INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper has two sections Aand B
- Answer all questions in section A
- In section B answer question 6 and any two questions
- All answers must be written in English in the booklet provided

QUESTIONS
SECTION A
ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS IN THIS SECTION
-
- What is the difference between a meteor and a meteorite (2mks)
- State three effects of earth’s revolution (3mks)
-
- List two elements of weather(2mks)
- Name three processes through which the atmosphere is heated (3mks)
-
- What is weathering (2mks)
- Give three processes of chemical weathering (3mks)
-
- Name three types of coral reefs (3mks)
- What are the benefits of coral reefs in the areas they have developed (2mks)
-
- State two factors which influence occurrence of surface run-off (2mks)
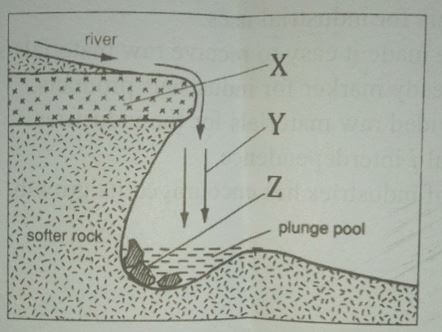
- The diagram below shows a waterfall. Name the features marked X,Y, and Z (3mks)
SECTION B
ANSWER QUESTION 6 AND ANY OTHER TWO QUESTIONS FROM THIS SECTION
- Study the map of Taita hills(scale 1:50.000) provides and answer questions while follows.
-
- Give the latitudinal position of the South Eastern corner of the map extract (2mks)
- State the four figure grid reference of the school at Mrabenyi (1mk)
- Identify the adjoining sheet number to the S.E of Taita hills (1mk)
-
- Measure the length of dry weather road D535 from the junction at grid 4028 to the east of the map (2mks)
- Calculate the area enclosed by the railway line to the south Eastern part of the map (2mks)
-
- Reduce the square enclosing Easting 37 to 42 and Northing 26 to 31 by 2, on the reduce square indicate the following.
- Ronge forest
- Road D535
- Outcrop rock (5mks)
- Give the new scale of the reduced square (2mks)
- Reduce the square enclosing Easting 37 to 42 and Northing 26 to 31 by 2, on the reduce square indicate the following.
-
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map (4mks)
- Identify two methods of representing relief used in the map extract (2mks)
- Citing evidence from the map give two economic activities carried out (4mks)
-
-
-
- What is artesian well? (2mks)
- List four conditions necessary for the formation of an artesian well.(4mks)
-
- With the aid of a well labeled diagram, describe the three zones of underground water(6mks)
- Identify three sources of underground waters (3mks)
- Explain three ways in which a Karst landscape would influence human activities (6mks)
- Your class intends to carry out a field study on limestone area near your school
- Name two surfaces features you are likely to identify (2mks)
- State two problems you are likely to identify (2mks)
-
-
-
- Define the term glaciation 2mks
- Name three types of glaciers 3mks
- Describe how the following features found in upland glaciated landscape are formed
- U-shaped valley(5mks)
- Pyramidal peak (5mks)
- Explain three significance of upland glaciated features to human activities(6mks)
- Suppose you were to carry out a field study of a glaciated lowland
- State two advantages of using oral interview to collect information during the field study(2mks)
- Name two features found in glaciated lowlands that you are likely to study (2mks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between a soil profile and soil catena(2mks)
- Draw a well labeled diagram of a mature soil profile(4mks)
-
- Other than topography name three factors that influence formation of soil(4mks)
- Explain how topography influences formation of soil (3mks)
- List three characteristics of desert soils (3mks)
-
- Give three types of soil erosion (3mks)
- Explain three effects of soil erosion on human activities (6mks)
-
-
- The diagram below represents zones of natural vegetation on a mountain within tropical regions, use it to answer questions (a) and (b)
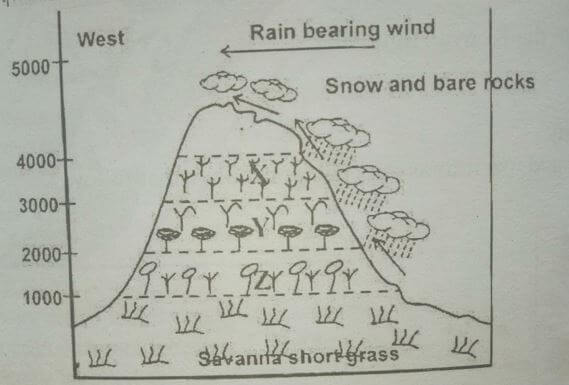
- Name the vegetation zones marked X,Y and Z (3MKS)
- Give two reasons why the mountain top has no vegetation (2mks)
- Describe the characteristics of savanna grasslands (4mks)
- Explain four factors that have led to the decline of natural grassland in Kenya (8mks)
- You carried out a field study of different tree species
- Identify three activities you would carry out during the field study(3mks)
- How would you identify the different tree species?(3mks)
- State two methods you would use to determine the height of the trees (2mks)
- The diagram below represents zones of natural vegetation on a mountain within tropical regions, use it to answer questions (a) and (b)

MARKING SCHEME
- Difference between a meteor and a meteorite
- Meteor-is a streak of light seen in the sky in a clear night and occurs as a result of meteoroid burning as it enters earth’s atmosphere while a meteorite is a meteoroid which has not completely burnt up and manages to reach the earth’s surface. 2x1
- Three effects of revolution
- Revolution causes the four seasons-summer, autumn, winter and spring
- Revolution causes changes in the position of the midday sun at different times of the year.
- Revolution causes varying length of day and night at different times of the year
- Revolution causes the lunar eclipse 3x1=3mks
-
- Two elements of weather
- Temperature
- Air pressure
- Precipitation
- Humidity
- Wind
- Sunshine
- Cloud cover 2x1=2mks
- Three processes of heating the atmosphere
- Radiation
- Conduction
- Convection 3x1=3mks
- Two elements of weather
-
- What is weathering
- This is the breaking down/decomposition of rocks/at or near the earth surface in situ by chemical or physical processes 1x2=2mks
- Give three processes of chemical weathering
- Hydrolysis
- Solution
- Oxidation
- Carbonation
- Hydration 3x1=3mks
- What is weathering
-
- Name three types of coral reefs
- Barrier reefs
- fringing reefs
- Atoll 3x1=mks
- Two benefits of coral reefs
- Shallow corals are a tourist attraction earning the county foreign exchange
- Sheltered water encourages growth of planktons/fish food 2x1mks
- Name three types of coral reefs
-
- Two factors which influence occurrence of surface run off
- Heavy rainfall increases surface run off
- Low rate of evaporation
- slopping ground or steep slopes
- Pressure of impervious rocks or soil surface
- Bare surfaces or absence of vegetation (2x1=2mks)
- Features of a water fall
- X-resistant rock or cap rock
- Y-water fall
- Z-rock boulder 3x1=3mks
- Two factors which influence occurrence of surface run off
-
-
- Give the latitudinal position of the South Eastern corner of the map 3° 30’s (2mks)
- Four figure grid reference of the school at Mrabenyi 4223 (1mk)
- Adjoining sheet number to the S.E of Taita hills 196/1/Sagala (1mk)
-
- Length of dry weather road D535 from the junction at grid square 4028 4.3km± 0.5 1x2=2mks
- Calculate the area enclosed by railway line to the South Eastern part of the map.
Incomplete square 30/2=15
full squares 17
15+17=32 sq km ± 1 (2mks)
Units a must for a student to score
-
- Reduced square enclosing easting 37 to 42 and Northing 26 to 31
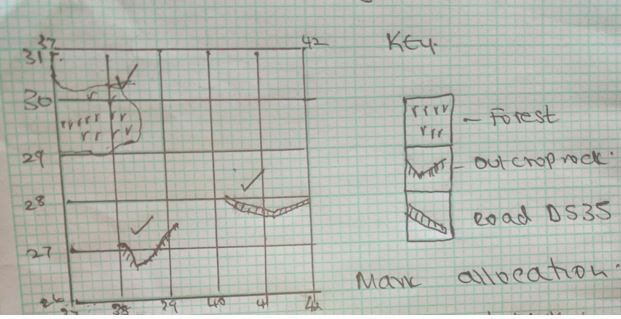
Mark allocation
Title- 1mk
Square- 1mk
Forest- 1mk
Out crop rock - 1mk
Road- 1mk
Total 5mks - New scale of the reduced area
Scale: 1:50,000 x 2=1:100,000
New scale 1:100000 (2mks)
- Reduced square enclosing easting 37 to 42 and Northing 26 to 31
-
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map.
- Most of the rivers are permanent eg. River Pringo
- The main river is river Voi(Goshi)
- The rivers make dendritic drainage pattern
- There are seasonal swamps
- River Voi has meaders ( 4x1=4mks)
- Methods of representing relief
- Contours
- Spot heights
- Trigonometric stations (2mks)
- Citing evidence from the map give two economic activities
- Trading-shops
- Transport-roads
- Farming/ Agriculture-agriculture office
2x2=4mks
NB:Evidence should be stated for a student to score
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map.
-
-
-
- What is an artesian well
- Artesian is a well sunk into the aquifer of an artesian basin from which water will come out without being pumped. 2mks
- Four condition necessary for formation of artesian well
- Aquifer to be sandwiched between impermeable rocks to prevent evaporation and percolation
- Aquifer to be exposed in a region which is a source of water eg rainy area or lake
- Aquifer to dip from the region of water intake
- Mouth of the well to be at a lower level than the intake area to develop hydraulic pressure which will force water out 4x1=4mks
- What is an artesian well
-
- Though aid of a diagram describe three zones of underground water
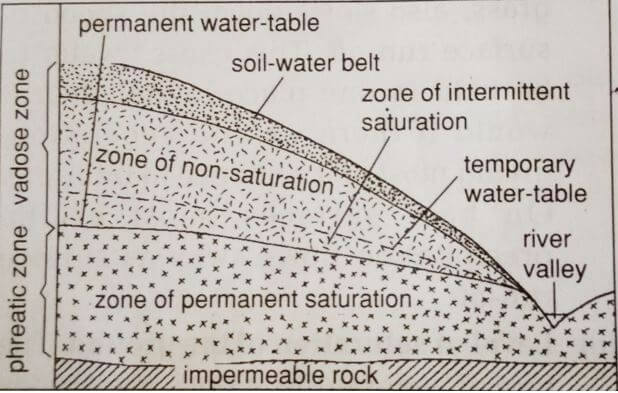
- Zone of permanent saturation –Zone were rock poles and air spaces are permanently filled with water
- Zone of intermittent saturation-Zone where water fluctuates according to season.
- Zone on non-saturation-zone without water 3x2=6mks
- Identify three sources of underground water
- Rain water
- Melt water (from snow)
- Surface water –rivers,lakes,oceans
- Magmatic water-water trapped beneath surface during vulcanicity 3x1=3mks
- Though aid of a diagram describe three zones of underground water
- Three ways in which a Karst landscape influence human activities
- Features formed eg.caves,gorges and dry valley are good tourist attraction sites hence earning foreign exchange.
- Limestone region have thin soils and dry surface suitable for grazing purposes-sheep
- Limestone rocks from karst bridge regions provide raw material for cement used in building industry
- The rugged terrain of limestone regions discourage settlement
Thin soil discourages agricultural/crop production 3x2=6mks
-
- Two surface features of limestone areas
- Poljes,doline,karst bridge,grike and clint, swallow holes/sink holes, uvalas 2x1=2
- Two problems likely to be identified
- Inaccessibility to some areas
- Harsh weather conditions-high temperature
- Injuries due to accidents in the field
- Snake and scorpions bites 2x1=2 mks
- Two surface features of limestone areas
-
-
-
- Define glaciation
- Glaciation refers to the action of moving ice/process by which glaciers change the landscape on large scale (2mks)
- Three types of glaciers
- valley glaciers
- piedmont glaciers
- cirque glaciers
- continental glaciers
- niche glacier 3x1=3mks
- Define glaciation
-
- Formation of U shaped valley
- A pre-existing V –shaped valley is filled with ice/glacier
- The gracier erodes the V-shaped valley by abrasion and plucking process vertically and laterally
- The valley is deepened and widened by vertical erosion and lateral erosion
- The end spurs are truncated/trimmed/cut
- The ice melts away leaving a U-shaped valley 5x1=5mks
- Formation of pyramidal peak
- Initially ice collects in several hollows on the maintain side
- The ice exerts pressure on the hollows/cracks
- The plucking action of the ice enlarges the hollow so that more ice collects in them
- Freeze and thaw action of the ice leads to the expansion of cracks/hollows making them large basins which are called cirques
- Nivation into back walls of the hollows make them recede into the mountain side/the cirques recede towards each other.
- Steep sided, knife edged ridges/arêtes converge at the top of the mountain forming a jogged peak called a peak/horn(surrounded by corries/cirques) 5x1=5mks
- Formation of U shaped valley
- Three significance of upland glaciated features to human activities
- The warm glaciated valleys are suitable for farming cultivation/glaciated uplands provided suitable grazing lands as they form fine benches on which summer pasture grows eg Switzerland
- Glaciated uplands form magnificent features that encourages recreation/sporting activities
- Glaciated mountains discourage human settlement hence growth of forests (lumbering)
- Water falls formed by the rivers in glaciated highlands provided suitable sites for hydroelectric production
- corrie lakes/tarn lakes are suitable areas for sports fishing
- The u-shaped valleys/glacier trough form natural route ways
- Fiords coastline form deep and well sheltered natural harbours as well as good fishing grounds 3x2=6mks
-
- Two advantages of oral interview
- Give first hand information
- Interviewer can seek clarification on any ambiguities
- Interviewer creates a good rapport with interviewee
- Interviewer can elicite more information by initiating further discussion
- The method is useful is collecting information from people who cannot write and read 2x1=2mks
- Two featurers of glaciated lowland likely to be identified
- Depression/glacial lakes
- Roche moutonee
- crag and tail
- drumlins
- erratic
- boulder train
- till plain
- Outwash plain 2x1=2mks
- Two advantages of oral interview
-
-
-
- Differentiate between soil profile and soil catena
- Soil profile is the vertical arrangement of soil in layers from the top to the bedrock while soil catena is the arrangement of soil in-layers along a slope 1x2=2mks
- Mature soil profile (4mks)
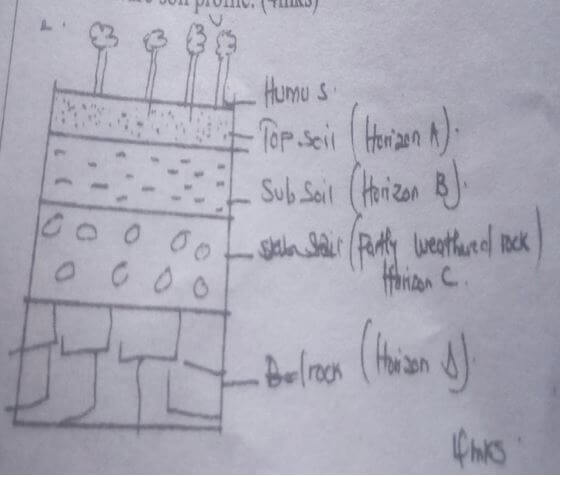
- Differentiate between soil profile and soil catena
-
- A part from topography name four other factors that influence formation of soil
- Climate
- parent rock
- living organisms
- time
- vegetation cover 4x1=4mks
- How topography influences formation of soils
- Valley bottoms/gentle slopes encourages the formation of deep and fertile soil due to deposition/accumulation of materials
- Steep slopes encourages erosion of top layer of soil thus slowing down formation of soils/thin soils
- Flat/flood plains are saturated with water therefore forming poor soils
- Slope influences arrangements of soil catena 3x1=3mks
- Three characteristics of desert soil
- Have very little humus/organic matter content
- They are thin/shallow
- They are sandy and saline
- They are loose ground
- They are yellow brown
- They are rich in calcium carbonate/high lime content 3x1=3mks
- A part from topography name four other factors that influence formation of soil
-
- Three types of soil erosion
- splash erosion
- sheet
- gulley
- rill erosion 3x1=3mks
- Three effects of soil erosion on human activities
- The productive top soil is lost and only unproductive stony soil is left lowering the agricultural productivity of land.
- Soil erosion leaves behind thin soils which cannot hold plants firms in the ground hence the plants are easily uprooted and blown away by the wind.
- When gullies are deepened up to or below the water table, underground water is exposed leading to some of it flowing away or evaporating causing the water table to be lowered.
- Loss of soil through wind and water erosion leads to destruction of vegetation cover which eventually turn the affected area into a semi –arid land area.
- Soil erosion cause sedimentation in water reservoirs constructed along rivers hence lowering water levels hence shortage of electricity and expensive to dredge.
- Soil erosion causes water pollution which may lead to death of aquatic animals/destroy mangrove vegetation
- Where soils is deposited after erosion it forms rich agricultural lands
- Sand eroded and when deposited on river valley is harvested for construction 3x2=6mks
- Three types of soil erosion
-
-
- Zone of natural vegetation on mountain on tropical regions
- X-heath and moorland
Y-Bamboo forest
Z-Rainfall forest 3x1=3mks - Reasons why the mountain top has no vegetation
- Surface is mainly bare rocks hence no soil to support any vegetation.
- Very low temperature to support any vegetation.
- Water is in snow form hence not available for plants 2x1=2mks
- X-heath and moorland
- Characteristics of savanna grasslands
- Has a mixture of grass and trees
- Grass dries up completely during the prolonged dry season
- Vegetation is dominated by tall grass e.g. elephant grass towards wetter areas
- Grass is short and tough towards drier areas
- Trees are scattered and stunted 4x1=4mks
- Four factors that have led to decline of natural grass land in kenya
- Frequent outbreak of fires that destroy grass
- Pests and diseases,which destroys grass and reduce the rate of growth and generation
- domestic and wild animals overgraze clearing vegetations and causing stunted growth of grasses
- Increase in human population encroaching into the grasslands replacing them with settlements and farms 4x2=8mks
-
- Activities carried out during field study
- Measuring and estimating the height of the plants
- Taking photographs of the area and the plants
- Collecting samples of plants
- Counting the plants
- Drawing sketches to show vegetation distributions
- Identifying the different tree species 3x1=3mks
- How to identify the different trees species
- Observing the colours
- Examining leaf sizes, patterns and types of leaves
- look at the nature of their bark
- xamining appearance of the plants
- Examining the root system of the plants 3x1=3mks
- Two methods of determining the height of trees
- By measuring the exact height of a sample of the tree and then generalize
- Reading through available records on the vegetations of the area
- By estimating the height 2x1=2mks
- Activities carried out during field study
- Zone of natural vegetation on mountain on tropical regions
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - KCSE 2022 Kapsabet Highschool Trial 1 Pre-Mock Examination.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

