SECTION A (30 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- Differentiate between pastoralism and nomadic pastoralism. (1mk)
- Give four reasons for sub-soiling. (2mks)
- State four advantages of drip irrigation. (2mks)
- Give three farming practices that will lead to pollution of water. (1 ½ mks)
- Outline four factors that influence quality of compost manure. (2mks)
-
- what is opportunity cost as used in agricultural economics? (1mk)
- State two conditions under which opportunity cost is said to be Zero. (1mk)
- Differentiate between under sowing and over sowing as used in pasture in production. (1mk)
- State four disadvantages of broadcasting in crop production. (2mks)
- Give four objectives of settlement schemes in Kenya soon after independence. (2mks)
-
- Name three types of legume trees used as a fodder. (1 ½ mks)
- Give four reasons for top-dressing pasture. (2mks)
- Name three insect pests of cabbages. (1 ½ mks)
- Give three importance of Agricultural Society of Kenya (A.S.K). ( 1 ½ mks)
-
- State two reasons for carrying out agroforestry on a river – bank. (2mks)
- Give four ways in which agroforestry seeds are prepared after collection in readiness for planting. (2mks)
- Give two reasons for processing agricultural produce. (1mk)
- State two functions of calcium in the soil. (1mk)
- List four methods of applying fertilizers in crops. (2mks)
- Give two reasons for cutting back in pyrethrum production. (1mk)
SECTION B (20 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- The diagrams below shows two weeds labeled A and B. Study them and answer questions that follow.
- Identify the weeds labeled A and B. (1mk)
- Give one reason why the weed labeled A is referred to as a parasitic weed. (1mk)
- Name two crops that the weed illustrated A above commonly attack. (1mk)
- Give one reason why it is very difficult to control weed labeled B. (1mk)
- State one cultural method of controlling weed labeled A. (1mk)
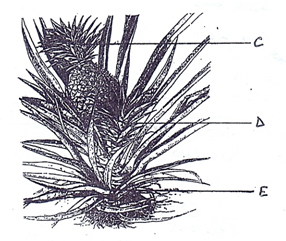
- The diagrams below illustrate a pineapple plant. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the parts of propagating pineapple labeledC,D and (1 ½ mks)
- Which of the vegetative material is more suitable for propagation? (½mk)
- Give a reason for your answer above. (1mk)
- State three advantages of vegetative propagation. (1 ½ mks)
- The following information was extracted from Mr. Njengas farm records on 31/12/2018. Use the information to answer the questions that follow.
Description
Kshs
Five year bank loan
400,000
One year loan with AFC
200,000
Creditors
45000
Debtors
20000
Land
600000
Buildings
420000
Dairy cattle
180000
Dairy meal
10000
Cash in hand
35000
- Prepare a balance sheet of Mr. Njengas farm. (5mks)
- Was Mr. Njengas business solvent or insolvent? (1mk)
- An experiment was carried out to investigate soil constituents as described below.
- A 250 cm3measuring cylinder was filed with water to 100cm3
- A 100cm3 beaker was filled with garden soil up to brim.
- The soil was emptied into one measuring cylinder and shook well.
- The final volume was 150cm3.- What was lost when the 100cm3 garden soil was poured to 100cm3 of water in the measuring cylinder? (½mk)
- Calculate one percentage content of the soil constituents investigated in the experiment. (2mks)
- Give two importance of the substance lost above in the soil. (2mks)
SECTION C (40 Marks)
Answer any two questions from this section in the spaces provided.
-
- Describe the production of beans under the following sub-headings
- Field preparation (3mks)
- Planting (3mks)
- Field management practices (5mks)
- Outline the procedure of harvesting sugarcane. (5mks)
- Describe the production of beans under the following sub-headings
-
- Explain five land tenure systems practiced in Kenya. (10 mks)
- Describe ten functions of agricultural marketing in Kenya. (10 mks)
-
- Explain five farming activities which may encourage soil erosion. (10 mks)
- Explain five factors determining stage and time of harvesting crops. (10 mks)
MARKING SCHEME
443/1
AGRICULTURE PAPER 1
- Pastoralism refers to the keeping of large herds of mammalian livestock or rearing of animals on the same farm while Nomadic pastoralism is the practice of moving from place to place in search of pasture and water.( 1mk, mark as a whole.)
- Reasons for sub-soiling
- To break hard pan layer for easy penetration of roots and water infiltration
- To improve aeration of the soil
- To improve water infiltration.
- To bring nutrients beneath the soil to the surface and mix the soil well.(4 x ½ = 2mks)
- Advantages of drip irrigation
- Little amount of water is required as compared to other types of irrigation
- Water under low pressure can be used so long as it can flow along the pipe
- It discourages fungal diseases i.e blight, CBD etc.
- It doesn’t encourage the growth of weeds between the rows.( 4 x ½ = 2mks)
- Farming practices that lead to water pollution
- Use of inorganic fertilizers
- Use of pesticides
- Poor cultivation practices such as over cultivation, overgrazing and cultivation along the river banks.( 1 x ½ = 1 ½ mks)
- Factors influencing quality of farm yard manure
- The type of animal producing the manure
- The quality of the food given to the animal
- Type of litter
- Method of storage
- Age of the manure age of the animal.( 4 x ½ = 2mks)
-
- Opportunity cost refers to the return forgone / the value of the best forgone alternative when the resource factor is taken from its best alternative.( 1 x 1 = 1mk)
- Conditions under which opportunity cost is at zero
When item is free/donation,
When there is no alternative
When it is a gift.( 2 x ½ = 1mk)
- Under sowing is planting of a pasture crop under an existing crop which acts as a nurse crop eg under maize, sunflower, wheat and barley, etc. while over sowing is growing of legume pasture (high quality pasture) onto an existing low quality pasture crop to improve its quality. ( 1 x 1 = 1mk) Mark it as a whole)
- Advantages for broadcasting
- It involves use of high seed rate, thus increasing cost of production.
- Leads to undue overcrowding hence competition for nutrients, light, space and moisture.
- It limits the mechanization of farm activities such as spraying and weeding etc.
- Lack of uniformity in land coverage/uneven land coverage
- Uneven planting depth/ uneven germination/ uneven growth.
- Difficult to carry out subsequent operations such as weeding, spraying and harvesting.( 4 x ½ = 2mks)
- Objectives of settlement schemes;
- To transfer land from Europeans to Africans to eneble the Africans to own land.
- To settle the landless by transferring landless/squatters to new land allocation.
- To make use of underutilized/ idle land so as to increase production
- To create employment by working on the farm given to produce crops and keep livestock.
- To increase agricultural production through better methods of land utilization and earn foreign exchange.
- To ease population pressure on land by transferring people from overpopulated areas to scarcely populated areas.( 4 x ½ mks)
- Legume trees used as fodders are
- Leucaenia
- Calliandra
- Atriplex
- Sesbania( 3 x ½ = 1 ½ mks)
- Reasons for top dressing pasture are;
- to replenish the soil nutrients
- T o increase the herbage yield
- To improve nutritive value of the crop
- To correct or amend both physical and chemical properties of the soil
- To enable the soil micro- organism to break down organic residues into available nutrients.( 4 x ½ = 2mks)
- Legume trees used as fodders are
- Insect pests of cabbages;
- Aphids
- Caterpillars
- Cut worms
- Mouse birds
- Slug( 3 x ½ = 1 ½ mks)
- Importance of Agricultural Society of Kenya (A.S.K) show;
- Holding competitive agricultural shows and exhibitions of livestock crops and farm produce.
- Encouraging breeding and importation of pure breeds of livestock and improvement of useful indigenous animals
- Encouraging and assisting in official milk recording scheme.
- Organizing the running of Young Farmers Clubs.
- Organizing the national Ploughing contest.
- Publishing a monthly journal known as “The Kenya Farmers’
- Publishing the Kenya Stud Book.
- Awarding bursaries for local and overseas studies/tours for its members.( 3 x ½ = 1 ½ mks)
- reasons for carrying out agro forestry on a river – bank;
- Stabilizes river bank/control river bank erosion
- Slow down speed of surface runoff
- Trap soil/debris in surface runoff
- Reduces risk of flooding.( 2 x ½ = 1mk)
- Ways in which agro-forestry seeds are prepared after collection;
- Extraction to remove seeds from pods/fruits
- Drying to reduce seed moisture content
- Testing to verify seed quality
- Seed dressing to control pests and diseases
- Seed inoculation to improve nitrogen fixation.
- Washing/ cleaning to remove mucilage.( 4 x ½ = 2mks)
- reasons for carrying out agro forestry on a river – bank;
- Reasons for processing agricultural products;
- Reduce its bulkiness
- Improve its keeping quality.
- Improve its quality and test.( 2 x ½ = 1mk)
- Functions of calcium in the soil;
- Increases bacteriological activities in the soil.
- Raises soil ph which in turn increases the Cation Exchange capacity (CEC) making more nutrients such as phosphorus and potassium available.
- Promotes formation of soil aggregates which in turn improve aeration, drainage and water retention.( 2 x ½ = 1mk)
- Methods of applying fertilizers in crops;
- Broadcasting
- Band placement
- Side dressing
- Ring placement
- Drip method
- Foliar spray( 4 x ½ = 2mks)
- Reasons for cutting back pyrethrum;
- Remove old stems to allow regeneration of new shoots
- Control bud disease( 2 x ½ = 1mk)
- A- Striga (Witch weed)/ Strigahermontheca ( ½ mk)
B – Couch grassDigetariaScalarum( ½ mk) - Attaches itself to the roots of cereal crops and obtain nourishment from them. ( 1 x 1 = 1mk)
- Maize, Millet and Sorghum. (1mk)
- Has well developed underground rhizomes. (1mk)
- Crop rotation and trap cropping. ( ½ mk)
- A- Striga (Witch weed)/ Strigahermontheca ( ½ mk)
- C- Crown
D – Slip
E – Sucker ( 1 ½ mks) - Crown ( ½ mk)
- they give a uniform growth. (1mk
- Advantages
Reduces maturity
Gives uniformity in growth
Gives quality products
its possible to get fruits of different qualities on the same plant especially in grafting and budding
A method used to propagate plant species which are not able to produce seeds or produce seeds with very low viability.( 3 x ½ = 1 ½ mks)
- C- Crown
- Mr. Njengas Farm Balance sheet as at 31st/12/2018 (5 ½ mks)
The business was solvent because the Assets exceed the liabilities by ksh. 580,000=( ½ mk)Liabilities
KSHS
CTS
Assets
KSHS
CTS
Five year bank loan
400,000
00
Land
600,000
00
One year loan AFC
200,000
00
Buildings
420,000
00
Creditors
45,000
00
Dairy Cattle
180,000
00
Debtors
20,000
00
Dairy meal
10.000
00
Cash at hand
35,000
00
Sub -Total
665,000
00
Net worth
580,000
00
- Mr. Njengas Farm Balance sheet as at 31st/12/2018 (5 ½ mks)
- Air (1mk)
- Expected volume = 100 cm3 + 100 cm3 = 200cm3
Final reading volume = 1500 cm3
Volume of air in the soil sample = 200cm3 – 150cm3 = 50cm3
Percentage of soil air = 50cm3 x 100 = 50 %
100cm3
= 50%
( 2 x 1 =2mks)
- Bean production;
- Field preparation;
Seed bed is prepared early enough (before onset of rains)to allow time for residues to rot.
Ploughing (primary cultivation) is done either manually or mechanically.
After primary cultivation, secondary cultivation is done where the seed bed is rough. Harrowing is done to achieve appropriate tilth i.e medium tilth ( 1 x 3 = 3mks) - Planting;
Crop planted at the onset of rains except during the long rains when planting may be delayed to avoid rotting of the crop before harvesting.
Two seeds are planted per hole
Spacing is 30cm – 45cm x 15cm
Depth of planting is 2.5cm – 10 cm depending on moisture availability and type of soil.
Diammonium phosphate is applied at the rate of 200kg/hac.
Seed rate is 50 – 60 kg/hac. ( 1 x 3 = 3mks)
Field management practices;
Gapping is done immediately after germination to replace the empty gaps.
Thinning is done to remove excess seedlings to maintain plant population.
Weeding is done when the field is dry to avoid spreading diseases.
Shallow weeding is done
Hand weeding is practiced
Weeding should be done before flowering to avoid knocking down flowers.
Pests such as aphids, bean bruchid, spotted borer , American boll worm, bean fly and golden- ring moth should be controlled by spraying with appropriate insecticides, i.e formathion, diazinon and dimethoate.
Disease control should be done because this causes great loss. Some of these diseases include bean rust, anthracnose, halo blight and mosaic etc. These are controlled by spraying with appropriate copper fungicide to control fungal diseases. Rogueing is also practiced to control some of the diseases.
(1 x 6= 6mks)
- Field preparation;
- Procedure of harvesting Sugar cane;
Harvest at the right stage when sugar content is high /18 -22 months from planting
Take samples of the lower , middle and top portions to the factory to be tested for sugar distribution.
Set one cane in the field on fire
Cut the cane to the ground level.
Remove the green tops and unburnt leaves.
Take the cane to the factory the same day.( 1 x 5 =5mks)
- Bean production;
- Five land tenure practices;
Leasehold / land Lordism/Tenancy;this give legal rights to an individual to own and use land at payment for specific time.
Company/ Concession; the company and the government enter an agreement on the use of land for a specific period of time.
Communal land tenure; the whole community has the right to the use of land.
Individual ownership; the land is owned by an individual who operates it.
State ownership/ government ownership; the government controls land use.
Co-operative land tenure; Land is owned by a group of members who run it on co-operative basis/principles.
( 5 x 1 = 5 mks for stating and 5 x 1 = 5mks for explanation = 10 mks) - Functions of marketing;
Buying farm produce from the producers
Storage to minimize loss and ensure availability through out the year
Processing to provide variety , increase value and prolong shelf – life products.
Grading and standardization to fix prices.
Collecting market information to know what, raw and when to produce in relation to price and demand.
( 5 x 2 = 10 mks)
- Five land tenure practices;
- Farming activities that encourage soil erosion;
Continuous cropping/ frequent cultivation, pulverizes the soil making it easy to detach and carry it away.
Burning of land to destroy vegetation cover and exposes soil to soil erosion.
Overstocking leads to overgrazing; which destroys ground cover exposing it to agents of erosion.
Ploughing up and down the slope; create channels which speed up and increase the speed and erosive capacity of water.
Cultivation of river banks; destroy riverine vegetation and destroys soil structure exposing to agents of erosion.
Cultivation of the soil when too dry; this destroys soil structure making it eroded.
Overstocking; detach and carry away soil particles
Deforestation/ clean weeding; Leave soil bare ,exposing to agents of soil erosion.
( 1 x 5 = 5mks for stating and 5 x 1 = 5mks for explanation. = 10mks)
- Farming activities that encourage soil erosion;
Download AGRICULTURE PAPER 1 - 2019 MOKASA II MOCK EXAMINATION.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students