-
- Explain any five roles played by a warehouse in the production process (10mks)
- Discuss circumstances under which a partnership my be dissolved. (10mks)
-
- Discuss four factors that have hindered the expansion of railway transport in Kenya (8mks)
- The following balance were extracted from the books of Rehema Traders on 1st January 2007
Kshs
Capital 600,000
Creditors 180,000
Motor van 200,000
Furniture 200,000
Stock 60,000
Debtors 80,000
Cash 240,000
The following transactions took place during the year ended 31st December 2007- Sold furniture worth Ksh 60,000 for which Ksh 40,000 cash was received and the balance was due at the end of the year. Purchased goods worth Ksh 100,000 for which cash of Ksh 70,000 was paid and the balance was still outstanding at the end of the year
- Cash Kshs 10,000 was taken from the business by the proprietor to settle the spoure's hospital bill.
Required
Draw Rehema Trader's balance sheet as at 31st December, 2007 showing the items their relevant classes.
-
- Explain five guidelines used by government in spending public resources.
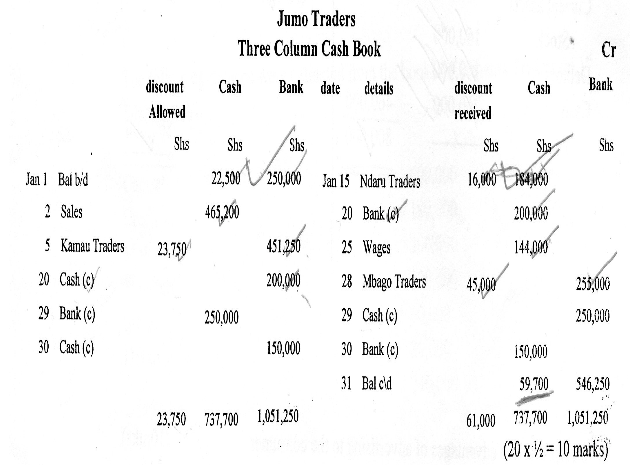
- On 1st January 2011, Jumo Traders had shs 225,000 in cash and shs 250,000 at bank. During the month, the following transactions took place.
Prepare a duly balanced three column cash book. (10mks)2nd Jan Made cash sales of shs 465,200 5th Jan Received a cheque for shs 451,250 from Kamau Traders in full settlement of their debt after allowing a 5% cash discount 15th Jan Paid Ndaru Traders Shs 184,000 in cash after deducting a cash discount of shs 16,000 20th Jan Deposited shs 200,000 from the cash till into the bank 25th Jan Paid wages shs 144,000 in cash 28th Jan Settled Mabgo Trader's account of Shs 300,000 by cheque, less 15% cash discount. 29th Jan Deposited all the cash into the bank. except shs 59,700
-
- Explain five ways in which the price of a product may be determined
- With the aid of an appropriate labeled diagram. Show increase in supply and state five factors leading to that increase.
-
- Explain five differences between a perfect competition and monopoly
- Explain five circumstances where hire-purchase is desirable.
-
- Explain five factors that influence the choice of a product to produce. (10marks)
- Discuss five errors that may not be noticed in a trial balance.

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Explain any five roles played by a warehouse in the production process. (10mks
- Preparation of goods for sales - where the goods are made ready for the consumers.
- Protecting goods against damages - they offer care for the goods
- Safety of the goods against theft; as they have secured them.
- availability of seasonally produced goods as they can be stored and are available in all seasons
- Assist good to be ready for sale - some goods when stored and they mature for sale to the consumers. Improve in quality
- Create room for further production of goods - as there is space available for production to take place continuity in production)
- Stable prices
- faccilitate inspectactive of goods before
- Discuss circumstances under which a partnership may be dissolved. (10mks)
- If the partners agree to dissolve- voluntary dissolutions
- When the business activity the partnership is dealing in becomes outlawed.
- Continued disagreement among partners
- In case of completion of the intended purpose or end of the agreed time.
- In case of retirement or admission of a new partner may lead to temporary dissolution
- In case of court order- which have to be observed
- Explain any five roles played by a warehouse in the production process. (10mks
-
- Discuss four factors that have hindered the expansion of railway transport in Kenya.(8mks)
- High cost-railway construction is an expensive venture requiring huge investments
- Existence of roads network. There exists relatively wide network/competition from other modes of transport
- Poor management - the railway transporting sub-sector has been poorly run, hence stagnation
- Slow speed , rendering it inappropriate for carrying certain goods
- Little government commitment. The government has commitied its resources more on other forms of transport.
- Low industrial base- Which has led to low demand for railway services.
- The following balance were extracted from the books of Rehema Traders on 1st January 2007
Kshs
Capital 600,000
Creditors 180,000
Motor van 200,000
Furniture 200,000
Stock 60,000
Debtors 80,000
Cash 240,000
The following transactions took place during the year ended 31st December 2007- Sold furniture worth Ksh 60,000 for which Ksh 40,000 cash was received and the balance was due at the end of the year. Purchased goods worth Ksh 100,000 for which cash of Ksh 70,000 was paid and the balance was still outstanding at the end of the year
- Cash Kshs 10,000 was taken from the business by the proprietor to settle the spoure's hospital bill.
Required
Draw Rehema Trader's balance sheet as at 31st December, 2007 showing the items their relevant classes. (10mks)- Furniture: 200,000−60,000=140,000
- Cash 240,000 − 40,000=280,000
Creditor 180,000+30,000=210,000 - Debtors 80,000+20,000=100,000
- Stock 60,000 + 100,000 =160,000
- Cash 20,000 − 10,000 = 200,000
- Capital 600,000 − 10,000 =590,000
Rehema traders
Balance sheet
As at 31st Dec 2007
Shs shs shs shs Fixed assets
Motor van 200,000
Furniture 140,000 340,000
Current assets
Stock 160,000
Debtors 100,000
Cash 200,000 460,000
800,000
Capital 590.00
Liabilities
creditor 210,000
800,000
- Discuss four factors that have hindered the expansion of railway transport in Kenya.(8mks)
-
- Explain five guidelines used by government in spending public resources.
- Sanction – before public resources are used, government must get approval from a relevant authority (e.g parchment)
- Proper financial management – proper accounting records should be kept and be audited for accountability /transparency .
- Maximum social benefit – it should be spent in such a manner that majority of the citizens benefits.
- Economy – public finance should be spent in a way to minimize waste
- Productivity - more of the resources should go towards development expenditure as opposed to recurrent expenditure.
- Flexibility – public resources should be use in non-right manner so that its possible to re-direct the resources to more urgent areas when need arises.
- Elasticity – It should be possible to increase or decrease the amount of public finance depending on economic situations e.g during inflation.
- Explain five guidelines used by government in spending public resources.
-
- Explain five ways in which the price of a product may be determined. (10mks
- Price-mechanism – the interplay of demand and supply curves(forces) provides a prevailing price.
- Tendering – where buyers of a product are invited to quote price independently- the one quoting favourable terms and price forms the price for the product.
- Auction – determination of a price through bidding, the highest bidder form the price.
- Price control – where government set a price ceiling where sellers are not supposed to sell beyond.
- Bargaining/haggling – price is decided through negotiation
- Taxation – tax imposed may raise or reduced in price.
- With the aid of an appropriate labeled diagram. Show increase in supply and state five factors leading to that increase.

- Improved technology
- Increased supply of inputs
- Decreased cost of production
- Entry of new firms to industry
- Increased government subsidy's
- Decreased taxation of input.
- Explain five ways in which the price of a product may be determined. (10mks
-
- Explain five differences between a perfect competition and monopoly (10mks)
Perfect completion Monopoly Many sellers
Commodities are homogeneous
There is a free entry and exit into the market by suppliers
Prices determined by the forces of demand and supply
No price discrimination
No government interferenceSingle seller many buyers
Commodities have no close substitutes
There are barriers to entering the market
There exists price discrimination
There may be government interferences - Explain five circumstances where hire-purchase is desirable. (10mks)
- When there is not down payment needed like in hire purchase
- Where the buyer wants to own the goods immediately unlike where in hire purchase ownership is delayed.
- Where the buyer wants to resell the goods immediately unlike in hire purchase
- Where the buyer wants to buy both durable and non-durable goods unlike in hire purchase where durable goods are accessed
- Where the buyer doesn’t want the goods to be re-possessed unlike in hire purchase.
- Where the buyer wants simple proceedings unlike in hire purchase where the procedures are lengthy and time consuming.
- Explain five differences between a perfect competition and monopoly (10mks)
-
- Explain five factors that influence the choice of a product to produce. (10 marks)
- Market/Supply-gap: The size of the unsatisfied market demand which constitute a source of business opportunity will dictate, to a great extent the need to select a particular product. The product with the highest chances of success as reflected in its demand will be selected. In essence, there must be existing obvious demand for the selected product.
- Finance/Fund: The size of the funds that can be mobilized is another important factor. Adequate fund is needed to develop, produce, promote, sell and distribute the product selected.
- Availability of and Access to Raw Materials: Different products require different raw materials. The source quality and quantity of the raw materials needed are factors to be seriously considered, Are the raw materials available in sufficient quantities? Where are the sources of raw materials located? Are they accessible? Could they be sources locally or imported? Satisfactory answers should be provided to these and many other relevant questions,
- Technical Implications: The production process for the product needs to be considered. There is need to know the technical implications of the selected product on the existing production line, available technology and even the labour force. The choice of a particular product may require either acquisition of the machineries or refurbishing of the old ones. The product itself must be technically satisfactory and acceptable to the user.
- Profitability/Marketability: Most often, the product that has the highest profit potential is often selected. However, a product may be selected on the basis of its ability to utilize idle capacity or complement the sale of the existing products. The product must be marketable.
- Availability of Qualified Personnel: Qualified personnel to handle the production and marketing of the product must he available. The cost of producing the product must be kept to the minimum by reducing wastages. This is achievable through competent hands.
- Government Policies: This is quite often an uncontrollable factor. The focuses of government policies can significantly influence the selection of product. For instance, a package of incentives from government for a product will boost its production.
- Companies objectives: The contributions of the product to the realization of the company's short and long range objectives must be considered before selection. For instance, the company goal maybe the achievement of sale growth, sales stability or enhancement of the company's social value.
- Discuss five errors that may not be noticed in a trial balance. (10 marks)
- Error of omission
This is an error where a transaction is completely omitted from the books. No entries were made at all for the transaction. It is as if the transaction has not existed. - Error of commission
In this case, double entry was observed but the transaction was posted to a wrong account of the same class. For example goods sold to John was correctly credited to Revenue (Sales) account but debited to Jane's account. - Error of principle
Double entry observed but an entry made in the wrong class of account. For example, payment by cheque for vehicle repairs correctly credited to bank account but debited to vehicle account instead. In this case, not only the account is wrong (vehicle instead of vehicle repairs) but also the class of account is different. Vehicle account is a real account (asset) whereas vehicle repairs account is a nominal account (expense). - Error of original entry
The transaction was correctly recorded according to the double entry system but with the wrong amount. For example, payment of telephone expenses in cash of shs560 was credited to cash account and debited to telephone expenses account but by shs600 in both accounts. - Complete reversal of entries
For a given transaction, the account to be debited was credited and the account to be credited was debited. For example, goods sold to Nadia for shs500 was debited to Revenue (Sales) account and credited to Nadia's account, both by shs500. - Compensating errors
Errors on the debit side of the ledger have been set off by errors on the credit side of the ledger. For example, vehicle account (debit balance) and commission received account (credit balance) were both understated by shs200.
- Error of omission
- Explain five factors that influence the choice of a product to produce. (10 marks)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Business Studies Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Momaliche Post Mock 2020 Exam.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students