443/1
AGRICULTURE
MARCH 2018
PAPER 1
MARKING SCHEME
CATHOLIC DIOCESE OF KERICHO (CDK) EXAMS – 2018
PRE-MOCK
AGRICULTURE PAPER 1
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in the space provided
-
State four advantages of plantation farming (2mks)
- Generate foreign exchange when products are exported
- create employment opportunities
- Products of high quality and quantity are obtained
- Huge economic benefits (profit) are obtained due to utilization of economies of scale
- May lead to provision of improvement of infrastructure and amenities eg roads, electricity etc
- Expands domestic / local market
- Government earns revenue from taxation. (1/2 mark each x 4) = 2 marks
-
List any four advantages of mixed farming (2mks)
- Mutual benefits between livestock and crops
- Income is earned throughout the year
- Diversification of farm enterprises / Security of income
- Livestock eg oxen are used to provide farm power
- Enables good distribution and use of farm power. (any 4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
-
State four ways through which pests affect agriculture (2mks)
- Feed on whole or part of plant, hence lower quantity and quality
- Transmit crop diseases
- Injure plant parts / lowers rotting / expose it to secondary infection
- Increase costs of providing crops / pesticide are expensive. (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
-
State four ways in which minimum tillage can be achieved (2mks)
- Application of herbicides for controlling weeds
- Use of mulch to control weeds
- Timing cultivation
- Restricting cultivation to planted ares
- Establishing cover crops
- Slashing weed. (4 x 1/2 = 2 mks)
-
Outline four importance of keeping breeding records in dairy farming (2mks)
- Selection and culling
- Controlling breeding
- Shows fertility and prolificacy of animals
- Shows ancestral history of the animal
-
Give a reason for each of the following practices during compost making (2mks)
- Adding top soil
To introduce micro organisms for decomposition. - Adding farm yard manure
Provides nutrients to micro-organisms - Adding ash
Improves levels of phosphorus and potassium - Adding calcium ammonium nitrate
To raise level of nitrogen in the manure.
- Adding top soil
-
State four characteristics of intensive farming (2mks)
- High capital investment
- High labour investment per unit area.
- High yield per unit area
- Use of skilled labour.
- Modern technology applied. 4 x 1/2 = 2 marks
-
Give the element whose its deficiency is characterized by the following
- Intervenial chlorosis of leaves (1/2 mk)
magnesium - Blossim-end-rot in tomato fruit (½ mk)
calcium - Scorched edges of a leaf (½ mk)
Potassium
- Intervenial chlorosis of leaves (1/2 mk)
- Give the practices done to achieve single stem capped system pruning in coffee production (2mks)
- Main stem capped at 53cm
- Best growing suckers allowed to grow upwards
- Second capping at 114 cm
- Final capping is done at 163 cm
- State three, areas that should be avoided when sampling soil (1½mk)
- Dead furrows
- Terrace stands
- Swampy areas
- Near trees and boundaries
- Between slope and bottom land
- Outline how you would prepare a store for grain storage (2mks)
- Clean by removing all debris of previous crops
- Dusting with appropriate chemical to control storage pests
- Clear vegetation around to keep off various vermin
- repair broken / worn out parts, replace thatch / roofing materials
- State four ways by which a farmer can improve his pasture (2mks)
- Controlled rotational grazing
- Re-seeding / over sowing
- Fertilizer application
- Mixed grass and legumes pastures
- deferment
- Give the importance of a land title deed (3mks)
- It is a proof of ownership
- Reduce land ownership disputes
- Can be a security in acquisition of loan
- The owner can lease out whole of part of his land for income
- It is an incentive for investment by the farmer on long term project.
- What do you understand by the term.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM) (1mks)
It is the use of a combination of more than one method to control pests. - List two factors that affect efficiency of pesticides in crop production (1mk)
- Concentration of pesticide
- Timing of application / development stage of pest
- weather condition at the time of application
- Persistence of pesticide
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM) (1mks)
- Name four methods of controlling smut disease in maize (2mks)
- Hot water treatment
- Use of certified seeds
- Crop rotation
- Field hygiene
SECTION B
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided
- A cow requires 4kgs of dry matter (DM) for every 100kg of body weight per day
- Calculate the amount of dry matter a cow weighing 500kg would require per day (show your working ) (2mks)
500kg/100kg x 4 = 20kg DM/day - Given the silage has 40% DM how many kilograms of silage should the cow be given per day (show your working) (2mks)
A cow should be given 50% of its daily DM requirements from silage and other 50% from other feeds.
Amount of DM required from silage is therefore 10kg
100kg silage contain 40kg DM
? 10kg DM
Let the amount of silage required to give 10kg DM be x.
x/100 = 10/40 (1mk)
x = 10 x 100kg/40 = 20kg
- Calculate the amount of dry matter a cow weighing 500kg would require per day (show your working ) (2mks)
-
- The diagram below shows various fencing post. Name post E, F, G and H (4mks)
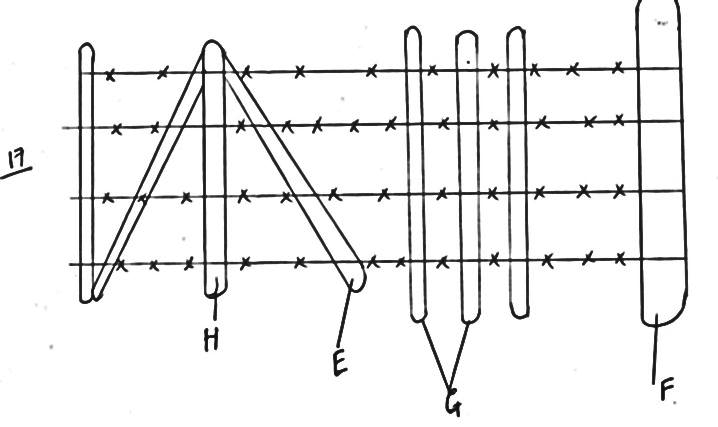
E - Strainer Post
F - Strut
G- Dropper
H- Standard - Give three ways of improving the above type of fence so that it becomes more effective Controlling animals and human movement (3mks)
- Adding wooven / barbed wire
- Planting thorny wire fences / trees along side
- Adding more droppers
- The diagram below shows various fencing post. Name post E, F, G and H (4mks)
- Below is an illustration of the stomach of a young ruminant animal
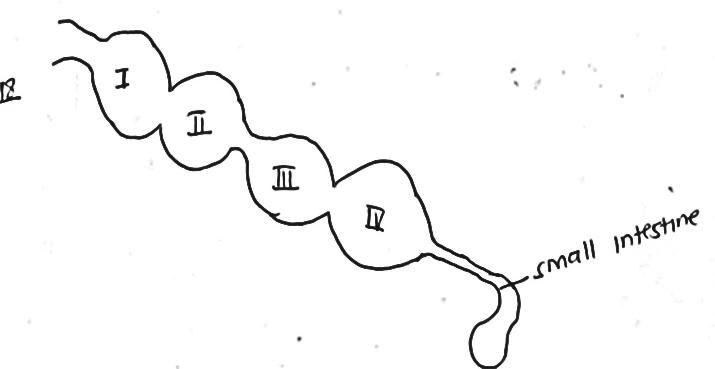
- Name the parts labeled I, II, III and IV (2mks)
- Rumen
- Reticulum
- Omasum
- Abomasum
- What are the functions of the parts labeled II (2mks)
- Trapping non food materials such as nylon
- Rejecting large food materials which are returned back to the mouth
- Why is the part labeled (IV) much bigger than (I) in type young ruminant animals (1mk)
It is not developed yet since it is not yet in use. - Give four difference between ruminant and non-ruminant (4mks)
Ruminant Non-Ruminant (i) They have four stomach compartments Have one compartment (ii) They regurgitate food material They cannot regurgitate food material (iii) They chew curd They cannot chew curd
- Name the parts labeled I, II, III and IV (2mks)
SECTION C (40MKS)
Answer any two questions in this section in the spaces provided
-
- Discuss the harvesting of cotton under the following subheadings
- stage of harvesting (3mks)
- 4-41/2 months after planting when balls open.
- Start picking as soon as the balls open.
- Do it on weekly intervals to prevent disolouration of lint.
- methods and procedure of harvesting (4mks)
- Picking is done manually.
- The seed cotton is sorted into two grades AR-first grade free from inset damage and foreign matter and be clean white. BR-may not have all these qualities.
- The picker carries two containers while harvesting one for grade AR and the other for BR.
- The seed cotton is sorted into two grades AR (Safi) BR (Fifi)
- precautions in harvesting (3mks)
- Ensure no foreign matter such as leaves and twigs are mixed with seed cotton
- Avoid picking when cotton is wet.
- Avoid handling harvested cotton using sisal bags since their fibres may mix with the seed cotton creating problems during ginning.
- stage of harvesting (3mks)
- Explain how various field practices help to control crop diseases (10mks)
- Crop rotation-breaks life cycles of pathogen.
- Rogueing-checks disease spread.
- Planting certified/clean seeds-prevents introductior of pathogens into the field.
- Early planting/timely planting-crops establish as ar before the outbreak of diseases.
- Proper spacing-creates unfavorable micro-climate or some pathogens.
- Weed control removes alternate hosts of some patogens.
- Use of clean tools and equipment reduces chances of contaminating crops with pathogens.
- Pruning-removes diseased plant parts and creates unfavorable micro -climate.
- Quarantine- prevents spread of pathogens.
- Heat treatment -kills pathogens.
- Destruction of crop residue-kills pathogens and destroys breeding grounds.
- Pest control reduces disease vector,
- Proper fertilizer / manure application controls deficiency diseases
- Close season breaks life cycles of pathogens (stating 1/2 mark explanation 1/2 mark)
- Discuss the harvesting of cotton under the following subheadings
- Describe the production of beans under the following sub headings
- Ecological requirements (4mks)
- Beans do best in well drained soils rich organic mater.
- Beans cannot tolerate water logged soils.
- It requires moderate rainfall.
- Heavy rain is destructive during flowering stage.
- Beans grow well at an altitude between 0-2709 above sea level.
- It requires less humid conditions.
- Seed bed preparation (5mks)
- Seedbed preparation should be done early enough!
- Clear the land and remove stumps.
- Remove all weeds ensure that underground roots are exposed to the sun
- Carry out primary cultivation
- Carry out secondary cultivation
- Carry out secondary cultivation to achieve medium till
- Planting (5mks)
- Planting - Timely planting should be observed.
- Beans should be planted at the onset of rains.
- Any delay in planting results into low yields.
- Dry planting can be done in semi-arid areas
- Use certified seeds.
- Seed rate of 50 kg -100kg/ha depending on Variety (pure stand)
- Use the spacing of 60 x 15cm for indeterminate varieties and 30-45 x15 cm for determinate varieties.
- Use 200kg DSP/ha pure stand 200 kg/ha can also be used on pure stand crop.
- Place fertilizer along planting furrows or holes and mix with soil before planting the seeds
- Place 2 seeds per planting hole.
- Cover the seeds or holes well.
- Pest and pest control (6mks)
- Bean fly - Early planting, crop rotation seed dressing spraying with dimethoate malathion
- Bean aphid --spray regularly especially during dry season with dimethout, malathion.
- Flower trips -spray with malathion, diazinon, dimethoote.
- American bollworm-spray with malatthion diazinon
- Bean bruchid
- Cutworm
- Golden ring moth
- Pea pod borer
- Spiny brown bugs
- Ecological requirements (4mks)
-
- Explain five advantages of mulching in crop production (5mks)
- Has an insulating effect thus modifies/regulates soil temperatures
- Prevents water evaporation therefore moisture is retained in the soil for the plant use.
- Controls soil erosion by intercepting rain drops before they hit the soil,
- Reducing the speed of runoff and increasing rate of water infiltration
- Organic mulch decomposes into humus thereby improving soil structure/water holding capacity/drainage/aeration
- After decomposition it improves soil fertility by releasing nutrients.
- Controls weed by covering the soil and sup repressing their growth.
- After decomposition organic mulch betters soil PH increases calcium exchange capacity
- Outline five activities that may be undertaken in organic farming (5mks)
- Mulching
- Application of organic manure/organic fertilizers
- Crop rotation
- Use of medicinal plant products to control diseases and parasites
- Rearing of livestock on natural/feedstuffs without use of chemical additives
- Physical/cultural/pests/weed parasite and disease control.
- Discuss ten benefits a farmer is likely to get using vegetative propagation in production of oranges (10mks)
- Production/development of early maturing crop
- Development of high yielding orange crop
- Makes the plant to assume the desired shape/size eg budding spread sideways easy to manage
- Can obtain two or more orange varieties on the same root stock
- Ensures maintenance of genetic clonal characteristics to ensure uniformity.
- Facilitates development of drought resistant crop
- It facilitate propagation of seedless orange varieties.
- It's used to develop tree plant that are less thorny
- Facilitates fast multiplication of the desired crop variety of oranges
- Is utilized to develop orange crop that is resistant to diseases
- Is utilized in repair treatment of damaged parts of orange trees. (10mks)
- Explain five advantages of mulching in crop production (5mks)
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Marking Scheme - CATHOLIC DIOCESE OF KERICHO (CDK) EXAMS – 2018 PRE-MOCK WITH MARKING SCHEME.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

