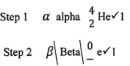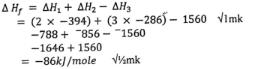INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Sign and write date of examination in the spaces provided above. Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided.
- Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used.
- All workings MUST be clearly shown where necessary.
-
- Name the method that can be used to obtain pure lodine from a mixture of Iodine and sodium chloride. (1 mark)
- A student was provided with a mixture of Maize flour, common salt and a red dye. The characteristics of the three substances in the mixture are given in the table below. (1 mark)
Substance Solubility in water Solubility in ethanol Maize flour Insoluble Insoluble Common Salt Soluble Insoluble Solid red dye Soluble Soluble
The student was provided with ethanol and any other materials needed. Describe how the student can separate the mixture into its three components.(3 marks) - The diagram shows part of the periodic table. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements. Use the diagram to answer the questions that follow.
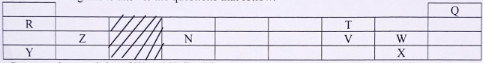
- Compare the reactivity of W and X. Explain. (2 marks)
- How do the melting points of R and T compare. Explain.
- From the letters indicated on the table, state the least reactive element (1mark)
- Element K is in period 2 of the periodic table and has an oxidation number of -3. Locate the element in the grid above. (1mark)
- Select an element that could be used for making overhead electric cables
(1 mark)
- The flow chart below shows a sequence of reactions starting with iron. Study it and answer the questions. that follow.
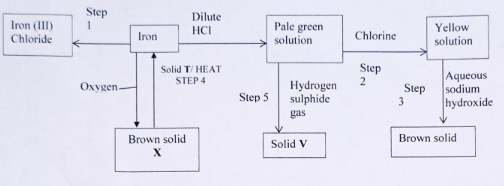
- Write balanced chemical equations and conditions where necessary for the reaction that takes place in
- Step 1 (1 mark)
- Step 2 (1 mark)
- Step 3 (1 mark)
- State the observation that will be made in step 5 (1 mark)
- Give a reason for the colour change in Step 2. (1 mark)
- Identify
X
(1 mark)
V
(1 mark)
T
(1 mark) - The mass of the product formed in step I was 2.0g. Calculate the volume of the gas used at r.t.p. (Fe =56. Cl = 35.5 and molar gas volume at r.t.p is 24 dm3
(3 marks)
- Write balanced chemical equations and conditions where necessary for the reaction that takes place in
-
- Use the table below to answer the questions that follow.
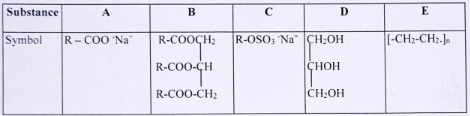
- Which substance is
- a soapless detergent.
- soapy detergent..
- an ester.....
- Propan – 1,2,3 triol
- polymer......
- Which substance forms a scum when used with hard water?
- Which substance is
- Study the reaction mechanism below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
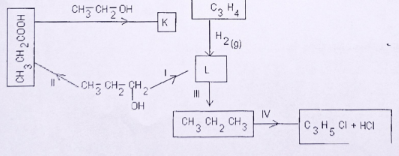
- Name substances
K
L - What observations would be made if L is passed through acidified potassium manganate(VII) solution?
(1 mark) - Identify the reagents used at stages:
I.
II.
III.
IV. - Name the reaction taking place at
II
III
- Name substances
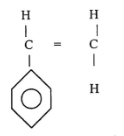
- The structure below is for polyphenylethene.
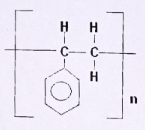
- Write down the structural formula of phenylethene.
(1mark) - Determine the number of monomers making the above compound if its relative molecular mass is 104,000. The benzene ring has six carbon and five hydrogen atoms. (C-12, H=1)
(2 marks)
- Write down the structural formula of phenylethene.
- Use the table below to answer the questions that follow.
-
- Below are standard electrode potentials of some elements.
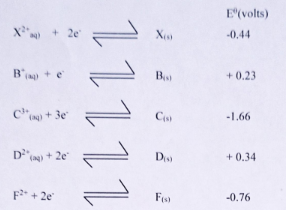
- Arrange the elements in order of their reactivity starting with the most reactive.
(1 mark) -
- In the space provided below, draw a well labelled electrochemical cell obtained by pairing up X and D.
(3marks) - On the cell drawn above, show the direction of electron flow. (1mark)
- Write a cell representation for the cell drawn in b(i) above. (1mark)
- Work out the electromotive force for the cell drawn in b (i) above. (1mark)
- In the space provided below, draw a well labelled electrochemical cell obtained by pairing up X and D.
-
- State two factors that determine the choice of a salt to be used in a salt bridge.
(2 mark) - State two roles of the salt bridge in an electrochemical cell.
(2 mark) - Below is a set of apparatus used in electrolysis of saturated potassium chloride solution using inert electrodes.
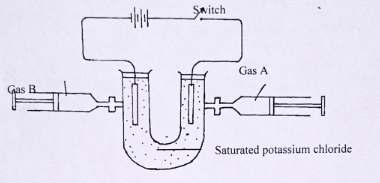
- Identify
- gas A.
(1⁄2 mark) - Gas B
(1⁄2 mark)
- gas A.
- Write an equation for the reaction taking place at the
- anode
(1mark) - cathode
(1mark)
- anode
- Describe how gas A can be tested.
(1mark) - After several hours of electrolysis, blue and red litmus papers were dropped into the electrolyte. State and explain observations made.
(1mark)
- Identify
- State two factors that determine the choice of a salt to be used in a salt bridge.
- Arrange the elements in order of their reactivity starting with the most reactive.
- Below are standard electrode potentials of some elements.
-
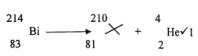
- The following is a radioactive decay series .Study it and answer the questions that follow
- Write the nuclear equation for step 1 (2 marks)
-
- 160g of Bi -214 has a half-life of 4 days and decays for 16 days. On the grid provided, plot a graph of the mass of Bi -214 against time
(3 marks)
Mass (grams) 160 80 40 20 10 Time (days) 0 4 8 12 16 
- Using the graph determine the mass of Bi after 10 days (2 marks)
- How is radioactivity used in paper industry (1 mark)
- 160g of Bi -214 has a half-life of 4 days and decays for 16 days. On the grid provided, plot a graph of the mass of Bi -214 against time
- The following is a radioactive decay series .Study it and answer the questions that follow
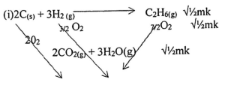
- Study the flow chart below and answer questions that follow:
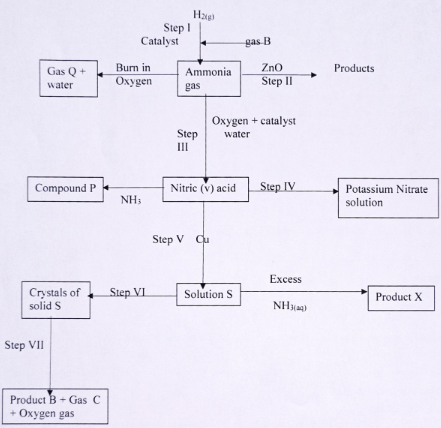
- State one source of gas B
(1 mark) - Name the catalysts used in;
- Step I (1 mark)
- Step III (1mark)
- Write chemical equations for reactions in; (1mark)
- Step II
- Step VII
- Name the process that takes place in; (1mark)
- Step IV
- Step VI
- Name and write the chemical formula of product X
Name
(1 mark)
Formula
(1 mark) - Identify any other gas that can be used instead of Ammonia in step II
(1 mark) - State one use of gas Q
(1mark)
- State one source of gas B
-
- State Hess's law
- Use the thermochemical equations below to answer the questions that follow.
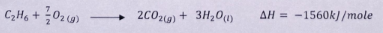

- Draw an energy cycle diagram to show the enthalpy of formation of ethane.
(11⁄2 marks) - Calculate the enthalpy of formation of ethane.
(11⁄2 marks)
- Draw an energy cycle diagram to show the enthalpy of formation of ethane.
- Give a reason why charcoal would be a fuel of choice for domestic heating. (1 mark)
- The following data was obtained during an experiment to determine the molar heat of combustion of ethanol.
Volume of water used = 500cm3
Initial temperature of wate = 24°C
Final temperature of water = 43.5°C
Mass of ethanol + lamp before burning = 130g
Mass of ethanol + lamp after burning = 128.5g
Calculate the;- Heat evolved during the experiment (density of water = 1 g/cm3, specific heat capacity of water = 4.2Jg-1K1). (1 mark)
- Molar heat of combustion of ethanol (C = 12, O= 16, H = 1). (2 marks)
- Write a thermochemical equation for the combustion of ethanol (1mark)
- Study the information in the table below then answer the questions that follows.
Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction.Bond Bond energy (kJmol-1) C - H 414 C1 - C1 244 C - C1 326 H - C1 431
CH4(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g)
(3mks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Sublimation
- Add ethanol to dissolve the red dye
Filter to obtain the solution of the red dye in the ethanol as the filtrate and maize flour and common salt as residue
Evaporate the ethanol to obtain the red dye
Add water to the residue so that common salt dissolves
Filter to obtain maize flour as the residue and common salt solution as the filtrate
Evaporate the water to obtain common salt - W is more reactive than X, has a smaller atomic radius than X an therefore gains electrons more easily/W accepts electrons more readily than X/W has less energy levels than X
- R has a higher m.p than T. R has a giant metallic structure with strong metallic bonds that require a lot of heat to break while T has a simple molecular structure with weak van der waals forces✓1⁄2mk that require little heat to break
- Q/He
- (check table) K then T
- Element N
-
-
- Step 1
2Fe (s) + 3Cl2 (g) → 2FeCl3 (s) - Step 2
2FeCl2 (aq) + Cl2(g) → 2FeCl3 (aq) - Step 3
FeCl3 (aq) + 3NaOH (aq) → Fe(OH)3 (s) + 3NaCl (aq)- Black precipitate / Black solid
- Iron II chloride is oxidized by chlorine to Iron III chloride
- X- Iron III oxide / Fe2O3
V - Iron II Sulphide / FeS
T-Aluminium / Zinc / Magnesium / Coke - Molar mass of FeCl3
56 + 3 (35.5) = 162.5
Moles of FeCl3
2.0/ 162.5 = 0.0123 moles
Moles of Cl2
3/2 X 0.0123 = 0.0185 moles
Volume of Cl2
0.0185 X 24
0.4431 X 1000 = 443.0769cm3
- Step 1
-
-
-
- I C
II A
III B
IV D
V E - A
- I C
-
- K - Ethylpropaoate
L - Propene - The solution is decolourised
- I Conc. H2SO4
II H+ KMnO4(aq) /H+K2Cr2O7(aq) accept in words
III H2
IV Cl2 - I Oxidation
II Addition
- K - Ethylpropaoate
-
- [(8 x 12 ) + (8 x 1)] n = 104,000
- (96+8)n = 104,000
104n= 104,000
n = 1000
- (96+8)n = 104,000
-
- C,F,X,B,D
-
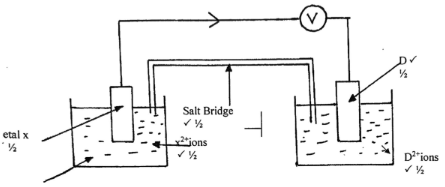
- As indicated above
- X(s)/X2+(aq) // D2+(aq)/ D(g)
- Emf reduced - Σθ reduced - Σθ oxidized
= 0.341⁄2 -(-0.44)
= 0.78
-
-
- Unreactive with electrolyte
- Highly soluble
-
- Completes circuit
- Balances ions of electrolytes
-
-
-
- Chlorine
- Hydrogen
-
- 2C1-(aq) → Cl2(aq) + 2e-
- 2H+(g) + 2e- →H2(g)
- Insert wet blue litmus paper;changes to red and then bleached/white
- Red turned blue hydroxide ions not discharged accumulated turning electrolyte alkaline
-
-
-
-
-
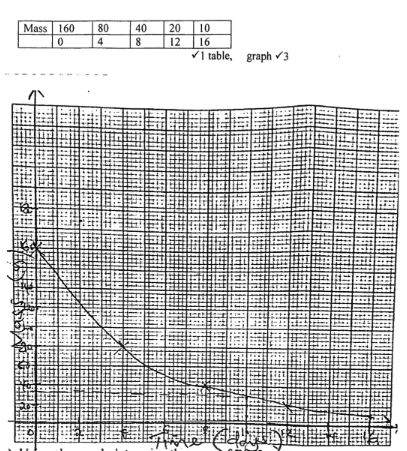
- 32g
- from graph 2Control in thickness of paper.
-
-
-
- Fractional distillation of liquefied air
-
- Finely divided iron
- Platinum Rhodium
-
- 3ZnO(s) + 2NH3(g) → 3Zn(s) + N2(g) + 3H20(l)
- 2Cu(NO3)(s) → 2CuO(s) + 4NO2(g) +O2(g) 1mk
-
- Neutralisation
- Crystalisation
- [Cu(NH3)4]2+
Tetra ammine copper(II)ion 1mk - Hydrogen gas
- Manufacture of ammonia in the haber process/refrigerant in light bulbs
-
- The energy changes in converting reactants to products is the same regardless of the route by which the chemical change occurs
-
-
- Readily available
- Easily transported
- No poisonous products when burnt
- Burns slowly
-
- Mass of water 500 x 1 = 500g
ΔT = 43.5-24 = 19.5°C = 19.5K
Heat evolved = 500 x 4.2 x 19.5 = 409.50 Joules - Mass of ethanol used 130 - 128.5 = 1.5g
RMM of ethanol = 46
1.5g of ethanol produced 40950 Joules
46g of ethanol produce 40950 x 46
1.5
= 1255800 Joules
= - 1255.8KJ mol- - C2H5OH(l) + 302(g) → 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(1) ΔH=(ans in ii above)
- Mass of water 500 x 1 = 500g
- Bond breaking
(414x4) +244= 1900kJ
Bond formation
- 326+ (-414 x3)+(-431)= – 1999kJ
Energy change = 1900 -1999= – 99kJ/mol
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Catholic Diocese of Kakamega Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students