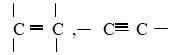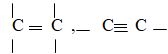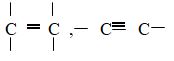CHEMISTRY
PAPER 3: PRACTICAL
- You are provided with the following solutions:
- M1 containing 95g of a mixture of sodium carbonate and sodium chloride per litre of solution.
- M2 which is 1MHCl.
You are to determine the percentage of sodium chloride in the mixture.
Proceed as follows. Fill the burette with M2. - Pipette 25.0cm3 of M1 and titrate with M2 from the burette using 3-4 drops of methyl orange indicator.
- Stop titrating when a permanent pink colour appears. Repeat experiment and complete the table below.
- Table 1
(4 marks )I II III Final burette reading (cm3 ) Initial burette reading (cm3 ) Volume of M2 used (cm3 ) - Determine the average volume of M2 used. Show your workings. (1 mark)
- Determine the number of moles of M2 used. (1 mark)
- Write down an ionic equation for the substances that react. (1 mark)
- Determine the number of moles of the carbonate used. (1 mark)
- Calculate the concentration of sodium carbonate (1 mark)
- Determine the mass of sodium carbonate in 1 litre of the solution ( Na = 23, C = 12,O = 16 ) ( 1 mark )
- Determine the percentage of sodium chloride in the mixture. (1 mark)
- Table 1
- You are provided with 5.0g of salt T. You are required to determine the solubility of salt T in water at different temperatures.
Procedure- Place all salt T into a clean boiling tube.
- Transfer 5cm3 of distilled water from 10ml measuring cylinder into the boiling tube containing salt T. Insert the thermometer into the boiling tube.
- Heat the mixture of salt T and water carefully until all the salt dissolves and the solution is clear
- Remove the boiling tube from the flame and allow it to cool while stirring with the thermometer carefully and gently. NOTE: The temperature (Ts) at which the crystals first appear.
Record this temperature in the table. - Using the same mixture from (iv) above, add from 10ml measuring 1cm3 of more water and repeat procedures (iii) and (iv) above. Carry out four (4) more experiments and enter you results in the table below.
NOTE:
You may fasten cooling for the first two temperatures readings by pouring cold water from the tap on the sides of the boiling tube or insert the boiling tube in a beaker containing cold water
Table 2 (6 marks)
Volume of water added (cm3) 5 6 7 8 9 10 Crystallization temperature, Ts (ºC) Solubility of salt T in g/100g water - Complete the table by calculating solubility at different temperatures
- Plot a graph of solubility of salt T against crystallization temperature Ts. (3 marks )
- Use your graph to determine the solubility of Salt T in water at 62ºC. (1 mark)
- From your graph determine the temperature at which 75g of T will dissolve in 100g of water. (1mark)
-
- You are provided with solid W. Carry out the test and record your observations in the spaces below. Put solid W in a boiling tube. Add about 10cm3 of distilled water and shake. Divide the solution into five portions
- To the first portion add sodium hydroxide drop wise then in excess
Observation Inference
(1mk)
(1mk) - To the second portion add 3 drops of sodium sulphate solution
Observation Inference
(1mk)
(1mk) - To the third portion add ammonium hydroxide drop wise then in excess
Observation Inference
(1/2mk)
(1mk) - To the fourth portion, add 3 drops of lead nitrate solution and warm
Observation Inference
(1mk)
(1mk) - To the fifth portion, add 3 drops of acidified barium nitrate
Observation Inference
(1mk)
(1mk)
- To the first portion add sodium hydroxide drop wise then in excess
- You are provided with solid X. Carry out the test and record your observations in the spaces below.
- Put half of solid X on a metallic spatula and heat using a Bunsen burner
Observation Inference
(1mk)
(1mk) - Put the second half in a boiling tube. Add about 10cm3 of distilled water and shake. Divide the resulting solution into four portions
Observation Inference
(1mk)
(1/2mk) - To the first portion add three drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) and shake
Observation Inference
(1/2mk)
(1mk) - To the second portion add three drops of bromine water and shake
Observation Inference
(1/2mk)
(1mk) - To the third portion add sodium hydrogen carbonate
Observation Inference
(1/2mk)
(1/2mk) - To the fourth portion add three drops of universal indicator. Compare the colour of the solution using pH colour chart
Observation Inference
(1/2mk)
(1/2mk)
- Put half of solid X on a metallic spatula and heat using a Bunsen burner
- You are provided with solid W. Carry out the test and record your observations in the spaces below. Put solid W in a boiling tube. Add about 10cm3 of distilled water and shake. Divide the solution into five portions
CONFIDENTIAL
- Each candidate should be provided with:
- 100cm3 of solution M2
- 80cm3 of solution M1
- Pipette
- Burette
- 2 conical flasks
- Filter funnel
- Pipette filler
- Methyl Orange Indicator
- Thermometer – 10 -110º C
- 200cm3 of distilled water
- 6 test tubes in a rack
- 2 boiling tubes
- Test tube holder
- About 1g of solid W in a stoppered container.
- About 1g of X in a stoppered container.
- 0.5g of NaHCO3
- 5.0g of solid T
- 250ml glass beaker
- spatula
- 10ml measuring cylinder
- ACCESS TO
- Source of heat
- Methyl orange indicator, supplied with a dropper
- Na2SO4 supplied with a dropper
- 2M NaOH supplied with a dropper
- 2M NH4OH supplied with a dropper
- Acidified potassium Manganate (VI1)
- Lead Nitrate solution
- Acidified Barium Nitrate Solution
- Universal Indicator
- PH Colour Chart
- Bromine Water
NOTE:
- Solid X is Maleic Acid
- Solid W Aluminium sulphate
- Solution M1 is prepared by mixing 53g of Na2CO3 solid and 42g of NaCl and diluting it to one litre
- Solution M2 is 1.0M HCl.
- Solid T is 5g Oxalic Acid
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Complete table (CT) =1
Decimal places (D.P) =1
Principal of averaging (P.A) =1
Accuracy =1
Final accuracy=1 - Titre (I) +(II)+ (III) = correct ans -1
3 - Ans in (b) x 1 = correct ans ✓ 1
1000 - 2H+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → H2O(l) + CO2(g) ✓1
- Moles of carbonate = ½ x ans in (c ) ✓ ½ = correct ans ✓ ½
- Ans in (e) x 1000 ✓ ½ = correct ans ✓ ½
25 - RFM of Na2CO3 = (23 x 2 ) + 12 + ( 16 x 3 ) = 106 ✓ ½
Mass = 106 x ans in (f) ✓ ½ - 95 – ans in (g) x 100 ✓ ½
95
= correct ans ✓
- Complete table (CT) =1
- Expected results
-
At filling the values of solubility 3 marks ( ½ mk each )Volume of water added (cm3) 5 6 7 8 9 10 Crystallization temperature, Ts (ºC) 82 71 54 45 40 36 Solubility of salt T in g/100g water 100 83.33 71.43 62.5 55.56 50
Trend 0.5
Accuracy ± 2 = 1
D.P ½
CT on temperature 1 - Graph - Curve 1
Plotting 1
Scale 0.5
Labelling axis 0.5
3 marks - 76g / 100g of water ✓1showing ½ correct ans½
60ºC ✓1
-
-
- You are provided with solid W. Carry out the test and record your observations in the spaces below. Put solid W in a boiling tube. Add about 10cm3 of distilled water and shake. Divide the solution into five portions
Observation Inference Solid dissolve to form a colourless solution
(1mk)Soluble salt present
Coloured ions absent
(1mk)- To the first portion add sodium hydroxide drop wise then in excess
Observation Inference White ppt formed soluble in excess
(1mk)Zn2+,Al3+ or Pb2+ present
(1mk) - To the second portion add 3 drops of sodium sulphate solution
Observation Inference No white ppt formed
(1/2mk)Zn2+,Al3+ present
(1mk) - To the third portion add ammonium hydroxide drop wise then in excess
Observation Inference White ppt insoluble in excess
(1mk)Al3+ present
(1mk) - To the fourth portion, add 3 drops of lead nitrate solution and warm
Observation Inference
White ppt formed which does not dissolve upon warming
(1mk)
C032-, SO32-,SO42- present
(1mk) - To the fifth portion, add 3 drops of acidified barium nitrate
Observation Inference white ppt formed
(1mk)SO42- present
(1mk)
- To the first portion add sodium hydroxide drop wise then in excess
- You are provided with solid X. Carry out the test and record your observations in the spaces below.
- Put half of solid X on a metallic spatula and heat using a Bunsen burner
Observation Inference
Solid melts and burns with a yellow sooty flame
(1mk)
(1mk) - Put the second half in a boiling tube. Add about 10cm3 of distilled water and shake. Divide the resulting solution into four portions
Observation Inference
The solid dissolves to form a colourless solution
(1mk)
Polar organic compound
(1/2mk) - To the first portion add three drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) and shake
Observation Inference Purple acidified potassium manganate (VII) turn colouless
(1/2mk)
R-OH Present
(1mk) - To the second portion add three drops of bromine water and shake
Observation Inference Yellow bromine water turn colourless
(1/2mk)
(1mk) - To the third portion add sodium hydrogen carbonate
Observation Inference Bubbling seen
(1/2mk)R-COOH
(1/2mk) - To the fourth portion add three drops of universal indicator. Compare the colour of the solution using pH colour chart
Observation Inference PH =1,2,3
(1/2mk)Strongly acidic
(1/2mk)
- Put half of solid X on a metallic spatula and heat using a Bunsen burner
- You are provided with solid W. Carry out the test and record your observations in the spaces below. Put solid W in a boiling tube. Add about 10cm3 of distilled water and shake. Divide the solution into five portions
Download Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and Answers - MECS Cluster Joint Pre Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students