Instructions to Candidates
- This paper has three sections A, B and C
- Answer all the questions in section A and B
- Answer any two questions in section C
For Examiner’s Use Only
|
SECTION |
QUESTIONS |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
|
A |
1 – 13 |
30 |
|
|
B |
14 – 17 |
20 |
|
|
C |
18 |
20 |
|
|
19 |
20 |
||
|
20 |
20 |
||
|
|
Total Score |
90
|
|

QUESTIONS
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
Answer All the Questions in This Section in the Spaces Provided
- State two biotic factors that are useful in agricultural production (1 mark)
- Give four reasons why it is important to stake tomatoes (2 marks)
- State two methods of utilizing sorghum as a forage crop (1mark)
- Give four signs that could enable a farmer to identify compost manure that is ready (2 marks)
- List four farming practices that may help to achieve minimum tillage on a farm (2 marks)
- Give four reasons why seed selection is important in the establishment of crops (2 marks)
- Give four reasons for keeping breeding records in a dairy farm (2 marks)
- State two characteristics of shifting cultivation (1 mark)
- State four factors that determine spacing of crop (2 marks)
- Differentiate between olericulture and pomoculture as used in crop production (1 mark)
- State two characteristics of a large scale farming system (2 marks)
- State four steps followed in land adjudication (2 marks)
- State two physical agents of weathering (1 mark)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
Answer All the Questions in the Spaces Provided
- The diagram below illustrates one of the arable field crops Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow
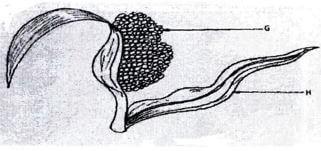
- Identify the field crop (1 mark)
- State the common disease that attack the parts labeled G and H (2 marks)
G……………………………………………… H………………………………………… - Name a variety of the crop that is resistant to birds attack (1 mark)
- State one cultural method to control the diseases named in (b) above (1 mark)
-
- Name the deficient nutrient element in plants showing the following symptoms;
- Stunted growth, die back of the plant tips, leaves roll up and chlorosis along margins of younger leaves (1 mark)
- Yellowing of leaves appears first on lower leaves; leaves turn brown and fall prematurely, stunted growth (1 mark)
- Leaf curling, yellowing of leaves tips and edges of leaves scorched and has small mottles (1 mark)
- Purpling of leaves, stunted growth, slender stalks and lateral buds remain dormant (1 mark)
- The diagram below show a practice out on various crops on the farm Study them carefully and answer the questions that follow
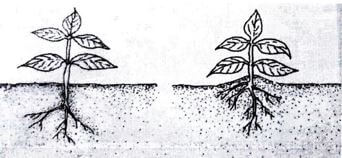
Identify the practice in the diagram above (1 mark)
- Name the deficient nutrient element in plants showing the following symptoms;
- Diagram G and H below show some weeds

- Identify the weeds G and H (2 marks)
G……………………………………………… H………………………………………… - State one economic importance of weed H (1 mark)
- Why is it difficult to control weed G? (1 mark)
- Name an example of a systematic herbicide which can be used to control weed G (1 mark)
- Identify the weeds G and H (2 marks)
- Study the structure below and answer the questions that follow
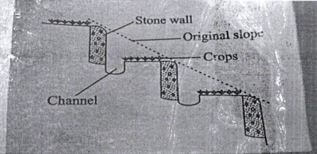
- Identify the type of terrace illustrated above (1 mark)
- Under what two circumstances should the construction of the above terrace be justified?
- Name two other types of terraces
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer Any Two Questions From This Section In The Spaces Provided
-
- Describe the production of tomatoes under the following;
- Transplanting (5 marks)
- Field management practices (5 marks)
- Give six advantages of drip irrigation (6 marks)
- Describe the precautions a farmer should put into consideration when harvesting cotton (4 marks)
- Describe the production of tomatoes under the following;
-
- Outline various ways through which vegetation cover reduces soil erosion (4 marks)
- Outline various conditions which necessitate land clearing (4 marks)
- Give six benefits of planting annual crops early (6 marks)
- Describe six practices carried out in a vegetable nursery to ensure healthy seedlings at transplanting (6 marks)
-
- Describe eight cultural methods of controlling diseases in crop production (8 marks)
- Explain three ways in which biotic factors discourages agricultural production (3 marks)
- State four effects of high temperature in crop production (4 marks)
- Describe five ways through which a farmer can maintain soil fertility in his coffee farm (5 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Predator
- Decomposer
- Pollinators
- Nitrogen fixing bacteria (½ X 2 = 1 mark)
-
- It makes it easy to control pests.
- Fruits are not contaminated by soil.
- Easy to harvest.
- Pruning is easy.
- Easy to weed (4 X ½ = 2 marks)
-
- Grazing
- Cut and given as green fodder.
- Making silage (2 X ½ = 1 mark)
-
- Volume of heap/materials in pit goes down.
- Materials easily breaks to small pieces when pressed between fingers.
- Growth of moulds/fungi in manure.
- Temperature within the material goes down.
- Materials are odourless.
- Turns dark brown in colour. (4 X ½ = 2 marks)
-
- Apply mulch to control weeds.
- Using herbicides to control weeds.
- Growing cover crops to control weeds.
- Heavy harrowing followed by planting.
- Timing cultivation/late weeding followed by planting.
- Slashing/uprooting weeds.
- Restricting cultivation to root zone of crop. (4 X ½ = 2 marks)
-
- To obtain seeds which provide high quality yields.
- To obtain seeds with high germination percentage.
- To reduce chances of disease and pest attack/ obtain healthy seeds.
- To identify seeds that are suitable to a given ecological area. (4 X ½ = 2 marks)
-
- Used when selecting animals for breeding.
- Used in planning and budgeting.
- Used when culling animals.
- To control breeding. (4 X ½ = 2 marks)
-
- Practice where land is plenty.
- Practicable with annual crops not with perennials.
- Agricultural output is low.
- Inputs like pesticides and fungicides are rarely used.
- Population is sparse.
- Use of simple tools. (2 X ½ = 1 mark)
-
- Type of machinery.
- Soil fertility.
- Size of the plant.
- Moisture availability.
- Use of the crop.
- Pest and disease control. (4 X ½ = 2 marks)
- Olericulture involves growing of vegetables while pomoculture is the growing of fruits.
(1 X 1 = 1 marks – marks as a whole) -
- Large tracks of land.
- Heavy capital investment.
- Skilled labour.
- High level of management. (2 X ½ = 1 mark)
-
- Establishment of ownership.
- Measurement of land.
- Description of land.
- Recording of land. (4 X ½ = 2 marks)
-
- Wind
- Moving water rej. Water only
- Moving ice rej. Ice only.
- Temperature (2 X ½ = 1 mark)
-
- Sorghum (1 X 1 = 1 mark)
- G – Loose smut; Head smut (1 X 1 = 1 mark)
H – Leaf blight; Anthracnose; Sooty stripe - Variety – Goose neck. (1 X 1 = 1 mark)
-
- Growing of improved resistant varieties /Use of resistant varieties.
- Seed dressing.
- Timely planting. (1 X 1 = 1 mark)
-
-
- Calcium. (1 X 1 = 1 mark)
- Nitrogen (1 X 1 = 1 mark)
- Potassium (1 X 1 = 1 mark)
- Phosphorous (1 X 1 = 1 mark)
- Earthing up; (1 X 1 = 1 mark)
Ridging.
-
-
- G – Oxalis (1 X 1 = 1 mark)
H – Mexigan Marigold (1 X 1 = 1 mark) -
- It taints milk if consumed by lactating cow.
- It competes with crops for water and nutrients thus reducing their yield.
- It increases cost of production in controlling it. (1 X 1 = 1 mark)
- It has underground bulbs/tubers which make it survive in adverse conditions (1 X 1 = 1 mark)
- 2, 4 – D
MCP (1 X 1 = 1 mark)
- G – Oxalis (1 X 1 = 1 mark)
-
- Bench terrace (1 X 1 = 1 mark)
-
- When high value crops are grown
- When there is an acute shortage of suitable land. (2 X 1 = 2 marks)
-
- Broad based terraces.
- Narrow based terraces.
- Fanya juu terraces.
- Fanya chini
- Level terrace (2 X 1 = 2 marks)
-
- Production ot tomatoes
- Transplanting
- The nursery should be watered before lifting the seedlings.
- Healthy and vigorous growing seedling is planted per hole and soil firmed around the seedling.
- Seedlings are mulched and watered regularly.
- Plant same height as it were in the nursery bed.
- Apply phosphate fertilizer at planting.
- Uproot seedlings when they have 4 – 5 leaves /penal thickness / 10 – 15cm high.
- Lift seedlings using garden trowel.
(5 X 1 = 5 marks)
- Field management practices.
- Gapping – Any seedling that dries after transplanting should be gapped /replaced to maintain the correct plant population.
- Top-dressing – at 25-30cm high, tomato plants should be top dressed with nitrogenous fertilizers at the rate of 100kg CAN or SA per ha.
- Weeding – the field should be kept weed free. Hand cultivation is done to control weeds.
- Staking – practice of supporting tomatoes especially tall varieties using sticks which are about 2m high.
- Pruning – practice of removing of many shoots growing from the main stem to remain with two or three. In tall varieties terminal buds are removed when plant reaches 1.5-1.8m high. This encourages the development of large fruits and control upward growth. (5 X 1 = 5 marks)
- Transplanting
- Advantages of drip irrigation
- Economical in the use of water.
- Water under low pressure can be used.
- Minimizes the outbreak of leaf fungal diseases.
- Reduces growth of weeds between the rows.
- Fertilizers may be applied with water.
- Suitable for both sloppy and flat land.
- Minimize water loss through evaporation.
- Accumulation of salts around plant is avoided. (6 X 1 = 6 marks)
- Precautions a farmer should consider when harvesting cotton.
- Do not pick when it is wet.
- Avoid any contamination.
- Pick on weekly basis.
- Sisal bags should not be used. (4 X 1 = 4 marks)
- Production ot tomatoes
-
- Ways through which vegetation cover reduces soil erosion.
- Reduces impact of rain drops and speed of wind lowering erosive power.
- Roots hold soil particles together thus preventing from being eroded easily.
- Vegetation cover on decaying act as a cementing agent of the soil.
- Promotes water infiltration rather than surface run-off.
(4 X 1 = 4 marks)
- Conditions that necessitate land clearing.
- When opening up a virgin land.
- Where a stalk growing crop was previously planted.
- Where the interval between primary and secondary cultivation is long.
- Where land was left fallow for a long time.
- Benefits of planting annual crops early.
- Early establishment lead to withstanding competition with weeds.
- There is use of available rainfall.
- Crop escape attacks by pests and diseases.
- There is better use of nitrogen like nitrogen flush before it is leached.
- Crops get good market prices/sell early when supply is low.
- Reduces competition for labour with other operations/give time for other practices. (6 X 1 = 6 marks)
- Practices carried out in vegetable nursery.
- Shading to protect seedlings against strong sunlight and heavy raindrops.
- Weed control to avoid competition for nutrients.
- Pest and disease control.
- Thinning /pricking out to avoid overcrowding and unnecessary competition for nutrients.
- Mulching before seeds germinate to conserve moisture and seeds being eaten by birds.
- Hardening off seedlings to avoid transplanting shock. (6 X 1 = 6 marks)
- Ways through which vegetation cover reduces soil erosion.
-
- Cultural methods of controlling diseases.
- Growing diseases resistant varieties.
- Heat treatment of planting materials against diseases.
- Proper drying of cereals and pulses before storage.
- Practicing field hygiene /to remove or destroy pathogen infested materials.
- Proper spacing of crops.
- Use of healthy planting materials /use of disease free planting materials.
- Control of weeds which may harbor pathogens.
- Proper seedbed preparation.
- Crop rotation.
- Closed season. (8 X 1 = 8 marks)
- Three ways in which biotic factors discourage agricultural production.
- Pathogens – cause diseases in crops and livestock reducing productivity.
- Pests – damage crops directly or indirectly reducing production.
- Parasites – cause weakening of animals, transmit diseases reducing production.
- Denitrifying bacteria – break down nitrates in the soil reducing fertility.
(6 X 1 = 6 marks)
- Effects of high temperature in crop production.
- Increases incidences of pests and diseases.
- Improves quality of certain crops.
- Lowers quality of some crops e.g. pyrethrum.
- Increases rate of evapotranspiration/wilting in plants.
- Increases growth rate for early maturity in crops. (First 3 X 1 = 3 marks)
- Five ways of maintaining soil fertility.
- Application of manures and fertilizers to replenish soil nutrients.
- Mulching to conserve soil moisture.
- Control of soil PH to maintain it within the required range.
- Maintaining good drainage.
- Weed control to avoid competition for nutrients.
- Practicing minimum tillage to maintain good soil structure.
- Intercropping coffee with low growing legumes for nitrogen fixation.
(5 X 1 = 5 marks)
- Cultural methods of controlling diseases.
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Arise and Shine Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
