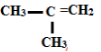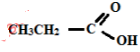Instructions to candidates
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- KNEC mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used for calculations. (d)All workings MUST be clearly shown where necessary.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
-
- Study the diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
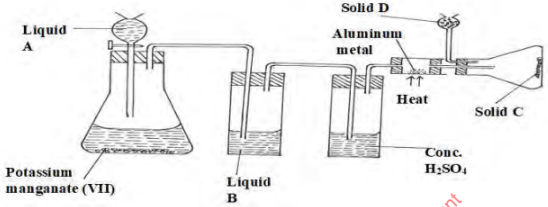
- Name liquids A and B
A………………………………………………………………(½mark) B…………………………………………………………….( ½mark) - Suggest the most suitable reagent that can be used as solid D (1 mark) ………
- State the role of Solid D (1 mark)
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction in the conical flask. (1mark)
- Explain why solid C collects further away from the heated Aluminium metal. (1mark)
- In the combustion tube above, 0.675g of Aluminium metal reacted completely with 1800cm3 of chlorine gas at room temperature. Determine the molecular formula of Solid C, given that its relative formula mass is 267 ( Al= 27.0, Cl= 35.5 molar gas volume at r.t.p = 24.0 litres) . (3marks)
- Name liquids A and B
- The reaction between hot concentrated sodium hydroxide and chlorine gas produces Sodium Chlorate (V) as one of the products
- Write the equation for the reaction. (1mark)
- Give one use of sodium chlorate.(V) (1mark)
- Explain the difference between bleaching by chlorine and bleaching by Sulphur (IV)oxide gases. (2marks)
- Study the diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
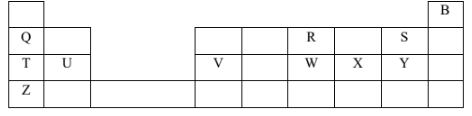
- The grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. Letters are not the actual symbols of the elements.
- Select a letter that represents the most reactive non-metal. Explain (2 marks)
- Select a letter that represents an element that forms an ion with a charge of 2- (1 mark)
- Select an alkaline earth metal (1 mark)
- Which group I element has highest first ionization energy? Explain (2 marks)
- What is the formula of the compound formed when V reacts with X? (1 mark) visit
- What type of chemical bond exists in a compound formed when R and S react? (1 mark)
- Explain why the atomic radius of S is smaller than that of Q. (2 marks)
- State and explain the observation made when sodium carbonate is added to a chloride solution of element V. (2 marks)
-
- The table below shows the solubility of potassium chlorate at different temperatures
Temperature (oC )
10o
20o
30o
40o
50o
60o
70o
Solubility g/100g water
27
30
36
55
80
110
140
- Plot a graph of solubilities of potassium chlorate against temperature (3 marks)
- Using your graph:
- Determine the solubility of potassium chlorate at 47oC (1 mark)
- Determine the concentration in moles per litre of potassium chlorate at 47oC
(K= 39, Cl = 35.5, O= 16) density of solution = 1g/cm3 (1 mark) - Determine the mass of potassium chlorate that would crystallize if the solution is cooled from 62oC to 45oC. (2 marks)
- In an experiment to determine the solubility of sodium hydroxide, 25cm3 of a saturated solution of sodium hydroxide weighing 28g was diluted in a volumetric flask and the volume made to 250cm3 mark. 20cm3 of this reacted completely with 25cm3 of 0.2M hydrochloric acid according to the equation.
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq)NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Calculate:- The number of moles of hydrochloric acid used (1 mark)
- The number of moles of sodium hydroxide in 20cm3 (1 mark)
- The moles of sodium hydroxide in 250cm3 of solution (1 mark)
- The mass in grams of sodium hydroxide in 250cm3 of solution (1 mark)
- The solubility of sodium hydroxide in g/100g water (1 mark)
- The table below shows the solubility of potassium chlorate at different temperatures
- Study the flow chart below and answer questions that follow:
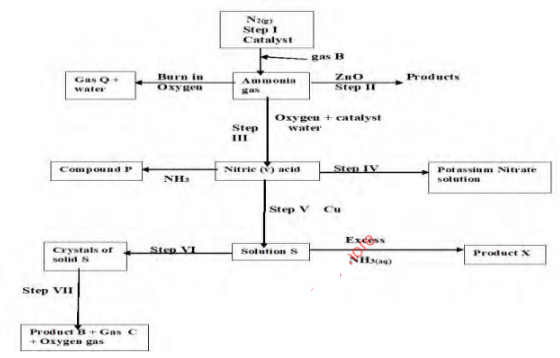
- State one source of gas B (1 mark)
- Name the catalysts used in; (1 mark)
- Step I
- Step III
- Write chemical equations for reactions in; (2 marks)
- Step II
- Step VII
- Name the process that takes place in; (2 marks)
- Step IV
- Step VI
- Name and write the chemical formula of product X
- Name (1 mark)
- Formula (1 mark)
-
- State one laboratory use of compound P (1 mark)
- Identify any other gas that can be used instead of Ammonia in step II (1 mark)
- State one use of gas Q (1 mark)
-
- Give the IUPAC names of the following (2 marks)
-
- Describe one chemical test that you would use to distinguish between the two compounds represented by the formulae C2H6O and C2H4O2 (2 marks)
- Study the below reaction scheme to answer the questions that follows.
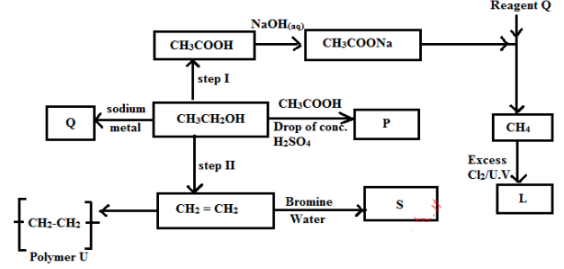
Identify- Reagent Q …………………………………………………..(1 mark)
- Substance S…………………………………………………( 1 mark)
- Write the formula of compound P …………………………(1 mark) i
- Draw the structural formula of L and give its name (1 mark)
- Name the type of reaction, the reagent(s) and condition for the reactions in the following steps (2 marks)
- Step I
- Step II
- If the relative molecular mass of U is 56000, determine the number of monomer samples n in the polymer (2mks)
- Give the IUPAC names of the following (2 marks)
- Below is diagram showing how hydrogen can be prepared in the laboratory and the study of the reducing action of hydrogen
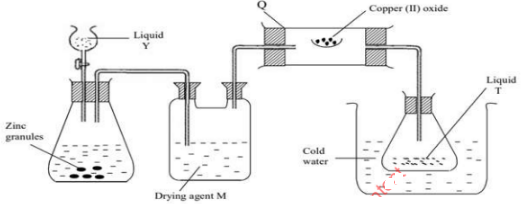
- Define the term reduction (1 mark)
- Identify apparatus Q (1 mark)
- Identify one mistake in the set up (1 mark)
- Suggest a suitable drying agent M (1 mark)
- What is liquid Y (1 mark)
- Explain chemical reaction taking place in apparatus Q (1 mark)
-
- Name liquid T (1 mark)
- Describe one physical test of liquid T (1 mark)
- Explain the role of hydrogen in the manufacture of margarine (2 marks)
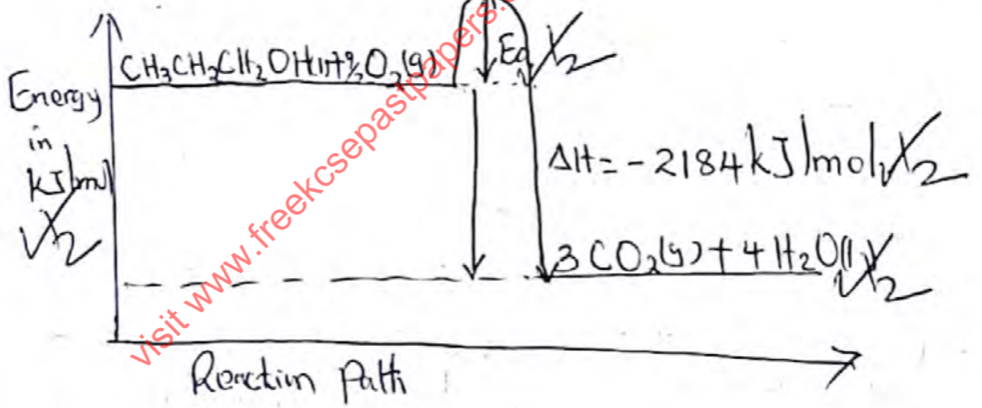
- The diagram below shows a set-up to determine the heat of combustion of propanol. The heat produced by burning fuel heats a known mass of water. By measuring the temperature rise of water it’s possible to approximate the value for the heat of combustion of propanol
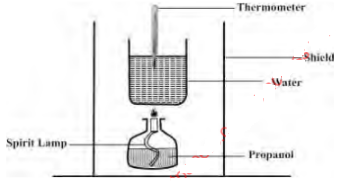
Volume of water = 400cm3
Initial temp. of water = 20oC
Final temp. of water = 33oC
Mass of propanol burnt = 0.6 g
Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2Jg-1k-1- Define molar heat of combustion. (1 mark)
- Calculate the number of moles of propanol that burnt (C=12, H=1, O=16) (1 mark)
- Calculate the enthalpy change in this experiment (2 marks)
- Find the molar heat of combustion of propanol (2 marks)
- The accurate value of molar heat of combustion of propanol is -2221kJ/mol. State one error that could account for this difference (1 mark)
- Draw an energy level diagram showing combustion of propanol (2 marks)
- State two precautions taken when using a fuel (2 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
-
- A - Concetrated Hydrochloric acid
- B - water
- Calcium oxide Accept quick lime/CaO rej. CaCl2
- Absorbs unreacted/excess chlorine
- 2KMnO4(s) + 16HCl(aq) → 2KCl(aq) + 2MnCl2(aq) + 5Cl2(g) + 8H2O(l)
- Aluminium Chloride sublimes; collects further away from heating point
- Al Cl
Moles 0.675 1800
27 24000
Mole ratio = 0.025 0.075
0.025 0.025
1 3
E.F is AlCl3
n = 267 = 2
133.5
M.F = (AlCl3)2 = Al2Cl6
-
-
- 6NaOH(aq) + 3Cl2(g) → 5NaCl(aq) + NaClO3(aq) + 3H2O(l)
-
- Used as herbicide/ weed killer
- Bleaching agent in paper industry
- Chlorine bleaches by oxidation by adding [O] to the dye hence the bleaching is permanent while SO2 bleaches by reduction by removing [O] from the dye hence temporary. Accept equations for each.
-
-
- S. Smallest atomic radius making it to gain electron easily./Most electronegative/ highest electron affinity
- X
- V/Mg
- Q/Li. Has the smallest atomic radius hence strongest positive nuclear charge
- V2X3/Al2S3
- Covalent rej Molecular bond
- S has more protons than Q leading to higher/stronger nuclear charge
- Bubbles/effervescence of a colourless gas. Chloride of V hydrolyses to give hydrochloric acid which reacts with the carbonate to give CO2
-
-
-
- 72g/100g of H2Ot3
showing ✓½
correct reading ✓½ - Ans a(ii) I × 1000 C₁
100
C₁
122.5 - Showing ✓½
reading. ✓½
Solubility at 62°C = 115.5g/100g of H2O
42°C = 60
Mass of crystals
115.5 − 60 ✓½
= 55.5g ✓½
- 72g/100g of H2Ot3
-
- 25 × 0.2 = 0.005 moles
1000 - Mole ratio = 1:1
∴ Moles of NaOH = 0.005moles Accept for 1 without ratio - If 20cm3 → 0.005
250cm3 → ?
250 × 0.005
20
= 0.0625moles - Mass = 0.0625 × 40 = 2.5g
- Mass of solvent = 28 − 2.5 = 25.5
Solubility = 2.5 × 100 = 9.804g/100g of H2O
25.5
- 25 × 0.2 = 0.005 moles
-
-
-
- Electrolysis of brine
- Cracking of alkanes
- Reaction of natural gas with steam
-
- Finely divided iron. Accept iron
- Platinum - rhodium/platinum
-
- 3ZnO(s) + 2NH3(g) → 3Zn(s) + N2(g) + 3H2O(l)
- heat
2Cu(NO3)2(s)2CuO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
-
- Neutralization
- Crystallization
-
- Tetra-amine Copper(II)ion
- [Cu(NH3)4]2+
-
- Preparation of N2O(g)
- Carbon (II) Oxide/ CO Accept H2
-
- Liquid Q used as refrigerant
- haber process
- in light bulbs
- Dilutes effect of O2 in deep sea diving
-
-
-
- 2 - methylprop-1-ene
- Propanoic acid
- Add Na2CO3/NaHCO3 into different solutions of C2H6O and C2H4O2 in test tubes. C2H4O2 produces bubbles of a colourless gas while C2H6O does not
-
- Sodalime rej NaOH
- 2-bromoethanol or
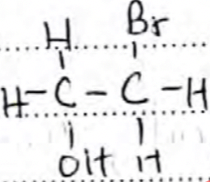
- CH3COOCH2CH3 Accept open structure
-
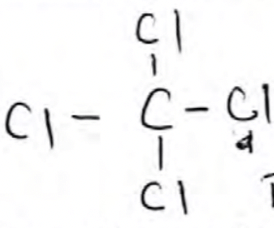 Tetrachloromethane. Accept 1, 1, 1, 1 - tetrachloromethane
Tetrachloromethane. Accept 1, 1, 1, 1 - tetrachloromethane -
- Type - oxidation; Reagent - H+/KMnO4/H+/K2Cr2O7 condition heat/180°C
- Rxn: dehyration
Reagent: Concentrated Sulphuric (VI) acid/Al2O3
Condition: Heat/ temp of 160°C-180°C
- n = 56,000 = 2,000
28
-
-
-
- Removal of chemically combined oxygen from a substance
- Loss of electrons
- Decrease/ Reduction in oxidation number
- Combustion tube
- Copper (II) Oxide is not heated
- Concentrated Sulphuric (VI) acid rej CaO CaCl2(s)
- Dilute hydrochloric acid/ Hydrochloric acid
- H2 reduces CuO to Cu metal and H2 is oxidised to water
-
- Water
-
- Heat to boil; b.p of 100°C
- Determine its density; has a density of 1g/cm3
- Freeze the liquid; freezes at 0°C
- Determine its refractive index; its refractive index is 1.33158
- Hydrogen breaks double bond in oil to form saturated fats.
Accept: Hardening of oils to fats
-
-
- Enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of a substance is completely burnt in oxygen
- 0.6 = 0.01moles
60 - ΔH = 400 × 4.2 × 13
= 21840J//21.84kJ (Accept if converted) rej. ½ for j - If 0.01 → 21.84kJ
1 mole → 21.84 = − 2184kJ/mol rej. ½ for wrong units or sign
0.01 -
- Propanol and water may have evaporated
- Incomplete combustion of Propanol.
- Heat lost to the sorrounding not accounted for
-
-
- Fuel storages be located away from populated areas.
- Ensure gas taps are closed tightly after use
- Gas cylinders should be kept away from heat
- Charcoal stoves to be used in well ventilated rooms to curb CO poisoning.
- Keep away from oil spills
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Maranda High Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students