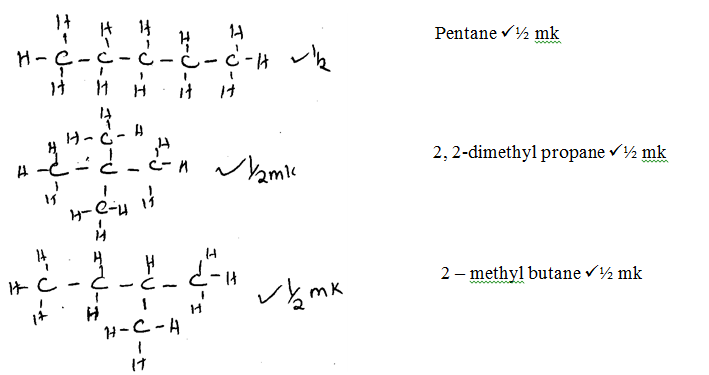Marking Scheme
-
-
- K
- J
- In methylbenzene HCl remains as s molecule / does not ionize hence is neutral
- L is a better conductor than J because L is a strong acid which ionizes fully to give more hydrogen ions
-
-
- Vulcanization
- Saponification
-
- Nitrogen
Argon - Used in hospitals by patients with breathing difficulties
Used by mountain climbers and deep sea divers
Mixed with hydrogen to provide fuel for space rockets
Oxyacetylene flame is used in welding and cutting metals (any 2 mks)
- Nitrogen
-
- Magnesium burns with a bright light
A white powder is formed - Mg(s) + H2O(g) → MgO(s) + H2(g)
- Remove the delivery tube form the water trough before heating is stopped to prevent sucking back
- Magnesium burns with a bright light
-
- Equilibrium shifts to the right ½ mk where there are few molecules ½ mk
- It will have no effect ½ mk because the number of molecules are equal on both sides ½ mk
- Heat the mixture, ammonium chloride sublimes
Add water to the remaining mixture, NaCl dissolves leaving silver chloride
Filter to obtain silver chloride as the residual and NaCl as the filtrate
Heat the filtrate to dryness to obtain solid NaCl
-
- Ag+(aq) + e- → Ag(s)
- Q = It
= 0.03 x 2 x 60 x 60
= 216C
96500C →108g
216C → ?
216 x 108/96500
= 0.242g
-
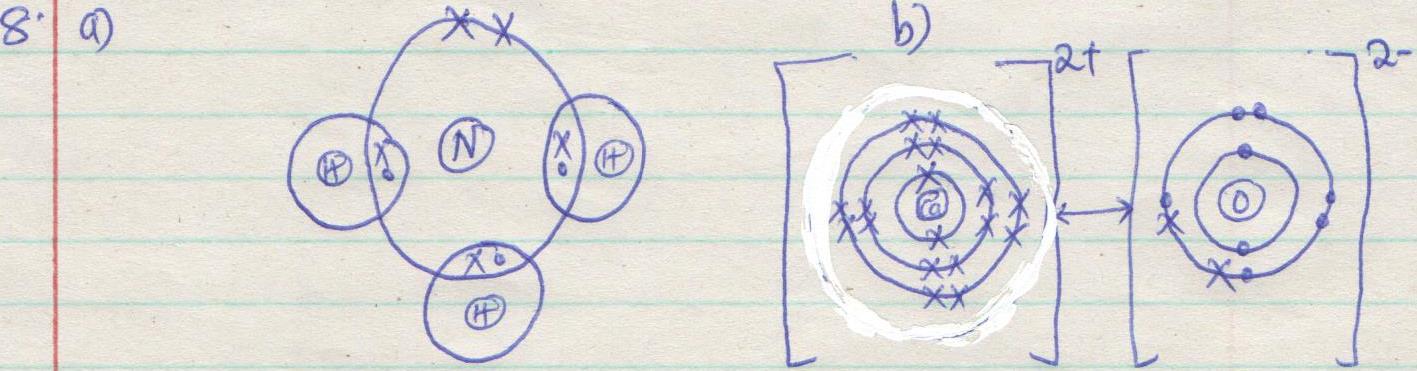
-
- Curve I- the concentration of F increases with time since F is the product
- After time (t) the concentration of E and F remains constant because equilibrium has been established
-
- The chloric (I) acid decomposes to form atomic oxygen ü1 mk the atomic oxygen attacks and bleaches the blue flower 1 mk
- 2HOCl(aq) → O2(g) + 2HCl(aq)
- Luminous non-luminous
Sooty non-sooty
Not very hot very hot
Not steady steady (any 2)
- KOH(aq) + HNO3(aq) → KNO3(aq) + H2O(l)
- MgO has a giant ionic structure while SiO4 has a grant covalent structure hence in molten state MgO conducts since it has mobile ions while SiO4 does not
-
- X – 143
Y – 50 - Energy generations
Food preparation
Pest control
Carbon dating (Any 2 each ½ mk)
- X – 143
-
- Brown fumes are observed ½ mk
Black solid is deposited ½ mk
Blue colour fades ½ mk - 2NO2(g) + H2O (l) → HNO3(aq) + HNO 2 (aq)
- It relights a glowing splint
- Brown fumes are observed ½ mk
-
- Soapless detergent
-
- Does not form scum
- Causes pollution since it is non-biodegradable
-
- The volume of a fixed mass of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at constant temperature 1mk. This is because particles of a gas are widely apart hence can be compressed 1mk
-
- Low pressure ½ mk
- High temperature ½ mk Specify
- In diamond each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms in a rigid giant atomic structure 1mk. In graphite each carbon atom is covalently bonded to their other carbon atoms in layers ½mk. The layers are held together by weak Vander walls forces which are easily broken ½mk
-
-
- An element is a substance which cannot be split into any simpler substance by any chemical process
- Atomic number is the number of protons in an atom
- T2(SO4)3
-
-
- Experiment 1 ½ mk
Experiment 3 ½ mk - In experiment 1, solid potassium carbonate has no free ions to conduct electricity 1mk
In experiment 3, sugar consists of molecules which do not conduct electricity 1mk
- Experiment 1 ½ mk
-
- Cotton / wool / silk 1mk
- Are strong than natural fibres
Not easily affected by chemicals
Last longer / are durable
Are cheaper (Any 1)
-
- X ½ mk - it has a completely filled outermost energy level ½ mk
-
- W and Y 1mk
- YW 1mk
-
- Copper pyrites ½ mk
Malachite ½ mk - In order to concentrate the ore
- Brass 1mk used in soldering wires and ornaments 1mk
- Copper pyrites ½ mk
-
- G
- The ionic radius of I is bigger than of E ü1mk since I has more energy level than E 1mk
-
- This is the energy change that takes place when one mole of a compound is formed from its constitute elements in their standard state
- ΔH4 = ΔH1 + ΔH2 + ΔH3
= (–286 x 3) + (–394 x 2) – (–277)
= – 1369 KJ/mol
-
- Oxidation state is the apparent charge that atoms have in molecules/ions
- (2 x 3) + 2N = 0
2N = – 6
N = – 3 - The heat is required to break the strong triple covalent bonds between nitrogen atoms
-
- The product form the nettle plant is acidic ü1mk hence aqueous ammonia solution being basic neutralizes the acidic product. 1mk
- Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron form an atom in gaseous state 1mk while electron affinity is the energy released when an in gaseous state gains an electron.
- Burning Magnesium produce heat energy enough to break the sulphur / oxygen bond setting oxygen free. Magnesium uses the free oxygen to continue burning.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 Marking Scheme - 2017 KITUI MOCK EXAMINATION.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students