QUESTIONS
SECTION A 40MKS)
- A student set up an experiment using a visking bag as shown
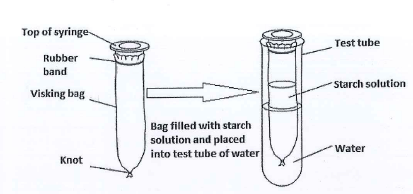
The student added some lodine solution to the water in the test-tube. After 30 minutes at room temperature, the contents of the visking bag were stained blue-black, but the water outside remained a yellow colour.- Explain these results. (4mks)
- State factors that influence the movement of molecules through visking bag (3mks)
- Use the diagram below to answer the questions that follow.
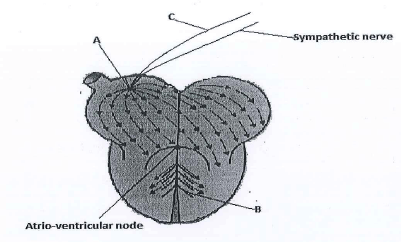
- Name the parts labelled A, B and C. (3mks)
- State the function of the part labelled C.
- What is the difference between pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation. (2mks)
- What is the advantage of having a double circulatory system over a single circulatory system? (2mks)
- Study the sickle cell pedigree below and answer the questions that follow.
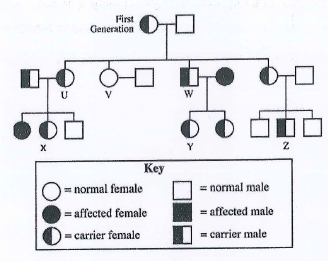
- Given that the allele for normal haemoglobin is expressed as Hb^ while the allele for abnormal haemoglobin is Hbs
- Complete the genetic diagram of marriage of two X and Z(4mks)
- What is the probability of having a sickle cell child
- Describe the effects of sickle cell anaemia on the body
- The figure below shows the human gas exchange system.
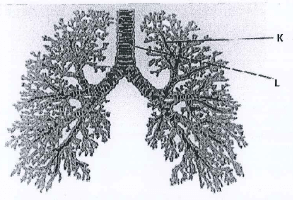
- Name structures K and L.
- Explain how structure L is adapted to its function
- Tobacco smoke affects the gas exchange system. Name one components of tobacco smoke and describe their effect on the gas exchange system.
(2mks)
Component...
effect........... - Name the part of the blood in which most carbon (IV)oxide is transported. (1mk)
- The diagram below illustrates the components of a simple reflex that takes place when during a knee jerk
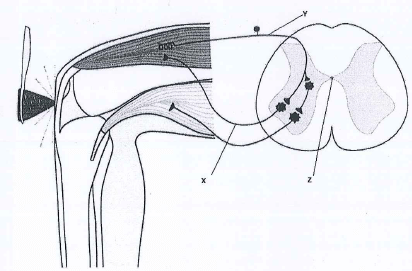
- Name the neurones labelled X and Y. (2mks)
- State one function of the fluid found in the part labelled Z.(1mk)
- Explain how the above simple reflex action takes place,(5mks)
SECTON B (40 MKS)
Answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided.
- A student grew two separate cultures of single celled organisms. One culture contained Paramecium caudatum and the other contained Paramecium aurelia. The cultures were grown under the same condition and the number of paramecia (per drop) in each culture was estimated every two days for a period of 16 days. The results are shown in the table below
No. of days 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 No. of Paramecia
caudatum present
(per drop)T. caudatum 4 10 30 48 58 62 60 61 60 T. aurelia 4 10 46 66 70 69 71 71 71 - Using the same axis, draw graphs of number of paramecia in the culture against time. (8mks)
- How many paramecia were present on the 7th day? (2mks)
P. caudatum...
P. aurelia... - Account for the change in the two populations between day 0 and 8. (4mks)
-
- What happens to P. caudatum between day 10 and 16?
- What biological phenomenon is represented by observation in (d) (i) above? (1mk) (1mk)
- State any four biological factors that regulate population growth of animals in their habitat. (4mks)
-
- Explain how a bony fish is adapted to swim ?
- State five functions of an insects exoskeleton.
-
- Explain the economic importance of fungi
- Describe various ways of breaking seed dormancy

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Iodine solution/molecules diffused into the visking bag; Iodine molecules small (enough to pass thro' the membrane); lodine solution /molecular Stain/react with Starch; No starch diffused out the bag/through Visking tubing.; starch molecules too large (to pass through membrane)OWITE
- Temperature; surface area; concentration gradient/water potential; thickness/distance/permeability of Membrane
-
- ¼ x 100
= 25% - Leads to defectue RBC's / abnormal shape transport oxygen Poorly causing anaemia/ deprives oxygen to vital organs/can cause death
-
- K - Bronchioles;
L - Trachea - Lined with Cilia to waft/sweep mucus/micro-organisms/pathogens. away from lungs; Lined with. mucus secreting cells/goblet cells to secrite mucus; Has lings of cartilage to keep it open; tubular to allow movement of gases
- Component. - Tar; Nicotine : Carbon Ui)oxide / carbon monoxide
Effect.. Tar; Caranogenic /cause mutation/cause lung cancer/
Nicotine: cause vasoconstriction bleed vessels/harder for oxygen rich cells
Carbon Monoxide; reduced ability of RBCs to transport oxygen - Plasma
- K - Bronchioles;
-
- X - Sensory. (nestone).
Y - Motor (neurone) - Shock absorber/prevents Mechanical damage/nourish
Supply nutrients and oxygen to spinal cord - Tapping of patella tendon causes stimulation; an impulse is generated; transmitted by Sensory neurone to the spinal cord; Impulse passed via a Synapse; cross to motor neorone;travels along motor neurone to muscle (extensor); extensor made contracts causing lower part of leg move forward / jerk forward
- X - Sensory. (nestone).
-
-
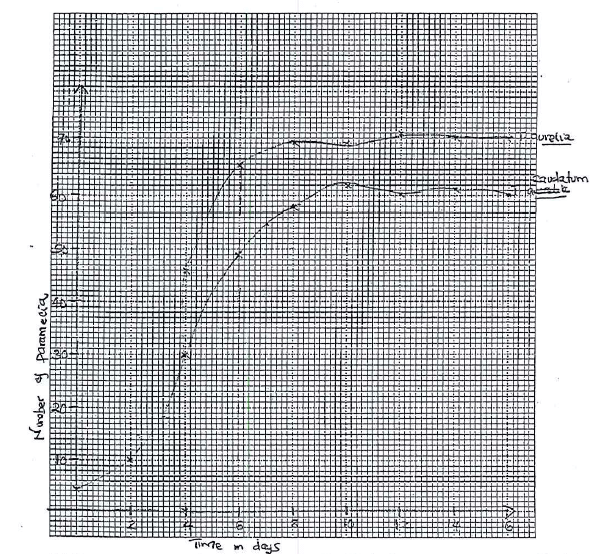
- P caudatum - 55±1;
P. aurelia - 68±1 - both population increase in number/ rapid increase in number between 0-5 days; slow population growth from day 6/7/7; reduced nutrients/space.
population of E - aurelia increase faster rate than E caudatum;
E - aurelia is better adapted to the ecosystem -
- Population remains constant (carrying capacity attained)
- competition/intra-specific competition
- competition; predation; diseases and parasites; social stress; overcrowding
-
-
-
- Vertebral column has series of vertebrae held together. loosely for flexibility (when swimming);
- Has myotomes/Segmented muscle blocks on either side of.. vertebral column whose antogenistic contractions and rolaxations produce movements;
- Head is not flexible / lacks neck to maintain forwars thrust;
- Body streamlined. to reduce resistance in water;
- presence of fins for propulsion and balance in water:
- Scales overlap / point. backwards; to reduce friction;
- Swimbladder / gas bladder/ air bladder; make fish buoyant / less dense when moves to high. levels,
- Body Is Mucord / covered with mucus ; lubricate / reduces friction;
- Paired fins (pectoral and pelvic) control pitching (tendency to vertically plunge) /braking and steering/change direction;
- Unpaired fins (dorsal ventral/ anal fins) Control yawing and rolling; caudal fin / tail fin; propel the fish foward
-
- Protects internal structuees from mechanical damage;
- Prevents / reduces/reduce water loss/dehydration/dessication;
- provides surface for attachment of muscles;
- Pigmentad for "Camouflage", "supports internal strictures; modified to form mouth parts, thin at joints to allow movement
- Scarification; Weakening.impermeable seed coats to allow water to enter /use of saprophyte bacteria/passing through guts of animals.
- Increasing conc of hormones that stimulate germination
- Providing favourable conditions/enough water/temp/oxygen;
- Providing suitable light wavelengths of light to trigger secretion of hormones
- Allowing more time for embryo to mature
- Heating/boiling/roasting someme seeds i.e Acacia
- Application of synthete plant hormones
-
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Alliance Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
