Instructions to Candidates
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided below each question.
- Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used.
- All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary.
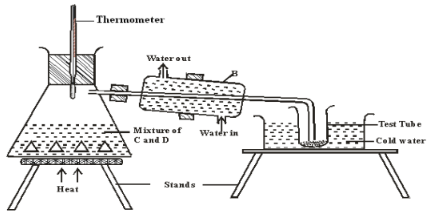
- The set up below represents the apparatus that may be used to separate a mixture of two miscible liquids C and D whose boiling points are 800C and 1100C.
- Name B ( 1 mark)
- What is the purpose of the thermometer (1mark)
- Which liquid was collected in the test tube? (1mark)
- Substances can be classified as either a mixture, compound or pure elements. Give two reasons why air is classified as a mixture. (2marks)
- Describe how you can extract oil from ground nuts. (3marks)
- Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
Substance
Solubility in water
Electrical conductivity
Solid
Molten
A
Insoluble
Good
Good
B
Soluble
Poor
Good
C
Insoluble
Poor
Poor
- Which of the substances is highly likely to be sodium chloride? Explain (1mark)
- What type of bond exists in substance A? (1mark)
- State a possible structure in substance C? (1mark)
- The table below shows behaviour of metals R, X, Y and Z. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Metal
Appearance on exposure to air
Reaction in water
Reaction with dilute hydrochloric acid
R
Slowly tarnishes
Slow
Vigorous
X
Slowly turns white
Vigorous
Violent
Y
No change
Does not react
Does not react
Z
No change
No reaction
Reacts moderately
- Arrange the metals in the order of reactivity starting with the least reactive. (2 marks)
- Name a metal which is likely to be Y. (1 mark)
- The table below gives information about ions of P and Y
Ion
P+
Y2-
Electron arrangement
2.8
2.8.8
Number of Neutrons
12
16
- Write the electron arrangement for the atom of Y (1mark)
- How many protons are there in the nucleus of (1mark) (i)
- P……………………………………………………………………………………...
- Y……………………………………………………………………………………
- Write the formula of the compound formed when P and Y reacts (1mark)
- Use the scheme below to answer the following questions.
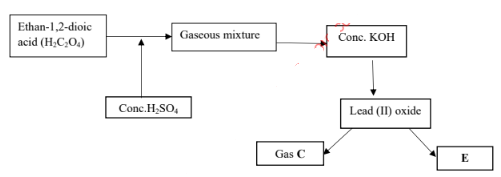
- Name the type of reaction which takes place between ethan-1,2-dioic acid and concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid (1mark)
- Why is the gaseous mixture passed through concentrated KOH? (1mark)
- Write a chemical equation that produces gas C and E (1mark)
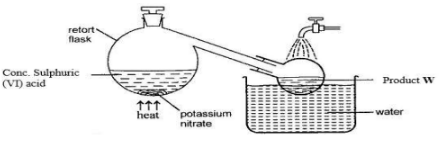
- The set up below can be used for the laboratory preparation of product W.
- Write chemical equation for the reaction that takes place in the retort flask. (1 mark)
- Explain why product W appears yellow in colour. How is the colour removed? (2 marks)
- Starting with 100cm3of 2.0M sodium hydroxide solution, describe how to prepare pure sodium sulphate crystals. (3marks)
- Study the set up below used to investigate the properties of ammonia gas.
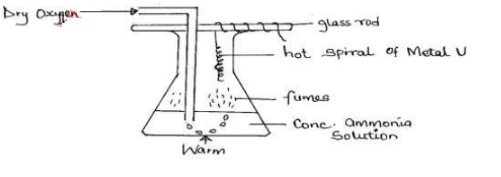
- State two observations made in this experiment. (1mark)
- What is the purpose of using the hot wire in this experiment? (1mark)
- State the identity of the hot spiral of metal U. (1mark)
- 3.1g of an organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen only, produced 4.4g of carbon (IV) oxide and 1.8g of water on complete combustion. Determine its molecular formula if its formula mass is 60. (3marks)
- A student collected samples of water from two different sources. She measured equal volume of water in two different test-tubes. She added soap solution from a burette until permanent lather was formed. She then boiled another two samples of the same waters and repeated the experiment. She recorded the results in the table below.
Sample of water
Volume of soap used before boiling (cm3)
Volume of soap used after boiling (cm3)
A
15
5
B
15
15
- Name the type of water hardness in sample A. Explain. (1mark)
- Name two salts that causes water hardness in water sample B. (1mark)
- Using a chemical equation, show sodium carbonate can be used to soften water sample B. (1mark)
- 60cm3of oxygen gas diffused through a porous partition in 40 seconds. If 80cm3of gas X diffuses through the same partition under the same conditions is 75.5 seconds, determine the molecular mass of gas X. (O=16.0) (3marks)
- The diagram below represents large scale manufacture of hydrochloric acid. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
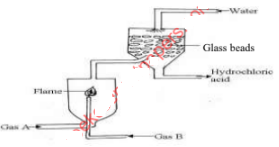
- State the function of the glass beads. (1mark)
- Identify gas A. (1mark)
- Explain why gas B is ignited as a jet as shown in the diagram. (1mark)
- Below is a structure of an element X. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the chemical family to which element X belongs. Give a reason. (2marks)
- State the type of bond illustrated above in the structure of element X. (1mark)
- The table below shows information of four elements A, B, C and D. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
Element
Electronic arrangement
Atomic radius
Ionic radius
A
2.8.2
0.136
0.065
B
2.8.7
0.099
0.181
C
2.8.8.1
0.203
0.133
D
2.8.8.2
0.174
0.099
- Which two elements have similar properties? (1 mark)
- Explain why B ionic radius is larger than its atomic radius. (2 marks)
-
- State the Bronsted – Lowry definition of an acid. (1mark)
- With a reason, identify a base in the equation below. (1mark)
Hph (aq) + H2O (l)H3O+(aq) + Ph-(aq)
- Distinguish between strong acid and concentrated acid (1mark)
- Some average bond energies are given below.
Calculate the energy change for the reaction below:Bond
Energy(kJ/mol)
C-C
348
C-H
414
Cl-Cl
243
C-Cl
432
H-Cl
340
C2H6(g) + Cl2(g)CH3CH2Cl(g) + HCl(g) (3marks)
- The solubility of salt Z at 600C is 40g/100g of water and 48g /100g of water at 800C .
- Define the term solubility (1mark)
- 150 g of saturated solution of Z at 800C is cooled to 600C.Calculate the mass of Z that crystallizes out. (2marks)
- Use the table below to answer the questions that follow.
Substance
A
B
C
D
E
Symbol
R-COO-Na+
CH2OH
|
CHOH
|
CH2OHR-COOCH2
|
R- COOCH
|
R- COOCH2R-OSO3-Na+
- Which substances is
- A soapless detergent: ……………………………………………...…………………………(½mark)
- An ester………….:…………………………………………..(½mark)
- Give name to substance B (1mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction between the structure of substance D and Sodium hydroxide solution. (1mark)
- Which substances is
- The figure below shows a simple extraction process of Sulphur
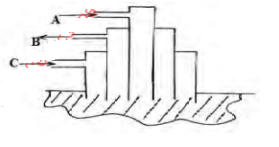
- State the name of substances represented by A and B (2marks)
- What is the function of the substance represented by C during the extraction process? (1mark)
- A hydrocarbon X was found to decolourise acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution. When two moles of X were burnt completely in air six moles of carbon (IV) oxide and six moles of water were formed.
- Draw the structural formula of X. (1mark)
- State the homologous series to which X belongs. (1mark)
- Name a pair of reagents that can be used to prepare X (1mark)
- The diagram below represents an experiment which was carried out by a student to investigate the effect of passing an electric current on molten Lead(II) bromide
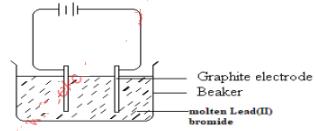
- Molten lead(II) bromide is a binary electrolyte. State the meaning of the term binary electrolyte. (1mark)
- State the observations made at the anode. (1mark)
- Write an equation to show what happens at the cathode. (1 mark)
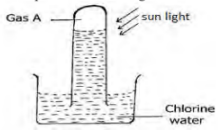
- The diagram below shows an experiment involving chlorine water.
- Describe the confirmatory test for Gas A. (2marks)
- Write an equation to show the formation of gas A. (1mark)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow:
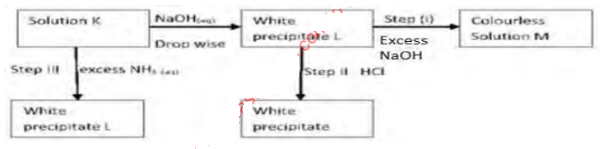
- Identify
- The cation present in solution K (1mark)
- The white precipitate L (1mark)
- Write down the formula of the complex ion present in the colourless solution M (1mark)
- Identify
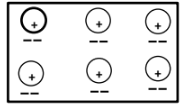
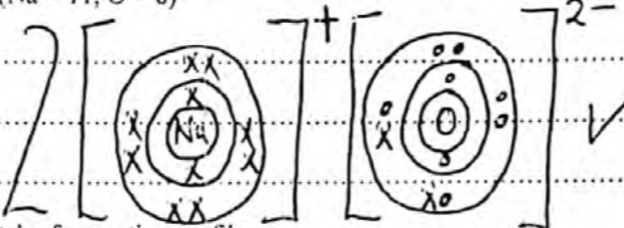
- Using dot (•) and cross (x) diagram, show the bonding in ;
- Phosphonium ion PH+4 ( P=15.0, H=1.0). (2marks)
- Sodium oxide (Na = 11, O = 8) (1 mark)
- Below is a sketch of a reaction profile.
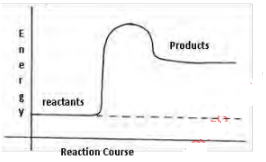
- On the diagram show the heat of reaction ∆H (1mark)
- State and explain the type of reaction represented by the profile (2marks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Liegbig condenser
- To measure the temperature at which the liquids boil
- C
-
- Components are physically combined - composition varies
- Separated by physical means
- Components retain their physical and chemical properties
- Crush the groundnuts using pestle and mortar. Add propanone/acetone as you continue crushing. Decant to obtain oil solution. Leave in the sun for propanone/acetone to evaporate. Wash in distilled water and separate the mixture using a separating funnel
-
- B. Conducts in molten state but not in solid state
- Metallic bond
- Giant covalent/atomic structure/Molecular
-
- Y, Z, R, X / X, R, Z, Y
←Increasing reactivity - Copper/Gold/Silver
- Y, Z, R, X / X, R, Z, Y
-
- 2.8.6
-
- P - 11
- Y - 16
- P2Y/Na2S rej YP2/SNa2
-
- Dehydration
- Absorb CO2
- P2bO(s) + CO(g) → Pb(s) + CO2(g)
-
- KNO3(s) + H2SO4(l) → KHSO4(s) +HNO3(l)
- Presence of dissolved NO2. The yellow colour is removed by passing air/oxygen through the acid
- Add 100cm3 of 2.0M sodium hydroxide to 100cm3 of 1.0M/50cm3 of 2MH2SO4 sulphuric (VI) acid ina beaker and stir. Heat the resultant solution to saturation and allow to cool for sodium sulphate crystals to form. Filter out crystals and dry.
-
-
- Hot spiral wire glows red
- Brown fumes mof NO2 observed
- Ammonia burns with a green flame
- Catalyses the reaction/increase the reaction rate. accept catalyst
- Platinum/Nichrome. Accept Cu.
-
- Mass of H2 = 2/18 × 1.8g = 0.2
Mass of C = 12/44 × 4.4g = 1.2g
Mass of O2 = 3.1 − (0.2 + 1.2) = 1.7g
C H O
Moles = 1.2/12 0.2/1 1.7/16
Mole ratio = 0.1/0.1 0.2/0.1 0.11/0.1
1 2 1
E.F.D = CH2O
n = 60/30 = 2
M.F is (CH2O)2
= C2H4O2 -
- Temporary water hardnes, softened removed by boiling
- Magnesium chloride/Magnesium Sulphate/ Calcium Chloride.
Accept: Nitrates of Mg or Ca rej. CaSO4 -
- MgCl2(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) → MgCO3(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
- CaCl2(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) → CaCO3(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
- MgSO4(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) → MgCO3(s) + Na2SO4(aq)
-
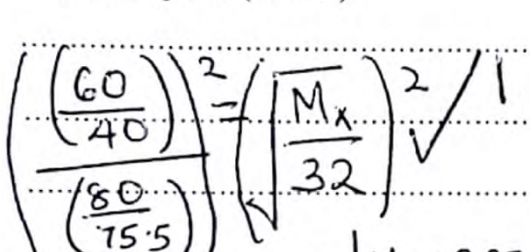
= 2.25 = Mx
1.2276 32
Mx = 2.25 × 32
1.12276
= 64.13
ALT
If 60cm3 → 40s
80cm3 → 80×40
60
= 53.3333
(75.5)2 = √x/32)2
(53.33)
2.004 = x
1 32
x = 64.13
Mx = 64.13 -
- Increase S.A for absorption of HCl(g)
- Chlorine/Cl2
- Mixture of H2 and Cl2 react explosively when heated.
-
- Alkaline Earth Metals. Has two valence electrons
- Metallic
-
- A and D
- Due to increased electron- electron repulsion between the incoming electrons and existing electrons. Accept shielding effect explained
-
- An acid is a proton donor
- H2O(l)
Accept a proton rej. lone pair of electron donor - Strong acid is one which ionizes fully in water to give more hydrogen ions while concetrated acid is one which has higher proportion of acid mas compared to water
-
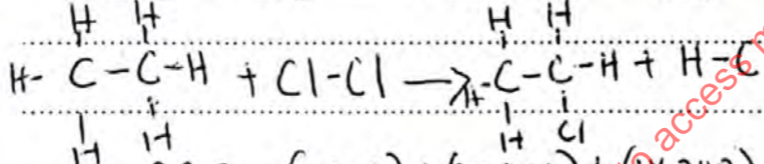
B.B.E = (1×348) + (6×414) + (1×243)
= +3075
BFE = (1×348) + (5×414) + (1×432) + (1×340)
= −3190
ΔH = + 3075 − 3190
= −115kJ/mol -
- Maximum mass of solute that can saturate 100g of water at a given temperature
- At 60°C
if 140g of sln → 40g of salt
150g → ?
150 × 40 = 42.86g
140
At 80°C
if 148g of sln → 48g of salt
150g → ?
150 × 48 = 48.65g
148
Mass of crystals
= 48.65 − 42.86 = 5.79g
-
-
- E/R-OSO3-Na+
- D or
R-COOCH2
|
R- COOCH
|
R- COOCH2
- Propan -1, 2, 3 - triol accept Glycerol
- R-COOCH2 CH2OH
| |
R- COOCH + 3NaOH → 3R - COO−Na+ + CHOH
| |
R- COOCH2 CH2OH
-
-
-
- A - Hot compressed air
- B - Molten Sulphur & water
- To melt Sulphur
-
-
-
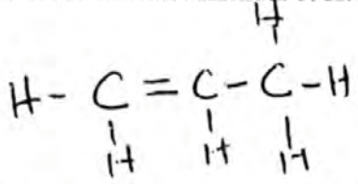
- Alkenes
- Propanol and Concentrated Sulphuric (VI) acid/ Aluminium oxide
-
-
- An electrolyte that contains one kind of cation and one kind of anion
- Brown fumes of bromine gas observed
- Pb2+(l) + 2e− → Pb(s)
-
- Lower/introduce a glowing splint into a gas jar containing gas A; the glowing splint is relit/ rekindled
- sunlight
2HOCl(aq)2HCl+ O2(g)
-
-
- Pb2+
- Lead (II) hydroxide/Pb(OH)2
- [Pb(OH)4]2−
-
-
-
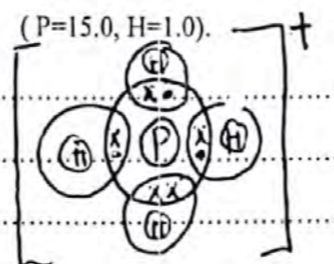
electron distribution -1
Charge - 1 -
-
-
-
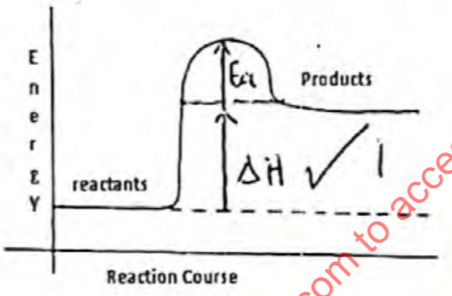
- Endothermic. Products have more energy/ higher energy compared to reactants
-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Maranda High Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students