onions
- Baby corn
- Cauliflower
- Tomatoes
- Cabbages
- Fruits
- Bananas
- Mangoes
- Apples
- Avocadoes
- Paws paws
- Pineapples
- Oranges
- Pears
- Flowers
- Roses
- Orchids
- Carnations
- Gladioli
Problems Facing Horticultural Farming To The Economy Of Kenya
- Delayed payment
- pest and diseases
- poor means of transport and communication
- high transport charges
- expensive farm inputs
- bad weather
- lack of cooperative societies
- long distance to the market
- lack of capital
- lack of refrigeration facilities
Horticultural Farming In Netherlands
- Netherlands is in Europe
- also known as Holland
- it is a lowland
- it grows flowers,fruits,and vegetable
- done on reclaimed land called polders
- they reclaim land using special walls called dykes
NB they practice farming in polders because the land is scarce - They mostly use green/glass houses
- This helps them to practice horticultural farming throughout the year
- Netherlands is densely populated and this provides a ready market.
Comparison of horticultural farming in Kenya and Netherlands .
| Kenya | Netherlands |
| .done on natural land | Done on polders |
| grows flowers fruits and vegetable | Grows flowers fruits and vegetable |
| few green houses are used | Mostly green houses are used |
| lack of capital for expansion | Capital is available for expansion |
| little mechanization | Highly mechanised |
| skilled labour is inadequate | Great ues of skilled labour is required |
| poor means of transport | Well developed transport |
| less scientific method used | Uses scientific method of farming |
| production is low | Production is high |
| farmers are indequately skilled | Farmers are andequately skilled |
Fish Farming
- This is the rearing of fish in ponds or tanks
- It is also called aquaculture
- The best soil to construct a fish pond is clay soil
- Fish kept
- trout
- tilapia
- mudfish
Fish Farming In Kenya
- Sagana - Kirinyaga County
- Kabaru - Nyeri County
- Kibos - Kisumu County
- Ljipe - Taita Taveta County
- Aruba Dam-taita Taveta
- Bamburi - Mombasa County
- Borabu - Kisii County
- Homa Bay - Homa Bay
Fish Farming In Japan
- Japan is in Asia
- It is the leading producer of fish in the world
- Done in the sheltered areas along the coast
- Practised in the four islands
- Hokkaido
- Kyoshu
- Honshu
- Shikoku
- it has large market for fish
- fish are sold through cooperatives
- fish farming is highly mechanized
- highly supported by the government
- fish have high demand
- fish kept
- oyster
- prawns
- trout eeels
Comparison Of Fish Farming In Kenya And Japan
| Kenya | Japan |
| Fish reared are trout,tilapia and mudfish | Fish reared are oyster, prawns,trout and eels |
| Capital is inadequate | Adequate capital |
| Few research and training centres | Many modern fisheries and research centres |
| Fish kept in fish ponds | Fishing done in the sheltered sea |
| Limited/small market | Large market for fish |
| Low demand for fish | High demand for fish |
| Cooperatives are not developed | Copperatives are well developed |
| Not highly supported by the government | Highly supported by the government |
| Most fish are consumed locally | Most of the fish are exported |
Creative Arts, Social Studies and Religious Education Questions and Answers - CBC Grade 6 KPSEA End Term 3 Exam 2022 Set 2
Questions
Creative Arts And Social Studies
- During our daily activites, when we step on dusty or muddy soils with our shoes we create a
- shoc print
- foot print
- hand print
- soil print.
- Grade 6 learners modelled the item shown below using clay. The modelled geometrical form is
- conical
- pyramidal
- cube
- cuboid
- The beautiful style of writing messages on seasonal cards using letters or words is called
- embellishments
- dabbing
- calligraphy
- printing
- Grade 6 learners were making rectangular flower vases using clay. The best technique to be applied in this lesson was
- pinch
- coil
- slip
- slab
- The process of joining two or more pieces or leather using thin strips as shown below is called
- strapping
- glueing sewing
- thonging
- The art of creating decorative designs by sewing or sticking pieces of Cabric onto another to form a picture or pattern is called
- collage
- applique technique
- montage
- tic and dye
- The main technique of making a marionette is
- construction and assemblage
- sculpture
- collage
- montage
- Which one of the following is not a 2D art work?
- Drawings.
- Crayon etching.
- Paintings.
- Basketry.
- Legs and hands are the most common parts of the body that shows movement. They are called
- limbs
- body
- trunk
- abdomen.
- Parts of a letter that goes down when writing a message as shown below is called
- body
- ascender
- descender
- upper case
- Which of the following verses are found in East African Community Anthem?
- Patriotism.
- Unity
- Hatred.
- Peace.
- A Grade 6 music teacher from Amani Primary school was icaching the Icarners about the type of song that was talking about issues affecting the society. Which of the following types of song was being taught?
- Topical song.
- Patriotic song.
- Action song
- Sacred song.
- The following are expressions that are used when singing. Which of the following expression talk about proper pronunciation of words inorder to understand the message?
- Dymamics.
- Diction.
- Tempo.
- Voice blend.
- Below is a wind instrument from a certain community. What is the name of the instrument?
- Milele.
- Abu.
- Nzumari.
- Coro.
- Name the musical note below.
- dotted minim
- crotchet
- minim
- semibreve
- Which hand(s) is used to play note D in a discand recorder?
- Left hand.
- Both Hands.
- Right hand.
- None.
- The diagram below shows a string instrument. Write the name and the community it belongs.
- Wandindi - Kikuyu
- Orutu - Luo
- Kimengeng' - Kalenjin
- Obekano - Kisii
- Abdi a Grade 6 learner was asked to state the element of music that describes the loudness or softness of a song. Which one was correct?
- Tempo.
- Rhythm
- Dynamics
- Pitch.
- The following are musical notes and their corresponding rests. Which one is correctly matched with its rest?
- String instruments are played by
- hitting
- plucking
- blowing
- shaking
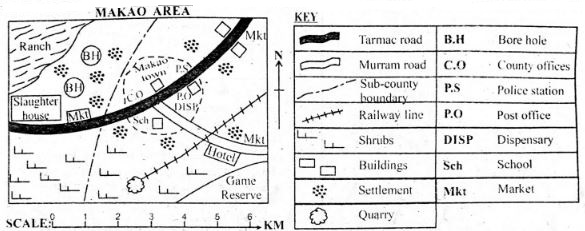
MAKAO AREA
Use the map above to answer questions 21 - 25
- The climatic condition experienced in the southern part of Makao area is
- cool and dry
- hot and wet
- hot and dry
- cool and wet.
- The location of slaughter house in the map has been influenced by
- availability of raw material.
- presence of borehole .
- nearness to road network
- availability of good climate.
- What evidence in nap indicated that there is tourism activities in Makao area?
- Markets.
- Railway line.
- Hotel
- Game reserve.
- The head or Makao area is likely to be
- Governor
- Deputy governor
- County commissioner
- Deputy County Commissioner.
- Three of the following economic activities are carried out in Makao arca except
- mining
- livestock keeping:
- trading
- lumbering
- Which one of the following language groups is correctly matched with the area they settled in during migration into Eastern Africa?
- Highland Nilotes - Around Mt. Elgon.
- Bantus - Along river Nile.
- Cushites - Around the highlands of Ethiopia.
- Semites - Around Lake Victoria.
- Grade 6 learners were told to download types of lakes from the internet, Michael was assisted by his guradian and downloaded the diagram below. What type of lake did they download?
- Crater lakes.
- Lava dammed lakes.
- Rift valley lakes,
- Ox-bow lakes.
- Which one of the following is a similarity between the traditional government of Buganda Kingdom and the Nyamwezi cheisdom?
- Their leaders were appointed by the council of elders.
- They both had hereditary leadership.
- They both had a traditional parliament.
- They both had a monarchial government.
- Which one of the following minerals is correctly matched with the method of mining?
- Gold - Dredging.
- Copper - Deep shaft.
- Limestone - Open cast.
- Soda ash - Drilling. 30.
- Grade 4 learners were asked by their socia! studies teacher to give the main reason why they started an entrepreneurship project in their school, who among them gave the correct answer?
- Amina- To make use of locally available resources.
- Peter - To help the school in buying land.
- Margaret - To help themn raise income.
- William - To help them create employment in school
- The headteacher of Kabarak Primary Schoool sabarak Primary School invited Mr. Kigen one of the officers from East African Community to talk about challenges facing the organization. Which one of the following was not mentioned as a challenge?
- Poor roads.
- Mistrust among members.
- Use of a common currency.
- Natural calamities.
- Below are examples of rights and freedoms of Kenya citizens.
- Freedom of Movement.
- Right to health care.
- Right to fair pay.
- Righi to privacy
- freedom of speech.
The Which one of these rights and freedoms are grouped as social?- (ii) and (iv)
- (i) and (v)
- (iii) and (iv)
- (i) and (ii)
- Study the poster below.
From the above posters, the message communicated isTAXES GRANTS
LOANS COUNTERFINES- types of expenditure
- sources of foreign exchange
- sources of revenue
- types of taxes.
- Which arm of county government is headed by the governor?
- County Executive Committee.
- County Assembly.
- County Education Office.
- County wards,
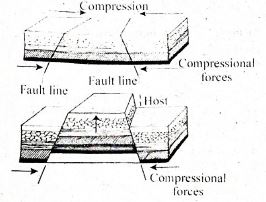
Use the diagram below to answer question 35
- Which one of the following mountains was formed through the process shown in the diagram above?
- Mt. Elgon.
- Mt. Kilimanjaro.
- Mt. Longonot.
- Danakil alps.
Christian Religious Education
- God created the world in seven days. What did he create on the fourth day?
- Sun, moon and stars.
- Light and darkness.
- Sea creatures and birds.
- The sky.
- Adam and Eve lived in the Garden of Eden. God chased them from the garden when they
- found that they were naked
- talked to the snake
- ate the fruit of the forbidden tree
- cultivated the land.
- Mr. Kioko explained to his grade 6 learners the books of the bible. Which of the following statements he did not mention?
- old testament has 27 books
- bible is divided into two parts
- gospel books are four
- bible was written by different authors.
- Shadrack, Meshack and Abednego were thrown into the blazing fire furnace. Why did the King command that they be thrown in the fire? They
- were not true Hebrews
- did not pay taxes
- worshiped the golden statue
- refused to worship the golden statue.
- During the last supper Jesus washed his disciples feet What else did he do? Hie
- spoke in tongues
- was covered by a cloud
- broke the bread and gave to his disciples
- baptised the disciples.
- How many boys were killed by the two she-bears after mocking Prophet Elisha calling him 'baldy'?
- 2
- 36
- 18
- 42
- After Jesus was born, the wisemen from the East Compression visited him with gifts. Which of the following was not among the gifts?
- Gold..
- Silver.
- Myrrh.
- Frankincense.
- Mrs. Kariuki a sunday school teacher in Blessed Worship Centre taught the young children the benefits of being kind using the story of how Jesus fed the 5000 men in the bible with loaves of bread and fish. How many baskets remained after feeding the people?
- 8
- 5
- 2
- 12
- Jesus Christ walked over the water. When the disciples saw him they were frightened, they thought he was
- mad
- a ghost
- an angel
- a spirit
- Jesus died and after three days he resurrected. Who informed Mary Magdalene and Mary that Jesus had risen?
- Peter.
- The Angel.
- Joseph of Arimathea
- Judas Iscariot
- We should be thankful to God for his good deeds in our lives. Which of the following is not a way of saying thankyou to God?
- Doing good things to other people.
- Sharing food with the needy.;
- Boasting about our wealth.
- Singing praises to God.
- Which of the following is the first statement in the Lords prayer?
- I believe in God, the father almighty....
- May the grace of the Lord Jesus.....
- Our father.....
- Oh God of all creation, bless......
- Tr. Dorcas asked her class to make cards with the fruits of the Holyspirit. Who among the following made them wrongly?
- James - Lovė, Peace, Gentleness
- Monica- Patience, Selfcontrol, faithfulness
- George- Prophecy, Preaching, Singing
- Jane - Peace, Joy, Humbleness
- During the Pentecost, the disciples of the sus did all the following except
- spoke in tongues
- preaches the word of God
- the were drunk
- they were filled with the Holyspirit.
- Jesus home town was
- Nazareth
- Bethelehem
- Galilee .
- Antioch
Islamic Religious Activities
- What is “Al-Kauthar”? A
- star in the darkness
- guidance in the ignorance
- mountain peak.
- river in paradise.
- In the Surah Al-Maun, Muslims should not mistreat
- orphans
- brother muslims
- the non muslims
- their neighbours.
- "Wama adiraaka mal-hutwama-Naarullahi muukada”. This is a quotation from Surah
- Al-Qaaria
- Al-Humaza
- Al-Quraish .
- Al-Kaafirun
- Which quotation completes this verse correctly?
- Truth and honesty.
- Kindness and respect.
- Truth and patience.
- Love and unity.
- "Allah suid in Surah Asr, "Man is in a loss except those who have faith, do righteous. deeds and advice each other on ...." In this Surah, Allah(s.w) swears by
- the sun.
- the still morning.
- wonders of creation.
- time.
- What are Hadith?
- Stories of Prophets.
- Sayings of Swahabas.
- The history of Islam
- Sayings of the Prophet.
- In the hadith of the prophet, we learn that Allah (s.w) judges people basing on their
- actions.
- appearance
- wealth
- race
- What did Allah promise those men who wear women clothes and women who wear the male clothings according to Hadith? A
- reward
- punishment
- curse
- confusion.
- There are pillars of Iman.
- three
- five
- six
- eleven
- What is Taqwa?
- The feeling of Allah.
- The fear of Allah.
- Seeing Allah.
- Reliance on Allah.
- A prophet of Allah was thrown in fire to burn off but Allah (s.w) ordered fire, “Be cool and safe on my servant”. This was Prophet
- Nuh (A.S)
- Yusuf(A.S)
- Musa (A.S)
- Ibrahim (A.S)
- How many brothers did Prophet Yusuf (A.S). had?
- 11
- 10
- 12
- 9
- All the following are forms of Hadath Akbar except one. Which one?
- Sexual intercourse.
- Mestruation flow.
- Blood after birth.
- Passing stool.
- Which one of the following is not a reason why muslims should take Tayammum before Swalah? When
- water is dangerous for your health
- there is no water
- you already have Wudhu .
- a dangerous animal is near water for Wudhu.
- Who among the following people is not a recipient of Zakkat? 'The
- orphans
- poor
- new converts
- needy.
Marking Scheme
| Creative Arts & Social Studies | CRE | IRE | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Integrated Science Questions and Answers - CBC Grade 6 KPSEA End Term 3 2022 Set 2
Questions
- A push or a pull on an object is referred as
- weight.
- force.
- energy.
- volume.
- Grade five learners were doing an experiment on different substances. What happened when they put red litmus paper in ash solution? It turned
- blue
- yellow .
- grey
- red
- Three of the following are safety precautions when handling plants. Which one is not?.
- wear gloves on your hands.
- wash hands using soap after handling plants.
- wear protective gears.
- any fruits or leaves.
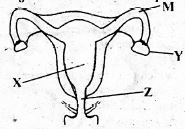
Use the diagram below to answer question 4
- Which part in the above diagram shows where the baby grows
- X
- Z
- Y
- M.
- Which part of a plant absorbs water and supports the plant firmly?
- Fruit
- Flowers
- Roots
- Stem.
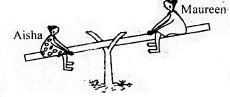
- Alisha and Maureen were playing on the see-saw as show below.
Which of the statements below is true? .- Alisha is heavier than Maureen.
- Maureen is heavier than Alisha.
- For them to balance they should both move away from the fulcrum.
- Alisha should move closer to the pivot for them to balance.
- The following are blood groups. Which group is referred to as universal donor?
- B
- O
- A/B
- A .
- Waste can be managed in the following ways except
- reducing.
- excretion
- reusing.
- recycling.
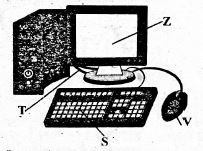
- Grade 4 learners were asked to type a friendly letter during their English lesson. Which part of the computer did, they use to enter the letters?
- Central Processing Unit:
- Monitor.
- Keyboard.
- Word.
- Below are characteristics of a certain group of animals.
- They live partly on land and partly in water.
- They lay eggs.
- They do not have a constant body temperulure.
- They breathe through lungs.
Which of the following groups fit then description above?- Reptiles .
- Fish
- Mammals..
- Bird.
- Which of the following parts is correctly matched with its function?
- S - used to give instructions
- T - used to type.
- Z - shows or displays what is happening.
- V - connects the digital device to the hardware.
- The following are water pollutants. Which one is not?
- Oils spills.
- Smoke
- Sewage.
- Factory water
- Four learners were asked to identify the state of matter that has the following characteristics.
- have definite shape.
- have definite volume.
- have definite mass.
Who gave the correct answer?- Juma - liquids.
- Mariam insulators.
- Abdi - gases.
- Sarah - solids.
- A metallic ball sinks in water while a plastic one will float. This is due to
- material.
- shape.
- size.
- mass.
- Which waterborne disease can be controlledby draining stagnant water?
- Dysentery.
- Bilharzia.
- Typhoid.
- Cholera.
- Which of the following is not a form of gardening?
- Vertical gardening.
- Kitchen gardening.
- Market gardening.
- Horizontal gardening.
- The following tools are used in farm. Which one is used for weeding?
- Jembe.
- Prunning saw.
- Sickel.
- Axe.
- Grade five learners in Makongeni school were asked to name the part of the vegetable eaten. Which pupil gave the correct answer?
Vegetables Part eaten A. Mercy carrots fruits B. Paul Onion bulb C. Tom Tomatoes leaves D. Natalie Kales roots - Mr. Mwema was adviced by an Agricultural officer to instal gutters to avoid soil erosion near his house. Which type of erosion was he controlling?
- Sheet erosion.
- Rill erosion
- Splash erosion.
- Gulley erosion.
- Which part of planting material is used to plant pumpkin?
- Seed.
- Leaves
- Cutting.
- Roots
- The following animals can be controlled by the use of a fence except a
- squirrel.
- Mongoose
- hare.
- bird
- The following are creeping crops except
- pumpkin.
- cabbage.
- calabash.
- watermelon.
- Birds kept for laying eggs are called
- broilers.
- dairy.
- layers.
- beef.
- Rice is grown in _______ type of soil
- clay soil
- cotton soil
- sandy soil
- loam soil
- The best way for controlling gulley erosion is by
- building gabbions.
- making terraces.
- planting cover crops.
- contour farming.
- Which term is used to describe the process of collecting soil from deposition sites and using it to replace the lost top soil?
- soil erosion.
- run-off.
- solid deposit
- soil recovery.
- Calton was seen in the school garden carrying out the practice below. Which gardening practice was this?
- Weeding.
- Mulching.
- Watering.
- Thinning.
- Which of the following crop is not a legume?
- Maize.
- Peas.
- Bean.
- Groundnuts.
- Three of the following crops are grown in a sunked seedbed except
- kale.
- spinach
- tomatoes
- Sugarcane
- Grade four learners made the structure below.
What was the function of the structure above?- make the farm attractive
- breed rodents.
- scare animals.
- entertainment.
- Grade 5 pupils from Heshima Academy grouped food in groups below. Which group consist of food that provide our bodies with fats and oil?
- Beans, groundnuts, lentils.
- Samosa, mandazi, pancakes.
- Butter, cheese, red meat.
- Chicken, ice cream, oily spinach.
- Identify the bleaching symbol shown below.
- Do not bleach.
- Any bleach is ok.
- Bleach with caution.
- Oxygen bleach only.
- The following are some of the measures that can be used to prevent common communicable diseases. Which one is not?
- Cleaning and disinfecting shared surfaces.
- Shaking hands.
- Avoid sharing personal items.
- Regular washing of hands...
- Which of the following diseases is caused by nutritional deficiency?
- Measles.
- Elephantiasis.
- Mumps.
- Kwashiokor.
- Name the embroidery stitch shown below.
- Chain stitch.
- Stem stitch.
- Satin stitch.
- Loop stitch.
- Below are some of the reasons for stuffing shoes after cleaning except to
- make them look smart
- maintain the shape
- improve the quality
- keep off small animals and snakes.
- Misuse of cosmetics can cause the following dangers except
- diarrhoea.
- headaches.
- face rash.
- skin irritation.
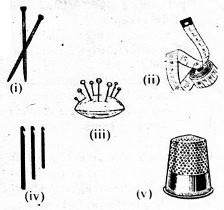
- Which of the list below consist of tools used sowing only?
- (i), (ii), (iii)
- (ii), (iii), (v)
- (ii), (iii), (iv)
- (iii), (iv), (v):
- Which is the best stitch to use in repairing a gaping seam?
- Backstitch,
- Chain stitch.
- Hemming stitch.
- Double stitch.
- Pupils in Lamu Academy were asked to nam one basic method of weaving used in fabri construction. Who among the following giri named the correct method?
- Mary - Double weave.
- Ann - Flat weave.
- Liz - Cotton weave.
- Terry - Plain weave
- Inorder to improve pool hygienes, which one of the following should be observed?
- Always use floaters and lifesavers to save you from drowning
- Do not swim immediately after taking meals
- Avoid diving at the shallow ends of the pool
- Visit the toilet before going to swim.
- Martin was scen swimming using the technique below.
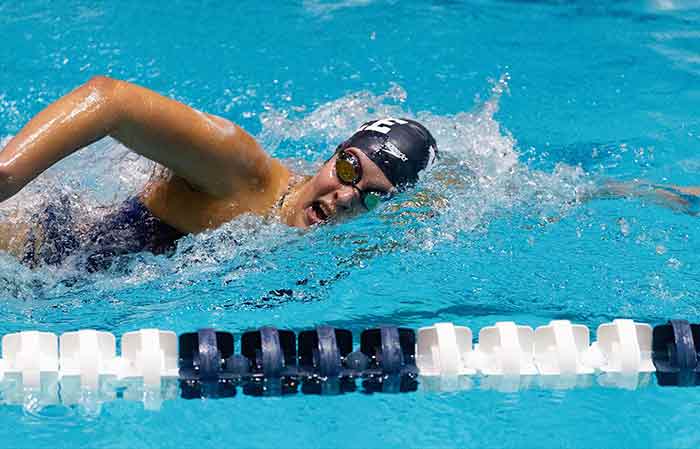

which swimming technique was Martin likely to be practising?- Breast stroke.
- Sidestroke.
- Diving
- Backstroke.
- The following are points to be followed while performing a one handed catch in a frisbee game except
- always aim to catch the disc with one hand
- avoid catching the disc using your thumb and fingers.
- Watch and time the oncoming disc carefully as it flies towards you .
- stand with your feet shoulder width apart with your knees slightly bent.
- Joel got hurt on his knce while playing a soccer game. Which one of the following steps of managing the wound should come first?
- Cleaning the wound well.
- Applying an antiseptic such as spirit or dettol.
- Bandages the wound well to avoid blecding.
- Apply alcohol or swap to the area.
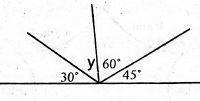
- A method of starting a race where the knees of the rear leg is opposite to the 10e of the Ieading leg with hand placed shoulder width apart is known as
- bunch start
- clongated print start
- medium spirit start
- standing start.
- Grade 6 boy was seen playing a handball skill shown below.
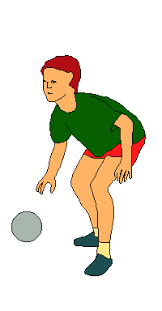
Which one of the following statements is false about the skill above?- It aims at making a score froin an ordinary . position.
- It allows one to advance with the ball.
- Enables a player to go past a defender.
- It is a defensive skill used by the goal keeper only.
- A game of rounders is played by ______ players.
- 9
- 7
- 8
- 11
- While practising for balance, a PHE instructor can encourage his learners to peerom the following skills except
- V-balance.
- T-balance.
- crouch balance.
- rope work skills.
- The following are attacking skills used in a Kabaddi game
The attacking skills shown above is known- toe touch.
- foot touch
- side kicking
- hand touch
- During a PHE practical lesson, leaners practised the following types of passes.
- Overarm pass
- Underarm pass
- Chest pass
- Bounce puss
Which of the above passes is ased to pass ihe ball over a short distance?- (iii)
- (iv)
- (ii)
- (i)
Marking Scheme
|
|
|
|
|
Kiswahili Questions and Answers - CBC Grade 6 KPSEA End Term 3 2022 Set 2
Maswali
Soma mzungumzo yafuatayo kishu ujibu maswali 1-4
Jona: Shikamoo dada? Umetulia sana hapa jikoni. Unafanya nini?
Hadija: Marahaba ndugu yangu. Nataka nimalize kuosha vyombo. Ningependa kumrahisishia mama kazi atakapokuja kuandaa chajio.
Jona: Huo ni uamuzi wa busara. Hebu nikusaidie ili tumalize kazi hiyo nawe ukafanye kazi ulizopewa shuleni.
Hadija: (Akitabasamu) Asante. Naona unaelewa kuwa kinga na kinga ndipo moto liwakapo.
Jona: (Huku ukizichukia suhuni azioshe kwenye kuro) Wajua ni jukumu letu kuwasaidia wazazi hapa nyumbani. Huu ndio mchango wetu katika kupunguza matumizi. Au wasemaje dada?
Hadija: Kweli kabisa. Hapo umegonga ndipo. Hakuna haja ya wazazi kuwaajiri vijakazi na vitwana wafanye kazi za nyumbani ilhali mzazi ana watoto wakubwa kama sisi.
Jona: Maadamu tumeimaliza shughuli ya usafi naomba uje unielekeze kufanya hesabu mbili zinazonitatiza.
Hadija: Hlewala, nitakusaidia.
Jona: Asante dada. Tahika ndugu ni kufaana, si kufanana.
- Mazungumzo haya yanaonyesha kuwa
- Jona ni mkubwa kuliko Hladija.
- Tadija ni mkubwa kuliko Jona.
- Hadija ni mkubwa kuliko Jona.
- Jona ni mwerevu kuliko Hadija.
- Watoto hawa ni wenye busara kwa sababu,
- wanajua umuhimu wa kuwasaidia wazazi.
- wanafanya kazi za nyumbani badala ya kusoma.
- wanafahamu ubaya wa vijakazi na . vitwana.
- wanaogopa kugombezwa na wazazi wao.
- Usemi hapo umegonga ndipo' una maana. kwamba
- aliyosema Jona si kweli.
- aliyosema Jona hayawezekani.
- aliyosema Jona yanashangaza.
- aliyosema Jona ni ukweli.
- Umuhimu wa ndugu kulingana na mazungumzo ni
- kuishi pamoja.
- kupeana msaada.
- kufanana sana.
- kufanya hesabu.
Soma kifungu kifuatacho kishú ujibu muswali 5 - 8
Kobe alikuwa akitoka cheteni kuuza mboga zake. Siku hiyo, mboga zilinunuliwa zote hata akahitajika kupeleka zaidi. Wateja wake walifurahishwa na mboga zake maadamu hakutumia kemikali zenya madhara. Hakutaka wale waliotumia mboga hizo wadhurike.
Njiani, alikutana na Pundamilia na Ngiri. Aliwasaili kuhusu walikokuwa wakitoka wakati ule. Pundamilia alimjibu, "Tumetoka kupanda miti upande wa mashariki wa msitu huu. Tumegundua kuwa binadamu ameikata miti mingi sana. Hali hii akiendelea kutatokea kiangazi.” Kobe aliwashukuru na kuwapongeza wenzake kwa uamuzi wao wa busara. Kisha akasema, “Hakika mtego wa panya huingia waliokuwemo na wasiokuwemo. Ni muhimu tuzuje hatari ya ukosefu wa mvua kwa kupanda miti. Nitaenda huko kesho nitimize wajibu wangu."
Baada ya hapo, wanyama wale walipungiana mikono, Kobe akajiendea zake. Akilini aliwaza, "kwa nini binadamu hatumii akili yake razini? Tamaa hii ya kukata miti kwa kutaka utajiri wa haraka, si itamwangamiza? Isitoshe, juzi nilipopita karibu na kijiji chao, niliona wamerundika taka kila mahali. Hakika wasipoubadili mkondo huo watajuta baada ya kuathirika.”
- Neno jingine lenye maana sawa na cheteni ni
- sokoni
- nyumbani
- shambani
- mjini
- Kwa nini wateja walizipenda mboga za Kobe? Kobe
- alikuwa rafiki wa kila mtu.
- alikuwa mkulima hodari.
- alijali afya ya wateja wake.
- aliziuza kwa bei nafuu.
- Ahadi aliyotoa Kobe ni kuwa,
- A. angezuia uharibifu wa msitu wao.
- angeenda kupanda miti siku iliyofuata.
- angemshauri binadamu aache kuharibu mazingira.
- angeenda kupeleka mboga upande wa mashariki.
- Tabia za binadamu zinazokashifiwa na Kobe ni
- uchoyo na uharibifu.
- ukatili na uvivu.
- mapuuza na kujitenga.
- tamaa na uharibifu.
Soma mazungumzo yafuatayo kisha ujibu maswali 9 - 12.
(Sunkuli na Malaika wamekutana njiani)
Sunkuli: Habari rafiki yangu?
Malaika: Nzuri mwenzangu sunkuli. Je, safari ya wapi jioni hii?
Sunkuli: Naenda kwa Mama Fatuma kumpekelekea chakula. Amekuwa akiugua tangu juzi. Mama amenituma nikamjulie hali na kumpa maziwa haya
Malaika: Ooh! Bi Fatuma yuaugua. Kumbe ndiposa sijamwona akipita karibu na kwetu hivi karibuni. Wajua hawezi kupita bila kutoa salamu.
Sunkuli: Kwa hakika Bi Fatuma ni mtu wa watu. Watu wote wangemwiga yeye, taifa lingekuwa na mshikamano mzuri sana. Maovu mengi yangeisha kwani kila mtu angemchukulia mwenzake kama ndugu.
Malaika: Haya ukifika kwa Bi Fatuma umpe salamu zangu. Nitaenda kumjulisha mama kuhusu maradhi yake. Nikipata kibali nitaenda kuzuru kesho mwendo wa adhuhuri.
Sunkuli: Sawa Malaika. Nina uhakika kuwa utapewa idhini hiyo. Wema hauozi. Hakuna mtu anayeweza kumnyima Bi. Fatuma msaada.
Malaika: Haya, hebu nenda usije kuchelewa. Kwaheri.
Sunkuli: Kwaheri na uwe na jioni njema,
- Sunkuli alipokutana na Malaika alikuwa,
- akitoka kumsaidia Bi Fatuma.:
- ameenda kuona kama Bi Fatuma aliugua.
- ameenda kumjulia hali Bi Fatuma.
- ametoka kuchukua maziwa kwa Bi Fatuma.
- Neno ooh! ni aina ya
- kielekezi
- kiingizi
- kihusishi
- kiwakilishi.
- Bi Fatuma ni mtu wa watu ndiko kusema,
- anajulikana na watu wengi.
- anasaidiwa na watu wengi.
- amewasaidia watu wote.
- anahusiana vyema na watu.
- Malaika anaahidi kuenda kumsaidia Bi fatuma. Msaada huu utatolewa ikiwa
- atapewa ruhusa.
- atapata wakati
- hatakuwa amepona.
- hatakuwa na kazi nyingine.
Soma kifungu kifuatacho kisha uyajibu maswali 13 - 15
Shawe alikuwa na mazoea ya kuenda msalani mara kwa mara kwa haja ndogo. Mwalimu wake aligundua jambo hilo. Alimwita mlezi wake ofisini mwake. “Asante kwa kuitikia mwito wangu, Naomba umpeleke mwana wako kwenye hospitali achunguzwe," Mwalimu akasema.
Shawe alipelekwa hospitalini kwanza alipimwa uzani wake. Baada ya kadi yao ya matibabu kukaguliwa, walitumwa maabarani. Damu yake ilifanyiwa vipimo. Daktari alimwuliza maswali kadhaa. “Daktari, kibofu changu hujaa haraka nami hushindwa kustahimili,” Shawe alimwambia tabibu. Shawe alipigwa picha ya eksirei. Picha hiyo ilionyesha kuwa mafigo yake yalikuwa na tatizo. Kwa bahati nzuri tatizo liligunduliwa mapema. Alipendekezwa kulazwa hospitalini ili atibiwe himahima. Ndugu zake, majirani na wanafunzi wenzake walimwombea apate afueni.
- Jambo linaloonyesha kuwa Shawe alikuwa na shida ni kwamba
- mwalimu alimwita mlezi wake shuleni.
- alikuwa akienda msalani mara mojamoja.
- alienda kujisaidia mara kwa mara.
- mwalimu alimwona amejikunyata darasani.
- Shawe alikuwa na bahati kwani,
- shida yake haikuwa hatari.
- hakuwa na shida yoyote.
- shida yake iligunduliwa mapema.
- watu wote walimwombea.
- Viungo vya mwili vilivyotajwa hulahta kazi gani?
- Kusukuma damu mwilini.
- Kusafisha damu.
- Kuyeyusha chakula.
- Kuhifadhi mkojo.
Soma kifungu kifuatacho. Kina nafasi 16 mpaka 20. Kwa kila swali umepewa majibu manne. Chagua jibu lifaalo zaidi kati ya yale uliyopewa.
Watu 16 wanashiriki, michezo huwa na afya 17 . Jambo hili huwasaidia 18 magonjwa 19 kuhatarisha maisha yao. Hata hivyo, mtu 20 mazoezi, huathirika kiafya.
| 16. | A. ambaye | B. ambapo | C. ambao | D. ambayo |
| 17. | A. mzuri | B. njema | C. jema | D. mwema |
| 18. | A. kuepuka | B. kuepusha | C. kuepukana | D. kuepukia |
| 19. | A. zinazoweza | B. inayoweza | C. yanaweza | D. yanayoweza. |
| 20. | A. akishiriki | B. alishiriki | C. anashiriki | D. asiposhiriki. |
Kutoka swali la 21 hadi la 30 chagua jibu lifaalo zaidi kulingana na maagizo uliyopewa.
- Tumia kiulizi kifaacho zaidi Kimaru aliwauza sungura
- ngapi
- mangapi
- wagani
- wangapi
- Lifuatalo ni jedwali la maneno. Kundi lipi lina vielezi pekee?.
A kali tamu safi bora B pole pole kwa kasi sana haraka C sahani kikombe maua uteo D juu ya kando ya katikati ya ndani ya - Bakari ni kaka' wa mama yangu. Kwa hivyo nitamwita
- mwamu
- mpwa
- ami
- mjomba
- Andika wingi wa:
Birika hilo lina chai nyingi.- Birika hizo zina chai nyingi.
- Mabirika hizo zina chai nyingi
- Mabirika hayo yana chai nyingi.
- Birika hayo yana chai nyingi.
- Tegua kitendawili kifuatacho: .
Chauma bila meno, chaumiza bila silaha.- Siafu.
- Moto.
- Chungu.
- Kiraka
- Nomino maziwa na mazingira huorodheshwa katika ngeli moja. Itambuc. ngcli hiyo.
- YA - YA
- I-ZI
- U - YA
- U-ZI
- Methali zifuatazo zinaonyesha ushirikiano.
Ni ipi iliyo tofauti?- Mgaagaa na upwa hali wali mkavu.
- Umoja ni nguvu.
- Wawili si mmoja.
- Kidole kimoja hakivunji chawa.
- . Shairi ambalo huwa na mishororo mitatu katika kila ubcri ni
- tarbia
- tathnia
- tathlitha
- kibwagizo.
- Mtu mwenye sifa ya upole hufananishwa na kiumbe yupi?
- Fisi
- Punda
- Paka
- Njiwa.
- Kufanya kazi kwa ushirikiano ni :
- kujifunga nira
- kupinda mgongo
- kufanya kikoa
- kupiga deki.
Majibu
|
|
|
English Questions and Answers - CBC Grade 6 KPSEA End Term 3 2022 Set 2
Questions
Read the following conversation and then answer questions 1 to 5
Shopkeeper: Yes customer. How can I help you?
Customer: (Scratching his head) Actually, I came to ask if you could lend me a packet of maize flour and cooking oil.
Shop keeper: Are you aware that this is the fourth time you are coming to borrow something from this shop and yet you never paid for the first three items you borrowed?
Customer; yes, I am aware. Just have mercy on me. I do not have anywhere to get money and my children are hungry.
Shop keeper: Are you mistaken or the alcohol that you took somehow got into your brain? Now listen and listen carefully. I do not entertain such nonsense in my work.
Customer: (angry) Who gace you the power to criticise me? I am better off than you. You think you are so rich that there is no day you will never go on your knees begging anbd yet all your sons are common thieves.
- According to this dialogue, the customer wanted to get some items on_____
- credit
- cash
- loan
- hire purchase
- The opposite of the word lend as used in the conversation could be
- buy
- borrow
- sell
- grant
- According to the dialogue, the customer had visited the shop ______ times before.
- two
- three
- four
- fourth
- The word aware could mean all the following except
- conscious
- sensitive
- alert
- clueless.
- According to the conversation, the shop keeper can be said to be ________
- compassionate
- sympathetic
- arrogant
- friendly
Read the passage below ans answer questions 6 to 9
In case of any accident or injury, it is very important to give help to the injured person before any medical treatment is given to the patient. The first help given to the patient is called First Aid. The right type of First Aid given to the patient sometimes saves lives. So everyone of us should know what quick actions to be taken in different types of accidents. I'll discuss bleeding.
As little bleeding is not dangerous, apply any antiseptic and then tie with a clean piece of cloth if necessary. If the bleeding is continous , we must stop it by placing a clean pad or cotton frimly over the wound until the bleeding stops or until the patient sees a doctor.
- In case of nay accident,what would be the first thing to do?
- Give medical treament
- Give help to the injured person
- Call others
- Rush the patient to hospital.
- What is the meaning of the word 'necessary' undelined in the story?
- Medical help.
- Wanted
- Not wanted
- Not available.
- Which word can be used instead of the word 'apply' as used in the passage?
- Put
- Place
- Placed
- Keep
- which would be the best title for the passage?
- First Aid
- First Aid and Bleeding
- Bleeding
- First Aid in bleeding.
Read the passage below and answer questions 10 to 12
A long time ago, there was a man and his wife. They had a girl. The girl fell sick many times. She then died and was thrown away so as to rot and be forgotten.
Suddenly, a dove appeared by her side. the dove revived her to life again. It took her to a cave wher she lived. After a short while, the girl said she wanted to be with her mother. The dove told her the need for them to stay in the caves, she insisted and the dove let her go. After going home, she felt sick again. She died and her parents threw her away. The dove revived her to life again.
The girl slipped into her home and the dove followed her, took the magic ornament which it used to revive the girl and she turned into bones.
While the parents were still wondering what to do with the boned, the dove revived the girl and they went far away to saty as friends forever.
- According to the passage, how many times did the girl die?
- Two
- Four
- Three
- One
- Ornament as used in the passage means?
- Decorations
- Rain
- Bones
- Rings
- From the passage we can conclude that the dove was a frind in _______ to the girl
- deed
- need
- true
- action
Read the passage below and answer questions 13 to 15
It was a clear, still night and the moon shone brightly through the water that Tom could not sleep. Suddenly , he saw a beautiful sight. A bright red light moved along the river-side and threw down into the water a long flame.
Tom, a curious little rogue, had to go and see what it was; so he swam to the shore and met the light as it stopped over a shallow edge of a low rock.
- Tom could not sleep because of the __
- clear night
- silent night
- still night
- bright moonlight
- What did tom see all of the sudden? A
- beautiful riverside
- bright red light
- long flame
- beautiful site
- Tom was curious, that means Tom was __
- brave
- coward
- dangerous
- eager to know.
Read the passage below. It contains blank spaces numbered 16 to 20. For each blank space , select the best alternative from the choices given
Snakes 16 poisonous 17 . 18 . thier tongue are not poisonous. The snake uses 19 tongue to 20 what is in front of it.
| 16. | A. had | B. has | C. have | D. are |
| 17. | A. fangs | B. teeth | C. canines | D. saliva |
| 18. | A. But | B. And | C. When | D. As |
| 19. | A. its | B. it's | C. its' | D. thier |
| 20. | A. feel | B. fill | C. suck | D. see |
For questions 21 to 23, choose the correct form of the verb to fill in the gaps
- She has ___ all her money
- loose
- losed
- lose
- lost
- They _____ him stealing books
- caught
- catched
- catch
- caughted
- I was ____ by his remarks
- hurted
- hurt
- hut
- heart
For questions 24 to 26, select the correct question tag.
- They like walking home, ______?
- do they
- don't they
- will they
- shouldn't they
- Let us observe the covid-19 protocols, ____?
- shall we
- is it
- will we
- let we
- We ate fish for dinner, _______?
- weren't we
- were we
- didn't we
- did we
For questions 27 to 29, select the correct form of adjective.
- My sister wore a ___________ dress
- red, cotton, pretty,
- pretty, cotton, red
- cotton, red, pretty
- pretty, red, cotton
- Yesterday I saw _____ birds
- tiny, three, beautiful
- three, beuatiful, tiny
- tiny, beautiful, three
- three, tiny, beautiful
- Her birthday present was a ___ shawl
- red, small, pretty, silk
- pretty, small, red, silk
- small, pretty, silk, red
- red, silk, small, pretty
For question 30, choose the correct alternative to fill in the gap
- This is the most tiresome journey I have _______ had
- ever
- whatever
- never
- whenever
COMPOSITION
Complete the story below and make it as interesting as possible
We had just sat arounf the fire when grandmother started this story. It was about .....
Marking Scheme
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mathematics Questions and Answers - CBC Grade 6 KPSEA End Term 3 2022 Set 2
Questions
- There are ten million one hundred twenty two thousand, three hundred and one people on a certain city. What is the number of the people in symbols?
- 10 122 301
- 11 223 010
- 10 120 301
- 100 012 231
- What is the place value of 4 in 3 468 521?
- Tens of thousands
- Thousands
- Hundred of thousands
- Tens
- In a fundraising ceremony, the amount collected was sh 957 342. What is the sum of the total value of 5 and 3 in the amount collected?
- 50 000
- 49 700
- 50 300
- 53 000
- During malaria outbreak, the government distributed 13 720 mosquito nets to 56 families. How many nets did each family get?
- 13 720
- 17 776
- 542
- 245
- Jame's coffee farm has 98 rows of trees. If there are 86 trees oneach row, how many coffee trees are there in the farm to the nearest thousand?
- 8 000
- 8 428
- 7 100
- 9 000
- What is the area of the square shown below?
- 60cm2
- 225cm2
- 60cm
- 225cm
- Bunyole school has 98 learners. the learners were given 98 098 pencils to share equally. How many pencils did each learner get?
- 1 001
- 10
- 101
- 100
- Find the reciprocal of 94/5
- 5/49
- 94/5
- 5/45
- 49/5
- A factory uses 245 000ml of milk every day. How many litres does the factory use in one day?
- 24 500l
- 245l
- 2 450 l
- 24.5l
- Kipkorir ran a distance of 7.25km in a race. What distance did he run as a fraction?
- 73/4
- 72/5
- 75/8
- 71/4
- John bought 721/2kg of sugar. He then packed this sugar into packets. How many 1/2 packets did he make?
- 144
- 73
- 145
- 36
- Work out the following
XXXIV + XLVI- 89
- 70
- 79
- 99
- The class wall clock read as shwon below
What will be the time after 5 hours 30 minutes- 5:00 pm
- 9:05 am
- 12:30 am
- 12:45 pm
- Work out the following:
31/4 x 11/2- 47/8
- 31/2
- 41/4
- 31/8
- What is the area of the shaded part?
- 280cm
- 140cm2
- 68cm
- 280cm2
- The following is a price list in a shop
Jane bought the following itemsItem Price A loaf of bread
A pencil
geometrical set
1kg of maize flour
A bar of soapShs 60
Shs 25
Shs 280
Shs 190
Shs 140- 6 pencils
- 5 loaves of bread
- 2 geometrical sets
- 3kg of maize flour
She gave a shopkeeper 2-shs 1000. How much did she receive as a balance?- Shs 420
- Shs 1 505
- Shs 495
- Shs 1 580
- A team obtained 32 out of 40 points in a competition. What is the source as a percentage?
- 20%
- 70%
- 80%
- 32%
- A lorry weighs 5 tonnes when empty. It was loaded with 50 bags of rice each weighing 90kgs. What is the total mass of the loaded lorry in kilograms
- 4 500kg
- 5 000kg
- 1 500kg
- 9 500kg
- Find the value of m in:
14m - 6 + 6m = 54- 6
- 60
- 20
- 3
- A basketball match takes a total time of 46minutes 35 seconds in 5 equal sessions. How much time does it take in one session?
- 8 min 27 sec
- 9 min 19 sec
- 9 min 27 sec
- 8 min 18 sec
- Amos uses a 135 litres 120ml of water in twelve days. How many litres and millilitres does he use in a day?
- 11l 10ml
- 10l 260ml
- 9l 10ml
- 11l 260ml
- Okiek farm is of the shape shown in the figure below
What is its perimeter in kilometes?- 20km
- 2km
- 200km
- 2 000km
- Arrange the following fraction in ascending order
2/5, 1/4. 3/8 , 1/2- 1/4 , 3/8, 2/5, 1/2
- 3/8, 2/5, 1/4, 1/2
- 2/5, 1/,. 3/8, 1/4
- 1/2, 2/5, 3/8, 1/4
- A piece of cloth measures 2,135m. What is the length of 25 such pieces of cloth? Give your answer to decimal places.
- 53.37
- 2.13
- 53.38
- 2.14
- What is the size of angle y?
- 135°
- 45°
- 130°
- 70°
- A swimming pool has a diameter of 56 metres. What is the circumference of the swimming pool?
- 176m
- 78m
- 626m
- 1 252m
- During the holiday, Joan visited her grandparents for 65 days. How mmany weeks and days did she spend there?
- 2 weeks 9 weeks
- 8 weeks 3 days
- 7 weeks 5 days
- 9 weeks 2 days
- How many layers are used to make the stack below?
- 120
- 5
- 24
- 8
The bar graph below shows the amount of milk sold in one week by a farmer. Use it to answer 29 and 30
- Which two consecutive days did the farmer receive the best income?
- Monday and Tuesday
- Tuesday and Saturday
- Friday and Saturday
- Tuesday and friday
- The cost of milk was sh 50 per litre. How much money did the farmer receive for the first three days of the week?
- Shs 3250
- Shs 5000
- Shs 8250
- Shs 6500
Marking Scheme
|
|
|