Instructions to Candidates:
- This paper has two sections: A and B.
- Answer all questions in section A.
- In section B, answer question6 and any other two questions.
FOR EXAMINERS USE ONLY
SECTION A
|
Question number |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
Sub Total |
|
Marks |
SECTION B
|
Question number |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
Sub Total |
|
Marks |

QUESTIONS
SECTION A
Answer ALL Questions in this Section
- The diagram below shows the angles of the sun’s rays at different latitudes when the sun is at the equator.
Use it to answer questions (a) (b).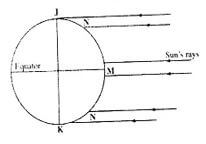
- Name the parts of the earth’s surface marked J and K. (2 marks)
- Giver two reasons why the intensity of the insolation is higher at M than at N. (2 marks)
-
- What is weathering? (2 marks)
- Give three factors that influence the rate of weathering. (3 marks)
- The diagram below shows a composite volcano.
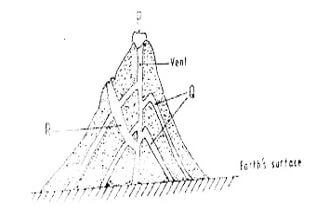
- Name the features marked P, Q and R. (3 marks)
- How is a parasitic cone formed? (3 marks)
-
- What is land breeze? (2 marks)
- Give two ways in which sea breezes influence the adjacent land. (2 marks)
-
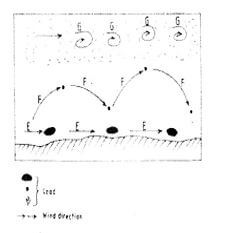
- Name the three ways labelled E,F and G. (3 marks)
- Name three features produced by wind abrasion in arid areas. (3 marks)
SECTION B
Answer Question 6 and Any Other Two Questions from this Section.
- Study the map of KISUMU EAST 1:50,000provided and answer the following questions.
-
- Convert the ratio scale into statement scale. (2 marks)
- Identify two methods that have been used to represent relief on the map. (2 marks)
- Name three physical features found in grid square 0298. (3 marks)
-
- Give the six figure grid reference of the Air Photo Principal point to the East of Obumba School. (2 marks)
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
-
- Citing evidence, name three social services offered in the area covered by the map. (6 marks)
- Explain three factors that may have influenced the distribution of settlements in the area. (6 marks)
-
-
- Describe the following characteristics of minerals
- Colour (2 marks)
- Cleavage (2 marks)
- Hardness (2 marks)
-
- Give two types of igneous rocks. (2 marks)
- Explain three conditions necessary for the growth of coral polyps. (6 marks)
- State four uses of rocks. (4 marks)
- You are planning to carry out a field study on the rocks within your school environment
- Give two secondary source of information you would use to prepare for the field study. (2 marks)
- State why you would need the following items during the field study:
- A fork jembe (1 mark)
- A polythene bag (1 mark)
- Suppose during the field study you collected: Marble, sandstone and granite, classify each of these samples according to its mode of formation. (3 marks)
- Describe the following characteristics of minerals
- The map below shows the location of some mountain ranges.
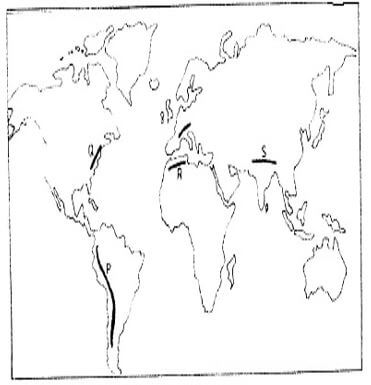
- Name the ranges marked P , Q, R and S. (4 marks)
-
- Apart from fold mountains, name three other features resulting from folding. (3 marks)
- With the aid of labelled diagrams, describe how fold mountains are formed. (10 marks)
- Explain the significance of fold mountains to human activities (8 marks)
-
-
- What are tides? (2 marks)
- Give three causes of ocean currents (3 marks)
- Name the three ocean currents along the western coast of Africa (3 marks)
-
- State three characteristics of submerged lowland coasts. (3 marks)
- Explain three factors that determine the rate of coastal erosion. (6 marks)
- With the aid of labelled diagrams, describe the process through which a stack is formed. (8 marks)
-
- The diagram below represents an artesian basin. Use it to answer question (a)
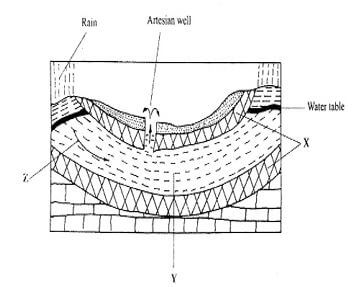
- Identify:
- The layers marked X and Y (2 marks)
- The process marked Z (1 mark)
- Explain how the following factors influence the amount of underground water in limestone areas:
- Rainfall (4marks)
- Vegetation cover (4 marks)
-
- Apart from stalagmites, name three other underground features formed in limestone areas. (3 marks)
- With the aid of a diagram, describe how a stalagmite is formed (8 marks)
- Give three reasons why there are few settlements in kartst landscapes. (3 marks)
- Identify:

MARKING SCHEME
- The diagram below shows the angles of the sun’s rays at different latitudes when the sun is at the equator.
Use it to answer questions (a) (b).- Name the parts of the earth’s surface marked J and K. (2 marks)
- J - North pole
- K - South pole
- Giver two reasons why the intensity of the insolation is higher at M than at N. (2 marks)
- There is a higher concentration of heat at M than at N because the surface area T is smaller than at N.
- The angle of incidence of the sun’s rays at M is higher than at N hence the variation in intensity.
- At N the sun’s rays travel over a longer distance than at M thus losing the heat resulting to low intensity
- Name the parts of the earth’s surface marked J and K. (2 marks)
-
- What is weathering? (2 marks)
- It is the breaking down/disintegration and decomposition of rocks at or near the Earth surface by physical or chemical processes in situ. (Any 2 x 1=2mks)
- Give three factors that influence the rate of weathering. (3 marks)
- Climate
- Nature of the rock
- Relief
- Living things
(Any 3x1=3mks)
- What is weathering? (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows a composite volcano.

- Name the features marked P, Q and R. (3 marks)
- P-Crater
- Q- Lava layers
- R- Dyke
- How is a parasitic cone formed? (3 marks)
- Pressure is educed causing the magma from the interior of the eth to fail to reach the top of a volcano. The upper part of the main vent of the volcano is blocked. Pressure builds up and mama escapes through aside vent. The successive outpouring of magma through the side vent builds alternate layers of ash and lava. This forms a conelet on the side of the composite volcano. The conelet is the parasitic cone. (any 3 x1=3mks)
- Name the features marked P, Q and R. (3 marks)
-
- What is land breeze? (2 marks)
- It is a mass of cool air blowing from the land to the sea during the night. (2x1 =2mks)
- Give two ways in which sea breezes influence the adjacent land. (2 marks)
- It lowers temperature of adjacent areas
- It may increases rainfall
- It may increase relative humidity
- It moderates diurnal range of temperature
- It may lead to convectional rainfall
(Any 2x1=2mks)
- What is land breeze? (2 marks)
-

- Name the three ways labelled E,F and G. (3 marks)
- E - traction/surface creep
- F - Saltation
- G -suspension
- Name three features produced by wind abrasion in arid areas. (3 marks)
- Rock pedestals
- Zeugens
- Yardangs
- Ventifacts/Drainkaters
- Mushroom blocks
(Any 3x1=3mks)
- Name the three ways labelled E,F and G. (3 marks)
- Study the map of KISUMU EAST 1:50,000provided and answer the following questions.
-
- Convert the ratio scale into statement scale. (2 marks)
- 1:50,000
- 1cm represnt50000cm
- 1ch represent 0.5km
- Identify two methods that have been used to represent relief on the map. (2 marks)
- Contours
- Trigonometrical station
- Cliff drawing
- Name three physical features found in grid square 0298. (3 marks)
- Hill
- Rivers
- River valleys
- Steep slope
- Scrub vegetation
(Any 3x1=3mks)
- Convert the ratio scale into statement scale. (2 marks)
-
- Give the six figure grid reference of the Air Photo Principal point to the East of Obumba School. (2 marks)
- 096897 or 097898 or 098899
- Give the six figure grid reference of the Air Photo Principal point to the East of Obumba School. (2 marks)
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
- There are Many Rivers
- Most of the rivers are permanent
- There is a lake to the south west
- There are seasonal swamps e.g. Kano plain
- The main river is R.Nyamasaria
- Generally rivers form dendritic drainage patterns
(Any 5 x1=5mks)
-
- Citing evidence, name three social services offered in the area covered by the map. (6 marks)
- Education service evidenced by schools
- Administration service evidenced by Kisumu DC/chief
- Health/Medical services evidenced by Hospital/Dispensary/ Health centre
- Rehabilitation service evidenced by prison
- Security service evidenced by Police station
(Any 3 x 1 = 3mks)
NB Evidence must be there to score
- Explain three factors that may have influenced the distribution of settlements in the area. (6 marks)
- Drainage- There are no settlements in the seasonal swamps because of waterlogging conditions which discourage farming and enhance the spread of waterborne diseases
- Transport- There are settlements along the motor able track fromRabuour Market to Nyamonge because the road facilitate movement of goods and services.
- Relief - There are no settlements on Nyando Escarpments because it is a steep slope hinder construction of houses
- Or there are many settlements to the North West because it is a gentle slope which is ideal for farming.
- Economic activities- there are many settlements in Kisumu town because it provides opportunities for trade to take place (Any 3 x 2=6mks)
- Citing evidence, name three social services offered in the area covered by the map. (6 marks)
-
-
- Describe the following characteristics of minerals
- Colour (2 marks)
- All minerals have their specific characteristics colour. Some change colour when exposed e.g. gold is yellow, copper oxide are blur or green etc.
- Cleavage (2 marks)
- Minerals have distinct cleavages. They have patterns in which they split or divide e.g. mica split into thin layers. Plant and glass has distinctive facture
- Hardness (2 marks)
- Minerals differ in hardness depending on their chemical constituents and mode of formation. E.g. Tale is soft, quartz is moderately hard and diamond is the hardest
- Colour (2 marks)
-
- Give two types of igneous rocks. (2 marks)
- Intrusive/plutonic rocks
- Extrusive/volcanic
- Hypabyssal rocks
- Explain three conditions necessary for the growth of coral polyps. (6 marks)
- Shallow water√C for the polps to thrive√E
- Well oxygenated water for the survival of the √Eorganisms
- Clear water and salty to enable the organisms extract lime√e
- Warm water with temperature 20oc for the organisms to survive
Condition 3 6mks
Explanation 3
- Give two types of igneous rocks. (2 marks)
- State four uses of rocks. (4 marks)
- Some contain valuable minerals
- Some store underground water I,e impermeable rocks
- Some rocks are extracted and sold to earn income
- Some rocks break down to produce spectacular features which favour tourism
- Some rocks are used in building and construction
- Some rocks are used for making artifacts e.g. soap stones
- Some rocks breakdown into fertile soils
(Any 4x1=4mks)
- You are planning to carry out a field study on the rocks within your school environment
- Give two secondary source of information you would use to prepare for the field study. (2 marks)
- Journals
- Maps
- Magazines
- Newspapers
- Extracts downloaded from the internet
- Books (any 2x1=2mks)
- State why you would need the following items during the field study:
- A fork jembe (1 mark)
- For digging out the rocks
- A polythene bag
- For collecting the rock samples (1 mark)
- suppose during the field study you collected: Marble, sandstone and granite, classify each of these samples according to its mode of formation. (3 marks)
- Marble - metamorphic
- Sandstone - sedimentary
- Granite - igneous
- Give two secondary source of information you would use to prepare for the field study. (2 marks)
- Describe the following characteristics of minerals
- The map below shows the location of some mountain ranges.
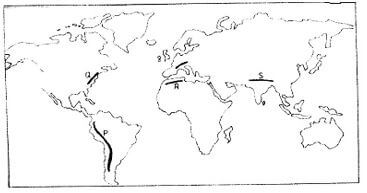
- Name the ranges marked P , Q, R and S. (4 marks)
- P- Andes
- Q- Appalachian
- R- Atlas
- S- Himalayas
-
- Apart from fold mountains, name three other features resulting from folding. (3 marks)
- Synclinal valleys
- Rolling plains
- Ridges
- Intermontane basins
- Intermontane plateaus
- With the aid of labelled diagrams, describe how fold mountains are formed. (10 marks)
- Strong compressional forces on crustal rocks leads to formation of extensive depression called geosyncline on the earth’s surface.
- Prolonged and extensive erosion occurs on the surrounding higher grounds
- Sediments are deposited in the geosynclines forming thick layers
- The weight of sediments causes subsidence of the geosyncline leading to accumulation of more sediments to great thicknesses
- Further subsidence of the geosyncline triggers off compressional forces which causes the sediments to fold
- The folded layers of sediments in the geosyncline ae thrust upwards to form fold Mountains (Text=6 mks,
Diagram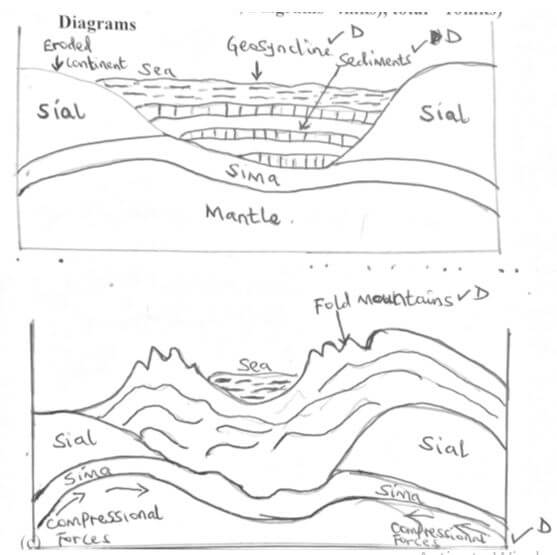
- Apart from fold mountains, name three other features resulting from folding. (3 marks)
- Explain the significance of fold mountains to human activities (8 marks)
- Fold Mountains are sources of rivers that provide water for generation of H.E.P/ domestic use/irrigation/industrial use.
- Fold Mountains are often forested and provide timber which is used in the building and construction industry/medicinal/aesthetic/wildlife habitat.
- Some fold mountains have exposed valuable minerals deposit which are mined
- Fold Mountains are tourist attractions. /snow covered slopes encourage sporting activities thus earning country’s foreign exchange.
- The wind ward slopes of fold mountains received heavy precipitation which enhances agricultural activities
- The rugged nature of some fold mountain landscapes hinder human settlement and agricultural activities.
- The leeward slope of some fold mountain create rains shadow effect which result into aridity discouraging crop farming
- Some fold mountains may act as barrier to transport and communication make the construction of transport and communication lines difficult/expensive
- Name the ranges marked P , Q, R and S. (4 marks)
-
-
- What are tides? (2 marks)
- Tides are the periodic rise and fall in the level of ocean as a result of the gravitational attraction of the Sun and moon
- Give three causes of ocean currents (3 marks)
- Differences in ocean water density/salinity
- Differences in ocean water temperature
- Winds blowing over the ocean
- Shape of coastal land mass
- Earth’s rotation
- Name the three ocean currents along the western coast of Africa (3 marks)
- Benguela
- Guinea
- Cannary
- What are tides? (2 marks)
-
- State three characteristics of submerged lowland coasts. (3 marks)
- The coasts have broad shallow indentation estuaries
- The coasts have several creeds
- The coast have extensive marshes/mudflats which are exposed at low tides
- The coasts have broad continental shelf.
- The coasts have gentle slopes
- Explain three factors that determine the rate of coastal erosion. (6 marks)
- The duration exposure of the coasts to wave erosion. The longer the exposure to coastal waves, the higher the rate of erosion.
- The degree of exposure of the coast to wave erosion. The exposed coasts are eroded more than the sheltered coast.
- The nature of material. Heavy materials have a higher erosive power than fine materials
- The nature of the coastal rock. A coast made up of soft rocks wears away easily when subjected to sea waves
- State three characteristics of submerged lowland coasts. (3 marks)
- With the aid of labelled diagrams, describe the process through which a stack is formed. (8 marks)
- Waves attack both sided of a head land at right angle
- The waves erode through abrasion and hydraulic action forming caves on both sides of the headland
- Continued wave erosion and weathering leads to merging of the caves. The meeting of the caves leads to formation of an arch
- The roof of the arch collapses leading to isolation of part of the headland on the seaward side. The isolated headland is the stack.
(Text=4mks, Diagrams=4mks, total=8mks)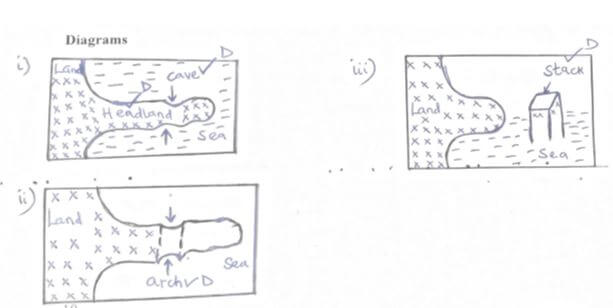
-
- The diagram below represents an artesian basin. Use it to answer question (a)
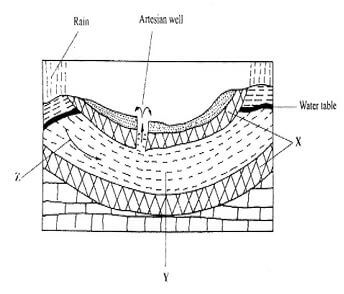
- Identify:
- The layers marked X and Y (2 marks)
- X - Impermeable rock/Aquifer
- Y- A aquifer/permeable rock
- The process marked Z (1 mark)
- Percolation/infiltration
- The layers marked X and Y (2 marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence the amount of underground water in limestone areas:
- Rainfall (4marks)
- Heavy downpour saturates the surface, thus blocking the passages that the water would pass into the ground. This reduces the rate of infiltration and increased surface run off Light rain which falls over a long period infiltrates the ground more than a heavy downpour which is short lived
(Any2x2=4mks)
- Heavy downpour saturates the surface, thus blocking the passages that the water would pass into the ground. This reduces the rate of infiltration and increased surface run off Light rain which falls over a long period infiltrates the ground more than a heavy downpour which is short lived
- Vegetation cover (4 marks)
- The presence of vegetation cover increases the amount of water infiltrating the ground and eventually the amount of underground water.
- Vegetation reduces the speed of surface run off and thus increases infiltration as well.
(Any 2x2=4mksd)
- Rainfall (4marks)
-
- Apart from stalagmites, name three other underground features formed in limestone areas. (3 marks)
Apart from stalagmites, name three other underground features formed in limestone areas- Stalactite
- Limestone pillar
- Underground cave and caverns
- With the aid of a diagram, describe how a stalagmite is formed (8 marks)

- Rain water dissolves carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. It forms a weak carbonic acid. The weak acid seeps through the roof of an underground cave. It reacts with the limestone rocks to form calcium hydrogen carbonate solution. The solution drips slowly through the roof of the cave to the floor. Each drop which falls on the floor spreads out and water in it evaporates. The residue of sodium carbonate which is in the form of tiny crystals is left on the floor. The accumulation of such crystals builds a structure upwards called a stalagmite.
(Text = 5ms, Diagram=3mks, total=8mks)
- Rain water dissolves carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. It forms a weak carbonic acid. The weak acid seeps through the roof of an underground cave. It reacts with the limestone rocks to form calcium hydrogen carbonate solution. The solution drips slowly through the roof of the cave to the floor. Each drop which falls on the floor spreads out and water in it evaporates. The residue of sodium carbonate which is in the form of tiny crystals is left on the floor. The accumulation of such crystals builds a structure upwards called a stalagmite.
- Apart from stalagmites, name three other underground features formed in limestone areas. (3 marks)
- Give three reasons why there are few settlements in kartst landscapes. (3 marks)
- The surface is rocky, which discourage settlements.
- The surface in most places has thin soils discourage agriculture.
- The vegetation in most places is poor and would not support livestock rearing.
- The surface is rugged, thus hindering construction of transport lines.
- Identify:
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Arise and Shine Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
