INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer all the questions.
- Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- All answers should be written in English.
- Metal Q displaces metals T and U from their oxides but does not displaces metal R. Metal T displaces U form its oxide. Arrange the metals according to their reactivity starting with the strongest reducing agent. (1 mark)
- Chlorine gas can be prepared in the laboratory using the following two methods;
Solid substance X and concentrated Hydrochloric acid
Solid substance X, concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid and solid Sodium Chloride.- Name the solid substance X (1 mark)
- What is role of concentrated sulphuric acid in the reaction? (1 mark)
- State how dry chlorine gas is collected. (1 mark)
- A white crystalline solid Q when heated to forms a brown gas, colourless gas that relights a glowing wooden splint and a yellow residue which turns white on cooling. Aqueous solution of Q forms white precipitate which dissolves in excess ammonia solution to form a colourless solution P.
- Write the name and chemical formulae of complex ion in solution P. (2 marks)
- Name;
- Chemical formula;
- State the observation made when the aqueous solution of P is reacted with few drops of sodium hydroxide. (1 mark)
- Write the name and chemical formulae of complex ion in solution P. (2 marks)
-
- Define term Lattice energy (1 mark)
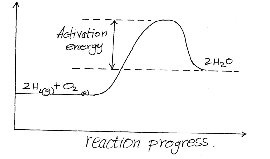
- The reaction between hydrogen gas and oxygen releases energy. A student drew the reaction profile for the reaction between hydrogen gas and oxygen gas.
State two errors made when drawing the reaction profile. (2mks)
- Ammonia gas is one of the substances recycled in the Solvay process.
- Other than water name another substance that is recycled in the process. (1 marks)
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction that regenerates Ammonia gas in the process. (1 mark)
- State an industrial use of the only waste product in the Solvay process. (1 mark)
- Lead (II) iodide is a toxic bright yellow solid which was used as a paint pigment known as ‘iodine yellow’. Describe briefly how you would prepare lead (II) iodide in the laboratory starting with lead (II) oxide. (3 marks)
- 5.0g of zinc carbonate were allowed to react with 25cm3 of 1M hydrochloric acid until there was no further reaction. Calculate the volume of gas that was formed at s.t.p. (Zn = 65.4, O = 16, C = 12, molar gas volume at s.t.p = 22400 cm3) (3 marks)
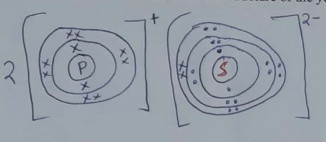
- Atoms of element P can be represented as
. Element P reacts with sulphur to form a yellow solid. Using dots (•) and crosses (X) represent electrons, draw the structure of the yellow solid. (S=16). (2 marks)
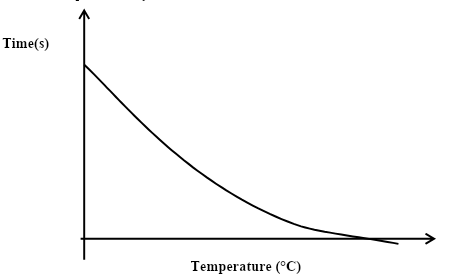
- The curve shown below shows the variation of time against temperature for the reaction between sodium thiosulphate and hydrochloric acid.
- Explain the shape of the curve. (2 marks)
- Other than temperature name one factor that affects the rate of reaction. (1 mark)
- Magnesium ribbon was added to a solution of hydrogen chloride in methylbenzene. Another piece of Magnesium ribbon was added to hydrogen chloride in hydrogen chloride in water. State and explain observations made. (2 marks)
- State two differences between luminous and non luminous flame of the Bunsen burner. (2 marks)
- A fuel gas contains 50% of hydrogen gas and 44% of carbon (II) oxide by volume. The rest of is incombustible. Calculate the volume of gas that remains at room temperature when the 100 cm3 fuel gas was ignited. (3 marks)
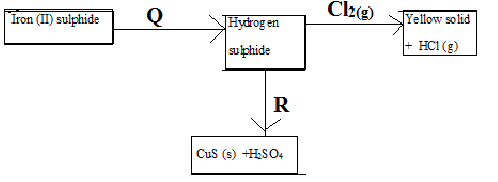
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name substances; ( 1 mark)
- Q………………………………………………………..
- R………………………………………………………..
- Write the equation for the reaction that leads to the formation of the yellow solid. (1 mark)
- Using a chemical test, describe how you would distinguish between hydrogen sulphide and sulphur (IV) oxide. (1 mark)
- Name substances; ( 1 mark)
- A gas occupies a volume of 400cm3 at 227oC and 760mmHg.What will be the temperature of the gas when the volume and pressure of the gas is 100cm3 and 380mmHg respectively. (2 marks
- For each of the following experiments, give the observations, and the type of change that occurs (Physical or chemical) (3 marks)
Experiment Observation type of change A few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid added to small amounts of sugar A few crystals of Iodine are heated gently in a test tube A few crystals of copper (II) Nitrate are heated strongly in a test tube. -
- Define solubility of a solute. (1 mark)
- The solubility of potassium nitrate is 120g/100g of water at 80°C and 70g/100g of water at 20°C.What mass of the salt would crystallize if 80g of potassium nitrate solution saturated at 8°C was cooled to 20°C ( 2Marks)
- Zinc metal reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid. The gas produced was then passed over heated copper (II) oxide in a combustion tube.
- State two precautions that must be considered when the gas reacts with copper (II) Oxide in the combustion tube. (2 marks)
- Write a balanced chemical equation between zinc and dilute hydrochloric acid. (1 mark)
- The table below shows ammeter readings recorded when two equimolar solutions were tested separately.
Electrolyte Current (A) Dilute Sulphuric (VI) Acid 7.210 Ethanoic Acid 4.011 - Explain the difference in the ammeter readings. (2marks)
- Compare the reactivity of equal length of magnesium ribbon with each of the electrolytes. (1 mark)
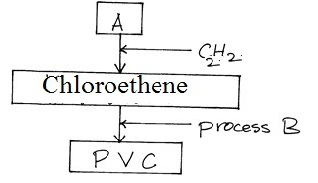
- Study the scheme below and answer questions that follow
- Identify reagent A. (1mk)
- Name process B (1mk)
- What does PVC stand for? (1mk)
- One of the disadvantages of hard water is wastage of soap.
- State one other disadvantage (1mk)
- The table below shows tests carried out in a sample of water and the results obtained.
Sample Results Observations A Addition of sodium hydroxide drop wise until excess White precipitate which dissolves in excess B Addition of excess ammonia solution White precipitate C Addition of dilute nitric (V) acid followed by barium chloride White precipitate - Identify the anion present in the water sample (1 Mark)
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction in C (1 Mark)
- A piece of sodium was burnt in excess oxygen gas. The product obtained was shaken with water to make a solution.
- Write a balanced equation for reaction between the product formed and water. (1 mark)
- State and explain the observation made when red and blue litmus papers are dipped into the solution. (2 marks)
- Aluminium chloride and sodium chloride are both chlorides of period 3 elements in the periodic table. Use this information to explain the following observations.
- A solution of Al2Cl6 in water turns blue litmus paper red while that of sodium Chloride does not. (1½ marks)
- Sodium chloride has a melting point 801°C is while Al2Cl6 sublimes 183°C. (1½ marks)
- The ionization energies of elements A and B are 495.9kJ/mol and 739.9kJ/ mol respectively.
Both elements are in the same group of the periodic table.- What is ionization energy? (1 mark)
- Compare the reactivity of elements A and B . Explain your answer. (2 marks)
- Study the information given in the table below and answer the questions below.
Bond Bond energy(kJ/mol) C-H
H-CI
C-CI
CI-CI
C-C413
431
346
244
347- Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction below.
C2H6(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3CH2Cl(g) + HCl(g) (2 marks) - State a condition required for the reaction in (a) above to take place. (1 mark)
- Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction below.
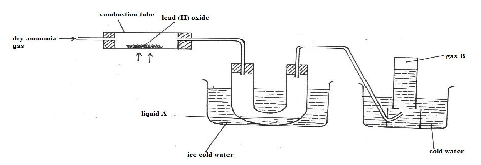
- The diagram below represents a set-up that can be used to obtain nitrogen gas in the laboratory. Use the information on the diagram to answer the questions that follow
- Describe the chemical test for liquid A. (1 mark)
- What observation is made in the combustion tube during the reaction? (1 mark)
- State two uses of gas B. (1 mark)
-
- State Graham’s law of diffusion. (1mk)
- 50cm³ of nitrogen (ii) oxide was allowed to diffuse through a porous membrane in 20 seconds. Calculate the time taken by equal volume of carbon (ii) oxide to diffuse through the same membrane. (C=12, N=14, O=16). (2mks)
- Nitrogen (IV) oxide dissolves and reacts with Sodium hydroxide solution to form two salts and water.
- What is the nature of Nitrogen (IV) oxide? {1 mark}
- Write the Ionic equation for the reaction that takes place. {1 mark}
- When powdered brass was reacted with excess dilute sulphuric (VI) acid, a solid residue was left.
- Name the residue. (1 mark)
- Explain why the residue was left. (1 mark)
- State another observation made (1 mark)
- During manufacture of sulphuric (vi) acid, sulphur (iv) oxide is oxidised to sulphur (vi) oxide in the presence of vanadium oxide catalyst as shown below:
2SO2(g) + O2(g)2SO3(g) ΔH = − 197kJ/mol
The reaction is carried out at a pressure of 3 atmospheres and a temperature of 4500C. State and explain the effect on the yield of sulphur (vi) oxide if the reaction is:- Carried out at 3 atmospheres and 600°C. (2mks)
- In absence of a catalyst. (2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
- R - Q - T - U
→ increasing -
- Manganese (IV) Oxide KMnO4
- It reacts with sodium chloride to produce hydrogen chloride which in turn reacts with Manganese (IV)Oxide to produce chlorine gas.
- It is collected by downward delivery since it is denser than air
-
-
- Tetra amine Zinc (ll) ions
- [Zn(NH3)4]2+
- White precipitate is formed.
-
-
- Energy change when one mole of an ionic compound is formed from mits constituent ions in gaseous state.
-
- Products should be at a lower energy than products
- Labelling of the y-axis ( energy in KJ/mol)
-
- Carbon (IV) Oxide
- Ca(OH)2(aq) + 2NH4Cl(aq) → CaCl2(s) + 2NH3(g) + 2H2O(l)
-
- Used as a drying agent of gases that do not react with it.
- Used to extract sodium metals.
-
- Add Lead (II) Oxide to Nitric (V) acid until it is in excess
- Filter to remove unreacted Lead (II) Oxide
- To filtrate add Sodium Iodide and filter off to remove Lead (II) Iodide as a residue.
- Wash the residue with distilled water.
- Dry the residue between the filter paper.
- ZnCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
1.0 mole = 1000cm3
? = 25cm3
25 × 1
1000
= 0.025moles
HCl : CO2
2 : 1
2 → 0.025
1 → ?
1 × 0.025
2
= 0.0125moles
1.0 moles → 22400
0.0125moles → ?
0.0125 × 22400
= 280cm3 -
P - 2.8.1
S - 2.8.6 -
- Time taken by reaction reduces with increase in temperature. Kinetic energy of reacting particles increases increasing then ftrequency of collision.
-
- Concentration of reacting substances/ Surface area
- Presence of a catalyst
-
- In methylbenzene there was no effervescence but in water there was effervescence.
- Hydrogen chloride ionises in water. Hydrogen ions react with magnesium producing hydrogen gas.
-
Luminous Non luminous Yellow and sooty Blue and non sooty Fairly hot Very hot Long and wavy Short and Steady - Hydrogen = 50/100 ×100 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l)
= 50cm3
Carbon (II) Oxide 44/100 × 100. 2CO(g) + O2(g) → 2CO2(g)
= 44cm3
Remaining gases ( 100 − 44)CO2
=6cm3 incombustible gas -
-
- Q - dilute hydrochloric acid.
- R - Copper (II) Sulphate solution
- H2S(g) + Cl2(g) → S(s) + 2HCl(g)
-
- Ignote the two gases - hydrogen sulphide burns while mSulpmhur (IV) Oxide does not burn
- KMnO4 - white + yellow - SO2
- K2Cr2O7 - green + yellow - green
-
- 227 + 273 = 500K
P₁V₁ = P₂V₂
T₁ T₂
T2 = P₂V₂T₁
P₁V₁
T₂ = 380 × 100 × 500
760 × 400
= 62.5K −210.5°C -
Experiment Observation type of change A few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid added to small amounts of sugar white/brown to black solid Chemical A few crystals of Iodine are heated gently in a test tube Dark grey to Purple vapour Physical A few crystals of copper (II) Nitrate are heated strongly in a test tube. Blue crystals to black solid, brown gas Chemical -
- Maximum mass of solute required to saturate 100g of the solvent at a particular temperature
-
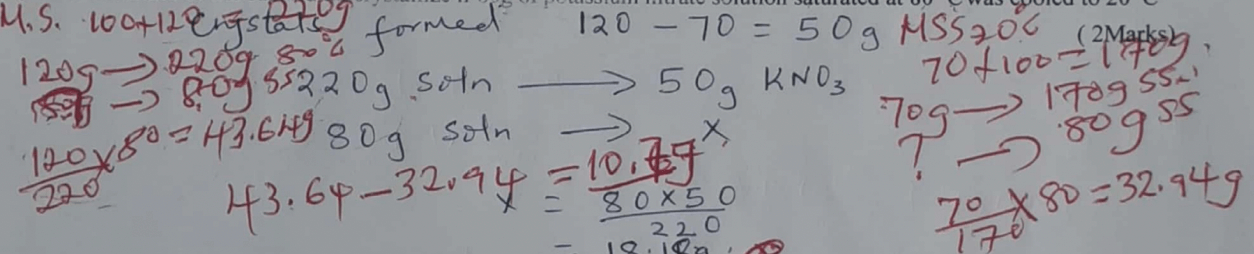
-
-
- Pass hydrogen through combustion tube before heating Copper (II) Oxide to drive out all air.
- Ignite the excess hydrogen to prevent it from exploding in air
- Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
-
-
-
- Sulphuric (VI) acid being strong acid inoises fully. Solution contains many mobile ions hence the high current.
- Ethanoic acid being weak acid, ionises partially. Solution contains few mobile ions.
- Reaction with H2SO4 is higher than with CH3COOH. H2SO4 has more H+ than CH3COOH
-
-
- Stains white clothes/ reduce efficiency in briters due to desposition of fur.
-
- SO42−
- Ba2+ + SO42− → BaSO4(s)
-
- 2Na2O2(s) + 2H2O(l) → 4NaOH(aq) + O2(g)
- Red litmus paper changes blue while blue litmus paper remains blue because the solution contain OH− which are basic in nature.
-
- Al2Cl3 hydrolyses/ ionises in water to produce mhydrogen chloride or (H+)(aq) which is acid while NaCl does not ionise/hydrolyse
- Sodium chloride has a giant ionic structure with strong ionic bond which require alot of energy to break while Al2Cl6 has a molecular structure.
-
- The minimum amount of energy required to remove an electron in the outermost energy level of an atom in gaseous state.
- A is more reactive than B; A has smaller ionization energy (495.9kJ/mol) than B which is (739.9kJ/mol)
-
-
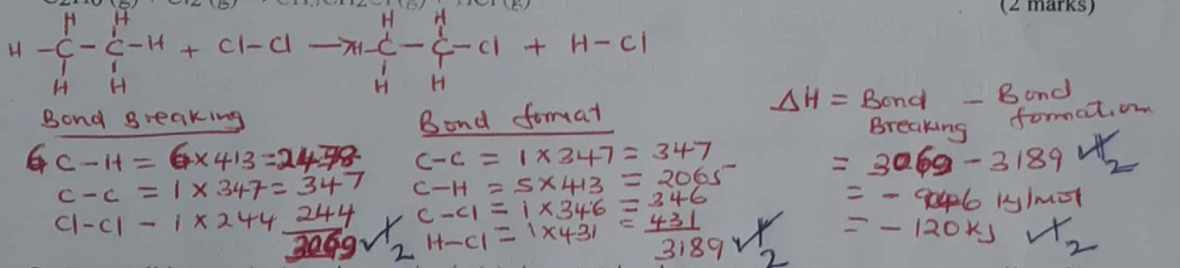
- U.V light
-
-
-
- To liquid A, add anhydrous Copper(II)Sulphate, white anhydrous Coper (II) Sulphate turns blue
OR - Add anhydrous Cobalt(II)Chloride to liquid A, it turns from Blue Cobalt(II)Chloride to pink
- To liquid A, add anhydrous Copper(II)Sulphate, white anhydrous Coper (II) Sulphate turns blue
-
- Orange Lead(II)Oxide turns to grey.
- Droplets of colourless liquid are formed on the cooler parts of the combustion tube
-
- Manufacture of ammonia in Haber process
- In light bulbs; because it is inert.
- As a refrigirant i.e in storage of Semen for artificial insermination.
-
-
- the ratio of the diffusion rate of two gases is the same as the ratio of the square root of the molar mass of the gases.
-
- It is acidic
- 2NO2(g) + 2OH−(aq) → NO3−(aq) + NO2−(aq) + H2O(l)
-
- Copper
- Brass is a mixture of zinc and copper. Zinc reacts with acid but Copper does not. Zinc being more reactive displacrs Hydrogen in the dilute acid faster.
- Effervescence is produced/ bubbles mof colourless gas.
-
- The yield decreases at 600°C; because the reversed mreaction is favoured; since its the reaction that leads to endothermic reaction. i.e SO3 decompose to SO2 and O2
- The yield remains the same. The rate of both reactions slows down / catalyst has no effect on a reaction at equilibrium
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Momaliche Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students