- You are provide with a food solution mixture labeled Y. you are also provided with the following reagents. 1% copper (II) sulphate solution, 10% sodium hydroxide solution, 0.1% DCPIP solution and a filter paper. Carry out tests to determine the food substances present in Y (12 marks)
Food substance being tested
Procedure
Observation
Conclusion
- The Diagram below shows two organisms (R and S) belonging to the same phylum
- Name the class in which the organisms shown above belong. (2 Mark)
- Organism R
- Organism S
- Other than presence of exoskeleton, listtwo observable similarities between the two organisms (2 Marks)
R
S
- Listtwo observable differences between the two organisms (2 Marks)
P
S
- Explain how the organism labelled P is adapted to safeguard itself from the predator (2 Marks)
-
- Name the gaseous exchange system exhibited by organism S (1 Mark)
- State the respiratory surface used by organism S (1 Mark)
- Discussfour functions of exoskeleton (4 Marks)
- Name the class in which the organisms shown above belong. (2 Mark)
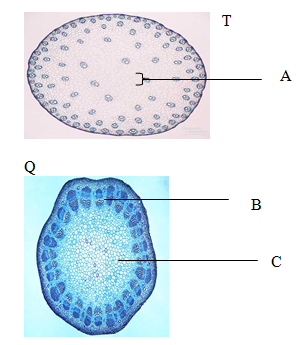
- The following micrographs show images taken from a transverse section of a various stems by a light microscope. Analyze them closely and use them to answer questions that follow.
- On the diagram, label part A, B and C (3 Marks)
- Explain the adaptation of the parts C and D to their functions (2 Marks)
- Identifyfive differences between cross section T and Q and record them in the table below. (5 Marks)
T
Q
- Explain how part B facilitates the process of secondary growth (4 Marks)

MARKING SCHEME
Question 1.
|
Food substance being tested |
Procedure |
Observation |
Conclusion |
|
Proteins; |
-Put the food substance in a test tube -Add sodium hydroxide solution -Add 1% Copper II Sulphate; |
Purple Colour; |
Protein present; |
|
Vitamin C; |
-Add DCPIP in the test tube -Add the food substance drop by drop as you shake; |
No colour change/ DCPIP is not decolorized; |
Vitamin C Absent; |
|
Lipids; |
-Rub/smear the substance being tested on the surface of filter paper -Warm the paper by bringing it close to the flame -Observe it through light; |
-The paper is translucent/ There are translucent spots OR -Permanent translucent mark persists; |
Lipids present; |
-4 mark each (12 marks in total). Marks for procedure occur at the end of the collect procedure.
-Reject colour stroking. If procedure is wrong, all the succeeding sections are wrong.
Question 2.
-
- Arachnida;
- Insecta; rej. When word start with small letter.
- - Jointed appendages;
- Bilateral symmetry;
- Have segmented body; -
R
S
-Body is divided into two parts (Cephalothorax)
- Body is divided into three parts;
- Two chelicerae each having a craw-like structures
-Does not have chelicerae;
- Each leg ends into two toothed craw
-Does not have toothed craw;
- Arachnids have no antennae
-Have a pair of antennae;
- -The body colour that matches with the surrounding and therefore the predator cannot be able to identify and attack the organism.
-Lower side of the hind limb/tibia has spikes to strike the predator/any other relevant explanation -
- Tracheal system
- Tracheole/tracheoles
- -It provides support to terrestrial arthropods;
-It also provides point of attachment for body muscles;
-It prevents desiccation of the body and by secreting wax;
-It protects the organism from mechanical injury;
Question 3.
- A-Vascular bundles;
B- Intravascular cambium/cambium;
C- Sclerenchyma;
labeling must be done on the diagram, not on the space provided. - C- Thickened by lignin to provide mechanical support and strengthening the plants;
D -Consist of numerous parenchyma cells that store water and food substances;
-Packed with storage tissues to store of food and water; -
T
Q
No pith
Pith present
Vascular bundles scattered
Vascular bundles in a ring
Numerous vascular bundles
Few vascular bundles
Cambium Absent
Cambium present
Small Vascular bundles
Large Vascular bundles
- -Inner cambium/cambial cells divide and increase in number thereby forming secondary xylem;
-Secondary xylem push primary xylem cells toward the center;
-Outer group of cambium/cambial cells divide and increase in number thereby forming secondary phloem;
- Secondary phloem pushes primary phloem cells toward the periphery;
- Plant stems increases in girth/diameter
5 max 4-each point one mark
Download BIOLOGY PAPER 3 - KCSE 2019 NYANDARUA PRE MOCK EXAMINATION.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students