SECTION A 25 MARKS
-
- What is Weather? (2mks)
- Give three main methods of forecasting weather. (3mks)
-
- Differentiate between Latitude and Longitude. (2mks)
- The Local time at town x which is on longitude 30oE is 10.30 A.M. What will be the Local time at town Y which is on Longitude 15oW (3mks)
-
- What is natural vegetation? (2mks)
- Give three characteristics of Mediterranean vegetation (3mks)
-
- Define the term soil. (2mks)
- Give three factors that determine soil leaching. (3mks)
- Give five conditions that favour the growth of coral. (5mks)
SECTION B
Answer question six and any other two questions in this section
- Study the map of Taita Hills 1:50,000 (Sheet 189/4) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- What is the name given to this type of a map. (1mk)
- Give the title of this map. (1mk)
-
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map. (2mks)
- Calculate the area covered by the Ronge Forest. (2mks)
-
- Give 3 physical features found at grid square 2318. (3mks)
- What is the bearing of point 230300 from the air photo principal point at grid square 2226. (2mks)
- Describe the distribution of settlements in the area covered by the map.(5mks)
-
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm represent 100 metres draw a cross-section along the line connecting point 280140 and point 370140. (4mks)
- On the cross-section mark and label the following.
- Hill (1mk)
- River (1mk)
- All weather road:- bound surface. (1mk)
- Calculate the vertical Exaggeration of the cross-section (2mks)
-
-
-
- What is Solar system (2mks)
- Give three components of the Solar system. (3mks)
- State Five characteristics of the sun (5mks)
-
- What is the name used to describe the shape of the earth. (1mk)
- Give the three forces that contribute to the shape mentioned above. (3mks)
- State Four effects of the rotation of the earth. (4mks)
- Describe the structure of the earth crust. (7mks)
-
-
-
- What is desertification? (2mks)
- Name three types of desert surfaces (3mks)
- Describe the three processes through which wind transports its load. (6mks)
- Using a well labeled diagram, describe how a mushroom block is formed. (6mks)
- Explain four ways through which desert features influence human activities.
-
-
-
- What is magma? (2mks)
- Name Four types of magma. (4mks)
- Briefly describe how the following features are formed.
- Geyser (5mks)
- Lava Plateau. (5mks)
- Explain two ways in which Volcanic Mountains positively influence human(4mks)
- Students carried a field study on volcanic rocks.
- Give two methods they would have used to collect data. (2mks)
- State three problems that they are likely to have experienced during the field study.(2mks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between an ice berg and an ice sheet. (2mks)
- Identify Four ways through which ice moves (4mks)
- Describe the following processes of glacial erosion.
- Plucking (4mks)
- Abrasion (3mks)
- Describe how a glacial trough is formed.(5mks)
- Students of Gatunguru secondary school carried out a field study on glaciation on Mt. Kenya.
- Give three reasons why they conducted a reconnaissance (3mks)
- Give three activities they may have been involved in during the study. (3mks)
- Formulate one hypothesis that would have been relevant for study. (1mk)
-

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A. 25 MARKS
-
- What is Weather? (2mks)
Dairy atmospheric condition of a given place at a specific time 1x2= 2mks - Give three main methods of forecasting weather. (3mks)
- Ancient methods
- Weather lore methods
- Modern methods.
3x1 = 3mks
- What is Weather? (2mks)
-
- Differentiate between Latitude and Longitude.
Longitude is an imaginary line drawn on a map or a globe running from East to West showing how far a place is North or South of the equator while Longitude is an imaginary line drawn on the globe or a map running from North to South showing how far a place is East or West of the Prime Meridian.
1x2 = 2mks - The Local time at town x which is on longitude 30oE is 10.30 A.M. What will be the Local time at town Y which is on Longitude 15oW (3mks)
y x
15oW oo 30o E
Longitudes difference = 30 + 15 = 45o
1 o = 4min
45o = 4 x 45 = 180 = 3hrs
10 : 30 AM = 7:30AM
- Differentiate between Latitude and Longitude.
-
- What is natural vegetation? (2mks)
This refers to the total mass of plant life that occupies a given area without interference and modification by human activities. 1 x 2 = 2 mks - Give three characteristics of mediteranean vegetation (3mks)
- The vegetation is composed of shrubs/thickets/bush thorn bush
- grasses dry off during summers draught and winter
- some trees are deciduous.
- some plants have fleshy leaves
- Trees have thick rough barks/many plant have waxy/spiny/small leaves.
- Plants have long tap roots.
- Many plants are evergreen.
any First 3 x 1 = 3 mks
- What is natural vegetation? (2mks)
-
- Define the term soil.
It is a naturally occurring thin layer of loose/unconsolidated materials which overlies the crystal rocks and on which plants grow. 1 x 2 = 2 mks - Give three factors that determine soil leaching.
- Nature of soil/solubility of minerals
- Amount of rainfall
- Nature of the slope.
Any First 3 x 1 = 3mks.
- Define the term soil.
- Give Five conditions that favour the growth of coral. (5mks)
- The water should be warm about 20o – 30oc
- The water should be shallow to allow sunlight to penetrate/depth up to 60m.
- The water should be clear from silt/mud.
- The water should be saline.
- There should be plentiful supply of plankton microscopic plant food.
- The water should be well oxygenated.
Any First 5 x 1 = 5mks.
- Study the map of Taita Hills 1:50,000 (Sheet 189/4) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- What is the name given to this type of a map. (1mk)
Topographical map.
1 x 1 = 1mk - Give the title of this map. (1mk)
Kenya 1 : 50,000
1 x 1 = 1mk
- What is the name given to this type of a map. (1mk)
-
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map. (2mks)
18.5cm = 5 ‘
11.9 cm = 5 x 11.9 = 3.2162 ‘ = 3’
38o 20 ‘ – 3 ‘ = 38o 17 ‘
Hence Longitudinal extent is 38o 17 ‘E to 38o 30’E - Calculate the area covered by the Ronge Forest. (2mks)
Full squares = 0
Half squares = 9
Area = 0 + (9 ÷ 2) = 4.5 km2 1 x 2 = 2mks.
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map. (2mks)
-
- Give 3 physical features found at grid square 2318. (3mks)
-River
-River valley
-Scrub
-gentle slope.
Any First 3 x 1 = 3mks. - What is the bearing of point 230300 from the air photo principal point at grid square 2226.
008o or N 8oE
1 x 2 = 2mks - Describe the distribution of settlements in the area covered by the map. (5mks)
- There are few settlements in the steep areas.
- There are few settlements in the area covered by forests
- There are many settlements along transportation lines forming Linear settlement.
- There are no settlements in the area covered by water reservoirs
- There are no settlements in the area covered by sisal plantation.
- There are many settlements in the area around junction.
- There are more settlements in the Western side than in the Eastern side.
Any 5 x 1 = 5mks
- Give 3 physical features found at grid square 2318. (3mks)
-
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm represent 100 metres draw a cross-section along the line connecting point 280140 and point 370140. (4mks)
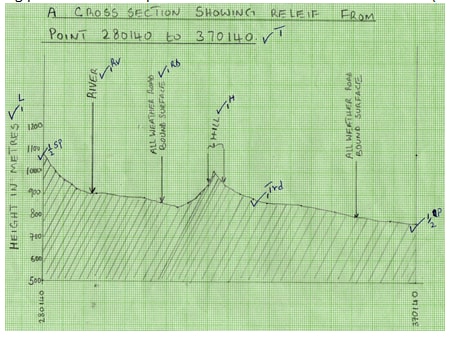
- On the cross-section mark and label the following.
Hill (1mk)
River (1mk)
All weather road:- bound surface. (1mk) - Calculate the vertical Exaggeration of the cross-section.
VE = V.S
H.S
= 1 ÷ 1
10,000 50,000
= 1 x 50,000
10,000 1
= 5 2mks
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm represent 100 metres draw a cross-section along the line connecting point 280140 and point 370140. (4mks)
-
-
-
- What is Solar system (2mks)
Refers to the sun, the plants and other celestrial bodies held together by the force of gravity and orbiting around the sun. 1 x 2 = 2mks - Give three components of the Solar system. (3mks)
- The sun
- The Planets
- Asteroids
- Meteors / meteoride / meteorites
- Comets
- Natural satellites(nouns
Any First 3 x 1 = 3mks
- What is Solar system (2mks)
- State Five characteristics of the sun (5mks)
- It is the centre of the Solar system.
- It is the largest member of the solar system.
- It produces its own light
- It Radiates solar energy to the earth, other planets and their satellites.
- It rotates on its axis in an anti-clockwise direction.
- All planets and some heavenly bodies revolve around it using elliptical orbits.
- It comprises of hot gases mainly hydrogen and helium.
- Has a very high temperature of about 6000oc
- Has a greater gravitational pull than planets which maintains heavenly bodies in their orbits.
- Has three layers i.e. corona, photosphere and chromosphere.
Any First 5 x 1 = 5mks -
- What is the name used to describe the shape of the earth. (1mk)
Geoid / oblate spheroid 1 x 1 = 1mk. - Give the three forces that contribute to the shape mentioned above. (3mks)
- Gravitational force
- Centrifugal force
- Centripetal force
3 x 1 = 3mks
- State Four effects of the rotation of the earth. (4mks)
- It causes the occurrence of day and night/apparent movement of the sun from East to West.
- It causes difference in time between places over the earth surface/difference 1 hr between two longitudes which are 15o
- It causes deflection of winds and ocean currents.
- It causes rising and falling of ocean/sea bides.
- It causes variation in atmospheric pressure on the surface of the earth.
Any First 4 x 1 = 4mks
- What is the name used to describe the shape of the earth. (1mk)
- Describe the structure of the earth crust. (7mks)
- Its rocks are generally brittle/solid
- It extends between 6 to 80 km.The sial contain mainly silica and aluminum
- The sima contains silica, magnesium and iron.
- The sial is lighter / has a density of 2.65 to 2.7 g/cc
- The sial has mainly granitic rocks
- The sial has basaltic rocks
- The sima has a density of 2.7 to 3.0 gm/cc.
- The sima is fairly flexible.
Any 7 x 1 = 7mks
-
-
-
- What is desertification? (2mks)
Refers to the encroachment of large areas of barren land which are covered with sand.
1x 2 = 2mks - Name three types of desert surfaces (3mks)
- Sandy desert/erg/Koum
- Stony desert/ Reg / Serrir
- Rocky deserts / Hamada
- Bad lands
Any First 3 x 1 = 3mks.
- What is desertification? (2mks)
- Describe the three processes through which wind transports its load. (6mks)
- Saltation – It is a process in which coarse grained sand particles are transported through a series of bouncing/jumps along the surface.
- suspension – It is a process in which very fine material/particles are picked by wind raised high and blown over long distances.
- Surface creep/traction – process in which large heavy materials are rolled and pushed forward by wind along the surface.
P - 3
D - 3 = 6mks
- Using a well labeled diagram, describe how a mushroom block is formed. (6mks)
- A rock mass with uniform rock structure (homogenous rock) stands on the desert surface.
- Weathering and wind abrasion attack the rock.
- Abrasion undercuts more near the base of the rock where larger and heavier particles are carried by the wind.
- There is less polishing and smothering at the top by the lighter materials carried by the wind.
- The process forms a mushroom shaped block with a narrow base and a broad rounded top called mushroom block…
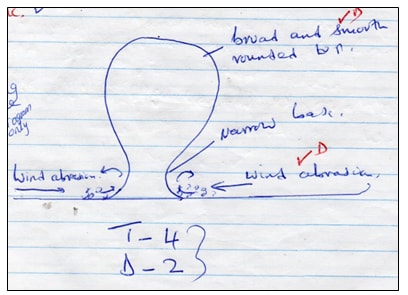
- Explain four ways through which desert features influence human activities. (8mks)
- Features such as barchans forms beautiful scenery which attract tourists thereby earning foreign exchange.
- Oasis are sources of water which is used for agricultural use and for domestic use.
- Wind deposited loess form fertile plains for farming.
- Salty flats are used for salt production leading to economic development.
- Shifting sand dunes forms barriers to transport network hindering transport activities.
- Desert features forms beautiful scenes which are ideal for film making.
- Vast sand seas are ideal for military training / nuclear testing.
Any First 4 x 2 = 8mks
-
-
-
- What is magma? (2mks)
Molten rock material which originate from the interior of the earth and cools while below the earth surface. 1×2=2mks - Name Four types of magma. (4mks)
- Acidic / Viscous magma
- Basic magma
- Ultra – basic magma
- Intermediate magma.
4×1=4mks
- What is magma? (2mks)
- Briefly describe how the following features are formed.
- Geyser
- Rain water percolates down through cracks in the rocks.
- The water gets into contact with hot igneous rocks.
- The water is superheated and gases/steam form.
- Pressure builds in the cracks
- The pressure causes steam and water to be ejected explosively as jets to the surface intermittently.
- The water and steam are emitted intermittently as pressure level changes forming a geyser.
Any 5 x 1 = 5mks.
- Lava Plateau. (5mks)
- Earth movement forms a series of fissures or vents in the earth crust.
- Lava which is extremely fluid is forced to flow through the fissures by underground pressure.
- On reaching the surface, the lava spreads evenly over a large surface.
- The lava fills and cover valleys and dispressions on the earth surface.
- The lava cools and solidifies.
- Successive eruptions leads to move and move layers of lava.
- The solidified layers of lava form an extensive fairly flat upland area called a lava plateau.
Any 5 x 1 = 5 mks
- Geyser
- Explain two ways in which Volcanic mountains positively influence human (4mks)
- Volcanic mountains are sources of rivers which provide water for domestic industrial transport and irrigation.
- Volcanic mountains influence the formation of relief rainfall that encourages agricultural activities on mountain slopes.
- Volcanic mountains forms beautiful scenery that attract tourists.
- Volcanic mountains are sources of volcanic rocks that provide materials for building and construction.
Any First 2 x 2 = 4 mks
- Students carried a field study on Volcanic rocks.
- Give two methods they would have used to collect data. (2mks)
- Observation
- Collecting samples
- Taking photographs
- Counting
- Experimentation.
Any first 2×1=2mks
- State three problems that they are likely to have experienced during the field study.
- Some students may have been cut / injured by rocks in High rainfall.
- In-ability to collect the right samples.
- In accessibility of some sample sites.
- Heavy weight of the rock samples.
Any First 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Give two methods they would have used to collect data. (2mks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between an ice berg and an ice sheet. (2mks)
An ice berg is a large block of ice broken from ice sheets and floating in the sea or ocean while an ice sheet is a continous mass of ice which covers a very large area in the lowland, of high altitude areas.
1x 2 = 2 mks. - Identify Four ways through which ice moves
- Plastic flowage / intergranular movement
- Internal shearing
- Basal slip
- Extrusion flow.
4 x 1 = 4 mks
- Differentiate between an ice berg and an ice sheet. (2mks)
- Describe the following processes of glacial erosion.
- Plucking (4mks)
- Pressure of overflowing mass of ice cause freeze thaw action at the bottom.
- Melt water enters the cracks and joint on the bed rock.
- As the water freezes it exerts pressure in the cracks enlarging them.
- enlargement of cracks leads to disintegration of the rocks.
- The broken rocks are then embedded or frozen into the ice.
- As the ice moves it tears out the frozen rocks from the parent rocks a process called plucking.
Any 4 x 1 = 4 mks.
- Abrasion
- Rocks materials frozen in the moving ice are dragged over the rocky floor and on the rocky sides of the gracial valley.
- The rocks grind and scratch the rocks on the floor and the sides of the gravel valley.
- The rocks grind and scratch the rocks on the floor and the sides of the valley.
- This wears and polishes the rocks on the valley bottom and valley sides in a process known as abrasion. Any 3 x 1 = 3mks.
- Plucking (4mks)
- Describe how a glacial trough is formed. (5mks)
- Initially there is a main river valley and several tributary river valleys.
- Once glaciations occurs, ice collects and moves in both the main valley and in the tributary valleys.
- Moving ices erodes the valley through abrasion and plucking processes.
- As the tributary valleys join the main valley the amount in the main valley increases.
- The main valley becomes deeper and wider resulting in a U-shaped, steep sided valley called a glacial trough.
Any 5 x 1 = 5mks
-
- Students of Gatunguru secondary school carried out a field study on glaciation on Mt. Kenya.
- Give three reasons why they conducted a reconnaissance (3mks)
- To enable them draw study objectives and hypothesis
- To assess the suitability of the area of study
- To enable them draw a route map
- To enable them prepare a work schedule or plan of activities
- To seek permission from the relevant authorities in the site of study.
- To enable them prepare financial requirements
- To identify the problems likely to be encountered during the study
Any first 3×1=3mks
- Give three activities they may have been involved in during the study. (3mks)
- Observing
- Taking photographs
- Counting
- Drawing sketches
- Climbing mountain
Any First 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Formulate one hypothesis that would have been relevant for study.
- Most of the glacialfeatures on mount Kenya are as a result of erosion.
- Most of the features on Mt.Kenya attract tourists.
Any First 1 x 1 = 1mk.
- Give three reasons why they conducted a reconnaissance (3mks)
Download GEOGRAPHY PAPER 1 - 2019 KCSE KASSU JOINT MOCK EXAMS (QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

