QUESTIONS
SECTION A
-
- Define mining (2marks)
- Give three ways in which minerals occur (3marks)
-
- Apart from tropical hardwood forests name two other types of natural forests (2marks)
- State three characteristics of tropical hardwood forests that make it difficult to exploit (3marks)
-
- Name two breeds of dairy cattle reared in Kenya (2marks)
- State three human factors that favour dairy farming in Denmark (3marks)
-
- Differentiate between fishing and fishery (2marks)
- State measures used by the Kenya government to conserve marine fisheries (3marks)
-
- State three physical factors which influence the location of settlements (3marks)
- Identify two functional zones of an ideal urban Centre (2marks)
SECTION B: ANSWER QUESTION 6 AND ANY OTHER TWO QUESTIONS
- The table below shows tonnage of trade items in Kenya from various parts of the world in 2005 and 2006. Use it to answer question (a) and (b)
Place of origin Tonnage per year 2005 2006 Europe 942000 985000 Africa 120000 154000 Asia 97000 128000 North America 94000 103000 Australia and New Zealand 19000 24000 All other countries 29000 41000 TOTAL 1,301,000 1,435,000 -
- Which continent had the highest increase in tonnage of trade items in Kenya between 2005 and 2006 (2marks)
- Calculate the percentage increase in trade tonnage from Australia and New Zealand between 2005 and 2006 (2marks)
- Draw a divided rectangle 15cm long to represent the tonnage of trade items in Kenya in 2006 (8marks)
-
- State two advantages of using divided, rectangles to represent geographical data (2marks)
- State four reasons why in 2005 and 2006 there was higher tonnage for trade items from Europe compared to that from Africa continent (3marks)
- Explain four ways through which the Kenyan government is promoting external trade (8marks)
-
-
-
- State three physical conditions that favour sugarcane farming in Kenya (3marks)
- Apart from Bungoma name two counties where sugarcane is grown on large scale (2marks)
-
- Describe the cultivation of sugarcane in Kenya (6marks)
- Explain four problems facing sugarcane farming in Kenya (8marks)
-
- Give three by-products from sugarcane (3marks)
- Give three uses of sugar (3marks)
-
-
-
- State two farming methods that assists in soil rehabilitation (2marks)
- Give two methods that are used to drain swamps in Kenya (2marks)
-
- Name two rivers that supply water to Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme (2marks)
- Give the method of irrigation used in Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme (1mark)
- Explain how the following factors influenced the establishment of Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme
- Soil (2marks)
- Government policy (2marks)
-
- Describe the process of land reclamation in Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme (4marks)
- State four characteristics of three the polders of Netherlands (4marks)
- Your class intend to carry out a field study on irrigation farming in Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme
- Name two crops that you are likely to identify in the scheme (2marks)
- State two reasons for the need of sampling the area of study (2marks)
- Give two the after study activities you are likely to engage in (2marks)
-
-
-
- What is industrialization? (2marks)
- Name a town in Kenya where each one of the following industries is located
oil refining (1mark)
Paper manufacturing (1mark)
Motor vehicle assembly (1mark)
Textile industry (1mark)
-
- Give five reasons why the development of Jua kali industry is encouraged in Kenya (5marks)
- Explain four factors that led to the development of iron and steel industry in the Ruhr region of Germany (8marks)
- Explain three causes of the decline in the textile industry in Kenya (6marks)
-
-
-
- Give three reasons why road transport is better developed than air transport is East Africa (3marks)
- Name two international airports in Kenya (2marks)
- Explain four factors that have hindered the development of river transport in Africa (8marks)
- The diagram below shows the great lakes -St Lawrence seaway. Use it to answer question C, i) ii) and (iii)
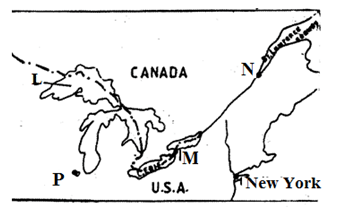
Name- the port marked N and P (2mark)
- the lake marked L (1marks)
- the waterfall marked M (1 mark)
- Explain four benefits of the Great lakes -St. Lawrence’s seaway to the economies of Canada and USA(8marks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals from the earth’s crust
- beds and seams
As weathering products
As alluvial deposits
Veins and lodes
-
- Coniferous forest
Temperature hardwood
Mangrove forest
Mixed forests
Mountain forest - Trees occur in mixed stand
Trees have lianias/buttress roots
Trees are usually heavy
Trees have huge trunks
Trees takes long to mature
Trees grows close to each other / thick forests
- Coniferous forest
-
- Frieshian / Holstein
Jersey
Guernsey
Ayrshire
Alderney
Swiss brown - Availability of markets
Availability of extension services
Well-developed transport/communication network
Plenty of fodder
Advanced technology / skills
Well-developed co-operative movement/ availability of capital
- Frieshian / Holstein
-
- Fishing refers to catching aquatic resources while a fishery is a water body from which aquatic resources are got
- Restocking overfished areas
Licensing fishermen to reduce their number
Enacting laws against water pollution
Standardizing size of net
Banning fishing in certain seasons/ part of the sea
Enforcing international agreements
-
- Water supply
Availability of land
Gently sloping land
Absence of pests/ diseases
Fertile soils
Suitability of climate
Good drainage - Central business district(CBD)
Transitional zone
Industrial zone
Residential zone
Sub-urban zone
- Water supply
-
-
- Europe
- 2006 = 24000
2002 = 1900
Difference = 5000
= 5000 x 100%
1900
= 26.3% or 266/19%
Or 26% - Europe = 985000 x 15 cm = 10.30cm
1435000
African = 154000 x 15cm =1.6cm
1435000
Asia = 128000 x 15cm =1.34cm
1435000
North America = 103000 x 15cm =1.10cm
1435000
Australia and New zea land 24000 x 15cm =0.25cm
1435000
All other countries = 41000 x 15cm = 0.43cm
1435000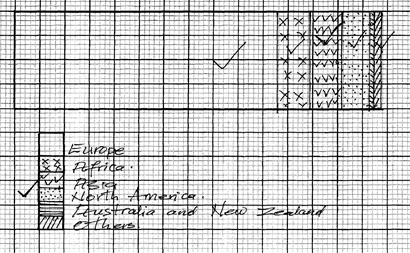
-
- Divided rectangles are easy to interpret
They can be used to represent a wide range of data
Easy to draw
They give a clear visual impression
They allow for comparison - Low level of technology Africa limits production of proceed goods
Different political ideologies among member countries in African restrict trade
Insufficient transport facilities between Kenya and other different countries in Africa limits volume of trade
Political instability / civil war in some part of Africa limit trade
Trade in Kenya still follow pattern i.e. Kenya was colonized by Britain (Europe) hence established trade / political pattern
Ignorance of what is produced in member countries of Africa.
Most of the countries in Africa produce similar goods to that of Kenya hence low volume of trade
- Divided rectangles are easy to interpret
- Signing international trade agreements with other countries like in COMESA to increase volume of export
Establishing the export processing zones (EPZ ) to produce more goods for export
Reducing import duty on raw materials to attract more industrial for products export
Encourages foreign investors to establish industries to increase export of goods
Introduced export compensation scheme on raw materials for producing export goods
Participating in trade fairs and international exhibitions to display export items so as to have a wider market
Improving transport and communication for easy flow of raw materials to the industries /commodities to the market
Looking for new markets especially in the far East to expand export market
Licensing investors willing to engage in export trade
Encouraging industries/ farmers to produce quality goods for export
-
-
-
- High temperature (20-27º C)
Gently sloping land/undulating land
High rainfall (1200-1500mm) well distributed throughout the year
Sunny condition for sugar concentration
Deep well drained day/black cotton soils - Kakamega
Kisumu
Siaya
Busia
Migori
Kwale
- High temperature (20-27º C)
-
- Land is cleared of vegetation and ploughed
Harrowing is done to loosen the large lumps of soils
Shallow furrows are dug 1.2 – 1.8m apart cutting are planted in the furrows
Top dressing fertilizers are applied
Weeding is done regularly/ herbicides are applied
After 18month the cane is ready for harvesting
The cane is cut using pangas
The cut cane is loaded into lorries for transportation to the factory - Pests e.g. termites, white grub/ diseases e.g. ratoon stunting and smut attack the crop and lowers the yields lowering /farmers income.
Prolonged drought often destroys the crops leading to low yields
Poor feeder road in some areas leads to delay in delivery of the cane to the factory lowering the quality / profit to the farmers
High cost of farm inputs reduces the farmers profit margins
Accidental fire/ fire set by arsonists destroy the cane resulting in heavy loses to the farmers
Delay in harvesting reduces the quality / tonnage of the cane reducing the farmers earnings
Flooding of the market by cheap imported sugar causes unfair competition thus lowering demand for locally produced sugar and payment to farmers
Closures of some factories has deprived farmers of their sources of income
Mismanagement of industries leads to low and delayed payments discouraging the farmers
Low / delayed payments demoralizes the farmers
- Land is cleared of vegetation and ploughed
-
- Bagasse
Molasses
Jaggery
Filter cake/ mud
Cane juice - As a sweetener
It is used in baking/ confectionary
Used in soft drinks
Used to make sweets/ ice cream
Is used in production of drugs
- Bagasse
-
-
-
- Soil terracing
Ploughing along the contour
Controlling / Regulating grazing
Planting cover crops
Mixed cropping
Crop rotation
Adding manure/fertilizers
Mulching
Agroforestry - Constructing drainage pipes
Digging open ditches / canals
Pumping out the water
- Soil terracing
-
- Thika
Nyamindi
Murubara - Basin / flood
- Thika
- Soil (2mks)
Presence of black cotton soil which is suitable for cultivation of rice/ retains water for along time
Government policy (2mks)
There was need to keep political detainees busy this made the colonial government to set up the scheme where there was large detention camp -
- Canals are constructed to direct water from rivers Thiba/Nyamindi/Murubara
The land is divided in rectangular portions surrounded by ridges/ bunds
Water is directed into canals then into the paddy fields
The plots is are ploughed/rotavated
The plants remained are buried in the mud to facilitate their decomposition
Leveling of the fields is done ready for planting - The soils are highly desalinated
They are protected by the dykes against gales/sea encroachments
They are surrounded by ring canals to facilitate drainage
They are divided into specific land use activities/rectangular portions
The land is intensively utilized
Horticulture is the predominant agricultural activity
The largely lie below sea level
They are large in size/area/ a crease
They are gently sloping
- Canals are constructed to direct water from rivers Thiba/Nyamindi/Murubara
-
- Rice
Beans
Maize
Tomatoes
Vegetables - To reduce the cost of study
To minimize biasness during the study
To save time during the study
Enables detailed study - Displaying the photographs taken during the field study
Writing a report about the study
Discussing the findings in groups
Reading further on the topic of study
Analyzing the data collected
Presenting the findings
- Rice
-
-
-
- Is the process and pace a country sets to establish industries
- Oil refining - Mombasa
Paper manufacturing - Webuye
Motor vehicle assembly - Nairobi, Mombasa,Thika
Textile industry - Thika, Nairobi,Mombasa,Eldoret,Kisumu,Nakuru, kitui
-
- Mainly produces for local market thus saving foreign exchange
It produces relatively cheap products that are affordable to many improving living standards
It facilitates decentralization of industries thus curbing rural-urban migration
It uses locally available/scrap metals/ recycled raw materials thus reducing cost of imports/conservers environment
Has promoted development of technical skills/innovations useful in other sectors of the economy
It creates employment raising living standards
It requires less capital to establish - Presences of navigable rivers e.g. Rhine/canals which provide cheap transport for bulky raw materials and finished products
Availability of raw materials iron ore /limestone/coal from the rhine valley for use in the industries
Presences of coal in rhine valley / imported petroleum which provided power
Availability of water from River Rhine//Lippe for various industries uses
The dense and affluent population in Germany/ Europe provided a large and ready large market for iron and steel
Highly skilled labour from within the region to work in industries
Availability of capital from rich families/merchants for stabilizing industries
- Mainly produces for local market thus saving foreign exchange
- Large scale importation of second hand clothes has reduced demand for locally produced textile/ second hand clothes are cheaper than locally produced new textile
These has been declined in the production of cotton which has led to limited supply of raw materials for the textile industry
Liberalization of the economy has encouraged business people to import textile from other countries instead of selling locally provided ones
Mismanagement of textile factories has led to closure of some industries
Belief that imported garments are superior to locally produced once has reduced demand for local garments
Decline in the economy has discouraged investors who would set up textile industries in Kenya
-
-
-
- Most vehicles are cheaper to buy and maintain than air crafts
Roads transport is more flexible than air transport
Construction of roads is cheaper than that of airports
Fare / freight charges on roads are lower than that of air transport
Motor vehicles require less skills to operate than aircraft - Jomo Kenyatta international airport / Nairobi
Isiolo international airport
Kisumu international airport
Eldoret international airport
Moi international airport /Mombasa
- Most vehicles are cheaper to buy and maintain than air crafts
- Many river passes through different climatic regions causing fluctuations in river water
Presences of rapids/waterfalls which hinders navigation
\Many rivers are short or shallow making it difficult for movement of water vessels
Presence of floating vegetation/sudd hinders navigation
Silting at river mouths hinder port development
Many rivers pass across political boundaries which hinder river transport development
Low levels of technology hinder process of developing rivers transport -
- N – Quebec
P - Chicago - Superior
- M- Niagara
- N – Quebec
- Dams/reservoirs found along the route provide HEP for domestic/ industrial use
The sea way /Niagara fall attract tourists who bring in foreign exchange used to develop other sector of the economy
Has created employment opportunities in the transport sector of the economy raising the standard of living of the people in the area
Provide cheap means of transport for both imports and export thus encouraging trade
It has led to the growth of towns/ ports which have become focal points for economic activities
There has been extensive industrial development in the area / growth of Pittsburg industrial conurbation due to accessibility to the raw materials
The countries earn revenue from tariffs charged on ships which is used to develop other sectors of the economy
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Cekenas Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
