Instructions
- Answer all the questions
- KNEC Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculator may be used.
- All the working must be shown clearly where necessary
- Candidates should answer questions in English.

QUESTIONS
-
- Bauxite is the chief ore found in the extraction of Aluminium. Name two impurities found in bauxite (2mks)
- Name the chief ores of both zinc and copper (1mk)
zinc
copper
-
- Identify the products formed when dinitrogen tetra oxide is dissolved in water (2mks)
- Write the balanced equation for the reaction above (1mk)
- State one use of the following substances (3mks)
AgBr
CaSO4.XH2O
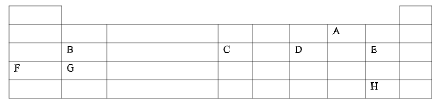
Tincture of iodine - The grid below represents part of the periodic table .Study it and answer the questions that follow .The letters given do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
- Select the element that can form a divalent anion (½mk).
- Name type of structure would the oxide of C have? (½mk).
- How does the melting point of A compare with that of E? (½mk).
- 2.6 g of B reacts completely when heated with 2.42 litres of chlorine gas (Cl2) at s.t.p, calculate the relative atomic mass of B.(1 mole of gas occupies 22.4 litres at s.t.p.) (11/2mk).
- Explain the differences in bleaching properties of chlorine and sulphur (use equations where necessary) (3mks)
- 6. Metals K and N were connected to form a cell as shown in the diagram below. Their reduction potentials are as shown below:
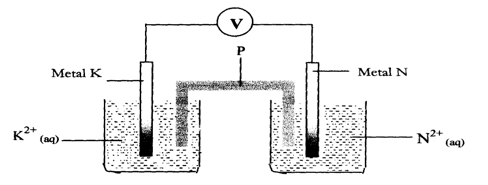
K+(aq) / K(s) ≡- 0.17V
N+(aq) / N(s) = + 1.1 6V- P is made by dipping a filter paper in a solution of sodium nitrate, on the salt bridge show the direction of flow of ions (1mk)
- On the diagram, show the flow of electrons (1mk)
- Write the equation for the half-cell reaction that occurs at (1mk)
Metal K electrode.
Metal N electrode
- Write equations for the reactions between the following metals and steam. (3mks)
Iron
Zinc
Copper - Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
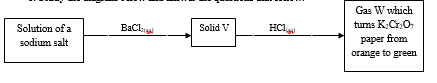
- Name (1mk)
Solid V
Gas W - Describe a chemical test for chloride ions (2mks)
- Name (1mk)
- Starting with ethanol, describe how a sample of tetrachloroethane can be prepared (3mks)
- A solution of bromine in water is a chemical reaction in equilibrium. The reaction involved is represented by the equation below;
Br2(aq) + H2O(l) ↔ 2H+(aq) + Br-(aq) + OBr-(aq)
Yellow Colourless- State and explain the observation made when dilute sulphuric (VI) acid is added to the mixture at equilibrium. (2mks)
- Define the term dynamic equilibrium (1mk)
-
- Apart from downward delivery name another method that can be used to collect the following gases (2mks)
Nitrogen (IV) oxide
Sulphur(VI) oxide - Name one gas that can be dried using anhydrous calcium oxide (1mk)
- Apart from downward delivery name another method that can be used to collect the following gases (2mks)
- Starting with magnesium metal describe how a sample of magnesium carbonate can be prepared. (3mks)
- With aid of well labelled diagrams show how a sample of sodium chloride, iodine and sand can be separated (3mks)
- Explain the following (3mks)
- Why number of protons and electrons are equal in an atom
- The role of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
- Cations are positively charged
-
- In an experiment 10.6g of a mixture of a anhydrous Sodium Carbonate and Sodium chloride were dissolved in water to make 100cm3 of solution .25cm3 of this solution required 20cm3 of 1M Hydrochloric acid solution for complete neutralization.
- Calculate the number of moles of Hydrochloric acid used (1mk)
- Write a balanced equation for the above reaction. (1mk)
- Calculate the mass of Sodium Carbonate in 25 cm3 of this mixture. (1mk)
- In an experiment 10.6g of a mixture of a anhydrous Sodium Carbonate and Sodium chloride were dissolved in water to make 100cm3 of solution .25cm3 of this solution required 20cm3 of 1M Hydrochloric acid solution for complete neutralization.
- Briefly describe how caffeine can be extracted from tea leaves. (3mks)
- State the two roles of platinised-platinum in a standard hydrogen electrode (2mks)
- Explain the following (3mks)
- Yellow phosphorus is stored under water
- Sodium is stored under paraffin oil
- Lime water and not potassium hydroxide is used to test for carbon(iv) oxide
- Study the information below and use it to answer the questions that follow

∆Hθlattice =MgCl2 - 2477kjmol-1
∆Hθ hydration Cl-1 (aq) -363kjmol-1
∆Hθ hydration Mg+2 (aq) -1891jmol-1- Differentiate between hydration energy and lattice energy? (1mks)
- Calculate the heat of solution of Magnesium Chloride (2mks)
- Nylon 6,6 is formed from two monomers, hexan-1,6-dioic acid(adipic acid) and hexan-1,6-diamine (hexamethylene diamine ) through condensation polymerisation as shown in the diagrams below .
- Define condensation polymerisation (1mk)
- Write the equation for the formation of Nylon 6,6 (2mks)
- According to Bronsteäd-Lowry theory, define an acid (1mk)
NH3(aq) + H2O(l) NH4+(aq)+ OH-(aq)
Identify the species that acts as;- A base
Explain (1mks) - An acid.
Explain(1mk)
- A base
-
- Explain how painting prevents iron from rusting (1mk)
- Apart from protection from rusting state another reason for electroplating (1mk)
- What is sacrificial protection , use an example to explain your answer. (2mks)
- The structure of RCOO-Na+ below represents a type of cleansing agent. Describe how the cleansing agent removes grease from a piece of cloth. (3mks)
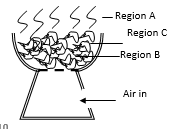
- The diagram below represents a ‘jiko’ when in use .Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Write equations for the reactions that occur in region
- B (1 mk)
- C (1 mk)
- Explain what happens in region A. (1 mks)
- Write equations for the reactions that occur in region
- A compound contains 82.75% carbon and the rest is Hydrogen. (C=12, H=1)
- Determine its empirical formula. (2 Mrks)
- Determine the molecular formula if its molecular mass is 58. (1 Mks)
- Determine the oxidation state of manganese in the following; (3mks)
KMnO4
Mn2O3 - Explain why the melting point of magnesium oxide is 3080°C while that of carbon IV oxide is -79°C. (2mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Name two impurities found in bauxite(2mks)
silica
iron (ii) oxide - Name the chief ores of both zinc and copper(1mk)
zinc-zinc blende
copper- copper pyrites
- Name two impurities found in bauxite(2mks)
-
- Name the products formed when dinitrogen tetraoxide is dissolved in water(2mks)
Nitric (V) acid
Nitric (III) Acid - Write the balanced equation for the reaction above (1mk)
N2O4(l) + H2O(l) →HNO3(aq) + HNO2(aq)
- Name the products formed when dinitrogen tetraoxide is dissolved in water(2mks)
- State one use of the following substances (3mks)
AgBr- light sensitive photographic plates
CaSO4.XH2O-plaster of Paris in reinforcing fractured bones
Tincture of iodine- as an antiseptic - The grid below represents part of the periodic table .Study it and answer the questions that follow .The letters given do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
- Select the element that can form a divalent anion (1/2mk).
A - Name type of structure would the oxide of C have? (1/2mk).
Giant ionic structure - How does the melting point of A compare with that of E? (1/2mk).
E has higher melting point than A - 2.6 g of B reacts completely when heated with 2.42 litres of chlorine gas (Cl2) at s.t.p, calculate the relative atomic mass of B.(1 mole of gas occupies 22.4 litres at s.t.p.) (11/2mk).
22.4----------------1mole
2.42-------------- 0.11mole
Raio B : Cl2
1 : 1
0.11: 0:11
2.6/0.11 = 23.6
- Select the element that can form a divalent anion (1/2mk).
- Explain the differences in bleaching properties of chlorine and sulphur (use equations where necessary) (3mks)
Chlorine bleaches by oxidation
-HClO (aq) + Dye →HCl (aq) + Dye +O
Coloured colourless
Sulphur (IV) oxide by reduction
-H2SO3(aq) + Dye H2SO4 + Dye-O - Metals K and N were connected to form a cell as shown in the diagram below. Their reduction potentials are as shown below:
K+(aq) / K(s) ≡ - 0.17V
N+(aq) / N(s) = + 1.1 6V- P is made by dipping a filter paper in a solution of sodium nitrate, on the salt bridge show the direction of flow of ions (1mk)
- On the diagram, show the flow of electrons (1mk)
- Write the equation for the half-cell reaction that occurs at (1mk)
Metal K electrode- K(s)→ K2+(aq) +2e-
Metal N electrode- N2+ (aq) + 2e- → N(s)
- Write equations for the reactions between the following metals and steam. (3mks)
Iron-3 Fe(s) + 4 H2O(g) →Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
Zinc- Zn(s) + H2O(g)→ ZnO(s) + H2(g)
Copper- no reaction - Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.

- Name(1mk)
- Solid V –Barium sulphite
- Gas W –Sulphur(iv) oxide
- Describe a chemical test for chloride ions (2mks)
to the solution of chloride ions add lead (ii) nitrate and warm,
a white precipitate if formed that dissolves on warming
- Name(1mk)
- Starting with ethene gas, describe how a sample of tetrachloroethane can be prepared (3mks)
Add excess hydrogen gas to ethene gas in presence of nickel catalyst and 200oC to form ethane gas
Add four moles of chlorine gas to ethane gas in presence of uV-light to form tetrachloroethane and hydrogen chloride gas
Fractionate to obtain tetrachloroethane -
- A solution of bromine in water is a chemical reaction in equilibrium. The reaction involved is represented by the equation below;
Br2(aq) + H2O(l)↔ 2H+(aq) + Br-(aq) + OBr-(aq)
Yellow Colourless
State and explain the observation made when dilute sulphuric (IV) acid is added to the mixture at equilibrium. (2mks)
The solution turns to yellow,
Increase in hydrogen ions cause the equilibrium to shift to the left and more of bromine and water are formed - Define the term dynamic equilibrium (1mk)
State at which the rate of forward reaction equals the rate of backward reaction
- A solution of bromine in water is a chemical reaction in equilibrium. The reaction involved is represented by the equation below;
-
- Apart from downward delivery name another method that can be used to collect the following gases (2mks)
Nitrogen (IV) oxide -Liquifaction/liquidification
Sulphur(VI) oxide –solidification/crystallisation - Name a gas can be dried using calcium oxide (1mk)
Ammonia gas
- Apart from downward delivery name another method that can be used to collect the following gases (2mks)
- Starting with magnesium metal describe how a sample of magnesium carbonate can be prepared (3mks)
Add magnesium into dilute hydrochloric acid to form magnesium nitrate
To magnesium sulphates solution add sodium carbonate solution to form magnesium carbonate and sodium nitrate.
Filter to obtain magnesium carbonate as the residue and sodium nitrate as the filtrate.
Wash the residue with distilled water and dry between filter papers. - With an aid of well labled diagram show how a sample of sodium chloride, iodine and sand can be separated (3mks)
- Explain the following (3mks)
- .Why protons and electrons are equal
To make an atom electrically neutral - The role of neutrons in the nucleus
To reduce the repulsion between the protons in the nucleus - Cations are positively charged
They have more protons than electrons
- .Why protons and electrons are equal
-
- In an experiment 10.6g of a mixture of a anhydrous Sodium Carbonate and Sodium chloride were dissolved in water to make 100cm3 of solution .25cm3 of this solution required 20cm3 of 1M Hydrochloric acid solution for complete neutralization.
- Calculate the number of moles of Hydrochloric acid used(1mk)
1mole---------------------1000cm3
.---------------------20cm3
=0.02moles - Which substance reacts with the Hydrochloric acid in this mixture? (1mk)
Sodium carbonate - Calculate the mass of Sodium Carbonate in 25cm3 of this mixture. (1mk)
Ratio: Na2CO3 : HCl
1 : 2
0.01 0.02
0.01--------------25cm3
100cm3
=0.04moles
0.04 X 10.6 = 4.24g
- Calculate the number of moles of Hydrochloric acid used(1mk)
- In an experiment 10.6g of a mixture of a anhydrous Sodium Carbonate and Sodium chloride were dissolved in water to make 100cm3 of solution .25cm3 of this solution required 20cm3 of 1M Hydrochloric acid solution for complete neutralization.
- Briefly describe how caffeine can be extracted from tea leaves.(3mks)
Grind a handful of tea leaves in a mortar using a pestle. Add a little propanone at a while as you continue crushing.
Decant the extract into an evaporating dish
Leave the extract in a sunny place to evaporate the solvent leaving behind caffeine - State the three roles of platinised-platinum in a standard hydrogen electrode (3mks)
- Act as inert metal connection to H/H+ system
- Provide a surface area for dissociation of H2
- Serves as an electrical conductr to the external circuit
- Study the information below and use it to answer the questions that follow
∆Hθlattice =MgCl2 - 2477kjmol-1
∆Hθ hydration Cl-1 (aq) -363kjmol-1
∆Hθ hydration Mg+2 (aq) -1891jmol-1- Differentiate between hydration energy and lattice energy? (1mark)
Hydration: energy when one mole of gaseous ions becomes hydrated
Lattice : energy change when 1 mole of an ionic compound is formed from its constituent ions in gaseous state - Calculate the heat of solution of Magnesium Chloride (2 marks)
Heat of solution= lattice + hydration energies
=-1891-(-363X2)+2477
=-140Kj/mol
- Differentiate between hydration energy and lattice energy? (1mark)
- Explain the following (2mks)
- yellow phosphorus is stored under water
To prevent smouldering in the air - Sodium is stored under paraffin oil
To prevent reaction with both air and water - Lime water and not potassium hydroxide is used to test for carbon(iv) oxide
Lime water forms a white precipitate while potassium hydroxide does not
- yellow phosphorus is stored under water
-
- Nylon 6,6 is formed from two monomers, Hexan -1,6-dioc acid and Hexan-1,6-diamine monomers through condensation polymerization.
- Define condensation polymerisation (1mk)
Identical or different monomers combine to form a long chain molecule with the loss of small molecules - Write the equation for the formation of Nylon 6,6 (1mk)
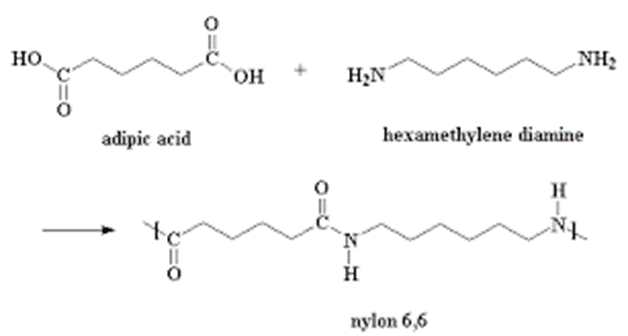
- Define condensation polymerisation (1mk)
- Nylon 6,6 is formed from two monomers, Hexan -1,6-dioc acid and Hexan-1,6-diamine monomers through condensation polymerization.
- According to Bronsteäd-Lowry theory, define an acid (1mk)
An acid is a proton donor
NH3(aq) + H2O(l) →NH4+(aq)+ OH-(aq)
Identify the species that acts as;- A base. (1mk)…NH3
Explain … acts a proton acceptor - An acid. (1mk) …H2O
Explain……act as proton donor
- A base. (1mk)…NH3
-
- Explain how painting prevents iron from rusting(1mk)
It prevents contact between iron and water and oxygen - Apart from protection from rusting state another reason electroplating(1mk)
Beauty/aesthetics - What is sacrificial protection , use an example to explain your answer. (2mks)
A corrosion protection where a more reactive element (metal is electrically attached to a less reactive metal eg zinc bar attached to a ship body or magnesium attached oil pipeline to prevent rusting
- Explain how painting prevents iron from rusting(1mk)
- The structure below represents a type of cleansing agent.
RCOO-Na+
Describe how the cleansing agent removes grease from a piece of cloth. (3mks)
The hydrophilic end dissolves in the water while hydrophobic end dissolve in the grease spot. Upon agitation of the garment the greasy spot is dislodged in form of small droplets micelles which are washed away by water upon rinsing - The diagram below represents a ‘jiko’ when in use .Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Write equations for the reactions that occur in region
- B (1 mk)
C(s) + O2(g)→ CO2(g) - C (1 mk)
C(s) + CO2(g)→ CO(g)
- B (1 mk)
- Explain what happens in region A. (1 mk)
Carbon(ii) oxide burns in a blue flame in excess supply of air
- Write equations for the reactions that occur in region
- A compound contains 82.75% carbon and the rest is Hydrogen.
- Determine its empirical formula. (2 Marks)
Element
Carbon
Hydrogen
Percentage
82.75%
17.25%
Atomic masses
82.75/12
17.25/1
mole
6.89
17.25
Mole ratio
6.895/6.895
17.25/6.895
1 1x2
2.5 2.5x2
= C2H5 - Determine the molecular formula if its molecular mass is 58. (1 Mark)
Efm =29
Mfm=58
58/29=2
C4H10
- Determine its empirical formula. (2 Marks)
- Determine the oxidation state of manganese in the following; (3mks)
- MnO2
X + (-2 x 2)=0
X=+4 - KMnO4
1+ x +(-2 x 4)= 0
X=+7 - Mn2O3
2x + (-2 x 3)=0
X= +3
- MnO2
- Explain why the melting point of magnesium oxide is 3080°C. (1mks)
Have a giant ionic structure and strong ionic bonds hence high melting and boiling points
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Nginda Girls Mock Examination 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students