QUESTIONS
SECTION A (20MARKS)
-
- Study the picture below and use it to answer the question that follows;
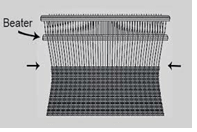
Identify the deformity and state any one way of preventing the above deformity (2mks) - Distinguish between dabbing and brush stroking in painting(2mks)
- Explain two roles of packaging design. (2mks)
- State and explain any two types of fires in pottery. (2mks)
- State the importance of spacers in design and production of ornaments. (1mk)
- Explain the term frottage as applied in printing (1mk)
- Study the picture below and use it to answer the questions that follow;
- state any two uses of line in the above illustration.(2mks)
- explain any two classifications of graphic design symbols (2mks)
- Illustrate a foreshortened manmade object in the space below. (2mks)
- Give examples of the following colour schemes. (2mks)
- Complementary
- Split complementary
- Explain two ways in which colour can be used to create aerial perspective. (2mks)
- Study the picture below and use it to answer the question that follows;
SECTION B (25MARKS)
- Study the picture below and answer the questions that follow;

- Identify the type of sculpture
- State two characteristics that would make one use the material above
- Explain the academic role of sculpture in a school.
-
- Explain the term “caricature”
- State two characteristics of a caricature
- What is the significance of a caricature to visual communication?
- Outline five steps involved in making a papier mache sculpture
-
- State the role of a fixative in fabric decoration
- Distinguish between a tjap and a tjanting
- Distinguish between structured and applied design in fabric decoration
-
- Name three components of a letterhead.
- Explain two functions of a letterhead.
SECTION C 15 MARKS
Answer any one question in this section.
Write your answer in the space provided after question 9.
-
- What is the difference between a logo and a trademark? (2mks)
- Outline the process of making a logo for a beverage manufacturing company (13mks)
-
- Give the other terms used for primary and secondary clays respectively. (1mk)
- Give two differences between primary and secondary clays (4mks)
- Explain the process of clay preparation (10mks)
-
- Define the following terms as used in ornaments and jewellery:
- Ornaments. (1mk)
- Jewellery. (1mk)
- Ornamentation (1mk)
- Beadwork (1mk)
- Explain the following beadwork techniques with the help of diagrams.
- Strung beadwork. (2mks)
- Strung and knotted beadwork(2mks)
- Woven beadwork (2mks)
- Top stitched beadwork (2mks)
- The function of an ornament determines its style. Discuss. (3mks)
- Define the following terms as used in ornaments and jewellery:

MARKING SCHEME
-
- wasting
- avoid over tightening wefts
- fixing the side waps to the loom (any 1x1 =1mk)
- Dabbing- tapping the brush with paint on the surface to achieve dotted effects
Brush stroking- making distinct movements in desired directions using brush loaded with paint -
- To tell more about the product
- To advertise the product/ give good qualities of the product
- Attract potential customers
-
- Bisque firing – firing at low temperatures to attain brittle state
- Glaze fire – firing to fix Glaze
- Decorative fires- firing to fix decorative oxides (any 2x1=2mks)
- to separate bands of colours of the beads used
- Frottage – printing by placing a textured object beneath paper and rubbing with a medium to transfer desired impression to paper
- uses line
- show movement
- outline form
- create texture
-
- Road signs
- sports symbols
- Identification symbols
- Visual symbols (any 2x1 =2mks appropriately explained)
- Applying the effects of depth, distance and space on an object drawn on a 2D surface
Appropriate sketch - Complementary colours with adjacent colours to either of the complementary colours e.g red, green, blue green and yellow green or red, green, red purple and red orange. (2mks)
- Sharp contrast in the foreground which reduces gradually to the background.
Rich and vibrant shades of colours in the foreground which looses intensity towards the background.
- wasting
-
- sculpture in the round (1mk)
- Strength – stones are strong and long lasting
colour – stones have different colours for aesthetic value (2x1= 2mks) - Used to explain concepts in other subjects e.g models of body parts in biology. (2mks)
-
- A branch of art which deals with exaggeration of people based on character for comic effect.
- Mostly dwell on weak points, failures, moral weakness deformities, poor reasoning etc.
Communicate ideas symbolically to produce a form of satirical story with a hidden meaning. - To discourage the society from the social evils.
-
- Soak paper in water for sometime to soften then smash
- Add glue and knead thoroughly
- Design the sculpture to be made and make an armature for it
- Make the body of the sculpture using the armature as the support
- Give the sculpture its shape and details then smoothen and leave to dry.
-
- To make the dye adhere permanently into the fibres of the fabric
- tjap- metal block with decorative reliefs used to stamp hot wax on fabric before dyeing is done to produce the patterns.
Tjanting- simple tools with spouts used to carry hot wax and trail designs on the fabric before dyeing. - Structured design – Design is made during weaving of fabric
Applied design – decorative designs made on the finished fabric e.g printing
-
-
- Name of company/organization/institution
- Logo of company/ institution
- Physical and contact address
- Motto/slogan/mission and vision
-
- To identify an institution
- To make a document authentic
-
-
- Logo- graphical symbol used to identify an institution/ organization
Trademark- graphical symbol/name used by a company on its product/s or services to show that they originate from a unique source. -
- identify the unique qualities of the beverage.
- discuss the qualities with the client to give a way forward
- research on the qualities required of the logo
- make preliminary sketches/ roughs
- refine the sketches to a single unit
- establish the best method of producing the logo according to the clients specifications eg. Free hand or by use of a computer.
- identify the materials and tools to be used.
- draft a schedule that is workable
- refine the logo and introduce meaningful colours
- present it to the client for verification and any changes
- ork on the corrections to the final product
- present the final product to the client for unveiling
- Logo- graphical symbol used to identify an institution/ organization
-
- Residual and sedimentary clays
-
Primary clays Secondary clays High fire
Have low plasticity
Found near original rock source
Rough/coarse
Has creamy, whitish translucent effect when fired
Highly porousLow fire
High plasticity
Obtained away from original source having been carried away by erosion
Fine/smooth
Opaque when fired
Less porous -
- digging- done from localities rich in clay
- slaking- soaking clay in water for a period of 3-4 days to reduce the lumps into a homogeneous mass
- Mixing- mixing clay by beating using a wooden stick/ pugmill as additives are added to form a malleable mass
- Wedging- kneading clay which is sticky to touch to expel air and render it into a smooth consistency
- Storing- wedged clay is then stored in polythene bags or plastic buckets with lids to prevent id from drying out. At this stage its ready for use. 1x2=10
-
-
- Objects that enhance the appearance of a person/objct
- a general term used for ornaments worn on human body
- the process of ornamenting items eg clothes, human bodies, clothing accessories eg belts, watches etc
- the use of beads in ornament construction and ornament embellishment
-
- Stringing beads using a strong wire or fishing rod
- Stringing beads and knotting at intervals
- Rows of warp threads hold rows of beads in place
- Beads are strung and stitched onto leather/fabric
-
- more intricate ornaments are highly used for high end functions eg weddings etc
- some ornaments are made with special features for specific purposes eg the glowing of the catholic rosary in the dark is symbolic
- beadwork used in men’s ornaments/jewellery is generally larger in size and less shinny than the ones used in women’s jewellery because the ones worn by women are usually more fragile and intricate.
-
Download Art & Design Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Kakamega Evaluation Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
