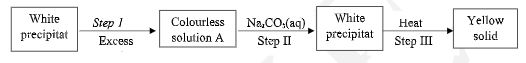Questions
Instructions to candidates
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- Non-programmable silent electronic calculators and KNEC mathematical tables may be used.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
-
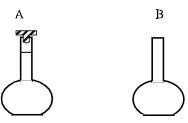
- Name the laboratory apparatus below ; (1 mark)
A _________
B _________ - Which laboratory apparatus is used to keep substances free from moisture? (1 mark)
- Name the laboratory apparatus below ; (1 mark)
- Describe how to experimentally separate a mixture of Iron (III) chloride and sodium chloride in the laboratory. (2 marks)
- An ion of element Q has 18 electrons,16 neutrons and 15 protons;
- Write the electron arrangement of an atom of element Q. (1 mark)
- What is the mass number of element Q. (1 mark)
- State the period and group of the periodic table where element Q is found. (1 mark)
Period ____________
Group ____________
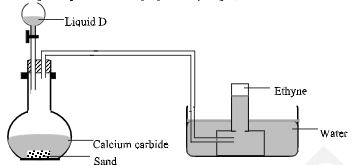
- The following set-up was used to prepare ethyne gas;
- Identify liquid D. (1 mark)
- Write the equation for the reaction in the flask. (1 mark)
- State and explain one precaution to be taken when performing the experiment. (1 mark)
- A saturated solution of a salt X at 25 0 C weighing 56g yielding 14g of solid when evaporated to dryness.
- Give one precaution to be taken when performing the experiment. (1 mark)
- What is the solubility of the salt at 25 0 C ? (2 marks)
-
- Use the equation below to answer the question that follow;
NH3(g) + H2O(l) ⇌ NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)
Identify the species that acts as a base and give a reason. (1 mark) - Study the flow chart below carefully.
- Identify the cation in solution A. (1 mark)
- Write the ionic equation for the reaction in step II. (1 mark)
- Use the equation below to answer the question that follow;
-
- Some Agriculture students wanted to test the pH of the soil in the school farm. Describe how this can be done in the school’s chemistry laboratory. (2 marks)
- The pH of the soil from the school farm was found to be 4.5. What should be done to raise the pH of the soil to 8.0? (1 mark)
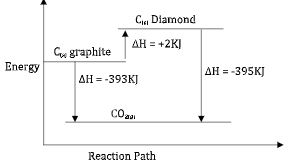
- Given that:
C(s) + O2(g) →CO2(g) H = -393 kJ mol-1
(Graphite)
C(s) + O2 → CO2(g) H = -395 kJ mol-1
(Diamond)- Determine H for : C(s) C(s) (2 marks)
(Graphite) (Diamond) - Represent the information above in an energy level diagram. (2 marks)
- Determine H for : C(s) C(s) (2 marks)
-
- State Charles’ law (1 mark)
- The volume of a certain gas was measured at 21 0 C. At what temperature will the volume be doubled if pressure remains constant? (2 marks)
-
- Name the chief ore of aluminium. (1 mark)
- Give a reason why aluminium is extracted using electrolysis. (1 mark)
- Give two uses of aluminium metal. (1 mark)
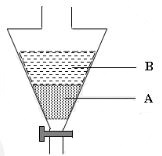
- The figure below shows an apparatus used to separate a mixture of water and hexane
- Name the apparatus. (1 mark)
- State the principle by which the mixture of the two liquids is separated. (1 mark)
- Identify the liquids, A and B if the density of hexane is 0.66g/cm 3 . (1 mark)
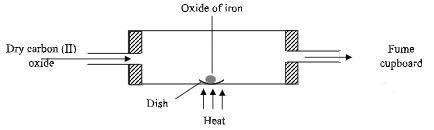
- Excess carbon (II) oxide was passed over a heated sample of an oxide of iron as shown in the diagram below. Study the diagram and use the data below to answer the questions that follow:
Mass of empty dish = 10.98g
Mass of empty dish and oxide of iron = 13.30g
Mass of empty dish and the residue = 12.66g- Determine the formula of the oxide of iron. (Fe = 56, O = 16) (3 marks)
- Write an equation for the reaction which took place in the dish. (1 mark)
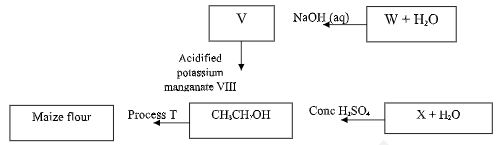
- Study the flow chart below and use it to answer the questions that follow;
- State two conditions required for process T. (1 mark)
- Give the formula of W (1 mark)
- State one use of X. (1 mark)
- When a certain mass of calcium carbonate was reacted with 200cm 3 of 1M HCl, 1440cm 3 of carbon (IV) oxide was produced. Determine the mass of calcium carbonate.
(Ca = 40, C = 12, O = 16, Molar gas volume is 24000 cm 3 ) (3 marks) - If you are provided with powdered zinc, distilled water, dilute nitric (V) acid and sodium carbonate crystals; describe how a sample of pure zinc carbonate crystals can be prepared in the laboratory. (3 marks)
- The reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen to manufacture ammonia is a reversible reaction;
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) H = -92 kJ/mol
How would the following changes affect the position of equilibrium?- Increase in temperature. (1 mark)
- Increasing concentration of nitrogen gas. (1 mark)
- Introduction of finely divided Iron catalyst. (1 mark)
- A student investigated the effect of electric current on substances by passing current through copper sulphate solution using copper electrodes.
- State two observations made during the experiment. (2 marks)
- Write the equation for the reaction at the anode . (1 mark)
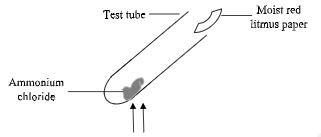
- The diagram below shows the heating of ammonium chloride in a test tube until there is no further change;
State and explain the observations made on the litmus paper. (2 marks) - A mixture of iron filings and Sulphur was placed in a crucible and heated strongly.
- Explain the following observations which were made;
- The mixture continued to glow red even when heating was stopped. (1 mark)
- The black solid produced was not attracted by a magnet. (1 mark)
- Write the equation for the reaction which took place. (1 mark)
- Explain the following observations which were made;
- A sample of water is suspected to contain chloride ions. Describe an experiment that can be carried out to determine the presence of chloride ions. (2 marks)
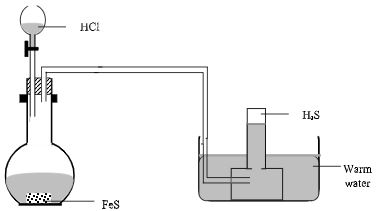
- Draw a well labeled diagram to show how to prepare and collect hydrogen sulphide gas using Iron (II) sulphide solid. (3 marks)
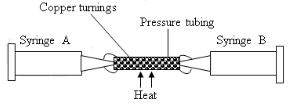
- The following set-up was used by Form one students to determine the percentage of oxygen in air.
About 200cm3 of air was passed repeatedly from syringe A to syringe B and back. After sometime, the volume of air was found to be 160 cm3 .- Calculate the percentage of oxygen in the initial sample of air. (1 mark)
- Write the equation for the reaction that took place. (1 mark)
- Why would Magnesium metal not be used in the experiment to replace the Copper metal? (1 mark)
-
- Define allotropy. (1 mark)
- Name the two allotropes of Sulphur. (1 mark)
- Calculate the oxidation number of Sulphur in H 2 SO 3 . (1 mark)
- A pea-size of potassium metal is dropped in a trough containing ethanol;
- State two observations made. (1 mark)
- What is observed when blue litmus paper is dropped in the resultant solution (1 mark)
- Write the equation for the reaction which takes place (1 mark)
- Calculate the volume of gas collected at the anode when a current of 3 amperes is passed through dilute sulphuric (VI) acid solution for 45 minutes and 30 seconds.
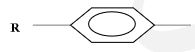
(Molar gas volume at r.t.p = 24.0 dm3 , 1F = 96500 coulombs) (3 marks) - Identify the organic compounds below and state their uses; (3 marks)
Name ………………………………………………………………………………………………
Use …………………………………………………………………………………………………- O O H H
|| || | |
- C – (CH2)4 – C – N – (CH2)6 – N –
Name ……………………………………………………………………………………………….
Use ………………………………………………………………………………………………… - H H H H
| | | |
-C - C - C - C
| | | |
H COOCH3 H COOCH3
Name ………………………………………………………………………………………………
Use …………………………………………………………………………………………………
- O O H H
-
- Define half-life. (1 mark)
- It takes 20 days for a certain radioisotope to disintegrate from 400g to 25g. Determine the half-life of the radioisotope. (2 marks)
- State one application of radioactivity in agriculture. (1 mark)
Marking Scheme
-
- A - Volumetric flask.
B - Flat bottomed flask - Desiccator
- A - Volumetric flask.
-
- Place the mixture in a beaker and cover with a glass watch containing cold water.
- Heat the beaker and the Iron(III)chloride sublimes.
- The sublimate is collected at the bottom of the glass watch.
- Sodium chloride remains in the beaker.
-
- 2.8.5
- 31
- Period 3
Group V
-
- Water
- CaC2(s) + 2H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + C2H2(g)
- The flask must be dry to prevent calcium carbide from reacting prematurely.
Sand is used to prevent the flask from breaking as then reaction is highly exothermic.
-
- Heating to complete dryness should be avoided to prevent the salt from thermal decomposition.
- 14g --- 42g
? ---- 100g
= 33.33 g / 100g of water
-
- NH3
It accepts H+ -
- Zn2+
- Zn2+(aq) + CO2-3(aq) → ZnCO3(s)
- NH3
-
-
- Take sample of the soil into a beaker, add water and stir.
- Filter and put the filtrate into a test tube.
- Use universal indicator and pH chart to estimate the pH.
- Liming // Addition of lime
-
-
- ΔH = ?
C(s) → C(s)
(Graphite) (Diamond)
∆H = -393 ∆H = -395
∆H = -393 - -395 = +2KJ/mol -
- ΔH = ?
-
- The volume of a fixed mass of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature provided pressure is kept constant.
- 588 – 273 = 315°C
-
- Bauxite
- Aluminium is more reactive than carbon
- Manufacture of aeroplane bodies
Manufacture of cooking utensils
Manufacture of electrical wire
Reducing agent in thermite process
Corundum(Aluminium oxide) is used as an abrasive
-
- Separating funnel
- The liquids are immiscible
- A – Water
B – Hexene
-
- Fe = 12.66 – 10.98 = 1.68
O = 13.30 – 12.66 = 0.64
Fe3O4Fe O 0.03 0.04 3 4 - 2Fe3O4(s) + 8CO(g) → 6Fe(s) + 8CO2(g)
- Fe = 12.66 – 10.98 = 1.68
-
- Yeast and Warmth/Heat
- CH3CH2COONa
- Fuel
Making polythenes
- CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
40 +12 + (16 × 3) = 100
1440 /24000 = 0.06moles of CO 2
(1 × 200) /1000 = 0.2moles of HCl
Mass = 0.06 × 100 = 6g -
- Add excess zinc to nitric (V) acid and filter to obtain zinc nitrate
- Add sodium carbonate to distilled water to form sodium carbonate solution
- Add sodium carbonate solution to zinc nitrate solution to form precipitates
- Filter and wash the residue with distilled water then dry.
-
- Equilibrium shifts to the left
- Equilibrium shifts to the right
- No effect
-
- The electrolyte remains blue in colour
Brown solid deposited at the cathode
Anode size reduces - Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2e
- The electrolyte remains blue in colour
- Red litmus changes to blue then to red
NH4Cl decomposes to NH3 and HCl
NH3 diffuses faster to change litmus to blue while HCl diffuses slowly and later changes litmus to red -
-
- Exothermic reaction // Heat is produced
- Iron chemically combined with Sulphur to form a compound iron II sulphide which is non- magnetic
- Fe(s) + S(s) → FeS(s)
-
- Add and warm. White ppt formed dissolves on warming.
-
Workability
HCl
Collection over warm water -
- 200 – 160 = 40
- 2Cu(s) + O2(g) → 2CuO(s)
- Mg would react with N2
-
- The existence of an element in two different forms without change in physical state.
- Rhombic
Monoclinic - 2(+1) + x + 3(-2) = 0
2 + x – 6 = 0
X = +4
-
- It darts on the surface producing a hissing sound
It melts into a silvery ball
It may burst into purple flame - Blue litmus paper remains blue
- 2CH3CH2OH + 2K → 2CH3CH2OK + H2
- It darts on the surface producing a hissing sound
- 4OH → 2H2O + O2 + 4e
Time = (45 ×60) + 30 = 2730
It = 3 ×2730
= 8190 coulombs
(24 ×8190) ÷ (4 × 96500) = 5.092dm3 -
- Name: Soapless detergent
Use: Cleaning - Name: Nylon
Use: Clothing - Name: Perspex
Use: Substitute for glass
- Name: Soapless detergent
-
- Is the time taken for a given mass or number of nuclides to decay to half its original mass or number.
- 400 – 200 – 100 – 50 – 25 25 = 400 () n
4 half lifes n = 5 days - Measuring absorption of phosphate fertilizers
Measuring carbon (iv) oxide take up by plants
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Bondo Joint Mocks Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students