INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
- Write your name and index number in the spaces provided.
- Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided
- This paper consists of three section A,B and C
- Answer all the questions in section A and B
- Answer any two questions in section C
- All the questions should answered in the spaces provided
FOR EXAMINER’S USE ONLY
|
SECTION |
QUESTIONS |
MAX SCORE |
CANDIDATES SCORE |
||
|
A |
1-18 |
30 |
|
||
|
B |
19 - 23 |
20 |
|
||
|
C |
|
20 |
|
||
|
20 |
|
||||
|
TOTAL |
90 |
|
|||
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
-
- What is a notifiable disease (1mk)
- Name two notifiable diseases of cattle (1mks)
- Give four faults in the eggs that are detected during egg candling (2mks)
- Give two reasons for maintaining farm tools (1mk)
-
- Give two roles of litter in a deep litter poultry house (1mk)
- State one role of footbath in a poultry house ( ½ mk)
- Mention four advantages of embryo transplant (2mks)
- Give functional difference between the following tools (2mks)
- Stock and die and pipe cutter
- Ball pein hammer and claw hammer
- State four features of an ideal calf pen (2mks)
- State four signs of furrowing observed in pigs (2mks)
- State three methods of restraining cattle ( 1 ½ mk)
- Give four ways of stimulating milk let down in a dairy cow (2mks)
- Differentiate between cropping and harvesting in fish keeping. (1 mark)
- Name the dairy breed of cattle which (1mk)
- Produces the highest yield of milk
- Produces milk with the highest butterfat content
- State four pre-disposing factors of mastitis (2mks)
- Name any two renewable sources of power in the farm (1mk)
- State four factors considered when computing a ration for livestock on the farm(2mks)
- State two ways in which digestion of food in pigs differs from that in Ruminants(2mks.)
- State two conditions which would make it necessary to feed bees (1mk)
- State two ways of caponization in poultry ( 2mks)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section in the spaces provided
- The diagram below is a cross section of part of a cow’s udder.
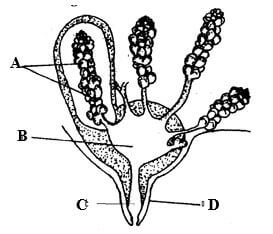
- Label the parts marked A,B,C and D (2mks)
A
B
C.
D. - Name two hormones that control milk - let down in a dairy cow. (2mks)
- What is a dry cow therapy (1mk)
- Label the parts marked A,B,C and D (2mks)
-
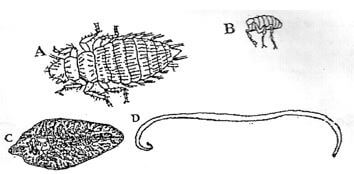
- Identify each of the parasites of livestock shown below. (2marks)
A
B
C
D - What is the difference between parasites A and Band parasites C and D? (1mark)
- Suggest an effective control measure of the parasites labelled C (1mark)
- Identify each of the parasites of livestock shown below. (2marks)
- Below are illustrations showing the behavior of chicks in various brooders. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow.
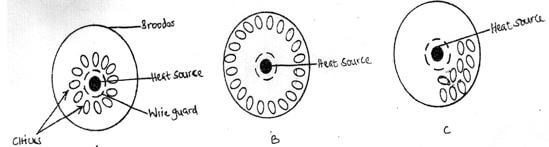
- State the environmental problem in each brooder as illustrated by the behavior of the chicks (3marks)
A
B
C - State two ways of overcoming the problem in B (2marks)
- Why brooder is recommended to be round in shape (1mks)
- State the environmental problem in each brooder as illustrated by the behavior of the chicks (3marks)
- Below is a diagram of a farm implement
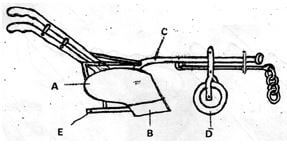
- Identify the implement (½ mark)
- Label the parts marked A, B, C, D and E. (2 ½ marks)
A..
B.
C.
D..
E - State the functions of the parts labelledC and E (2mks)
SECTION C (40 mks)
Answer any two questions from this section in the spaces provided after question
-
- Discuss the management of layers from one day old to the start of laying in a deep litter System. (14mks)
- Explain management practices that would improve fish production. (6mks)
-
- State the daily maintenance and servicing of a tractor (10marks)
- Describe the structural requirement to be considered when constructing a calf pen (10marks)
-
- Explain four factors that affect digestibility of food in livestock. (8mks)
- Explain the essentials of clean milk production (7mks)
- State five disadvantages of natural method of mating. (5mks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Notifiable disease is a highly contagious and infectious diseases whose out break must be reported in police / livestock authority. (1 mk)
-
- Rinder pest
- Foot and mouth disease
- Newcastle
- African swine flu
- Gumboro
- Fowl pox (2x ½=lmk)
-
- double yolk
- meat spot
- hair cracks
- broken egg shell
- very porous egg shell
- very small size of air space (4x½= 2 mks)
-
- To make them efficient
- To make the last long
- To avoid injury
- To avoid damage (2 x ½ = 1 mk)
-
-
- Absorb moisture
- keep the floor warm (2 x ½=lmk)
- To disinfect the feet of the farmer (½mk)
-
-
- possible to implant embryo from a high quality female to less quality female hence improving performance of off springs.
- Stimulates milk production in female that was not ready to produce
- A highly productive female can be spread over a larger area to benefit many farmers.
- It is easier to transport embryo in test tubes than the whole animal
- Embryo can be stored for long periods awaiting availability of a recipient female. (4x½=2mks)
-
- stock and die —used for cutting threads on pipes Pipe cutter — used for cutting PVC pipes 1 mark
- Ball pein hammer — used for riveting and striking the head of cold chisel /straighten bent metal surface. Claw hammer —used for driving and removing nails from wood /straightens bent nails ( 1 mk)
- Factors that determine water intake
- Type of feed
- Physiological status of the animal
- Ambient temperature
- Species of the animal
- Age of the animal/size /weight
- Level of production (4 x½=2 mks)
-
- Signs of furrowing in pig (2mk)
- Restlessness
- Vulvas swells and reddens
- Udder becomes full with a milky substance
- Sow starts to build a nest by collecting some bedding at one corner
- Signs of furrowing in pig (2mk)
-
- a crush
- ball ring and a lead stick
- with halters
- use of lead yoke
- ropes (3x½=l½mks)
-
- Washing the udder with warm water
- Familiar noises
- Sucking from calf
- Feeding with concentrates
- Presences of milk man
- Presences of milk utensils
- Milking at regular times (4x ½ =2mks)
- Cropping is the removal of fish of marketable size from the pond while harvesting is the removal of all the fish from the pond.
-
- Friesian (½mk)
- Jersey (½mk)
-
- Ages
- stage of caetation period
- udder attachment / loosely/ pendudus
- incomplete milking
- Mechanical injuries
- poor sanitation
- poor milking technique (4 x ½ = 2 mks)
-
- Solar energy
- Wind power (2 x ½= lmk)
-
- Body size / body weight
- Available feeds stuffs
- Nutrient composition of feedstuffs available
- cost of feeds
- ingredients required
- level of production of animals
- Age /stage of growth
- Type of production e.g. broiler (4 x½= 2mks)
-
- Pigs Ruminants
- Do not chew cud chew cud
- cannot regurgitate regurgitate food
- cannot digest cellulose can digest cellulose
- enzymatic digestion in the mouth presence of ptyalin No ptyalin hence no enzymatic digestion in the mouth
- Most digestion and absorption takeplace in the Most digestion and absorption takes place in small intestine rumen
-
- When flowers are not available / during dry season
- When a big number beehive is kept (2 x ½= 1 mk)
-
- injecting the male chick with stilbestrol
- Inserting pellets of female sex hormones undernearth the skin of male chick
-
-
- A-Aveoli
- B-Gland cistern
- C-Teat Cistern
- D- Teat
-
- Oxytocin
- Adrenalin
-
-
- identification of
- A – Lice
- B – Flea
- C – Liver fluke / fasciola SSp ( 4x ½ =2mks)
- D- Roundworm / Ascaris SSP
- Differences
- A and B are External / Ectoparasites (2x ½ =1mk)
- C and D are internal parasites / Endoparasites
- Effective control liver fluke
- Eradicate water snail / round snail/ lymnac SPP
- Deworming / Use of Antihelruintics (1x1=1mk)
- Draining marshy areas
- identification of
-
-
- A- very cold
- B- very hot
- C- Draught from one side (3x1=3mks)
-
- Reduce the amount of heat
- Increase ventilation (2x1=2mks)
- To avoid suffocation of chicks (1mk)
-
-
- Farm implement – ox- plough ( ½ mrk)
-
- A- Mould board (2 ½ mks)
- B – Share
- C – Main beam
- D - Land – wheel
- E – Land – side
- Function of (1 mrk)
- C – Attachment of all parts
- Adds weight for deeper ploughing
- E – Stabilizes plough against thrust by furrows slices (1 mrk)
-
- Disinfect the brooder 2 — 3 days before the day old chicks are brought in.
- Spread newspaper over the litter to prevent chicks from eating litter. V1
- Spread some food on the newspaper so that chicks can learn to eat.
- Remove the newspaper when the chicks have learnt to eat from feeders
- Feed on chkk mash upto 8” week.
- Gradually introduce growers mash from week z
- Debeak (on the 1th day)
- Keep chicks in the brooder for 6—8 weeks.
- Provide and maintain source of heat as necessary.
- Provide adequate clean water
- Vaccinate against common diseases especially New castle.
- Control external parasites
- Insulate sick chicks
- Treat sick chicks.
- Introduce roosts for perching (on 6th week)
- Introduce grit / sand to help in digestion.
- Hang green vegetable to keep them busy.
- Feed on growers marsh to 18th — 20th week.
- Gradually replace by layers mash from 18°’ week.
- A specific day/week must be indicated to award mark. (1 x½= ½mks)
-
- Ensure correct and adequate supply of food for fish through regular pond fertilized on.
- Control stocky rate to avoid overpopulation
- Control water pollution by removing debris
- Lime the fishpond regular.
- Maintain a steady supply of flowing water. This ensures that there is sufficient
- oxygen in the water
- Maintain appropriate level of water in the pond by regulating the flow of water in and out of the pond.
- Harvest the fish at the right stage of maturity.
- Control predators by facing off the pond
- Remove weed or grass that grows on the pond lining.
- Ensure correct and adequate supply of food for fish through regular pond fertilized on.
- Disinfect the brooder 2 — 3 days before the day old chicks are brought in.
-
- Daily maintenance and servicing of a tractor (10x1=10 mrks)
- Check engine oil using dip stick and adjust accordingly
- Check fuel level
- Check water level in radiator
- Check level of electrolyte in the battery
- Check for loose nuts and bolts and tighten
- Grease moving parts
- Check tyre pressure
- Check and remove sediments in sediment owl
- Check fan belt tension and adjust accordingly
- Check the breaks and maintain break fluid level on recommended
- Structural requirements in construction of a calf pen (10 mrks)
- Concrete floor – for easy cleaning.
- Spacious – to allow exercise and placement of equipment
- Singly – crawl spread of parasites
- Preventing licking one another and to control formation of hair balls
- Proper drainage – prevent dampness which predispose to infections
- Drought free – prevent cold winds which predispose to pneumonia
- Leak proof – Avoid damp conditions / wetness which predispose to navel ill; pneumonia
- Warm and dry – to avoid infections
- Well ventilated – allow proper air circulation in the structure
- Lockable / secure – provide security against predators / thieves
- Daily maintenance and servicing of a tractor (10x1=10 mrks)
-
- Factors affecting digestibility of food in livestock
- Chemical composition of the feed e.g. % of lignin or cellulose will influencedigestibility
- The form in which the feed is offered to the animal e.g. crushed maize is more digestible than whole grain.
- The species of the animal e.g. the digestibility of grass is higher in sleep than inPigs.
- The ratio of energy to protein will affect digestibility. The higher the ratio the lower the digestibility
- The quantity of feed already present in the digestive system of an animal.
-
-
- Healthy milking heard
- Should be free from milk-borne diseases such as brucellosis‘ and tuberculosis which is easily transmitted to man
-
- Clean milking cows
- The flanks underline and the whole udder should be washed and dried thoroughly before milking
-
- Healthy and clean milk –man
- A milker suffering from any contagious diseases should not be allowed to milk or handle milk
-
- Clean milking shed
- Milking she or palour should be kept clean ,free from dust or odours
-
- Clean milking utensils
- The milking utencils and equipments should be seamless, smooth with joinfillefacilitate easy cleaning
-
- Milk filtration /cooling and storage to 5ºC immediately after milking immediately after milking
- Milk should filtered and cooled down
- Avoid flavours in milk
- Bad flaours in milk are caused by foodstuffs and ovulation should be avoided before milking (7 x1 = 7mks)
-
- Disadvantages of Natural method of mating
- High chances of in breeding or in breeding is not controlled.
- High chances of breeding disease transmission ie brucellosis or parasites such as trichonomas spp
- Males require extra pasture to feed on.
- Large males can injure small females.
- A lot of semen is wasted as single ejaculation produce semen that can serve several cows.
- It is cumbersome and expensive to transport a bull to hot areas to serve cows. (5 x 1 = 5mrks)
- Factors affecting digestibility of food in livestock
Download Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Sunrise 2 Evaluation Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
