INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer all questions
- Mathematical tables and silent electronic calcualtors may be used and all working must be clearly shown where necessary
Question 1
You are provided with
- Solution B containing NaOH
- Solution C containing 2M HCI
- Solid D containing 2g NaCI
- 5cm piece of Magnesium ribbon
You are required to- Determine effect of concentration of HCl on the rate of reaction.
- Percentage of impure Sodium chloride in Hydrochloric acid solution.
PROCEDURE I
- Label six test tubes 1,2,3, and 4, place them in a test tube rack.
- Using a 10ml measuring cylinder, Measure the volumes of solution C as indicated in table 1 and pour them into the test tubes.
- Wash the measuring cylinder and use it to measure volumes of water as indicated in table 1 and pour into the test tubes shake all the test tubes to ensure the solutions mix uniformly.
- Cut out five pieces each of exactly 1cm length of Magnesium. Transfer all the solution in the test tube 1 into a clean 100ml beaker.
- Place one piece of magnesium into the beaker containing contents of test tube 1, and immediately start a stop watch. Swirl the beaker continuously ensuring that the Magnesium is always inside the solution.
- Record in the table 1 the time taken for Magnesium to disappear. Wash the beaker each time.
- Repeat procedure (e) above using the remaining test tubes 2.3.4 and 5 and complete table 1 below.
- Table 1 (3mks)
Experiment Volume of C (cm3) Volume of water (cm3) Time (seconds) 1 12 0 2 10 2 3 8 4 4 6 6
Table 2
Experiment Concentration of C (moles/litre) Rate 1/Time (sec−1) 1 2 3 4 - Complete table 2 above by determining for 1/Time (Rate) and concentrations of solution (4mks)
- Plot a graph of 1/Time (Vertical axis) against concentration of solution B1 (3mks)
- From the graph determine the time taken mfor Magnesium to disappear when 7.5cm3 of solution C is used
- Table 1 (3mks)
PROCEDURE II
- Measure 75cm3 of solution C and transfer into 250ml volumetric flask, Add all the solid D and shake the mixture thoroughly.
- Add 100cm3 of distilled water to the volumetric flask, shake the mixture and add more water up to the mark. Label the resulting solution as Solution C1
- Fill the burette with solution C1 up to 0.0 mark
- Pipette 25cm3 of solution B into a clean conical flask, Add 2-3 drops of phenolphthalein indicator.
- Titrate the two solutions until pink colour changes to colourless. Record your results in table 3 below. Repeat this titration two more times and complete table 3 below.
- Table 3 (4 mks)
I II III Final burette Reading (cm3) Initial burette Reading (cm3) Initial burette Reading (cm3) - Calculate the average volume of solution C1 used (1mk)
- Determine the number of moles of the following solutions used in titration.(2mks)
- Hydrochloric acid, Solution C1
- Sodium Hydroxide, Solution B
- Calculate the Molarity of sodium Hydroxide in Moles per Litre (1mk)
- Calculate the following present in 250cm3 of solution of C1
- The mass of Hydrochloric acid in the solution H=1, Cl= 35.5
- The percentage purity of Sodium Chloride, Solid D in the solution (1mk)
- Table 3 (4 mks)
Question 2
You are provided with solution G and Soiid H, use them to answer the questions that follow.
Place about 2cm3 of solution G into five clean test tubes in a test tube rack
- To the 1st test tube add 3 drops of Sulphuric (VI) acid
Observation (1mk) Inference (2 mks) - To the 2nd portion madd 3 drops of Barium Nitrate
Observation (½mk) Inference (½mk) - To the 3rd portion madd 3 drops of Lead (II) Nitrate
Observation (1mk) Inference (1mk) - To the 4th portion add Sodium Hydroxide solution dropwise until in excess
Observation (1mk) Inference (1mk) - Place all the solid H into a clean test tube, add 10cm3 of water, shake the mixture thoroughly until all soild dissolves. Label the resulting solution as solution H
- To the 5th portion of solution G add 2cm3 of solution H
Observation (1mk) Inference (1mk) - Place 2cm3 of solution H into a clean test tube, add 3 drops of Nitric (V) acid followed by 3 drops of Barium Nitrate
Observation (1mk) Inference (1mk)
- To the 5th portion of solution G add 2cm3 of solution H
Question 3
You are provided with Organic substance L in a boiling tube. Use it to answer questions that follow. Put 2cm3 of substance L into five test tubes.
- To the 1st portion add 2cm3 of distilled water
Observation (½mk) Inference (½mk) - Transfer the 2nd portion into a clean watch glass mignite it using a burning wooden splint.
Observation (½mk) Inference (½mk) - To the 3rd portion add all the Sodium hydrogen carbonate provided.
Observation (½mk) Inference (½mk) - To the 4th portion add 3 drops of acidified potassium dichromate (VI) and warm
Observation (½mk) Inference (½mk) - To the 5th portion add all the solid K and test any gases produced using a burning splint.
Observation (½mk) Inference (½mk)
CONFIDENTIAL
- 1 Burette
- 1 Pipette
- 1250ml Volumetric flask
- 100ml beaker
- Complete stand
- 7 test tubes in a rack (five labelled 1,2,3,4 and 5)
- 2 boiling tubes
- 2 labels
- Stop watch
- Distilled water in a wash bottle
- 10ml measuring cylinder
- 100ml measuring cylinder
- 2 pieces of wooden splint
- Watch glass
- 100cm3 of 0.5M NaOH labelled as solution B
- 150cm3 of 2M HCl labelled as solution C
- 2g NaCl labelled as Solid D
- 0.5g of Sodium Sulphate labelled as H
- 15cm3 0.3M Lead(II) Nitrate labelled as solution G
- 15cm3 of Absolute ethanol labelled as Substance L
- 6cm piece of Polished Magnesium ribbon
- 0.1g of Calcium turnings labelled as Solid K
- 0.5g of Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate.
Access to:
- Phenolphthalein indicator
- Sodium Hydroxide
- Barium Nitrate
- Lead(II)Nitrate
- Sulphuric(VI)acid
- Acidified Potassium dichromate (VI)
- Source of heat
- Nitric(V)acid
MARKING SCHEME
Question 1
Procedure I
a)Table 1
- Time increases
- uniform decimals
b)Table 2
| Experiment | Concentration of C (moles/litre) | Rate 1/Time (sec−1) |
| 1 | 2M | |
| 2 | M1V1 =M2V2 2×10 = M2 ×12 M2 = 1.667/1.666 |
|
| 3 | M1V1 =M2V2 2×8 = M2 ×12 M2 =1.333M |
|
| 4 | M1V1 =M2V2 2×6 = M2 ×12 M2 = 1M |
- Accept values at least 3dp unless exact otherwise penalize FULLY
- Correct entry of 1/Time to at least 3d.p otherwise penalize fully to less than 3d.p
c)
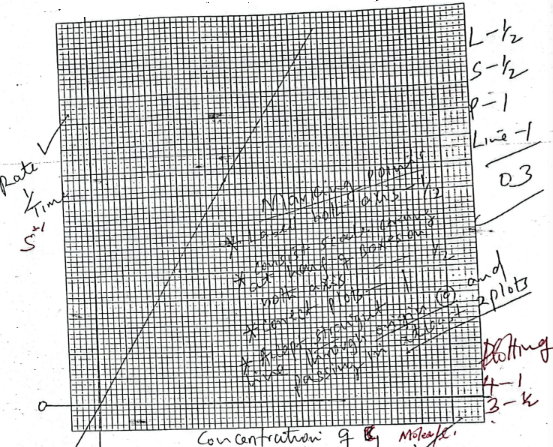
- Corect value of 1/T from correct graph
- Correct value of Time with correct units (otherwise penalize for wrong units used)
N/B graph must be correct. pass through the origin.
Procedure II
- Acc. 24 ± 2
- Correct average titre values
-
- Moles in 250cm3
2 × 75 = 0.15 moles
1000
Moles used in titration
0.15moles → 250
→ correct average litre - NaOH : HCl
1 : 1
Ans in c(i) above
At least 4d.p both in (i) and (ii)
- Moles in 250cm3
- Moles in C(ii) × 1000
25
= correct ans
(At least 3d.p unless exact) -
- 0.15 moles in 250 × 36.5
= Correct to atleast 2d.p in g
Penalize ½ for missing units - Ans in C(i) + 2g = Total mass
2 × 100% = correct %
Total mass
- 0.15 moles in 250 × 36.5
Question 2
-
Observation (1mk) Inference (2mks) - No effervescence
- White ppt is formed- SO32− , CO32−, HCO3− Absent
- Ca2+ ,Pb2+ ,Ba2+ present -
Observation (½mk) Inference (½mk) No white ppt SO42 Absent
Ignore SO32−, CO32− Absent -
Observation (1mk) Inference (1mk) -No white ppt
- No yellow ppt- Cl−//Br− Absent
- I− Absent -
Observation (½mk) Inference (½mk) - White ppt is formed soluble in excess - Pb2+ present
Penalize fully for contradiction -
-
Observation (½mk) Inference (1mk) - White ppt is formed H contains (must mention)
SO42− , SO32−, CO32− , CI− , Br− , -
Observation (1mk) Inference (1mk) - No efferevescence
- White pptSO42− Present
Must be mentioned in (i) above otherwise penalize fully.
-
Question 3
-
Observation (½mk) Inference (½mk) Miscible with H2O// forms uniform layer Polar compound -
Observation (½mk) Inference (½mk) Burns with a blue non sooty flame l l
C = C or −C≡C− Absent
l l -
Observation (½mk) Inference (½mk) No effervescence produced R − COOH Absent -
Observation (½mk) Inference (½mk) Orange colour of H+/ K2Cr2O7 changes to green R−OH Present -
Observation (½mk) Inference (½mk) Effervescence of colourless gas that extinguishes the burning splint with a pop sound K is a metallic/ a metal
(Tied to the pop sound)
Download Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and Answers with Confidential - Mokasa II Joint Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
