Instructions to Candidates:
- This paper has two sections: A and B.
- Answer all questions in section A
- Answer question 6 and any two other questions from section B.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English
FOR EXAMINER’S USE ONLY
SECTION A
|
Question number |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
Sub total |
|
Marks |
|
Question number |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
Sub total |
|
Marks |

QUESTIONS
SECTION A.
Answer All the Questions in the Section
-
- Name two provinces in Canada where wheat is grown in large scales. (2 marks)
- List three economic factors that influence agriculture. (3 marks)
-
- Name two horticultural crops grown in Kenya. (2 marks)
- State three reasons why horticulture is more developed in the Netherlands than in Kenya. (3 marks)
-
- State three reasons why marine fisheries in Kenya are underdeveloped. (3 marks)
- State three ways through which fish farming contributes to the economy of Kenya. (3 marks)
-
- Differentiate between transport and communication. (2 marks)
- State three modern means of communication used in Kenya besides cellphones. (3 marks)
- The table below represents information on population change in Kenya by region between years 2000 and 2005.
Region
Population in Millions
Years
2000
2005
Nairobi
2.229
2.751
Central
3.882
4.038
Coast
2.662
2.927
Eastern
4.840
5.120
North-Eastern
1.054
1.438
Nyanza
4.598
4.916
Rift-Valley
7.386
8.366
Western
5.532
3.885
Total
30.183
33.441
- Which region had the highest change in population between 2000 and 2005? (2 marks)
- Calculate the percentage increase in population in Kenya between 2000 and 2005. (2 marks)
SECTION B
Answer Question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
- Study the photograph below and use it to answer question (a).

-
- Name the type of photograph shown. (1 mark)
- Draw a rectangle measuring 15cm by 10cm to represent the area of the photograph. (1 mark)
- On the rectangle, draw a sketch of the photograph and label three physical features. (3 marks)
- Explain two physical conditions that would discourage setting up of a game park in the area shown on the photograph. (4 marks)
- Apart from national parks, outline four other ways in which wildlife is conserved in Kenya. (4 marks)
- Give four reasons why domestic tourism is being encouraged in Kenya. (4 marks)
- Explain four factors which make switzerland receive more tourists than Kenya. (8 marks)
-
-
-
- What is forestry? (2 marks)
- Explain three factors that favour the growth of natural forests on the slopes of Mt. Kenya. (6 marks)
- State five factors that have led to the reduction of the area under forest on the slopes of Mt. Kenya. (5 marks)
- Explain four measures that the govrnment of Kenya is taking to conserve forests in the country. (8 marks)
- Give the differences in the exploitation of softwood forests in Kenya and Canada under the following sub-headings:
- Period of harvesting (2 marks)
- Transportation (2 marks)
-
-
- The map below shows some major tea growing areas in Kenya.
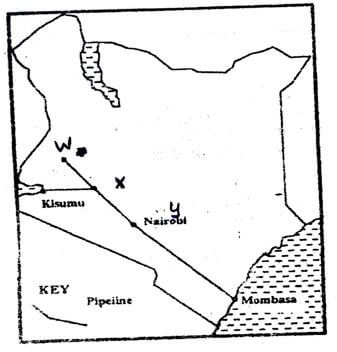
- Name the areas marked W, X and Y. (3 marks)
- State four physical conditions that favour tea growing in Kenya. (4 marks)
- The table below shows tea production in Kenya for two years.
Years
Tea Produced (in tonnes)
1975
56,000
1985 137,000 - Calculate the percentage increase in tea production over the ten years period between 1975 and 1985. (2 marks)
- Give two reasons why there was such an increase in tea production over the given period. (2 marks)
- Describe the stages through which tea is processed from picking to the time its ready for marketing. (6 marks)
- Explain four problems experienced in small scale farming in Kenya. (8 marks)
- The map below shows some major tea growing areas in Kenya.
- A map of East Africa showing minerals distribution.
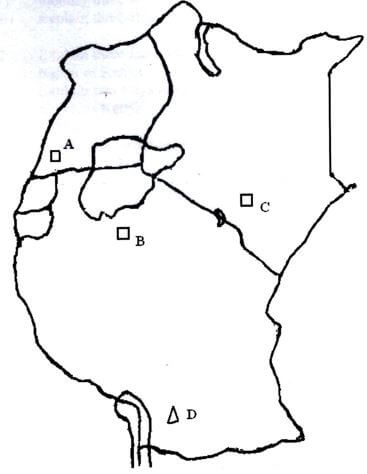
Use the map of East Africa above to answer question (a).-
- Name the mineral mined at points A, B, C, D. (4 marks)
- Give three by products obtained when crude oil is refined. (3 marks)
-
- Explain how trona is processed after reaching the factory. (7 marks)
- List three uses of soda ash. (3 marks)
- Explain four effects of the rising prices of crude oil in the economy of Kenya. (8 marks)
-
-
-
- Apart from water and air pollution, name two other types of pollution. (2 marks)
- Identify three ways through which water is polluted (3 marks)
- Explain three effects of air pollution on the environment. (6 marks)
-
- Explain three factors that lead to frequent flooding in the lake region of Kenya. (6 marks)
- Explain two ways through which floods are controlled in the lake region of Kenya. (4 marks)
- State four effects of wind as an environmental hazard in Kenya. (4 marks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Name two provinces in Canada where wheat is grown in large scales. (2 marks)
- Manitoba
- Alberta
- Saskatchewan. (Any 2 X 1 = 2 marks)
- List three economic factors that influence agriculture. (3 marks)
- Operation costs/ Transport costs / marketing expenses.
- Price flactuations
- Government policy/ subsidies
- Trade restrictions / quota system. (Any 3 X 1 = 3 marks)
- Name two provinces in Canada where wheat is grown in large scales. (2 marks)
-
- Name two horticultural crops grown in Kenya. (2 marks)
- Vegetables / tomatoes /onions / carrots (allow any correct vegetable)
- Fruits/ oranges /pinapples /plums /mangoes (allow any correct fruit)
- Flowers /roses /carnations e.t.c (Any 2 X 1 = 2 marks)
- State three reasons why horticulture is more developed in the Netherlands than in Kenya. (3 marks)
- There is high demand both local and foreign for horticultural crop products in Netherlands than Kenya.
- Farmers in Netherlands have more access to thr capital needed for horticultural farming than in Kenya.
- There is more advanced appropriate technology in the Nehterlands which has enhanced horticultural farming than in Kenya.
- Netherlands unlike Kenya, has well- developed means of transport which enables fast movement of horticultural products.
- Netherlands unlike Kenya, has highly skilled labour for production and handling of horticultural products.
- There is more advanced horticultural farming related research in Netherlands than in Kenya.
- Netherlands unlike Kenya, has a well organised marketing procedure/co-operatives /auction.
(Any 3 well compared points, 3 X 1 = 3 marks)
- Name two horticultural crops grown in Kenya. (2 marks)
-
- State three reasons why marine fisheries in Kenya are underdeveloped. (3 marks)
- The continental shelf is narrow.
- Poor transport connections to fisheries.
- Coastline is fairly straight /has few indentation.
- The water is warm for fish breeding /shallow continental shelf/ lack of upwelling water
- Low demand for fish locally.
- Fishermen lack modern equipment /presentation /storage facilities.
- Inadequate storage facilities – competition from developed countries.
- State three ways through which fish farming contributes to the economy of Kenya. (3 marks)
- Fish are exported earning foreign exchange.
- It creates employment raising living standards.
- Fish farmers earn income through the sale of fish.
- It stimulates growth and expansion of fish related industries.
- State three reasons why marine fisheries in Kenya are underdeveloped. (3 marks)
-
- Differentiate between transport and communication. (2 marks)
- Transport is the act of carrying or conveying goods or people from one place to another while communication is the transmission of messages or information from one place to another.
- State three modern means of communication used in Kenya besides cellphones. (3 marks)
- Telephone
- Fax
- Telex
- Telegram
- E-mail /internet
- T.V
- Radio
- Newspapers
- Posters (Any 3 X 1 = 3 marks)
- Differentiate between transport and communication. (2 marks)
- The table below represents information on population change in Kenya by region between years 2000 and 2005.
- Which region had the highest change in population between 2000 and 2005? (2 marks)
Western = 1.647 Rift valley = 0.98 Nyanza = 0.318 North Eastern = 0.384
Eastern = 0.28 Coast = 0.265 Central = 0.156 Nairobi = 0.5- Western
- Calculate the percentage increase in population in Kenya between 2000 and 2005. (2 marks)
- 33.441 – 30.183 = 3.258 (3.258/30.183 x 100) = 10.7941%√
Or = 10.79%√
Or = 10.8%√
- 33.441 – 30.183 = 3.258 (3.258/30.183 x 100) = 10.7941%√
- Which region had the highest change in population between 2000 and 2005? (2 marks)
- Study the photograph below and use it to answer question (a).
-
- Name the type of photograph shown. (1 mark)
- Ground photograph / ground general view.
- Draw a rectangle measuring 15cm by 10cm to represent the area of the photograph. (1 mark)
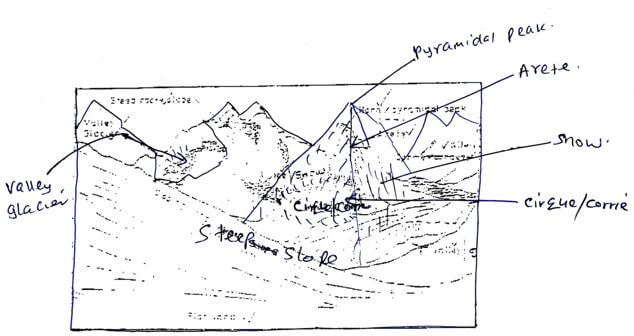
- On the rectangle, draw a sketch of the photograph and label three physical features. (3 marks)
- Explain two physical conditions that would discourage setting up of a game park in the area shown on the photograph. (4 marks)
- Inadequate vegetation that would provide food for wildlife / the area lacks vegetation to provide shelter/ hiding habitation for wild animals.
- The area is high above sea level where atmospheric pressure may be too low to allow some living things to survive.
- The high altitude /presence of snow indicate low temperature unsuitable for survival of living things.
- The mountain top experiences avalenche /snow fall killing wildlife.
- The steep slope /rugged terrain hinders movements of animals in the game parks.
- Name the type of photograph shown. (1 mark)
- Apart from national parks, outline four other ways in which wildlife is conserved in Kenya. (4 marks)
- Encouraging individuals to set up game ranches.
- Banning of trade in wildlife products.
- Encouraging wildlife conservation education.
- Employing anti-poaching unit /forest rangers in the game park.
- Protecting the endangered species in orphanages /sanctuaries /arboretum /natural reserves.
- Promotion of peaceful co-existence between wildlife and human beings.
- Setting up game/forest reserves.
- Give four reasons why domestic tourism is being encouraged in Kenya. (4 marks)
- To make use of tourist facilities during the low tourist seasons.
- In order for Kenyans to be exposed to know more about their own country.
- To facilitate interaction /culural exchange among different communities and thus enhance national unity /patriotism.
- To expose people locally to produce articrafts.
- To expose Kenyans to a wider variety of recreational facilities.
- To create employment /income to government or individuals.
- Explain four factors which make switzerland receive more tourists than Kenya. (8 marks)
- Switzerland is located in central Europe making it easily accessible to tourists of European origin while Kenya is far from Europe.
- Some of the tourist attractions in the two countries are similar hence tourists prefer to visit those that are nearer home.
- The peaceful atmosphere /political neutrality in Switzerland provides easy access to tourists as opposed to Kenya where there are reports of insecurity which scare away tourists.
- Switzerland mounts more effective marketing promotions than Kenya.
- The well-developed transport network in Switzerland provides easy access to tourist sites while in Kenya many roads are poorly maintained.
- In Switzerland tourists are charged fairly for services while in Kenya charges are relatively high.
- In Switzerland there is more encouragement on package tours which lowers the rates charged for tourists facilities while in Kenya, this is not common.
-
-
-
- What is forestry? (2 marks)
- It is the science of planting, caring and using trees/ forests and their resources.
- It is the practice of managing and using trees/forests associated resources.
- Explain three factors that favour the growth of natural forests on the slopes of Mt. Kenya. (6 marks)
- The area receives high rainfall 1000 – 22000mm throughout the year which encourages continuous growth of trees.
- The area has deep fertile volcanic soils that allow the roots to penetrate deep into the ground to support the trees.
- The area has well drained soil thus there is no water logging which can choke plants and interfere with their growth.
- The area has moderate cool condition/climate is ideal for the growth of a variety of trees.
- The area is a gazetted forest reserve / settlement and cultivation is prohibited hence allowing forests to grow without interference.
- The steep slopes discourages human activities thus enabling forests to thrive well.
(Explanation 1mark, factor 1 mark)
- State five factors that have led to the reduction of the area under forest on the slopes of Mt. Kenya. (5 marks)
- The illegal encroachment of human activities.
- The illegal cultivation has led to clearing of parts of the forest.
- Prolonged droughts have caused drying of some forests
- Plant disease/ pests destroy some trees in the forest.
- Outbreak of forest fires/ charcoal burning destroy some trees in the forest.
- Over exploitation of certain species of trees.
- What is forestry? (2 marks)
- Explain four measures that the govrnment of Kenya is taking to conserve forests in the country. (8 marks)
- Registering/ recognizing the efforts of NGOs like the green Belt Movement which have mounted campaigns on planting of trees.
- Gazeting forested areas to reduce encroachment of the public.
- Creating public awareness through mass media/ public bazaars on the importance of conserving forest resources.
- Enacting laws to prohibit the cutting of trees without a license/ protecting indigenous tree species.
- Establishing NEMA/ ministry of environment and natural resources to coordinate environmental management and conservation activities.
- Setting aside national tree planting day to encourage people to plant more trees.
- Advising people to practice agro-forestry so as to avoid cutting trees from the forests.
- Employing forest guards to protect forests form fires/ other illegal human activities.
- Encouraging recycling of papers/ wood based products/ use of other sources of energy to reduce demand of trees.
- Carrying out research through KEFRI and ICRAF in order to come up with ways of controlling diseases/ pests/ develop species suitable for different ecological regions.
- Give the differences in the exploitation of softwood forests in Kenya and Canada under the following sub-headings:
- Period of harvesting (2 marks)
Kenya Canada Period of harvesting is done throughout the year Harvesting is in winter and early spring - Transportation (2 marks)
Kenya Canada Transportation mainly road transport Mainly water transport
- Period of harvesting (2 marks)
-
-
- The map below shows some major tea growing areas in Kenya.
- Name the areas marked W, X and Y. (3 marks)
- W - Kapenguria Kitale/Cherangani/Mt. Elgon
- X - Kericho Kisii /Nyamira Bomet/Gucha/Bureti
- Y- Meru/Embu/Nyeri / Kirinyaga/Mt. Kenya region/Nyambene
- State four physical conditions that favour tea growing in Kenya. (4 marks)
- Cool/ warm climate /moderate to high temperatures throughout the years during the growing period.
- High rainfall/1000-2000 mm of rain.
- Well distributed rainfall throughout the year.
- The areas are frost free.
- The tea growing areas have deep soils.
- The areas have well drained soil / have gently sloping land.
- Name the areas marked W, X and Y. (3 marks)
- The table below shows tea production in Kenya for two years.
- Calculate the percentage increase in tea production over the ten years period between 1975 and 1985. (2 marks)
- 136,000
56,000
81,000
81,000 X 100 = 56,000
= 144.6% increase 145%
- 136,000
- Give two reasons why there was such an increase in tea production over the given period. (2 marks)
- Expansion of tea growing areas and the establishment of the Nyayo tea zones.
- Increase in the number of small-scale tea farms in the country.
- Improved marketing strategies through KTDA.
- Expansion//increase in the number of tea factories.
- Calculate the percentage increase in tea production over the ten years period between 1975 and 1985. (2 marks)
- Describe the stages through which tea is processed from picking to the time its ready for marketing. (6 marks)
- When the tea bushes are ready only the two top leaves and a bud/ flush are picked.
- The green leaves are transported in airy baskets to a collecting centre/ for weighing.
- The weighed leaves are transported by lorries fitted with bags to the processing factories and the tea leaves are again weighed in factory.
- The tea leaves are again weighed in factory.
- The leaves are then withered by blasts of warm air from beneath the trays.
- The dry leaves are passed through a set of rollers to chop stem/ the leaves are crushed.
- The leaves are placed in containers for fermenting, reducing tannic acid and changing the colour to grey-brown.
- The leaves are passed through a conveyor belt which takes them to a tunnel which is at a temperature of 1000C roasting/dry based after which they turn black.
- The leaves are sifted grading tasted for classification.
- The graded tea is packed tea chest for export and small packages for local market.
- Explain four problems experienced in small scale farming in Kenya. (8 marks)
- Poor feeder roads in the growing areas lead to delays in collection/delivery of the green leaf hence causing wastage.
- Delayed payments for the tea delivered/mismanagement of funds lowers the morale of the farmers.
- Long droughts/ hailstorms lead to destruction of the crop/ lower the quality and the quantity of the yield.
- Fluctuation of prices in the world market makes it difficult for the farmers to plan ahead.
- High prices of farm inputs/ reduce the farmers profit margin/ leads to low yields as some farmers cannot afford.
- The map below shows some major tea growing areas in Kenya.
- A map of East Africa showing minerals distribution.
Use the map of East Africa above to answer question (a).-
- Name the mineral mined at points A, B, C, D. (4 marks)
- A – Copper
- B – Diamond
- C – trona
- D – Coal (1 X 4 = 4 marks)
- Give three by products obtained when crude oil is refined. (3 marks)
- Bitumen/Tar/Asphalt
- Wax/paraffin/Wax
- Sulphur
- Lubricants such as grease
- Petro-chemicals/Resin (3 X 1 = 3 marks)
- Name the mineral mined at points A, B, C, D. (4 marks)
-
- Explain how tron is processed after reaching the factory. (7 marks)
- Trona is put on a large sieve-like tray.
- Water from trona is directed back into the lake.
- The trona is washed to remove mud and salt. It is dried.
- It is heated in huge cylinders (desiccators)
- Heating separate sodium carbonate (soda ash) and sodium bicarbonate.
- Soda ash is allowed to cool.
- Soda ash is then ground into powder and sieved.
- The powder is packed in paper/jute bags ready for transportation to the market.
Max. 7 marks NB - the order must be followed
- List three uses of soda ash. (3 marks)
- To manufacture glass.
- To manufacture soap.
- To manufacture caustic soda.
- To manufacture detergents.
- Making table salt.
- Explain how tron is processed after reaching the factory. (7 marks)
- Explain four effects of the rising prices of crude oil in the economy of Kenya. (8 marks)
- The country spends more of their exchange on importation of oil, thus leading to decline of other sectors of the economy.
- There has been increasing cost of transport causing a rise in the cost of movement of people, goods and services.
- Production costs have increased leading to an increase in prices of commodities thus reducing the demand on the commodities.
- Some industries that rely on by-products of petroleum have reduced leading to redundancy/unemployment.
- The country has experienced low-economic growth leading to general poverty among the citizens.
- It has led to the need to establish/look for cheaper sources of energy to replace/supplement the oil.
- It has created damn awareness on the need to conserve energy.
- The country has started exploring the possibilities of drilling their own oil to reduce/stop importation.
(2 X 4 = 8 marks)
-
-
-
- Apart from water and air pollution, name two other types of pollution. (2 marks)
- Land pollution
- Soil pollution
- Noise pollution/sound
- Thermal pollution
- Radiation (Any 2 X 1 = 2 marks)
- Identify three ways through which water is pilluted (3 marks)
- Discharge of industrial waste/oil spillage/radioactive waste into water bodies.
- Discharge of domestic waste into water bodies.
- Discharge of agriculture chemicals into rivers/ lakes by rain water.
- Discharge of raw sewage into water bodies.
- Abuse of water bodies by human beings.
- Natural causes e.g. Soil erosion/ terrestrial gas.
(Any 3X1 = 3 marks)
- Explain three effects of air pollution on the environment. (6 marks)
- Gases emitted from some factories contain substances which corrode roofs of houses and metal structures.
- Some gases from factories contain substances which dissolve in water to form acid which make plants maim or kill animals.
- Inhalation of smoke and soot particles /bad smell lead to discomfort/irritation of the respiratory system/discolouring of vegetable/building.
- Gases emitted from factories may contain poisonous substance which can lead to poor health/death when inhaled /plant leaves turn yellow.
- Gases/excess carbon dioxide increases the temperature affecting the climate of the affected areas/ depletion of Ozone layer.
- Smoke/dust/smog reduces visibility which may lead to motor accidents.
- Dust particles that settles on leaves inhibits photosynthesis.
(Any 3 X 2 = 6 marks)
- Apart from water and air pollution, name two other types of pollution. (2 marks)
-
- Explain three factors that lead to frequent flooding in the lake region of Kenya. (6 marks)
- Most of the land is low lying which causes the rain water to spread over wide area.
- The adjacent highlands receive torrential rainfall which releases large volumes of water resulting to rivers overflowing their banks.
- Silt has filled the river beds making them shallow thus spilling their water over banks.
- The rivers are at their old stage, thus they have wide flood plains which allows water to spread over large areas.
- The area has black cotton soil which is non-porous and when soaked up allow water to flow and spread on the surface.
- The heavy rainfall received in the area is discharged into Lake Victoria making its level to rise thus flooding the adjacent lowlands.
(Any 3 X 2 =6 marks)
- Explain two ways through which floods are controlled in the lake region of Kenya. (4 marks)
- Dams have been constructed across the rivers to check their velocity thus reducing the incident of flooding.
- Several dykes have been constructed/artificial levees to restrict the rivers within their channels/diversion channels have been constructed in the flood plain and water used for irrigation thus reducing the effect of the excess water.
(Any 2 X 2 = 4 marks)
- Explain three factors that lead to frequent flooding in the lake region of Kenya. (6 marks)
- State four effects of wind as an environmental hazard in Kenya. (4 marks)
- Strong winds destroy trees.
- Winds blow off roofs of houses.
- Winds cause strong sea storms and lead to boats capsizing/communication lines are destroyed/destruction of transport line.
- Winds cause soil erosion.
- Winds spread air-borne diseases.
- Winds spread bush fires. (Any 4 X 1 = 4 marks)
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Arise and Shine Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
