INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
- Answer all the questions in section A and B.
- Answer any two questions in section C.
For Examiner’s Use Only
|
SECTION |
QUESTIONS |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATES SCORE |
|
A |
1-18 |
30 |
|
|
B |
19-22 |
20 |
|
|
C |
|
20 20 |
|
|
TOTAL |
90 |

QUESTIONS
SECTION A : 30 MARKS
Answer all questions in this section
- Name four tools that are used when laying concrete blocks during construction of a wall. (2 marks)
- Why is it necessary to have guard rails in a farrowing pen? (1 mark)
- Give two reasons for having a footbath in a cattle dip. (1 mark)
- Distinguish between crutching and ringing in sheep management. (2 marks)
- State four signs that indicate that a doe is about to kindle. (2 marks)
- Name two developmental stages of a liverfluke (Fasciola sp.) which occur in the fresh water snail (Limnaea sp). (1 mark)
- State four uses of a spring tine harrow. (2 marks)
- State four signs of mite attack in poultry. (2 marks)
- State three advantages of natural feeding in calf rearing. (11/2 marks)
- Give three ways in which infectious diseases can spread from one livestock to another within a farm. (1½ marks)
- State four reasons for castration in pig production. (2 marks)
- State four characteristics of roughage livestock feeds. (2 marks)
- State two functions of the crop in poultry digestive system. (1 mark)
- State four roles of worker bees in a colony. (2 marks)
- Give four reasons for controlling livestock diseases. (2 marks)
- State three ways of caponisation in poultry. (11/2 marks)
- State four advantages of using animals instead of tractors as a source of power on the farm. (2 marks)
- Name one livestock disease that is transmitted by each of the following parasites:
- blue ticks; (1/2 marks)
- Brown ear ticks; (1/2 marks)
- tsetse flies. (1/2 marks)
SECTION B: 20 MARKS
- The illustration below shows a practice carried out to prevent mastitis infection in a dairy cow.
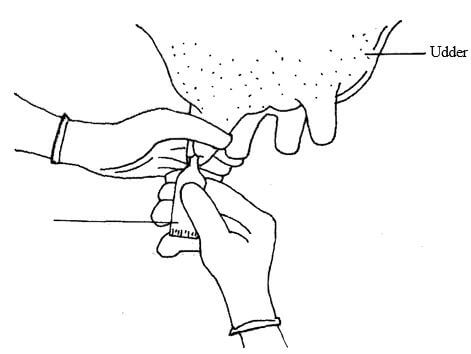
- Identify the practice. (1 marks)
- At what stage is the practice carried out? (1 marks)
- State two other practices that are carried out on the udder to prevent mastitis infection. (2 marks)
- Name the equipment labelled X in the diagram. (1mark)
- A dairy farmer is required to prepare 200 kg of dairy meal containing 20% Digestible Crude Protein (D.C.P.). Using the Pearson's Square Method, calculate the quantity of soya bean (40% D.C.P.) and rice (16% D.C.P.) the farmer requires for the dairy meal. (5 marks)
- The following diagram shows a disc plough. Use it to answer the following questions.
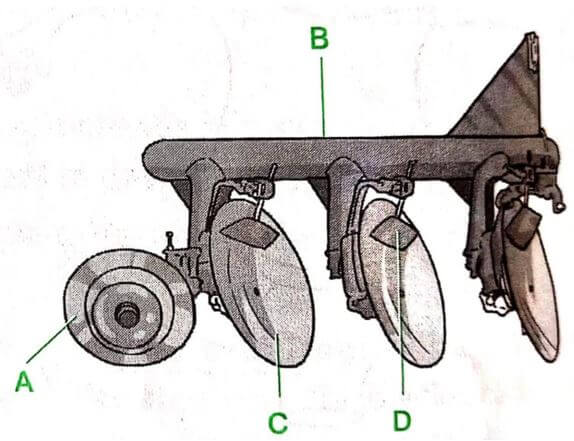
- Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (2 marks)
A ................................................................
B ................................................................
C ................................................................
D ................................................................ - Give one function of each of the parts labelled A and D. (2 marks)
- Identify the implement. (1 mark)
- Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (2 marks)
- The following illustrations show the behavior of chicks in a brooder. Study them carefully and answer the questions that follow.
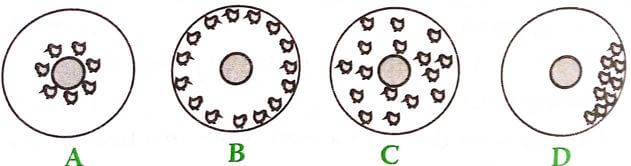
- Explain the cause of behavior observed in chicks for each of the illustrations labeled A, B and D. (3 marks)
- Give a reason for making the brooder wall round in shape. (1 mark)
- State two requirements of a good brooder. (2 marks)
SECTION C : 40 MARKS
-
- Explain the factors considered when culling livestock. (5 marks)
- Describe poultry management under the following sub-headings:
- Causes of stress; (8 marks)
- Control measures for cannibalism. (7 marks)
-
- State the function of any six parts of a zero grazing unit (6 marks)
- Describe Nagana disease under the following sub-headings.
- Cause. (1 mark)
- Symptoms of attack. (4 marks)
- Control measures of the disease. (4 marks)
- Explain five ways in which ticks can be controlled in a livestock farm. (5 marks)
-
- Describe ten physical characteristics a poultry farmer would use to identify poor layers from a flock of hens. (10 marks)
-
- Outline three characteristics of clean milk. (3 marks)
- Explain seven factors that affect milk composition in dairy farming. (7 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Tools used when laying concrete blocks during construction of a wall.
- Plumb bob/plumb line
- Mason’s trowel
- Spirit level/pipe level
- Wood float/steel float
- Masons square
- String/masons line/line (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- Importance of guard rails in a farrowing pen.
- Prevents sow from crushing piglets .
- Prevents sow from eating creep feeds. (1 x 1 = 1 mark)
- Reasons for having foot bath in a cattle dip.
- Clean the feet of animals
- Control foot rot Rej. Control of diseases (2 x 1/2 = 1 mark)
- Crutching and ringing
- Crutching is the cutting of wool around the external reproductive organs of a female sheep to facilitate mating
- Ringing is the cutting of wool around the sheath of the penis in rams to facilitate mating.
(Mark as a whole 1 mark)
- Signs of kindling in a doe.
- Nest building
- Plucking of fur From the body
- Lose of appetite.
- Restlessness. (4 x ½ = 2 marks)
- Developmental stages of liver flukes in a fresh water snail.
- Sporocyst.
- Cercaria
- Redia. (2 x ½ = 1mark)
- Uses of a spring -tine harrow.
- Levelling the seedbed.
- Breaking soil clods.
- Burying trash
- Aerating the soil.
(4 x ½ =2 marks)
- Signs of mite attack in poultry,
- Irritation/scratching of the body.
- Anaemia,
- Presence of mites below the plumage in patches.
- Falling off of feathers.
- Dermatitis due to burrowing effects.
- Formation of crusts. (4 x ½ = 2 marks)
- Advantages of natural feeding in calf rearing.
- Calf takes milk at body temperature,
- Milk is free from contamination
- it prevents scouring in calves.
- Milk is provided ad libitum. (3 x ½ = 1 ½ marks)
- Ways in which infectious diseases can spread
- through vectors
- through ingestion of contaminated food and water/through food and water
- Through contact
- Through inhalation of contaminated air/through air. (3 x 1/2 = 11/2 marks)
- Reasons for castration
- Prevent uncontrolled mating.
- Improve the quality of meat
- Promote faster growth/facilitate weigh gain
- Make then docile
- Control breeding diseases
- Control inbreeding (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- Characteristics of roughages
- Bulky
- High fibre content
- Low nutrient content
- Low digestibility
(4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- Functions of the crop in poultry digestive system.
- Softening/moistening food
- Temporary food storage. (2 x 1/2 = 1 mark)
- Roles of worker bees .
- Kills the drones after mating the queen
- Scouting for a new home
- collect nectar/water/gum/propolis/pollen
- Make honey combs
- Protect the colony
- Clean the hive
- Make honey and bees wax
- Seal the cracks and crevices. (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- Reasons for controlling livestock diseases.
- Reduces spread of livestock diseases/production of healthy young ones
- Promote fast growth and early maturity - rej to maintain good health in livestock
- Make them have long productive life.
- Improve quality and safety of products
- Improve quantity of products
- Reduce cost of production. (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- Caponisation in poultry.
- Surgical /open method.
- Implanting pellets of the female sex hormone beneath the skin of the bird.
- Injecting with stilbestol hormone when whey are one day old.
(3 x ½ = 1 ½ marks)
- Advantages of using animal power.
- Animals are cheap to acquire /maintain.
- Require less skilled labour.
- Can be used on,small holdings.
- Are appropriate in very steep areas.
(4 x ½= 2 marks)
-
- Blue ticks - Anaplasmosis
- Brown ear ticks - E.C.F,
- Tsetse flies - Trypanosomiasis (nagana)
(3x ½ =1 ½ marks)
-
- Dry cow therapy. (1mk)
- At the end of drying off. (1/2 mark)
-
- teat dipping
- complete milking
- proper milking technique
- applying milking jelly after (2x1=2 marks)
- Hypodemic needle and syringe
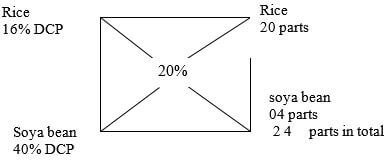
Rice - 20/24 x 100 = 83.3 kg
Soya bean - 4/24 x 100 = 16.7 kg
(1 x 5 = 4marks)-
-
- Furrow wheel /Rear depth wheel / Control wheel /Thrust wheel
- Beam
- Disc
- Disc scrapper
- A -Controlling ploughing depth
-Stabilising the plough/controlling side thrust
D -Asisting in furrow slice inversion.
-Removing soil from the disc during ploughing - Disc plough
-
-
- Causes of chicks’ behaviour in the illustrations A, B and C.
- Presence of draught makes the chicks to crowd on one side of the brooder
- Cold/inadequate heat makes the chicks to crowd around the heat source.
- High/Excess heat makes the chicks to move away from the heat source.
(3 x 1 = 3 marks)
-
- Reasons for making brooder wall round in shape.
- To discourage overcrowding of chicks at the corners to avoid suffocation.
(1 x 1 = 1 mark)
- Requirements of a good brooder.
- Should have enough feed and water troughs
- It should be well aerated.
- Should be spacious enough
- It should be easy clean
- It should be properly drained.
(4 x ½= 2 marks)
- Causes of chicks’ behaviour in the illustrations A, B and C.
-
- Factors considered when culling livestock.
- Cull livestock of:
- Poor health;/chronic sickness
- Old age;
- Physical deformities;
- Hereditary defects;
- Infertility;
- Poor mothering ability
- Poor quality products;
- Low production;
- Bad temperament.
(1 X 5 = 5 marks)
- Description of poultry management under:
- Cause of stress.
- Any sudden change in routine
- parasite infestations
- Lack of food and water
- Strangers and predators in the birds' house.
- Sudden noise such as passing tractors and thunder.
- Poor handling of birds during routine practices.
- Overcrowding which leads, to competition for space.
- Sudden climatic changes
- Poor lighting in poultry house.
- Inadequate laying nests. (1x8 marks )
- Control measures for cannibalism
- Control external parasites.
- Keep birds busy by hanging green leaves or vegetables in the house.
- Feed the birds on a balanced diet.
- Provide adequate floor space.
- Provide adequate laying nests.
- Provide dim lights in the brooder.
- Keep birds as per the age group.
- Debeak hens which peck others.
- Cull perpetual cannibals. (7 x 1 = 7 marks)
- Cause of stress.
- Factors considered when culling livestock.
-
- Use of the various parts of a zero grazing unit in dairy farming.
- Milk recording room - weighing and milking records
- Milking stall - rearing calf to weaning
- Calf pen - rearing calf up to weaning
- Sleeping cubicles - provide shelter and warmth
- Loofing area - dunging, feeding, exercise and sunning
- Feed and water troughs - feeding and watering the animals
- Feed preparation room - preparing feed rations and cropping fodder rej. chaff cutter region
- Store - storing/keeping dairy equipment/feeds
- Manure storage areas storing measure.
Parts is tied to the function
( 6 x 1 = 6 marks)
- Trypanosomiasis Disease under the following sub-headings.
- Cause.
- Protozoa .-Trypanosoma spp
- Trypanosoma brucei.
- Trypanosoma evansi.
- Animals affected.
- Cattle.
- Sheep.
- Goats
- Horse.
- Pigs.
- Symptoms of attack.
- Fever.
- Loss of appetite/anorexia.
- General boby weakness.
- Swolen lymph nodes
- Lachrimation which leads to blindness.
- Diarrhoea.
- Rough coat and sometimes without hair and may be cracked.
- Swelling in parts of the belly.
- Drop in milk production.
- Loss of hair at tail end.
- Anaemia.
- Abortion may occour in pregnant females.
- Control measures.
- Treating animals with trypanocidal drugs.
- Effective vector (tsetsefly ) control .
- Confinement of wild animals in game parks.
- Cause.
- Use of the various parts of a zero grazing unit in dairy farming.
-
- Characteristics of a poor layer.
- Combs and wattles - small/shrivelled/shrunken. dry scaly and place.
- eyes - dull and pale yellow.
- Beak - yellowish in colour.
- Abdomen/breast - hard and full
- Vent - round, dry and less active
- Space between keen and pelvic bone - small and fits only one or two fingers
- Plummage - preened & glossy (smooth) beautiful
- Moulting - early moulting
- Shanks/feet - Yellowish in colour
- Broodiness - Is common/early moulting
- Temperament - easy and dull
- poor layer is inactive.
Mark as a whole (10 x 1 = 10 marks)
-
- Characteristics of clean milk
- Free from disease causing micro-organisms/pathogens
- Free from hair, dirt or dust./contamination.
- Free from bad odours and tastes/has good flavours.
- Chemical composition within expected standards. (3 x 1 = 3 marks)
- White in colour.
- Factors influencing milk composition
- Age of animal
- Butter fat in milk becomes less as an animal grows old thus young animals produce milk with higher BF than older animals.
- Breed differences rej. species of the animal
- Different breeds of cattle produce milk with differing percentage composition e.g Jersey produce higher BF than Friesian.
- Type of food eaten by an animal
- Roughage feeds produce milk with higher fats, lactose and protein compared to grains.
- Diseases
- Diseases such as mastitis reduce the lactose composition in milk because bacteria attack milk sugars.
- Physiological condition of the animal.
- Sick/extremely emaciated animals register low percentage of BF/during late pregnancy cows produce milk with low BF content.
- Stage of lactation
- The BF content in milk is highest at the middle phase of the lactation period and lowers towards end of lactation.
- Completeness of milking
- Milk drawn last from udder during contains high BF content/last drop milk has BF content produce in the milk.
- Season of the year - accept environmental condition
- BF content increases during cold seasons.
- Time of milking
- Milk produced in the morning has a lower BF content than milk produced in the evening
(1/2 factor ,1/2 mk explanation) (7 x 1 = 7 marks)
- Milk produced in the morning has a lower BF content than milk produced in the evening
- Age of animal
- Characteristics of clean milk
- Characteristics of a poor layer.
Download Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Bunamfan Post Mock 2021 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

