Instructions
- Answer ALL the questions
- All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary.
- The diagram below was used to separate a mixture of liquid W (b.p = 110°C) and liquid Z (b.p = 88°C).
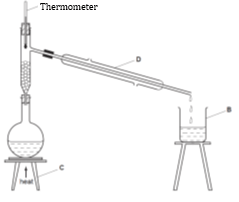
- Name the apparatus labelled B and C (2 marks)
- Using an arrow, indicate on the diagram where the water leaves apparatus D (1 mark)
- Which liquid was collected in apparatus B first? Give a reason for your answer. (2 marks)
- State the role of fractionating column in this experiment (1 mark)
- You are provided with a boiling tube, test tube, beaker, delivery tube, cork, ice cold water, stand & clamp, copper (II) sulphate crystals and source of heat. Draw a setup of apparatus that can be used by a student to study the effect of heat on hydrated Copper (II) sulphate (3 marks)
- When steam is passed over heated iron in a combustion tube, a black solid is formed. Write an equation of the reaction that leads to the formation of the black solid (1 mark)
- Study the scheme given below and answer the questions that follow:-
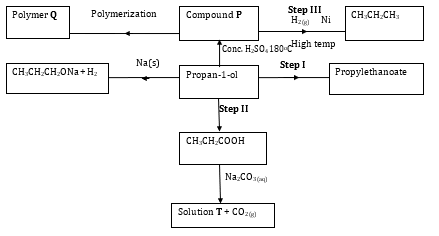
-
- Name compound P and solution T (2 marks)
Compound P
Solution T - Write an equation for the reaction between CH3CH2COOH and Na2CO3 (1 mark)
- Name compound P and solution T (2 marks)
- State one use of polymer Q (1 mark)
- Name one oxidizing agent that can be used in step II (1 mark)
- A sample of polymer Q is found to have a molecular mass of 4200. Determine the number of monomers in the polymer (H = 1, C = 12) (2 marks)
- Name the type of reaction in step I (1 mark)
- State one industrial application of step III (1 mark)
- State how burning can be used to distinguish between propane and propyne. Explain your answer (2 marks)
- 1000cm3 of ethene (C2H4) burnt in oxygen to produce Carbon (II) Oxide and water vapour. Calculate the minimum volume of air needed for the complete combustion of ethene (Air contains 20% by volume of oxygen) (2 marks)
-
-
-
- Sulphur exhibits allotropy. What is transition temperature? (1 mark)
- Briefly describe how an allotrope of Sulphur stable below 96°C can be prepared. (2 marks)
- Sulphur is used during vulcanization of rubber. State the role of Sulphur in vulcanization of rubber. (1 mark)
- Explain why old newspapers turn brown after sometime. (1 mark)
- State the observation made when Sulphur (IV oxide gas is bubbled into a solution of acidified potassium dichromate (VI) in a boiling tube. (1 mark)
- A rock was found in one of the valleys at Kilongolo. The rock was suspected to contain high percentage of zinc metal.
- Explain how you could confirm that the rock contains zinc metal. (3 marks)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the following questions.
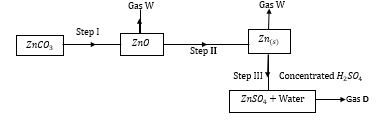
- State the condition necessary for the reaction in step I to occur. (1 mark)
- Name
- Gas W - (1 mark)
- Gas D - (1 mark)
- When a current of 0.82A was passed for 5 hours through a solution of metal Z, 2.65 g of metal Z were deposited. Determine the charge on the ion of metal Z. (1F = 96500C, RAM of Z = 52) (3 marks)
-
-
- Determine the electronic configuration of:
- Oxygen in H2O2 (1 mark)
- Sulphur in SO2⁄4 - (1 mark)
- A piece of Magnesium ribbon was placed in a solution of copper (II) chloride in a beaker.
- State any one observation that was made. (1 mark)
- Write the ionic equation for the reaction that took place. (1 mark)
- The following are standard reduction potentials for some metals. The letters do not represent the actual elements.
Eθ(volts) A2+ (aq) + 2ē →A(s) -2.93 B2+(aq) +2ē →E(s) -2.38 C2+(aq)+2ē →C(s) +0.34 D+(aq)+2ē →D(s) +2.87 E2+(aq)+2ē→E(s) +1.44 - Which is the most reactive metal? Give a reason. (2 marks)
- Draw electrochemical cell when A and D combine ,indicate the flow of electron (3 marks)
- Calculate the e.m.f of the cell in (ii) above. (2 marks)
- Explain if it is advisable to store a solution containing C2+ons in a container made of D. (2 marks)
- Determine the electronic configuration of:
-
- Define the following terms as used in radio activity (2 marks)
- nuclear fission
- Nuclear fusion.
- Study the information below and use it to answer the question that follows.
Time (days Mass of radio isotope 0 800 4.1 400 8.2 200 16.4 100 24.3 50 32.4 25 - Plot a graph of mass of Isotope (y-axis) against time (days) (3 marks)
- Use your graph to-
- Determine the half-life of the Radio Isotope (1 mark)
- The fraction of the original amount remains after 16.4 days (1 mark)
- If the sample continues to decay, predict how long it will take to decay to Zero. (1 mark)
- State one application of radioactivity in ; -+(2 marks)
- History
- Medicine
- Define the following terms as used in radio activity (2 marks)
- Study the ionization energies in Kilojoules per mole and answer the questions below.
Element Ionisation energies in kj/mol 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th A 1590 2780 4700 6500 8100 12500 B 1010 1900 4900 5000 6300 7300 C 940 4800 6300 9180 12000 1600 D 1680 2010 3400 10900 12400 16500 -
- What is meant by the term Ionization energy (1 mark)
- Identify the group to which each element belongs to A, B, C, D (1 mark)
- Write the formula of the oxide of D. (1 mark)
- What type of bond will be formed when C reacts with fluorine? Explain (2 marks)
- The table below gives some physical properties of elements in the third period of the period table and their chlorides. The letters used are not actual symbols of the elements. Study the information and use it to answer the questions that follows
.Element Melting point Boiling Point Chloride
Formula
Chloride
M.P(°c)
H 98 883 HCl 801 I 649 1107 ICl2 714 J 660 2467 JCl3 190 K 1410 2355 KCl4 -70 L 44 280 LCl3 -161 M 119 443 MCl2 -78 N -101 -38 - - O -189 -186 No compound - -
- Element K has a very high melting point. Explain why? (1 mark)
- Explain why element O has a very low boiling point. (1 mark)
- Explain why O does not form a chloride. (1 mark)
- Name the types of bonding and structure in the following chlorides (2 marks)
Chloride Bonding type Type of structure
ICl2
MCl2
-
-
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follows
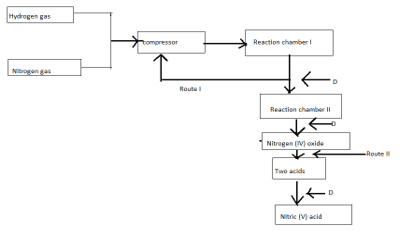
- State one source of nitrogen (1 mark)
- Name substances that goes through (2 marks)
- Route I
- Route II
- Name gas D (1 mark)
- Name the catalyst used in the reaction chamber ; (2 marks)
Chamber I
Chamber II - Write equation for the reactions taking place in reaction chamber II (1 mark)
- Identify the two acids formed above (2 marks)
- Write an equation for the reaction between one of the two acids above with reagent D (1 mark)
- State one use of nitric (V) acid (1 mark)

MARKING SCHEME
- The diagram below was used to separate a mixture of liquid W (b.p = 110°C) and liquid Z (b.p = 88°C).
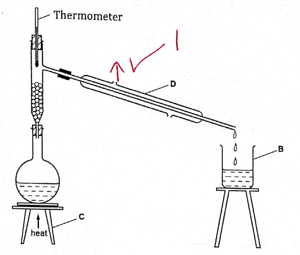
- Name the apparatus labelled B and C (2 marks)
B-Beaker
C-tripod stand - Using an arrow, indicate on the diagram where the water leaves apparatus D (1 mark)
On the diagram - Which liquid was collected in apparatus B first? Give a reason for your answer. (2 marks)
Liquid Z- has low boiling point - State the role of fractionating column in this experiment (1 mark)
Allow vapour of liquid where boiling point has not been reached to flow back into the flask after condensing. - You are provided with a boiling tube, test tube, beaker, delivery tube, cork, ice cold water, stand & clamp, copper (II) sulphate crystals and source of heat. Draw a setup of apparatus that can be used by a student to study the effect of heat on hydrated Copper (II) sulphate (3 marks)

- When steam is passed over heated iron in a combustion tube, a black solid is formed. Write an equation of the reaction that leads to the formation of the black solid (1 mark)
3Fe(s) +4H20(g)→Fe3O4(s)+4H2(g)
- Name the apparatus labelled B and C (2 marks)
- Study the scheme given below and answer the questions that follow:-

-
- Name compound P and solution T (2 marks)
Compound P - popene pop-l-ene
Solution T - propanote - Write an equation for the reaction between CH3CH2COOH and Na2CO3 (1 mark)
2CH3CH2CCH3+Na2CO3→2CH3CH2COONa+CO2+H2O
- Name compound P and solution T (2 marks)
- State one use of polymer Q (1 mark)
- Name one oxidizing agent that can be used in step II (1 mark)
Acidified potassium magnae(VII)
Acidified Potassium dichromate (VI) - A sample of polymer Q is found to have a molecular mass of 4200. Determine the number of monomers in the polymer (H = 1, C = 12) (2 marks)
C3H6 12*3+1*6
42
N=4200/42
=100 - Name the type of reaction in step I (1 mark)
Eserification - State one industrial application of step III (1 mark)
hardening of oil to fets - State how burning can be used to distinguish between propane and propyne. Explain your answer (2 marks)
Propane is an Alkane burns with blue flame
propyne is an Alkyne burns with yellow sooty flame - 1000cm3 of ethene (C2H4) burnt in oxygen to produce Carbon (II) Oxide and water vapour. Calculate the minimum volume of air needed for the complete combustion of ethene (Air contains 20% by volume of oxygen) (2 marks)
C2H4(g)+3O2(g)→2CO2(g)+2H2O(I)
1→1000cm3
3 ?
if 20% →3000cm3
100%
=15000cm3
-
-
-
- Sulphur exhibits allotropy. What is transition temperature? (1 mark)
Temperature of which one allotrope changes to the other - Briefly describe how an allotrope of Sulphur stable below 96°C can be prepared. (2 marks)
Sulphur is heated in a boiling tube containing carbon(IV) sulphide, Filration is done using dry filter paper, paper filtrae is evaporaed slowly to obtain rhombi sulphur. - Sulphur is used during vulcanization of rubber. State the role of Sulphur in vulcanization of rubber. (1 mark)
Making rubber harder and stronger - Explain why old newspapers turn brown after sometime. (1 mark)
Due to oxidation - State the observation made when Sulphur (IV oxide gas is bubbled into a solution of acidified potassium dichromate (VI) in a boiling tube. (1 mark)
Acidified paassium dhchromate change from orange to green
- Sulphur exhibits allotropy. What is transition temperature? (1 mark)
- A rock was found in one of the valleys at Kilongolo. The rock was suspected to contain high percentage of zinc metal.
- Explain how you could confirm that the rock contains zinc metal. (3 marks)
- Take small portion of the rock. Crush and grind into fine powder add HNO3 acid followed by ammonia hydroxide deposit fill in excess,, white precipitate dissolve in excess.
- Study the flow chart below and answer the following questions.

- State the condition necessary for the reaction in step I to occur. (1 mark)
Heat - Name
- Gas W - Carbon(IV) oxide (1 mark)
- Gas D - Sulphur(IV) oxide (1 mark)
- When a current of 0.82A was passed for 5 hours through a solution of metal Z, 2.65 g of metal Z were deposited. Determine the charge on the ion of metal Z. (1F = 96500C, RAM of Z = 52) (3 marks)
Md=Q*RAM/96500*F
0.82*5*3600*52/96500*X
X=3.0001
charge is 3+
- State the condition necessary for the reaction in step I to occur. (1 mark)
- Explain how you could confirm that the rock contains zinc metal. (3 marks)
-
-
- Determine the electronic configuration of:
- Oxygen in H2O2 (1 mark)
2O+2H=O
2(O)+2(+1)=
2(O)=-2
O=-2/2
=-1 - Sulphur in SO2⁄4 - (1 mark)
s+4(-2)=*2
s=*2+8
s=+6
- Oxygen in H2O2 (1 mark)
- A piece of Magnesium ribbon was placed in a solution of copper (II) chloride in a beaker.
- State any one observation that was made. (1 mark)
blue color fades, brown deposites - Write the ionic equation for the reaction that took place. (1 mark)
Mg(s)+Cu2+(aq)→Mg2+(aq)+Cu(s)
- State any one observation that was made. (1 mark)
- The following are standard reduction potentials for some metals. The letters do not represent the actual elements.
Eθ(volts) A2+ (aq) + 2ē →A(s) -2.93 B2+(aq) +2ē →E(s) -2.38 C2+(aq)+2ē →C(s) +0.34 D+(aq)+2ē →D(s) +2.87 E2+(aq)+2ē→E(s) +1.44 - Which is the most reactive metal? Give a reason. (2 marks)
A- the most negative - Draw electrochemical cell when A and D combine ,indicate the flow of electron (3 marks)
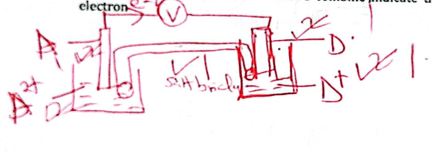
- Calculate the e.m.f of the cell in (ii) above. (2 marks)
+2.87--2.93
=5.8V - Explain if it is advisable to store a solution containing C2+ons in a container made of D. (2 marks)
No, D will displace C from its ions
- Which is the most reactive metal? Give a reason. (2 marks)
- Determine the electronic configuration of:
-
- Define the following terms as used in radio activity (2 marks)
- nuclear fission - This is the spliting process of heavy nuclide undergo when hit by removing neutron.
- Nuclear fusion. - The combination of nuclears at high velocityy resolting to formation of a heavy nucleus.
- Study the information below and use it to answer the question that follows.
Time (days Mass of radio isotope 0 800 4.1 400 8.2 200 16.4 100 24.3 50 32.4 25 - Plot a graph of mass of Isotope (y-axis) against time (days) (3 marks)

- Use your graph to-
- Determine the half-life of the Radio Isotope (1 mark)
8.1 days - The fraction of the original amount remains after 16.4 days (1 mark)
Approximately "96-97-98"
96/97/400 98/400 Any
- Determine the half-life of the Radio Isotope (1 mark)
- If the sample continues to decay, predict how long it will take to decay to Zero. (1 mark)
from graph when the curve cuts X-axsis
Approximately (567) days - State one application of radioactivity in ; -+(2 marks)
- History - determine age of fosil
- Medicine - monitor growth in bones
destroy damaged tissue
- Plot a graph of mass of Isotope (y-axis) against time (days) (3 marks)
- Define the following terms as used in radio activity (2 marks)
- Study the ionization energies in Kilojoules per mole and answer the questions below.
Element Ionisation energies in kj/mol 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th A 1590 2780 4700 6500 8100 12500 B 1010 1900 4900 5000 6300 7300 C 940 4800 6300 9180 12000 1600 D 1680 2010 3400 10900 12400 16500 -
- What is meant by the term Ionization energy (1 mark)
minimum energy required o remove an electron from outermost energy level in gaseous state - Identify the group to which each element belongs to A, B, C, D (1 mark)
group (IV) - Write the formula of the oxide of D. (1 mark)
D4O2 - What type of bond will be formed when C reacts with fluorine? Explain (2 marks)
Covalent bond- sharing of valence elecrons between C and Flourine.
- What is meant by the term Ionization energy (1 mark)
- The table below gives some physical properties of elements in the third period of the period table and their chlorides. The letters used are not actual symbols of the elements. Study the information and use it to answer the questions that follows
.Element Melting point Boiling Point Chloride
Formula
Chloride
M.P(°c)
H 98 883 HCl 801 I 649 1107 ICl2 714 J 660 2467 JCl3 190 K 1410 2355 KCl4 -70 L 44 280 LCl3 -161 M 119 443 MCl2 -78 N -101 -38 - - O -189 -186 No compound - -
- Element K has a very high melting point. Explain why? (1 mark)
Strong covalent bond with giant atomic structure - Explain why element O has a very low boiling point. (1 mark)
Due to weak van der waals forces of atraction - Explain why O does not form a chloride. (1 mark)
Has a stable elecron configuration
cannot gain or lose electron
- Element K has a very high melting point. Explain why? (1 mark)
- Name the types of bonding and structure in the following chlorides (2 marks)
Chloride Bonding type Type of structure
ICl2 ionic bond giant ionic
MCl2 covalent bond simple molecular
co-ordinate/Dative bond
-
-
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follows

- State one source of nitrogen (1 mark)
- fractional distillation of liquified air
- Name substances that goes through (2 marks)
- Route I
Unreacted Nitrogen (II) Oxide - Route II - water
- Route I
- Name gas D (1 mark)
Oxygen reject air - Name the catalyst used in the reaction chamber ; (2 marks)
Chamber I
Finely divided ion
Chamber II
platinum - Write equation for the reactions taking place in reaction chamber II (1 mark)
4NH3(g)+5O2(s)→4NO(g)+6H2O(I) - Identify the two acids formed above (2 marks)
Nitric (V) acid
Nitric (III) acid - Write an equation for the reaction between one of the two acids above with reagent D (1 mark)
2HNO2(aq)+O2(g)→2HNO3(aq) - State one use of nitric (V) acid (1 mark)
- Preparation of fertilizers and explosives
- State one source of nitrogen (1 mark)
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Kassu Jet Joint Mock 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
