Instructions to Candidates
- Answer ALL the questions in section A in the spaces provided below each question in the question paper
- In section B, answer question 6(Compulsory) and either question 7 or 8
-
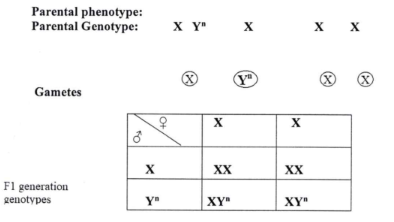
- Disease X is caused by a recessive gene located only on Y sex chromosome. A man suffering from the disease X got married last year, 2022. Using a punnet square show the probability of their 3rd born child suffering from the disease X Use letter N to represent the gene for disease X. (4 marks)
- An individual has XXX sex chromosome is formed as a super female. Explain how this condition comes about. (2 mark)
- A mother at Kenyatta National Hospital gave birth to triplets and were separated at birth and brought up under different conditions. The table below gives information about them when they met after 20 years.
Features Alice Grace Aby Weight 70kgs 69kgs 64kgs Height 1.82m 1.86m 1.7m IQ 120 120 122 Blood group B O B Tongue rolling Non-roller Non-roller Non-roller - Which of the triplets are likely to have been identical (1 mark)
- Give a reason for your answer (1 mark)
-
- Describe the process of fertilization in humans (3 marks)
- What determines primary sexual characteristics and secondary sexual characteristics (2 marks)
- Urethra is an organ involved in two organ systems in the body. Name the organ systems (1 mark)
- Give the functions of the following cells in seminiferous tubules of male reproductive system (2 marks)
- Sertoli cells
- Interstitial cells
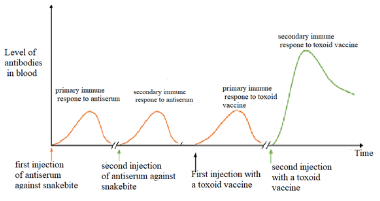
- The graph below depicts the concentration of two antibodies from a patients’ blood sample: one in response to injection with antiserum against snake bite and the other in response to injection with a toxoid vaccine.
- Account for the shape of the curves of injection with toxoid vaccine (2marks).
- Name the type of immunity conferred to the patient when; (2 marks)
- Given second injection of antiserum against snakebite
- Given first injection with a toxoid vaccine
- A farmer was attacked by a swarm of bees and died. Explain how the bee sting caused death.
(3 marks) - State how monocytes destroy pathogens (1 mark)
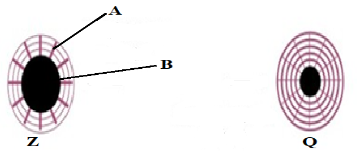
- The figure below shows the iris and pupil subjected to different environmental conditions.
- Identify the parts labeled A and
- Describe the event that leads to the appearance of B in diagram Z. (2 marks)
-
- What is the importance of the event occurring in (b) above (1 mark)
- Identify one cause of hypermetropia (1 mark)
- Distinguish between Rods and Cones (2 marks)
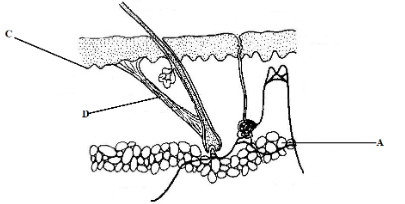
- The diagram below shows a section through the skin of a polar bear.
-
- Name the part labeled D. (1 mark)
- Explain the thermoregulatory function of D named in a (i) above. When the body temperature is below optimum (3 marks)
- What is the effect of bleaching creams to the part labeled C (1 mark)
- Name two homeostatic roles of the skin (2 marks)
- Describe how part labeled A adapts the organism to its habitat (1 mark)
-
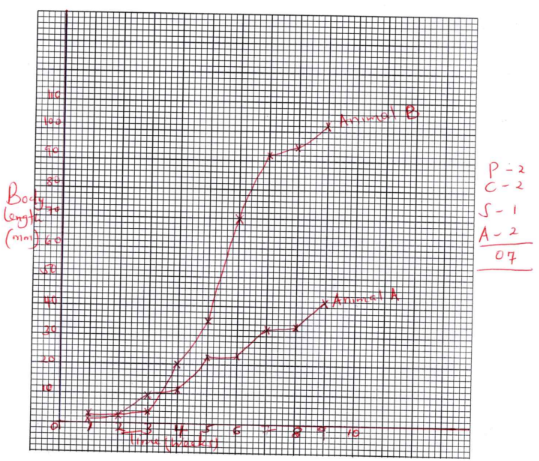
- The table below shows the growth of two types of animals. Animal A and animal B from the time they were hatched for a period of 60 days. The growth was measured in millimeters after every week for a period of nine weeks. The two animals were provided with adequate space, food and optimum temperature
Time (weeks) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Body length Animal A 3 3 10 11 23 23 32 33 42 (mm) Animal B 2 3 4 20 35 70 92 95 102 - Plot the growth curve of the body length against time of the two animals on the same axis. (7 marks)
- Name the growth pattern represented by;
- Graph of animal A (1 mark)
- Graph of animal B (1 mark)
- Account for the growth pattern of the animal A (3 marks)
- Account for the shape of the graph for animal B between;
- Week 1 – week 3 (3 marks)
- Week 3 – week 7 (3 marks)
- Name two hormones responsible for the increase in length of the animal A. (2 marks)
-
- Discuss various ways in which man has artificially used plant growth hormones in agriculture and horticulture (8 marks)
- Describe how xerophytes are adapted to conserve water (12 marks)
-
- Describe the process of digestion of skimmed milk along the alimentary canal (10 marks)
- Discuss the practical applications of Anaerobic respiration (10 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
-
Probability - ½ - Non-disjunction of sex chromosome in a female; leading to a gamete with two sex chrmosomes
-
- Alice and Aby
- They have the same blood group determined by genes and can't be altered by environmental conditions
-
-
- A sperm cell meets the ovum, acrosome burst and release of lytic enzymes to digest egg cell membrane, a filament is formed for penetration of the sperm head into the ovum
* Fusion of male and female nuclei -
- Primary - Genes located on sex chrmosomes
- Secondary - hormones
-
- Urinary system
- Reproductive system
-
- Nourishment of sperm cells
- Secretion of testosterone hormone
- A sperm cell meets the ovum, acrosome burst and release of lytic enzymes to digest egg cell membrane, a filament is formed for penetration of the sperm head into the ovum
-
- On first injection with toxoid with a vaccine few slow antibodies are produced and on second injection antibodies are produced faster and more; due to the body's memory cells of the first exposure/injection of toxoid vaccine.
-
- Artificially acquired passive immunity
- Artificially acquired active immunity
- Chemical in sting stimulate allergic reaction and cells secrete histamine; causing anaphylaxis dilation of blood vessels; lowering blood pressure resulting to death.
- Engulf and ingest pathogen/phagocytosis
-
-
- Radical muscle
- Pupil
- There was dim light hence radical muscles contract while circular muscles relax.
-
- Allows more light to enter the eye hence improve vision
-
- Long eye ball
- Weak refractive power of lens
-
RODS CONES Perceive light of low intensity Perceive light of high intensity Not sensitive to colour Sensitive to colour Low visual acuity High visual acuity Have retinal convergence No retinal convergence Photochemical pigment (Rhodospin) Photochemical pigment (iodospin)
-
-
-
- Erector pili muscle
- Thermoreceptors in the skin and hypothalamus detect the low body temperature as blood flows over it; sends impulses to erector pili muscle which are stimulated to contract; hair shaft on skin surface stand erect; traps a layer of air; air is poor conductor of heat hence insulate against heat loss.
- Destroys the melanocyte cells hence no formation of melanin which protects against harmful ultraviolet rays
-
- Thermoregulation
- Osmoregulation
- Thick layer of adipose tissue to insulate against heat loss
-
-
-
-
- Intermittent/discontinuous
- Continuous/ Sigmoid
- Growth is discontinuous; the rigid exoskeleton limits growth; the exoskeleton is shed during moulting/ecdysis; to allow rapid growth/cell expansion before formation and hardening of new exoskeleton.
-
-
- Slow growth/ increase in length;
- due to small/few number of cells dividing;
- the young environment;
- females not yet mature,
- few animals reproducing
-
- Rapid growth/experimental growth;
- due to large number of cells dividing;
- the animal has adjusted to the enviromment/ no limiting factors such as food space, mates
-
-
- Ecdysone
- Moulting stimulating hormone
-
-
-
- Auxins
- Young plants are sprayed with plant growth auxins to simulate rapid growth.
- Cuttings/propagated crops are dipped in auxins to stimulate rapid formation of roots.
- In temperature countries trees that have begun to bear fruits are sprayed with auxins to inhibit/delay fruit fall and allow economical harvesting.
- Auxins are used as herbicides to kill broad leaved weed pests that grow among cereals such as wheat.
- Fruit development by parthecocarpy i.e seedless oranges artificially stimulated by spraying the fruit blossom with auxin.
- Gibberellins
- In dwarf varieties plants are treated with gibberellins to simulate rapid cell elongation in stems to increase height.
- Seeds are treated with gibberellins to break seed dormancy and stimulate germination.
- Stimulate flowering in plants
- Stimulate parthenocarpy in some plants
- Stimulate lateral bud development leading to many side branches
- Auxins
-
- Some leaves are reduced in size/scale like leaves reduced to spinal thorns, to reduce surface area over which transpiration occurs.
- Some shed leaves during dry season to reduce surface area exposed to transpiration.
- Some leaves have thick cuticle, to increase distance covered by water to minimize cuticular transpiration.
- Some leaves have waxy cuticle, which is waterproof to minimize cuticular transpiration.
- Some leaves are folded to reduce surface area exposed to environmental factors.
- Some have sunken-stomata which accumulate moisture; lowering saturation deficit to reduce transpiration.
- Most have reduced stomata to reduce surface area exposed.
- Some have reversed stomatal rhythm to reduce surface area exposed
- Some store water in large parenchyma cells in succulent stems and leaves
-
-
-
- Skimmed milk is ingested; mixed with saliva and swallowed, moves by peristalsis along esophagus; cardiac sphincter muscles relax and open to allow food into stomach.
- Arrival of food substance in the stomach stimulates walls of stomach to secrete gastrin hormone which stimulate gastric gland to secrete gastric juice. The gastric juice has pepsinogen activated by HCI to pepsin to digest proteins to peptide/polypeptides
- Pro-rennin activated by HCI to rennin to digest caseinogen to casein which is then digested by pepsin to peptides.
- Goblet cells secrete mucus to prevent corrosion of walls of stomach and lubricate food.
- Oxyntic cells secrete HCI to activate pepsinogen and pro-rennin; destroy pathogens in food provide acidic pH suitable for enzyme activity. Longitudinal and circular muscles in stomach churn the food material to form chyme.
- Chyme moves by peristalsis into the duodenum. Arrival of chyme in duodenum stimulates duodenal walls to secrete secretin and cholecystokinin.
- Secretin stimulate pancreas to secrete NaHCO3 and liver to secrete bile salts to neutralize acidic chyme.
- Cholecystokinin stimulates the pancease to sectere pancreatic juice that contains lactase enzyme to digest lactose in the chyme to glucose and galactose,peptidase enzyme to digest peptides to amino acids, polypeptidase to digest polypeptides to amino acids.
-
- Dairy industry - Lactobacillus bacteria; breakdown lactose in milk anaerobically to form lactic acid; which curdles milk. The curdled milk can be floured to form Yoghurt.
- Baking industry-zymase enzyme in yeast; breakdown glucose/sugar in wheat flour anaerobically to produce CO2; making dough to rise as it escapes leaving behind spaces hence spongy texture. Ethanol produced evaporates leaving flavor in bread.
- Brewing industry - Yeast present naturally on fruit peel produce z;ymase enzyme which breakdown fructose/sugars in fruits anaerobically to ethanol and CO2;
Grains/barley/sorghum has amylase enzyme which breakdown starch in grains to maltose; maltase enzyme then breakdown maltose to glucose. Yeast is added to respire anaerobically glucose to ethanol and CO2. - Manufacture of organic acids - Glucose in organic matter is anaerobically broken down/fermented; by micro-organisms to various organic acids; such as citric acid used to flavor food.
- Production of biogas
Saprophytes/micro-organisms breakdown organic matter anaerobically; to produce biogas/methane and CO2 gas; Methane gas is tapped and used for cooking while CO2 is used for photosynthesis by plants. - Sewage Treatment
Micro-organisms breakdown organic matter in sewage anaerobically; to produce biogas and CO2. The biogas is tapped and used as source of green electricity - Production of sillage
Glucose in green plants/ green fodder is broken down anaerobically; by bacteria/saprophytes; to produce silage. The sugar contained in green fodder is anaerobically broken down to lactic acid which preserve the fodder for longer period.
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Mokasa II Joint Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students