INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and index number in the spaces provided above
- Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided above
- This paper consists of three sections: A, B and C
- Answer all the questions in section A and B and any two questions from section C
- Do not remove any pages from this booklet
For Examiner’s Use Only
|
Section |
Question |
Maximum Score |
Candidate’s Score |
|
A |
1 – 18 |
30 |
|
|
B |
19 – 23 |
20 |
|
|
C |
20 |
||
|
20 |
|||
|
Total Score |
90 |
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided
- State two ways in which agriculture contributes directly to the development of industries (1mk)
- What is a micro catchment ? (½ mk)
- State any three details contained in a delivery note (2mks)
- Outline any four problems farmers face when marketing their products (2mks)
- Name three sites for agro forestry trees (1 ½ mks)
-
- State two ways in which land consolidation improves farm management (1mk)
- State four advantages confers to a farmer with land title deed (2mks)
- Give four reasons for earthing up some crops (2mks)
- Give two reasons for testing soil in the farm (1mk)
- List four examples of variable inputs in maize production (2mks)
- Name four books of account kept by a farmer (2 mks)
- Give two functions of the Agricultural Finance corporation (AFC) (2mks)
- State two common symptoms of viral infection in crop (1mk)
- State four conditions under which opportunity cost equals to zero (2mks)
- Name four factors that may affect the selectivity and effectiveness of herbicides (2mks)
- Give two means by which water can be conveyed from the place of storage to where it is needed on the farm (1mk)
- List four pieces of information likely to be found in a field operation record (2mks)
- Give four qualities of good silage (2mks)
- A farmer was advised to apply 200kg of CAN/ha, while top dressing bean crop CAN contains 21% N Calculate the amount of CAN applied per hectare (2mks)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided
- Below are diagrams of common weeds on the farm Use them to answer the questions that follow
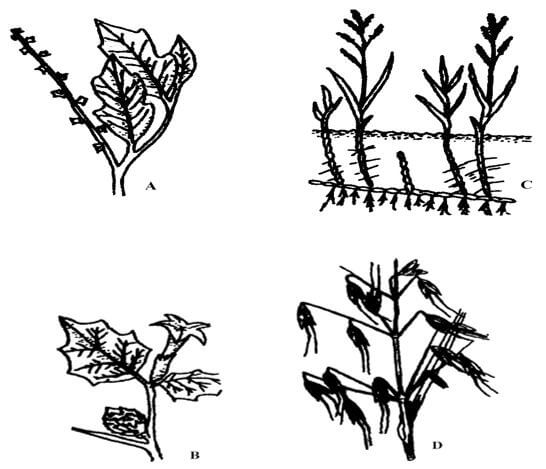
- Identify the weeds A, B, C and D (1mks)
A
B - Give one negative effect of weed labeled B in livestock (1mk)
- Suggest the most appropriate method of controlling weed labeled D (1mk)
- Identify the weeds A, B, C and D (1mks)
- The diagram below illustrates a method of collecting soil samples from a field
- Identify the method illustrated above (1mk)
- Describe four steps that should be followed when collecting soil samples (2mks)
- State two precautions a farmer should take when collecting a representative soil sample from the field for testing (1mk)
- The diagram below shows a method of forage preservation
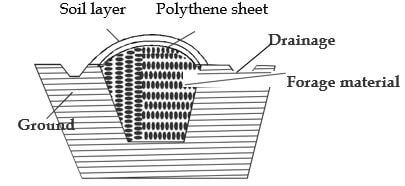
- Identify the structure above (1 mk)
- State the form in which the forage is preserved as illustrated above (1 mk)
- Give the role played by each of the following in the structure above
- Polythene sheet (1 mk)
- Drainage (1 mk)
- Name two other methods of forage conservation (1 mk)
- The document shown below is a sample of a delivery note Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow:

- Name the column labeled A and B (1mk)
A
B - What is the purpose of this document in business transaction? (1mk)
- Outline four details that the document should contain for it to be complete (2mks)
- Name the column labeled A and B (1mk)
- Study the illustration in the diagram below and answer questions that follow
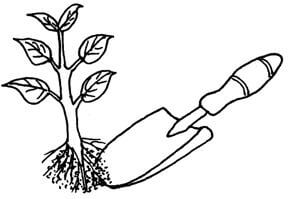
- Identify the practice being illustrated above (1mk)
- State three activities that should be carried out for successful results in the practice shown above (3mks)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any two questions from this section in the spaces provided after question 26
-
- Explain the terms risks and uncertainties in farming (2 mks)
- State the various risks and uncertainties farmers face in fanning (12 mks)
- Explain various ways in which farmers adjust to risks and uncertainties in farming (6mks)
-
- Describe the characteristics of ideal agroforestry tree species (10mks)
- Explain five physical methods of pest control (10mks)
-
- The following information was extracted from Bidii farm’s book records as at 31st December 2022 The farm had borrowed a long term loan of 1 million from the co-operative bank and owed Ksh10,000 to the co-operative society shop for coffee sprays and cattle feeds The farm is owed Ksh10,000 for milk delivered to New KCC Salaries amounting to Ksh9,500 had not been paid The valuations of the farm were as follows
Item Ksh
Cattle 125,000
Goats 19,000
Poultry 35,000
Coffee trees 95,000
Equipment 40,000
Farm buildings 145,000
Stored cattle feed 4,000
Stored cattle spray 21000
Money in cash box 2,000
Land valued at 600,000- Prepare a balance sheet for Bidii farm as at 31st December, 2022 (7mks)
- Show whether Bidii farm was solvent or insolvent (1mk)
- Explain your answer in (ii) above (1mk)
- Explain principles governing formation of cooperatives (8mks)
- Describe three advantages of mixed stand of pastures (3mks)
- The following information was extracted from Bidii farm’s book records as at 31st December 2022 The farm had borrowed a long term loan of 1 million from the co-operative bank and owed Ksh10,000 to the co-operative society shop for coffee sprays and cattle feeds The farm is owed Ksh10,000 for milk delivered to New KCC Salaries amounting to Ksh9,500 had not been paid The valuations of the farm were as follows
Marking scheme
-
- Provision of raw materials;
- Provide a market for industrial good
- Provides capital for starting industries; (2 x ½ ) = 1mk
First 2 correct
- A Micro catchment is a structure constructed in the farm to collect and trap run-off water for productive use.
-
- Details contained in a delivery note. (1 ½mk)
- Date of delivery of goods
- Means of delivery
- The quantity of goods delivered.
- The recipient of the goods are received
-
- Problems farmers face when marketing their agricultural products. 2mks
- Most agricultural products are bulky. The bulkiness reduce the quantity that can be transported.
- Agricultural products are seasonal in nature and are abundant only during harvest time and scarce when out of season. This result to many produce going to waste.
- Most agricultural products require to be stored in well designed and constructed structures. Most of the product go to waste due to poor storage facilities.
- Sites for agroforestry trees. (1 ½mks)
- Boundary/Borders
- Homesteads
- River banks
- Terraces
- Slopes
-
-
- saves time
- Makes easy for sound farm plan
- Easy supervision in the farm
- Facilitates mechanizations
- Advantages of owing a title deed (2mks)
- Reduces land disputes.
- It is an official prove of land ownership.
- Can be used as security for loans
- Confers full rights of ownership hence act as incentive to invest on long term projects.
- How to increase light intensity in the field crops
-
-
- promotes tuber expansion
- Conserve moisture
- Control soil erosion
- Provides anchorage
-
- To establish the nutrients those are deficient in the soil.
- To determine the soil pH and hence correct it in case it is too high or too low.
- To establish a suitable crop that can be grown in a given area.
- To determine the type of the soil
-
- Seeds
- Fertilizer
- Pesticides
- Labour
- Fuel (4 x ½ = 2mks)
-
- journal
- Cash book
- Ledger
-
- Providing agricultural credit to farmers at reasonable interest rates with a grace period;
- Providing technical services to the farmers to ensure the best utilization of the borrowed capital.
- Ensure repayment of the loans by farmers
-
- Mosaic/leaf chlorosis;
- Mottling;
- Leaf curling;
- Stunting/ resetting/ short internodes;
- Malformation/ distortion of parts; (2 x ½ = 1mk)
First 2 correct
-
-
- where there is no alternative
- Gift from friends
- Free goods
-
-
- Rooting system;
- Growing points;
- Stage of growth of plant;
- Leaf angle;
- Height difference;
- Leaf texture; (4 x ½ = 2mks)
First 4 correct
-
- By transporting it in containers (by vehicles / animals);
- By piping;
- By use of canals/channels/furrows; (2 x ½ = 1mk)
First 2 correct
-
- Season;
- Crop grown/variety;
- Ploughing date;
- Inputs used;
- Pest controlled/method;
- Disease controlled/method;
- Weeds controlled /method;
- Harvesting date
- Yield
- Planting date
- Plot/field number
- Area of plot/land (4 x ½ = 2mks)
First 4 correct
- Factors that determine quality of silage (2mks)
- Type of forage/crop used Stage of harvesting
- Presence of air during ensiling/presence of moulds/bad smell.
- Texture
(4 x ½ = 2mks)
First 4 correct
- If 100kg of CAN → 21kgN
∴ 200 kg of CAN → 200 x 21
100
= 42kgN (2mks) -
- A – Double thorn/ Oxygonum sinuatum;
B – Datura / Thornapple / Datura stramonium
C – Wild oats / Avena fatua
D – Couch grass / Digitaria scalarum (4 x ½ = 2mks) - Poisonous (1mk)
- Using herbicides eg Dalapow, MCPA or Glyphosphate (1mk)
- A – Double thorn/ Oxygonum sinuatum;
-
- Zigzag method (1mk)
-
- Clear vegetation from sampling spot;
- Make a vertical cut 15 – 20cm deep for crop land / 5cm in pasture land;
- Put the soil in clean polythene bag using different parts of the field (15 – 20 spots;
- Repeat the above steps in different parts of the field;
- Mix the soil from different spots thoroughly and dry it
- Take a sub-sample from the mixture for testing in the laboratory
(4 x 1= 4mks)
-
- Avoid any contaminations with the soil e.g ash from cigarettes;
- Avoid sampling soils from unusual areas such as ant-hills, manure heaps;
- Avoid mixing top soil with subsoil; (2 x ½ = 1mk)
-
-
- Identification of structure
Trench silo
( 1 x 1 = 1mrk)
Form in which forage is presented as illustrated above ˗ Silage 1x1 = lmk
Role played bv:-
Polythene -keep the structure air-tight/
Prevents rainfall from getting in ( l x l = l mrk) - Drainage -Drain off rain water/prevents entry of water into the silage ( 1 x 1 = 1 mrk)
Two other methods of forage conservation
Hay
Standing forage / hay(2 x 14 = 1 mrk
- Identification of structure
-
-
- A – particulars/ Description; ( ½ mk)
B – Quantity of goods delivered; (½mk) - This document is written by the seller and always accompanies goods to be delivered to serve as evidence that goods have been physically delivered from the supplier to the buyer.
-
- The date of delivery;
- The quantity and type of goods delivered;
- The name of the supplier and the buyer;
- The method of delivery
- The person who delivers/reseives the goods
- Condition in which the goods are received;
- Delivery note serial number; (4 x ½ = 2mks) First 4 correct
- A – particulars/ Description; ( ½ mk)
-
- Lifting of a seedling; (1mk)
-
- Watering the nursery bed thoroughly before lifting;
- Lifting the seedling using a garden trowel/lifting the seedling with a ball of soil on the roots;
- Lifting the seedlings in the evening/on a cloudy day;
- Select only healthy and vigorously growing seedlings; (3 x 1 = 3mks)
-
- risks and uncertainities (2mks)
- Risk is the divergence between expectations and the actual outcome / difference betweenwhat a farmer could predict and the actual outcome
- Uncertainity is a state of imperfect knowledge about future events or outcome / a state of not knowing about the future events
- Types of risks (12mks)
- Weather changes eg drought
- Fire or arson on farm produce
- Theft of crops or livestock
- Accident to employer or employees
- Outbreak of pests and diseases
- Health of the farmer
- Types of uncertainties
- price fluctuations
- uncertainty of physical yields
- uncertainty of new production techniques
- breach of contract
- obsolescence eg of machinery
- ownership uncertainties eg about security of tenure
- government policy
- transport reliabilities
- unavailable labor or inputs
- Ways in which farmers adjust to risks and uncertainties (6mks)
- decreasing inputs applied so that incase of failure it will be less than if maximum amount was used / input rationing
- diversification so that incaseof failure of an enterprise thefarmer will besupported by others
- flexibilities in farm organization and production methods ,that is the ability of the farmer to change from producing one product to another
- adopting modem methods of production /mechanization
- insuring production
- contracting production
- risks and uncertainities (2mks)
-
-
- Nitrogen fixing ability – The trees should be preferably legumes. They should be capable of fixing Nitrogen into the soil for use by other crops;
- Fast growing ability – trees chosen should be fast growing and early maturing so that they can be put into other uses – thus should have a high biomass production e.g fuel wood
- Multipurpose nature – the chosen trees should be able to meet other uses such as provision of fuel woods, fodder, poles and timber.
- By – product production – The best agroforestry tree species should be able to produce economic products and by-products which can be used or sold for income e.g those producing edible leaves, fruits, medicinal products, poles and fodder.
- Deep rooted with a narrow root zone – when agro-forestry trees have deep roots, they acquire their nutrients from lower soil horizons where most plant roots do not reach-hence minimal competition for nutrients;
- Non-competitive ability with main crop- a good agroforestry tree species should not compete with the main crops for light and nutrients unnecessarily.
- Nutritious and palatable – trees used for this purpose should be both nutritious and palatable as leaf fodder for livestock use.
- Easily coppiced – the trees species which will be able to regenerate after cutting back for pruning are preferred. (5 x 2 = 10mks)
(Characteristic – 1mk, explaination – 1mk)
-
- Use of lethal temperature – These are too hot or too cold conditions which kill pests;
- Proper drying of produce – drying of grains makes them too hard for pests to penetrate;
- Flooding – drowns underground pests eg moles and cutworms;
- Suffocation – pumping carbon(IV) oxide into hermetic Cyprus bins deprives pests of oxygen;
- Physical destruction – done through trapping, hand picking and killing them.
- Use of scare crows/ devices – for scaring large animals and birds from crop fields;
- Use of physical barriers – Barriers such as trenches fences, rat quards prevent pests from getting into crop fields or stores.
- Use of electromagnetic radiation – electromagnetic radiations are used to kill insect pests through deactivation of enzymes (5 x 2 = 10mks)
(Method – 1mk, Explanation – 1mk)
-
-
-
-
(7mks)LIABILITIES
ASSETS
Ksh.
Cts.
Ksh.
Cts
Current Liabilities
Current Assets
Debts payable to co-operative society
10,000
00
Money in cashbox
2,000
00
Salaries
9,500
00
Debt receivable from new KCC
10,000
00
Total Current Liabilities
19,500
00
Stored cattle spray
2,000
00
Long Term Liabilities
Poultry
35,000
00
Bank loan
1,000,000
00
Goats
19,000
00
Cattle
125,000
00
Total Liabilities
1,019,500
00
Stored cattle feed
4,000
00
Total current Assets
197,000
00
Net worth
57,500
00
Fixed Assets
Coffee trees
95,000
00
Equipment
40,000
00
Farm buildings
145,000
00
Land valued
600,000
00
Total Fixed Assets
880,000
00
Total Assets
1,077,000
00
TOTAL
1,077,000
00
TOTAL
1,077,000
00
- Bidii farm is solvent (1mk)
- The value of assets is more than that of the liabilities hence the farm can meet all her liabilities and still have net capital (1mk)
-
-
- open membership
- equal rights.
- principles of share limit.
- interest on shares.
- withdrawal from membership
- loyalty.
- education.
- co-operative principle.
- non-profit motive.
- three advantages of mixed stand of pastures.
- Economizes on nitrogenous fertilizers.
- Provide a good soil cover hence control soil erosion.
- High nutritive value.
- High herbage yield.
- Diversification.
-
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Sunrise 2 Evaluation Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
