INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
- Write your name and index number in the spaces provided above.
- Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided.
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used.
QUESTIONS
- The grid below shows part of the periodic table study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the true symbols.
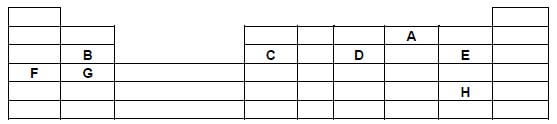
- Which element forms ions with charge of 2-? Explain (2mks)
- What is the nature of the oxide formed by C. (1mk)
- How does the reactivity of H compare with that of E. Explain? (2mks)
- Write down a balanced equation between F and Chlorine. (1mk)
- Explain how the atomic radii of B and C compare. (2mk)
- If the oxides of F and D are separately dissolved in water, state and explain the effects of their aqueous solutions on litmus. (2mks)
-
- The scheme below was used to prepare a cleansing agent. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
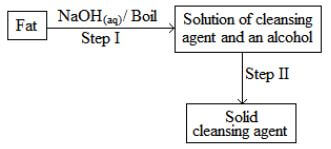
- What name is given to the type of cleansing agent prepared by the method above? (1mark)
- Name one chemical substance added in step II. (1 mark)
- What is the purpose of adding the chemical substance named in a (ii) above? (1 mark)
- Other than NaOH ,name any other suitable substance that can be used in step I. (1 mark)
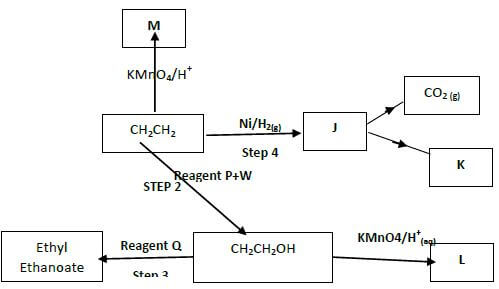
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
-
- Name the following organic compounds: (2mks)
M……………………………………………………………..……..
L………………………………………………………………….. - Name the process in step (2mks)
Step 2 ………………………………………………………….….
Step 4 ………………………………………………………….… - Identify the reagent P and Q (2mks)
P ………………………………………………………………..
Q……………………………………………………………. - Write an equation for the reaction between CH3CH2CH2OH and sodium metal (1mk)
- Name the following organic compounds: (2mks)
-
- The scheme below was used to prepare a cleansing agent. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Define radioactivity (1mk)
- Give two differences between chemical reactions and nuclear reactions. (2mks)
Chemical reactions Nuclear reactions - Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow
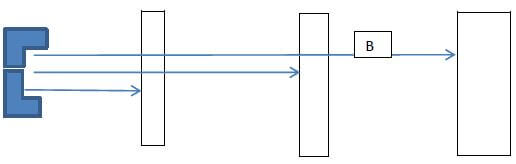
- What property of radiations is being investigated by the illustration above ( 1mark)
- Give the name of the radiation B and give a reason. (2mks)
- Below is the radioactive decay starting with 214?? study it and answer the questions that follow.
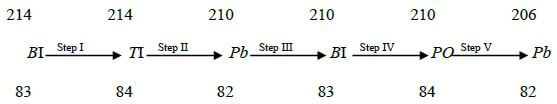
- Identify the particle emitted in step I and II. (2mks)
Step 1.....................................................................
Step 11………………………………………….... - Write the nuclear equation for the reaction which takes place in step V (1mk)
- Identify the particle emitted in step I and II. (2mks)
- State one danger associated with frequent exposure to radiations. (1mk)
- The isotope X-31 has a half life of 2.5 hours.Calculate the ramaining percentage (%) of the isotope left after 7.5 hours? (2mks)
- The following diagrams show the structure of two allotropes of carbon. Study them and answer the questions that follow.
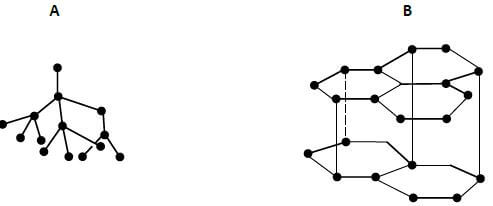
- Name the allotropes. (1mark)
A ………………………………………………………………………………..
B …………………………………………………………………………………. - Give one use of A. (1mark)
- Which allotrope conducts electricity? Explain (2 marks)
- The flow below represents the main steps in the manufacture of sodium carbonate
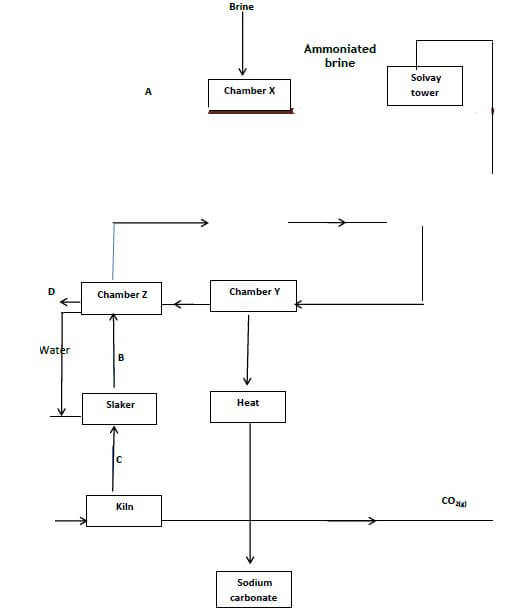
- Identify the substance labeled. (2marks)
A ……………………………………………………………………………………….
B…………………………………………………………………………………………
C ………………………………………………………………………………………….
D ……………………………………………………………………………………………. - Cold water is made to circulate around solvay tower. What does this suggest about the reaction between A and brine. (1mark)
- What process takes place in chamber Y? (1mark)
- Name two by-products that are recycled in this process. (2 marks)
- Why is recycling important? (1mark)
- Write the equation for the reaction that takes place in the Solvay tower. (1mark)
- Give two industrial uses of sodium carbonate. (2marks)
- Identify the substance labeled. (2marks)
- Name the allotropes. (1mark)
- Fractional distillation of air is used in the industrial isolation of oxygen. The diagram below shows the process.
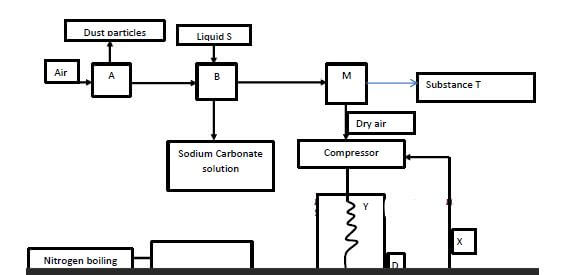
- What processes are taking place in chamber A,B,M and D 2marks
A…………………………………………………………………………………………..……..
B…………………………………………………………………………………………….
M……………………………………………………………………………………………..….
D……………………………………………………………………………………………..…. - Name;
- Liquid S (1mk)
- Substance T (1mk)
- Explain why part Y in chamber D is curved? (1mark)
- Give two industrial uses of oxygen gas? (2marks)
- In the laboratory preparation of oxygen, manganese (iv) oxide and hydrogen peroxide are used. Write an equation to show how oxygen gas is formed. (1mark)
- An investigation was carried out using the set-up below. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
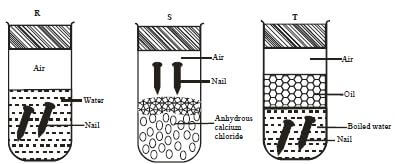
-
- State and explain what will happen in the three test-tubes R, S and T after seven days. (2marks)
- Give one reason why some metals are electroplated. (1mark)
- What processes are taking place in chamber A,B,M and D 2marks
-
- Define the following terms
- Saturated solution (1mk)
- Fractional crystallization (1mk)
- Solubility of salt X and Y were determined at different temperatures as shown in the following data.
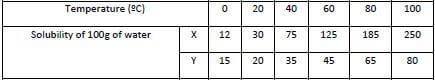
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of solubility (vertical axis) against temperature. (4mks)
- From the graph determine the solubility of each at 50ºC.
X ……………………………………………………….. (1mk)
Y ………………………………………………………… (1mk) - At what temperature was the solubility of both salts equal. (1mk)
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of solubility (vertical axis) against temperature. (4mks)
-
- What is permanent hardness of water? (1mk)
- Saturated solution of salt X at 70ºC was cooled to 20ºC. What mass of the crystal were deposited. (1mk)
- Define the following terms
-
- The set-up below is used to investigate the properties of hydrogen.
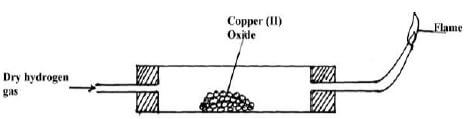
- On the diagram, indicate what should be done for the reaction to occur (1mk)
- Hydrogen gas is allowed to pass through the tube for some time before it is lit. Explain (2mks)
- Write an equation for the reaction that occurs in the combustion tube (1mk)
- When the reaction is complete, hydrogen gas is passed through the apparatus until they cool down . Explain (2mks)
- What property of hydrogen is being investigated? (1mk)
- What observation confirms the property stated in (v) above? (1mk)
- Why is zinc oxide not used to investigate this property of hydrogen gas? (1mk)
- The set-up below is used to investigate the properties of hydrogen.
MARKING SCHEME
- The grid below shows part of the periodic table study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the true symbols.

- Which element forms ions with charge of 2-? Explain (2mks)
A(1)- gains two electrons to become stable(1) - What is the nature of the oxide formed by C. (1mk)
amphoteric - How does the reactivity of H compare with that of E. Explain? (2mks)
H is less reactive than E(1)
H has a larger atomic radius hence lower attraction to electrons(1) - Write down a balanced equation between F and Chlorine. (1mk)
2F(s) + Cl2(g) → 2FCl(s)
2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s) - Explain how the atomic radii of B and C compare. (2mk)
C has a smaller atomicradius than B(1), Chas more protons hence stronger nuclear charge/attraction for outermost electrons(1) - If the oxides of F and D are separately dissolved in water, state and explain the effects of their aqueous solutions on litmus. (2mks)
Oxideof F changes litmus to blue (½)–dissolves in water to form alkaline/ basic solution(½)
Oxide of D changes litmus to red(½)- dissolves in water to form acidic solution(½)
- Which element forms ions with charge of 2-? Explain (2mks)
-
- The scheme below was used to prepare a cleansing agent. Study it and answer the questions that follow.

- What name is given to the type of cleansing agent prepared by the method above? (1mark)
Soap. ½ - Name one chemical substance added in step II. (1 mark)
Concentrated NaCl/ Brine/ NaCl(l) - What is the purpose of adding the chemical substance named in a (ii) above? (1 mark)
To precipitate out the soap - Other than NaOH ,name any other suitable substance that can be used in step I. (1 mark)
potassium hydroxide/ KOH(aq)
- What name is given to the type of cleansing agent prepared by the method above? (1mark)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow

-
- Name the following organic compounds: (2mks)
M..Ethan-1,2-diol/Glycol
L Ethanoic acid - Name the process in step (2mks)
Step 2 …Hydrolysis
Step 4..Hydrogenation - Identify the reagent P and Q (2mks)
P …Concentrated sulphuric(vi) acid
Q…Ethanoic acid - Write an equation for the reaction between CH3CH2CH2OH and sodium metal (1mk)
2CH3CH2CH2OH(l) + 2Na(s) → 2CH3CH2CH2ONa(l)+H2(g)
- Name the following organic compounds: (2mks)
-
- The scheme below was used to prepare a cleansing agent. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Define radioactivity (1mk)
Process where unstable nuclide breaks up to yield another nuclide of different composition with emission of particles and energy - Give two differences between chemical reactions and nuclear reactions. (2mks)
Chemical reactions Nuclear reactions 1Occur in energy levels
2 Involve deloclised electrons
3Produce less energy
4Affected by environmental condition
5.Do not form new element1 occur in nucleus
2Involve protons and neutrons
3Produce huge amount of energy
4 Not affected by environmental conditions
5 Form new element - Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow

- What property of radiations is being investigated by the illustration above ( 1mark)
Penetration power of radiations - Give the name of the radiation B and give a reason. (2mks)
Gamma radiation ,
Can penetrate paper and aluminium foil but only stopped by lead - Below is the radioactive decay starting with 214?? study it and answer the questions that follow.

- Identify the particle emitted in step I and II. (2mks)
Step 1...Beta
Step 11..Alpha - Write the nuclear equation for the reaction which takes place in step V (1mk)

- Identify the particle emitted in step I and II. (2mks)
- State one danger associated with frequent exposure to radiations. (1mk)
Cause cancer
Cause mutation - The isotope X-31 has a half life of 2.5 hours.Calculate the ramaining percentage (%) of the isotope left after 7.5 hours? (2mks)
n = 7.5/2.5
=3
X = (1/2)3 ×100
X = 1/8×100
Remaining % = 12.5%
- What property of radiations is being investigated by the illustration above ( 1mark)
- Define radioactivity (1mk)
- The following diagrams show the structure of two allotropes of carbon. Study them and answer the questions that follow.

- Name the allotropes. (1mark)
A …Diamond
B …Graphite - Give one use of A. (1mark)
Making drilling bit
Making jewerelly - Which allotrope conducts electricity? Explain (2 marks)
B, Has one delocalized electron that conducts electricity - The flow below represents the main steps in the manufacture of sodium carbonate

- Identify the substance labeled. (2marks)
A ……Ammonia
B…Calcium hydroxide
C .Calcium oxide
D .Calcium chloride - Cold water is made to circulate around solvay tower. What does this suggest about the reaction between A and brine. (1mark)
Reaction is exothermic - What process takes place in chamber Y? (1mark)
Filtration - Name two by-products that are recycled in this process. (2 marks)
Ammonia
Carbon ()oxide
Water. - Why is recycling important? (1mark)
Makes process economical/less expensive - Write the equation for the reaction that takes place in the Solvay tower. (1mark)
NH3(g)+NaCl(aq)+CO2(g)+H2O(l) → NaHCO3(s)+NH4Cl(aq) - Give two industrial uses of sodium carbonate. (2marks)
Making glass
Making detergents
Softening hard water
- Identify the substance labeled. (2marks)
- Name the allotropes. (1mark)
- Fractional distillation of air is used in the industrial isolation of oxygen. The diagram below shows the process.

- What processes are taking place in chamber A,B,M and D 2marks
A Electrostatic precipitation/Filtration
B…Absorption
M Condensation/Isolation of ice
D Cooling - Name;
- Liquid S (1mk)
Concentrated NaOH (aq) - Substance T (1mk)
Ice / water
- Liquid S (1mk)
- Explain why part Y in chamber D is curved? (1mark)
To increase surface area forcooling - Give two industrial uses of oxygen gas? (2marks)
- In the laboratory preparation of oxygen, manganese (iv) oxide and hydrogen peroxide are used. Write an equation to show how oxygen gas is formed. (1mark)
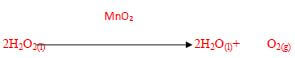
- An investigation was carried out using the set-up below. Study it and answer the questions that follow.

-
- State and explain what will happen in the three test-tubes R, S and T after seven days. (2marks)
R -Rusting occurred √1 ½ mk because of air and water being present √½ mk
S - No rusting √½ mk Water is absent √½ mk
T - No rusting √ ½ mk Air is absent √½ mk - Give one reason why some metals are electroplated. (1mark)
To prevent rusting √1mk
To increase aesthetic value of the metal
- State and explain what will happen in the three test-tubes R, S and T after seven days. (2marks)
- What processes are taking place in chamber A,B,M and D 2marks
-
- Define the following terms
- Saturated solution (1mk)
A solution that cannot dissolve any more of the solute at that particular temperature. - Fractional crystallization (1mk)
Scientific technique used to separate substances due to their differences in their crystallization temperature. or w.t.t.e
- Saturated solution (1mk)
- Solubility of salt X and Y were determined at different temperatures as shown in the following data.

- On the grid provided, plot a graph of solubility (vertical axis) against temperature. (4mks)

- From the graph determine the solubility of each at 50ºC.
X … 100g/100ml ±1
Y … 40g/100ml ±1 - At what temperature was the solubility of both salts equal. (1mk)
5ºc
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of solubility (vertical axis) against temperature. (4mks)
-
- What is permanent hardness of water? (1mk)
Type of water hardness that cannot be removed by boiling - Saturated solution of salt X at 70ºC was cooled to 20ºC. What mass of the crystal were deposited. (1mk)
Mass at 70ºC - Mass at 20ºC
155-30
125g
- What is permanent hardness of water? (1mk)
- Define the following terms
-
- The set-up below is used to investigate the properties of hydrogen.

- On the diagram, indicate what should be done for the reaction to occur (1mk)
Heating of copper (ii) Oxide to be shown on the diagram - Hydrogen gas is allowed to pass through the tube for some time before it is lit. Explain (2mks)
To drive out air because mixture of air and hydrogen is explosive when lit
- On the diagram, indicate what should be done for the reaction to occur (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction that occurs in the combustion tube (1mk)
CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(g) - When the reaction is complete, hydrogen gas is passed through the apparatus until they cool down . Explain (2mks)
To prevent re-oxidation of hot copper by the atmospheric oxygen - What property of hydrogen is being investigated? (1mk)
Reducing agent - What observation confirms the property stated in (v) above? (1mk)
Black copper (ii) Oxide turns to brown showing that copper (ii) Oxide has been reduced to copper - Why is zinc oxide not used to investigate this property of hydrogen gas? (1mk)
Zinc is more reactive than hydrogen and therefore cannot be reduced by hydrogen
- The set-up below is used to investigate the properties of hydrogen.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Lanjet Joint Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
