INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- Scientific calculators may be used.
- Answer all questions in English
Questions
-
- Draw a simple diagram of a wooden splint after being passed through the inner region of a non- luminous flame of the Bunsen burner flame (2 mks)
- Explain why butane is not commonly used as domestic fuel in gas cylinders. (1 mk)
- Element T whose atomic number is 16 and mass number 32,combines with Oxygen whose atomic number is 8.
- Determine the number of protons and neutrons in element T. (1mark)
- Name the type of bond formed between T and Oxygen. (1mark)
- State the nature of solution formed when Oxide of T is bubbled through water. (1mark)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
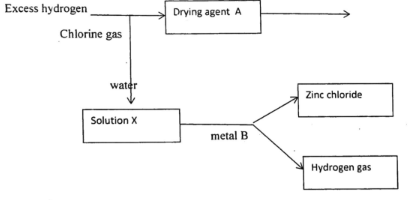
- Name
- A (1⁄2 mk)
- X (1⁄2 mk)
- Give a reason why potassium metal cannot be used as metal B (1 mk)
- State any two uses of hydrogen chloride gas (1 mk)
- Name
- A monomer has the following structure
CH = CH2
I
C6H5- Give the name of the monomer (1 mk)
- A sample of a polymer formed by the monomer above has a molecular mass of 4992.
Determine the number of monomers that formed the polymer (C=12, H=1.0) (2 mks)
- Below is a nuclear equation. Study it and answer the questions that follow.

- Find the values of x and n in the nuclear equation below (2mks)
- State two uses of radioisotopes in health (1mk)
- 100 cm3 of sulphur (IV) oxide diffuses through a porous pot in 72 seconds. What is the molecular mass of a gas P if 50 cm3 of the gas diffuses through the same porous pot in 37.92 seconds under the same conditions (S=32, O=16) (3mks)
- The table below shows the pH values of solutions of compounds J, K, L and M
Compound J K L M pH Value 1 6.5 7 10 - State which one of the compounds is likely to be
- Water obtained from an ion exchange resin (1mk)
- anti-acid tablet (1mk)
- A certain soil sample was found to be acidic. State two activities that would have led to decrease in the soil pH (1mk)
- State which one of the compounds is likely to be
- Starting with copper metal and dilute sulphuric (VI) acid, describe how you would prepare pure crystals of copper (II) sulphate. (3marks)
- The figure below shows an energy level diagram for decomposition of hydrogen peroxide using a
catalyst.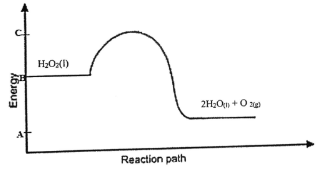
- Using the energy values A,B and C,write an expression for:
- Η for the reaction (1mk)
- activation energy (1mk)
- On the same axis sketch a curve that would be obtained if the reaction was carried out without a catalyst (1mk)
- Using the energy values A,B and C,write an expression for:
- The table below is part of the periodic table. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements. Study it and answer the questions that follow

- Select an element stored under water in the laboratory (1mk)
- How do the ionic radii of C and E compare? Explain (2 mks)
- The set-up shown below was used to separate a mixture T.
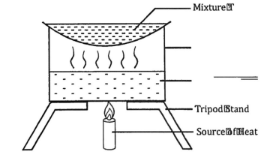
- Name the apparatus missing in the set-up. (1 mark)
- Give one example of mixture T (1 mark)
- What is the name of this method of separation? (1 mark)
- Below is a representation of an electrochemical cell Pb(s)/Pb2+(aq)// Ag+(aq)/Ag(s)
- What does // represent? (1mk)
- Explain why it is not advisable to use aqueous sodium carbonate as the salt bridge in this electrochemical cell. (2mks)
- The set up can be used to prepare oxygen gas. Use it to answer the questions that follow
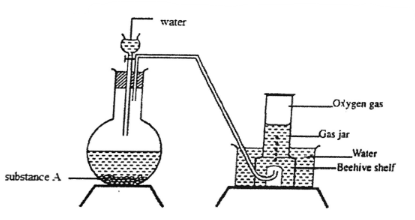
- Name substance A (1 mk)
- Name the method used to obtain oxygen on large scale (1 mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction which occurred in the flask. (1 mk)
- An oxide of nitrogen was bubbled through a solution of sodium hydroxide in which methyl orange indicator had been added. The solution changed to orange after sometime.
- Identify the oxide. (1mk)
- Write the equation for the reaction to explain the observation. (1mk)
- When 87.1g of hydrated barium hydroxide [Ba(OH)2.nH20] were heated to constant mass, 61.3g of anhydrous barium hydroxide were obtained. Determine the value of n in hydrated barium hydroxide. (Ba = 137,0=16, H = 1) (3marks)
- In an experiment to study properties of carbon, a small amount of charcoal is placed in a boiling tube. 5.0cm3 of concentrated nitric acid is added. The mixture is then heated.
- State one observation made. (1mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place in the boiling tube. (1mark)
- What property of carbon is shown in this reaction? (1mark)
-
- State the Le-Chatelier's principle.
(1mark) - The equation for dissolution of bismuth (III) chloride in water is
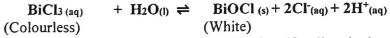
Explain the effect on the position of equilibrium if sodium hydroxide solution is added to the mixture at equilibrium. (2marks)
- State the Le-Chatelier's principle.
- The following table gives the melting points of oxides of elements in period 3. Study it and
answer the questions that follow:-
Formula of oxide Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 P4O10 SO3 Melting point (°C) 1190 3080 2050 1730 560 −73 - Explain the difference in melting points of MgO and P4010 (2marks)
- Name the compound in the above table that will react with both dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute sodium hydroxide. (1mark)
- The formula of the complex ion formed when aqueous copper (II)sulphate reacts with excess
aqueous ammonia solution is given as [Cu (NH3)4]2+- Name the complex ion above (1mk)
- State one use of the complex ion in (a) above (1mk)
- Explain how the +2 charge is obtained (1mk)
- The scheme below was used to prepare a cleaning agent. Study and answer the questions that follow.
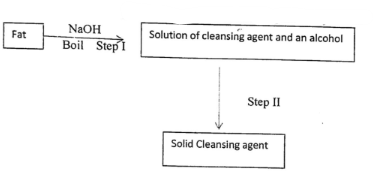
- What name is given to the type of cleaning agent prepared by the method shown in the scheme? (1⁄2mk)
- Name one chemical substance added in step II (1mk)
- Explain how the cleaning agent removes dirt from clothes (1/2mk)
- Blue petals were dropped into a gas jar containing sulphur (IV) oxide as shown below.
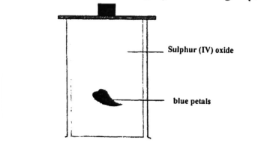
- Which observation was made? (1 mark)
- Which property of sulphur (IV) oxide is exhibited above? (1 mark)
- Write the equation for the reaction above. (1 mark)
- A substance contains 40.32g of substance XOH per litre. 25cm3 of this solution required 30.0 cm3 of 0.3 M Sulphuric (VI)acid for complete neutralization
- Calculate the number of moles of XOH that reacted (1mk)
- Determine the relative atomic mass of X (2mks)
- During the extraction of aluminium from its ores, the ore is first purified to obtain alumina
- Name
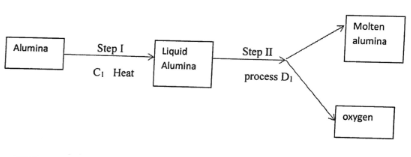
- Substance C1 (1mk)
- Process D1 (1mk)
- Give a reason why copper is a better conductor of heat and electricity than aluminium (1mk)
- Name
- Study the scheme below and use it to answer the questions that follow.

- Write down the formulae of two possible anions present in salt solution P. (2marks)
- Write an ionic equation for the formation of white precipitate. (1mark)
- Hydrogen gas exhibits reduction properties. Use the set up below to answer the questions that follow.
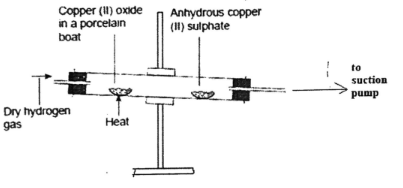
State and explain two observations made in the combustion tube (3mks) - The diagram below represents an in complete set up for preparation of a dry sample of gas R.
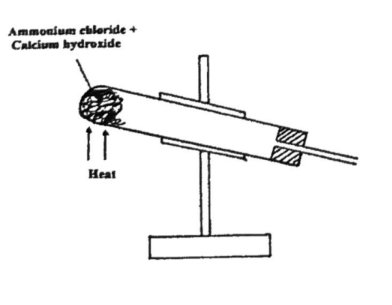
- Complete the set up to show how a dry sample of gas R is collected. (2 marks)
- Write a chemical equation for the reaction that produces gas R. (1 mark)
- Below is a diagram of set-up of apparatus that is used to investigate the effect of electric current on a binary electrolyte, lead (II) bromide.
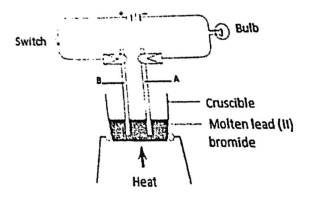
- Explain what is meant by a binary electrolyte. (1 mark)
- State the importance of heating in the above experiment. (1 mark)
- Write the ionic equation for the reaction taking place at the anode. (1 mark)
MARKING SHEME
-

- Burns with a yellow sooty flame which would dirtify the apparatus
-
- 32=16 +N
N=16
P=16 - Covalent
- acidic
- 32=16 +N
-
- A- concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid// anhyd. Calcium chloride
X- Hydrochloric acid / spirit of salt -
- Reacts explosively with dilute hydrochloric acid
- Production of chlorine and chlorides
- In tanning industry
- Dyeing calico printing
- In several medicines
- Production of glucose
- A- concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid// anhyd. Calcium chloride
- polyphenylethene/polystyrene
- n= 4992 = 4992 = 48
8(12)+8(1) 104
104(1mk)
48(1mk)
-
- n=3(1), x= 88(1)
-
- Cobalt-60 and caesium -137 are used to destroy cancerous tissues
- Gamma rays are used to sterilize surgical instruments
- Iodine-131 is used to treat patients with defective thyroid
- Flouride-18 is used to detect fractures in bones etc
- Tp = 100 x 37.92
50
= 75.84cm3
= 72 = 64
75.84 x
= 71 sec -
-
- K
- M
-
- Excessive use of nitrogeneous fertilisers such as NH4NO3, (NH4)2SO4 which are slightly acidic 1
- Acid rain due to release of acidic gases in the region such as SO2
-
-
- Burn copper // heat in air/oxygen obtain copper (II) oxide
- Add excess copper (II) oxide with dilute sulphuric (VI) acid.
- Filter the unreacted copper (II) oxide as residue and get copper (II) sulphate solution as the filtrate
- Heat the solution to saturation and then cover it with perforated filter paper & then leave crystals to form
- Dry the crystals between filter papers.
-
- shown on graph
- ΔH=C - A
- ΔHEa=C - B
-
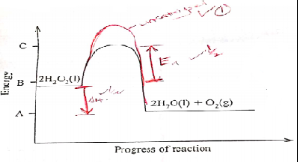
- shown on graph
-
- J
- C3- has a larger ionic radius than E- effective nuclear pull on outer electrons in C3- is stronger than
- in E- // ion of E more protons/stronger nuclear charge than ion of C
-
- Wire gauze
- Sodium chloride solution
- Evaporation.
- Salt bridge will
- Reacts with electrolytes(1) forming insoluble salts/ppt(1)// PbCO; insoluble will be formed (1) no flow of ions. (1)
-
- Sodium peroxide
- Fractional distillation
- 2Na2O2(s) + 2H2O(l) → 4NaOH(aq) + O2(g)
-
- nitrogen(IV) oxide
- 2NaOH(aq) + 2 NO2(g) → NaNO3(aq) + NaNO2(aq) + H2O(l)
- Mass of water of crystallization= 87.1 - 61.3 = 25.8
Mass of Ba(OH)2 = 61.3
Compound Ba(OH)2 2H2O
Mass 61.3 25.8
No. Of moles 61.3/171 25.8/18
Mole ratio 0.3585/0.3585 1.4333/0.3585
3.9981 = 4
n = 4 -
- A brown gas was formed at the boiling tube.
- C(s) + 4HNO3(aq)-4NO2(aq) + CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l)
- Reducing property.
-
- When a system at equilibrium is put under stress, it tries to readjust itself to possibly overcome the stress.// when a change in condition is applied to a system in equilibrium, it moves so as to oppose the change
- Sodium hydroxide removes the hydrogen ions in the mixture thereby causing instability in the system.
The equilibrium position shifts to the right to try and replace the lost hydrogen ions.(1)
- white colour intensifies
-
-
- MgO- it is an ionic compound with giant ionic structure which requires a lot of heat energy to separate
the ions. - P4O10 -it is a molecular substance where discrete molecules are joined by weak vanderwaal's forces of attraction that require little heat energy to separate.
- MgO- it is an ionic compound with giant ionic structure which requires a lot of heat energy to separate
- Al2O3 -Aluminium oxide
-
-
- Tetraaminecopper(II)ion
-
- Imparting blue, green or red tints in glasses and enamels
- Production of cellulose fibres in production of rayon
- Cu has a charge of +2 while NH3 has zero hence
charge of ion = +2 +4 (0)
= + 2
-
- soapy detergent
- Sodium chloride
- Has polar end (-COO–Na+) which dissolves in water and non-polar which dissolves in dirt, when rinsed the dirt is washed away.
-
- Blue petals turned white // colourless
- The bleaching property of S02.
- Dye + H2S03 (aq) → (dye - Oxygen) + H2SO4
(Blue) (White)
SO2 gas has reducing agent ability thus takes oxygen from the dye hence bleaching it
- 2XOH(aq)+ H2SO4(aq) → X2SO4(aq) + H2O(1)
mole ratio XOH: H2SO4
2:1
moles of H2SO4 = 30x3 = 0.009
1000
moles of XOH = 2×0.009
= 0.018 - 0.018 x 1000 = 0.72
25
40.32 = 56
0.72
X + 16 + 1 = 56
X+17 = 56
X = 56 - 17
=39
- 2XOH(aq)+ H2SO4(aq) → X2SO4(aq) + H2O(1)
-
-
- C1 - Sodium hydroxide
- D1- Electrolysis
- Has high density than Al hence higher density of free electrons in Cu than A1
-
-
- CO32- (1mk) or SO32- (1mk)
- Ba2+(aq) + CO32- (aq) → or BaCO3 (s)
Ba2+(aq) + SO32-(aq) → BaSO3 (s)
- Black copper(II)oxide changed to brown(1/2) and white anhydrous copper(II)sulphate crystals formed a blue substance(1/2), hydrogen gas reduces copper(II) oxide to copper metal(1) and itself is oxidized to steam which condenses on the cooler parts of the and combines with anhydrous copper(II)sulphate to form hydrated copper(II)sulphate solution.(1)

-
- Electrolyte that contain only one type of cation and anion.
- To melt lead(II)bromide for the ions to be free and mobile.
- 2Br ‾ (l) → Br 2 (g) + 2e¯
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Catholic Diocese of Kakamega Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
