INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper has two sections A and B.
- Answer All questions in section A.
- In section B, Answer question six and any other two questions.

QUESTIONS
SECTION A: 25 MARKS
-
- Apart from oil, name two other non- renewable sources of energy. ( 2 mks)
- State three ways in which Kenya can reduce the use of petroleum as source of energy.
(3mks)
-
- Give two similarities in function between Nairobi and New-york city. ( 2mks)
- Identify three function zones of an ideal urban center. (3 mks)
-
- Name three types of fish. ( 3 mks)
- State two problems facing fishing in Japan. (2 mks)
-
- Give two minerals that occur in form of alluvial deposits. ( 2mks)
- State three ways in which soda ash contributes to the economy of Kenya. (3 mks)
-
- Name two types of environment. ( 2 mks)
- dentify three sub-branches of Geography in human and economic geography. ( 3 mks)
SECTION B: 75MARKS
Answer all question 6 and any other two questions in this section.
- The table below shows total number of livestock in Kenya in 1986 and 1996.
TYPE OF LIVESTOCK
NUMBER IN MILLIONS
1986
1996
CATTLE
19.0
20.7
SHEEP
17.0
26.7
GOATS
18.5
27.3
CHICKEN
20.0
40.0
- Using a scale of 1cm represents 5 million livestock, draw a comparative bar graph to represent the above given data. ( 8 mks)
- State three advantages of comparative bar graphs. ( 3 mks)
-
- Discuss nomadic pastrolism under the following subheadings.
- Types of cattle breed kept. ( 2mks)
- The pattern of movement. ( 2mks)
- The marketing of animals. ( 2mks)
- Give two reasons why nomadic pastrolists keep large heads of animals. ( 2 mks)
- Discuss nomadic pastrolism under the following subheadings.
- Explain three ways in which the government of Kenya assist nomadic pastoralists improve quality of their livestock. ( 6 mks)
-
- Define the term wildlife. ( 2 mks)
- Name two characteristics of National parks. ( 2 mks)
- State four physical factors that would discourage setting up a game park within the slopes of Mt. Kenya. ( 4 mks)
-
- Name three main inland attraction sites in Kenya. ( 3mks)
- Compare tourism in Kenya and Switzerland under the following sub heading.
- Climate. ( 2 mks)
- Scenery. ( 2 mks)
- Culture. ( 2 mks)
- Explain four ways in which Kenya is planning to expand her tourism. (8 mks)
-
- Apart from floods, name two other environmental hazard associated with climatic conditions. ( 2 mks)
- Name two ways that have been used to reclaim land from swamps. ( 2 mks)
- State three factors which have led to frequent flooding in L.Victoria region. ( 3 mks)
- Explain four ways in which land is being rehabilitated in Kenya. ( 8 mks)
-
- state four benefits of land reclamation in Netherlands. ( 4 mks)
- Give three differences of land reclamation in Kenya and Netherlands. ( 6 mks)
-
- Give two types of international trade. ( 2 mk)
- Differentiate between visible and invisible exports. ( 2 mks)
- Name three member countries of COMESA. ( 3 mks)
- State four problems facing COMESA. ( 4 MKS)
- Explain four reasons why Kenya earns little foreign exchange from agriculture. ( 8 mks)
- Explain three ways though which the government can improve future trade. ( 6 mks)
-
- Differentiate between indigenous and exotic forests. ( 2 mks)
- Give three examples of softwood trees in Kenya. ( 3 mks)
-
- State four characteristics of natural forests in Kenya. ( 4 mks)
- Explain three physical factors that favour growth of natural forests in Kenya. ( 6 mks)
- State four measures which have been taken to manage forests in Kenya. ( 4 mks)
- Give the difference between forestry in Canada and Kenya under the following subheadings.
- Distribution. ( 2 mks)
- Problems. ( 2 mks)
- Marketing. ( 2 mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- Apart from oil, name two other non- renewable sources of energy. ( 2 mks)
- Uranium
- Natural gas
- Coal/peat ( ANY FIRST 2x1=2 mks)
- State three ways in which Kenya can reduce the use of petroleum as source of energy.
(3mks)- Encouraging people to use bicycles over short distances
- Developing alternative source of energy such as biomass, wind, solar
- Encouraging people to use public transport rather than private means
- Importing cars with low engine capacity
- Improving traffic flows to reduce usage of fuel
- Improving roads to avoid delay that increase consumption of petrol
- Proper maintenance of vehicles to avoid high consumption of oil
(ANY FIRST 3x1=3mks)
- Apart from oil, name two other non- renewable sources of energy. ( 2 mks)
-
- Give two similarities in function between Nairobi and New-york city. ( 2mks)
- Both are financial centres
- Both are industrial centres
- Both are international centres
- Both are educational centers
- Both are residential centers ( ANY FIRST 2x1= 2 mks)
- Identify three function zones of an ideal urban center. (3 mks)
- Central business district
- Transitional zone
- Industrial zone
- Residential zone
- Commuter zone. ( ANY FIRST 3x1=3 mks)
- Give two similarities in function between Nairobi and New-york city. ( 2mks)
-
- Name three types of fish. ( 3 mks)
- Dermasal fish
- Pelagic fish
- Anadromous fish
- Salty water fish/marine fish
- Fresh water fish ( ANY FIRST 3x1=3mks)
- State two problems facing fishing in Japan. (2 mks)
- High pollution of Japanese waters by industrial effluents and oil spillage
- Overfishing /overexploitation
- Restriction of Japanese fleet from other nation territories ( ANY FIRST 2x1= 2 mks)
- Name three types of fish. ( 3 mks)
-
- Give two mineral that occur in form of alluvial deposits . ( 2mks)
- Diamond
- Gold (2X1=2MKS)
- State three ways in which soda ash contributes to the economy of Kenya. (3 mks)
- when exported earns country foreign exchange
- create employment opportunities improving the standard of living
- has led to the development of social amenities
- has led to growth of Magadi town
- is raw materials of some industries promoting growth of industries
- provide the government with revenue through the payment of taxes
(ANY FIRST 3x1-3 mks)
- Give two mineral that occur in form of alluvial deposits . ( 2mks)
-
- Name two types of environment. ( 2 mks)
- Human environment
- Physical environment (2X1=2MKS)
- Identify three sub-branches of Geography in human and economic geography. ( 3 mks)
- Demography
- Economics
- Forestry
- Political science ( ANY FIRST 3x1=3 mks)
- Name two types of environment. ( 2 mks)
-
SECTION B: 75MARKS
Answer all question 6 and any other two questions.
- The table below shows total number of livestock in Kenya in 1986 and 1996.
TYPE OF LIVESTOCK
NUMBER IN MILLIONS
1986
1996
CATTLE
19.0
20.7
SHEEP
17.0
26.7
GOATS
18.5
27.3
CHICKEN
20.0
40.0
-
- Using a scale of 1cm represents 5 million livestock, draw a comparative bar graph to represent the above given data. ( 8 mks)
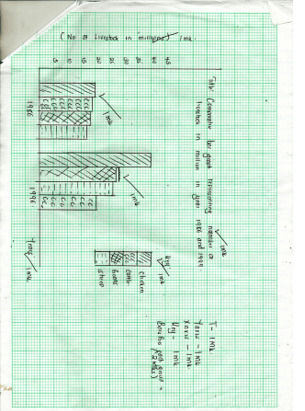
- State three advantages of comparative bar graphs. ( 3 mks)
- They are easy to compare
- They are easy to read and interpret
- They are easy to draw
- They easily show the trend of the given data. (ANY FIRST 3x1= 3mks)
- Using a scale of 1cm represents 5 million livestock, draw a comparative bar graph to represent the above given data. ( 8 mks)
-
- Discuss nomadic pastoralism under the following subheadings.
- Types of cattle breed kept. ( 2mks)
- Indigenous : zebu and boran
- The pattern of movement. ( 2mks)
- Movement is seasonal
- During the dry season pastoralist migrate with their animals to highlands where there is pasture and water
- Wet season move to the plains since pasture is available ( 1x2=mks)
- The marketing of animals. ( 2mks)
- Sold to slaughter houses/individual
- Sold through community groups
- Sold to the livestock marketing department
- Sold to the Kenya meat commission ( 1x2=2mks)
- Types of cattle breed kept. ( 2mks)
- Give two reasons why nomadic pastoralists keep large heads of animals. ( 2 mks)
- Forms insurance against calamities
- Sign of wealth/prestige
- To pay dowry
- Source of income
- Source of food/milk/meat/blood ( ANY FIRST 2x1=2mks)
- Discuss nomadic pastoralism under the following subheadings.
- Explain three ways in which the government of Kenya assist nomadic pastoralists improve quality of their livestock. ( 6 mks)
- Encouraging pastoralists to start ranching in order to improve the quality of their animals
- Encouraging cross breeding of traditional breeds with exotic breeds so as to improve the quality
- Strengthen community education to teach/train farmers on better livestock management
- Construct roads to make services accessible/marketing easier
- Replacing coarse grass with nutrious pasture to improve quality of the animal
- Sinking boreholes/ constructing dams to provide water
- Reviving Kenya meat commission so as to buy animals directly from farmer for slaughter
- Providing extension services to pastoralists to advise them and offer drug treatment. ( ANY FIRST 3x2=6 mks)
-
-
-
- Define the term wildlife. ( 2 mks)
- the plant and animals in their natural habitat√√
- Name two characteristics of National parks. ( 2 mks)
- established by an act of parliament
- managed by the national government
- no other form of human activities is allowed
- fenced to keep off people and prevent animal from going out. ( ANY FIRST2x1=2mks)
- Define the term wildlife. ( 2 mks)
- State four physical factors that would discourage setting up a game park within the slopes of Mt. Kenya. ( 4 mks)
- Insufficient vegetation that would provide food for wildlife/habitats for wild animals
- The area is high above sea level where atmospheric pressure may be too low for the survival of wildlife
- Presence of snow/low temperature unsuitable for survival of wildlife
- Steep slope/rugged terrain discourage the movement of animals in the game park ( ANY FIRST 4x1= 4mks)
-
- Name three main inland attraction sites in Kenya. ( 3mks)
- wildlife in national parks and game reserves
- famous wild beast migrations
- snowcaps of Mt Kenya
- great rift valleys lakes and hotsprings
- diverse culture of the maasai people
- historical attraction sites of Kariandusi,orgessaile
- national museums of Kenya in Nairobi ( ANY FIRST 3x1=3 mks)
- Compare tourism in Kenya and Switzerland under the following sub heading.
- Climate. ( 2 mks)
- Kenya’s climate is warm throughout the year while Switzerland experience warm summer and cold winters ( 1x2=2 mks)
- Scenery. ( 2 mks)
- Kenya’s has beautiful scenery such as lakes, mountains, great rift valleys and sandy beaches while Switzerland has many glaciated lakes with winter vegetation. 1x2=2mks)
- Culture. ( 2 mks)
- Kenya there is various/diversity of African cultures while in Switzerland the main culture is European. ( 1x2=2mks)
- Climate. ( 2 mks)
- Name three main inland attraction sites in Kenya. ( 3mks)
- Explain four ways in which Kenya is planning to expand her tourism. (8 mks)
- Improving transport networks in semiarid areas in-order to make the areas accessible.
- Aggressive promotion and marketing of Kenya as a tourist destination in other countries making the country known.
- Intensify domestic marketing to reduce the over reliance on foreign tourists
- Improving security in the country and tourist sites to ensure safety of tourists
- Marketing the country as tourist attraction in the newer areas to reduce the over-reliance on traditional markets
- Diversify tourist attractions sites to reduce competition with other tourist destinations
- Lowering tariffs levied on accommodation and food in hotels to encourage tourist to visit more. ( ANY FIRST 4x2=8mks)
-
-
-
- Apart from floods, name two other environmental hazard associated with climatic conditions. ( 2 mks)
- Lightening
- Windstorms
- Hailstones (ANY FIRST 2x1=2mks)
- Name two ways that have been used to reclaim land from swamps. ( 2 mks)
- Digging ditches for water to ooze into and flow away by gravity
- Planting eucalyptus which takes up a lot of water e.g. at Kakuzi in Makuyu.
- Laying perforated pipes in ditches which water will seep into and flow away by gravity ( ANY FIRST2x1=2mks)
- State three factors which have led to frequent flooding in L.Victoria region. ( 3 mks)
- Most of the land is low lying causing the rain water to spread over a wide area
- The adjacent highlands receive high amounts and torrential rainfall which releases large volumes of water resulting in rivers overflowing in their banks
- Silting has made the river beds shallow spilling their water over the banks
- The rivers in the area are in their old stage thus have wide flood plains which allow water flow and spread over large areas
- The area have black cotton soil which is non porous allowing water to flow and spread on the surface
- The heavy rainfall received in the area is discharged into the lake making it’s water level to rise thus flooding the adjacent lowlands. ( ANY FIRST3x1= 3 mks)
- Apart from floods, name two other environmental hazard associated with climatic conditions. ( 2 mks)
- Explain four ways in which land is being rehabilitated in Kenya. ( 8 mks)
- Filling open pits in order to use the land for farming and agriculture/settlement
- Controlling grazing in order to allow regeneration of pasture/control soil erosion
- Mulching/planting cover crops to add humus to the soil
- Constructing dykes/ dams along the river banks to control flooding
- Constructing drainage ditches to remove excess water from the land
- Applying manure/fertilizers on derelict land in order to restore fertility
- Irrigating the semi-arid areas during dry season in order to provide water required for plant growth
- Practicing bush fallowing in order to allow land to regain fertility
- Constructing terraces reducing the surface run off/ soil erosion
- Planting trees to reduce soil erosion ( ANY FIRST 4x2= 8 mks)
-
- state four benefits of land reclamation in Netherlands. ( 4 mks)
- Has increased the land for agriculture and settlement
- Has increased agricultural input/more raw materials for industries
- Roads and canal have been constructed thus improving transportation
- Has improved fresh supply of fresh water for domestic and industrial use
- Creation of fresh water lakes such as lake Ijssel has provided water for domestic, industrial and irrigation use
- Has created tourist attraction sites earning the country foreign exchange ( ANY FIRST 4x1= 4mks)
- Give three differences of land reclamation in Kenya and Netherlands. ( 6 mks)
- In Kenya land reclamation is thorough draining of swamps, using ditches and planting of trees while in Netherlands land reclamation is from constructing of dykes and canals
- In Kenya land reclamation is on small scale while in Netherlands land reclamation is large scale
- In Kenya land being reclaimed in mainly inland while in Netherlands land being reclaimed is mainly covered by sea water ( 3x2=6mks)
- state four benefits of land reclamation in Netherlands. ( 4 mks)
-
-
-
- Give two types of international trade. ( 2 mk)
- Regional trade
- Bilateral trade
- Multi-lateral trade (ANY FIRST2x1=2 mks)
- Differentiate between visible and invisible exports. ( 2 mks)
- Visible exports are tangible goods sold outside the country while invisible goods are intangible goods sold outside the country.
- Give two types of international trade. ( 2 mk)
-
- Name three member countries of COMESA. ( 3 mks)
- Burundi, Angola, Lesotho,Madagascar,Djibouti,Kenya,Ethiopia,Namibia,Zimbambwe
- Eritrea,Zambia,Swaziland,Uganda,Mauritius,Comoros,Seychelles,Sudan,Egypt,Malawi ( ANY FIRST 3x1=3mks)
- State four problems facing COMESA. ( 4 MKS)
- Production of similar agricultural goods limiting trade between member states
- Unplanned industrial development leading to low quality goods being produced
- Inaccessible roads delaying transportation of goods and people
- Increased population has led to consumption rather than investment
- Civil strife/political instability/wars among member states limiting production
- Low technology among member states producing low quality goods (ANY FIRST 4x1=4 mks)
- Name three member countries of COMESA. ( 3 mks)
- Explain four reasons why Kenya earns little foreign exchange from agriculture. ( 8 mks)
- Fixed quotas reduce foreign exchange
- Agricultural export are mainly raw materials which are semi-finished hence low values in the world market
- Fluctuation of world market prices reducing profitability/earnings
- Weakening of the Kenyan shillings against the other world currencies lowering value of products
- Expensive agricultural machines/farm inputs lowering profits
- Some agricultural products are poor quality reducing earnings
- Stiff competion which reduces market for agricultural exports. ( ANY FIRST4x2=8mks)
- Explain three ways though which the government can improve future trade. ( 6 mks)
- signing of bilateral and multi -lateral trade treaties/agreements which will improve exports by expanding her market
- establishing more manufacturing industries to improve the quality of good being exported
- establishment of east African custom unions so as to increase trade between Kenya and her neighbors
- joining trading blocks to find wider market for her goods
- improving transport and communication networks to have efficient transaction of business
- exploring new markets in far east countries to avoid over reliance in traditional markets
- Kenya to aggressively advertise her products to attract more buyers for her products
- Kenya to undertake partial processing of some agricultural products before export to improve on her quality increasing earning
- Some business men setting up branches in the neighboring countries so as to attract/expand trading activities
- Diversify her export products to attract wider market for her goods. ( ANY FIRST 3x2=6 mks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between indigenous and exotic forests. ( 2 mks)
- These are trees whose trees are natural/originate from the country while exotic forests are whose trees are alien/new to a country.√√
- Give three examples of softwood trees in Kenya. ( 3 mks)
- African pencil, cedar, juniper podo, pine cypress, bluegum/eucalyptus, kei apple
- Jacaranda, Granville, (any first 3x1=3mks)
- Differentiate between indigenous and exotic forests. ( 2 mks)
-
- State four characteristics of natural forests in Kenya. ( 4 mks)
- most of the forests occur in mixed stands
- most of the forest the trees grow at different heights
- most of the trees take a long time to mature
- most of the trees form canopies
- most of the forest have few undergrowth
- most of the trees are closely packed ( ANY FIRST4x1=4 mks)
- Explain three physical factors that favour growth of natural forests in Kenya. ( 6 mks)
- moderate temperatures/cool climate favour the growth of a variety of trees
- high well distributed rainfall/1000-2000mm through out the year support the growth of trees
- steep and rugged terrain discourages agriculture and settlement allowing growth of forests
- deep well drained volcanic soils allows the roots to penetrate deeper into the ground to support trees. ( ANY FIRST 3x2=6 mks)
- State four characteristics of natural forests in Kenya. ( 4 mks)
- State four measures which have been taken to manage forests in Kenya. ( 4 mks)
- enacting laws so as to ban/prohibit the cutting down of trees/ protect the indigenous trees
- establishing of the forest research station to conduct research on trees
- encouraging the establishment of NGO’S who encourage the protection of threatened forests
- encouraging the use of alternative source of energy to reduce the overreliance of wood fuel
- gazzetment of forested areas to reduce encroachment by people/protecting endangered forests
- establishment of training institution to train personnel on forestry
- creating awareness through the media on importance of conserving forests
- setting aside tree planting days to encourage people to plant more trees
- employing of forest guards to protect the forests
- encouraging the recycle of wood products to reduce the demand for trees ( ANY FIRST4x1=4mks)
- Give the difference between forestry in Canada and Kenya under the following subheadings.
- Distribution. ( 2 mks)
- in Kenya the softwood forests are found in the highlands while in Canada the forests are found in both highlands and lowlands (1x2=2mks)
- Problems. ( 2 mks)
- in Kenya the main problems are pest and diseases while in canada the main problems are the rugged landscape, inaccessibility during winter (1x 2=2mks)
- Marketing. ( 2 mks)
- in Kenya most of the forest products are sold locally while Canada most of the forest products are sold locally and internationally. ( 1x2=2mks)
- Distribution. ( 2 mks)
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Wahundura Boys Mock Examination 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
