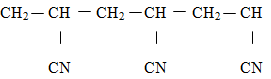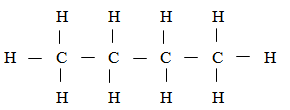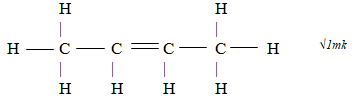INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided in the question paper
- KNEC Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used for calculations
- All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary
- Candidates should answer the questions in English
- An element Y has the electronic configuration 2.8.5
- Identify its period. (1mk)
- Write a formula of the most stable anion formed when Y ionizes. (1mk)
- Explain the differences between the atomic radius of element Y and its ionic radius. (2mks)
- The table below shows tests carried out on a sample of water and the results obtained.
Test Results I Addition of sodium hydroxide solution White precipitate which dissolves in excess II Addition of excess aqueous ammonia Colourless solution obtained III Addition of dilute hydrochloric acid and barium chloride White precipitate - Identify the anion present in the water. (1 mark)
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction in III. (1 mark)
- Solutions can be classified as acids bases or neutral. The table below shows solutions and their pH values
Solution
PH - VALUES
K
L
M1.5
7.0
14.0- Select any pair that would react to form a solution of pH 7. (1mark)
- Identify two solutions that would react with aluminum hydroxide. Explain. (1mark)
-
- State Graham’s Law of diffusion. (1mk)
- 60cm3 of oxygen gas diffused through a porous partition in 50 seconds. How long would it take for 60cm3 of sulphur (IV) oxide gas to diffuse through the same partition under the same conditions?
( S = 32.0, O = 16.0) ( 3 marks )
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the metal oxide. (1mk)
- Write an ionic equation leading to the formation of the white precipitate X. (1mk)
- Give the formula of the ions responsible for the colourless solution Y. (1mk
- Two compounds of barium are barium sulfide and barium chloride.
- The hazard symbol shown in Figure below is on bottles containing barium metal.
State the meaning of this hazard symbol. ( 1mk) - Give the names of the elements combined in barium sulfide. (1mk)
- Hydrogen sulphide gas is highly poisonous. Sate one safety precaution that should be taken when handling hydrogen sulphide. (1mk)
- The hazard symbol shown in Figure below is on bottles containing barium metal.
- Study the information in the table and answer questions that follow:
Isotope 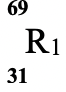
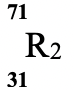
Relative abundance % 61.3 38.7 - Determine the number of neutrons of R1 (1mk)
- Calculate the relative atomic mass of element R. (2mks)
-
- Identify the type of bond formed compound below. (1mk)
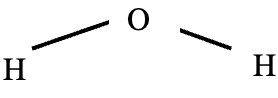
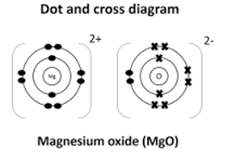
- Using dots (∙) and crosses (x) to represent electrons show bonding in magnesium oxide (2mks)
- Identify the type of bond formed compound below. (1mk)
- Show the products formed when the following salts are heated by writing a balanced chemical equation. (2 marks)
- KNO3(s)
- (NH4)2 CO3(s)
- KNO3(s)
- Explain why when one is stung by a bee application of a little solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate helps to relieve the pain. ( 2 marks )
- The following table gives the melting point of oxides of the third period elements.
Study it and answer the questions that follow.Formula of oxides
Na2O
MgO
Al2O3
SiO2
P4O10
SO2
Melting point (°O)
1190
3080
3050
1730
560
-73
- Explain the large difference in the melting points of Na2O and P4O10. (2 mark)
- Write the equation for the reaction between Al2O3 with;
- NaOH (1 mark)
- H2SO4 (1 mark)
- A hydrocarbon slowly decolourlises bromine in presence of sunlight but does not decolourise acidified potassium permanganate. Name and draw the structural formula of the fourth member of the series to which the hydrocarbon belongs. (2 marks)
- Distinguish between ionization energy and electron affinity. (2mks)
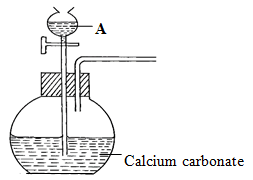
- The set-up below was used to prepare a carbon (IV) oxide gas.
- Give the name of substance A (1mk)
- Complete the diagram to show how the dry gas can be collected. (2mks)
- Write the equation for the reaction (1 mark)
- Calculate the mass of sulphur which on complete combustion would yield 7dm3 of sulphur (IV) oxide measured at 182oc and 722 mm Hg pressure. (0=16, S=32, molar gas volume = 24dm3 at r.t.p). (3 mks)
- Form two students from Achiever’s secondary school reacted three elements as shown in the table below
Which element (s) is likely to be:(3mks)Element
Reaction with Oxygen
Reaction with water
X
Formed acidic oxide
No reaction
Y
Formed basic oxide
Formed soluble hydroxide gave off hydrogen gas
Z
Formed acidic oxide
Dissolved to form an acidic solution
- Non-metal (s)
- Metal (s)
- Insoluble in water.
- A polymer has the following structure
A sample of this polymer is found to have a molecular mass of 5194. Determine the number of monomers on the polymer. ( H = 1.0, C = 12.0, N = 14.0 ) ( 2 marks ) -
- State the likely products of the electrolysis of molten potassium chloride at the:-
- Cathode ……………………………………………………………………………….(½mk)
- Anode ………………………………………………………………………………. (½mk)
- Write the equations that occur at the anode and cathode. (2mks)
- Anode……………………………………………
- Cathode…………………………………………
- State the likely products of the electrolysis of molten potassium chloride at the:-
- Give two reasons why helium is used in weather balloons. (2mks)
- A Bunsen burner produces a yellow flame when airhole is close. Explain. (2mks)
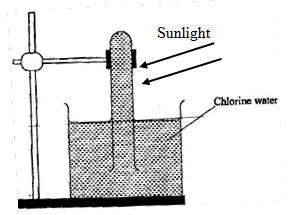
- In an experiment, a boiling tube full of chlorine gas was inverted into a trough of water as shown below.
- State and explain the observations. (2mks)
- If the experiment is repeated with tetrachloromethane instead of water.
- State the observations made. (1mk)
- Explain your observations in b(i) above. (1mk)
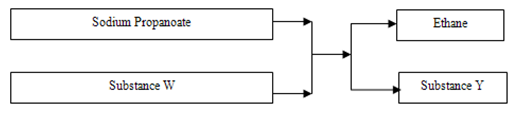
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name substances
- W ……………………………………………………………………………..….(½ mark)
- Y …………………………………………………………………………….…..(½ mark)
- An organic compound K reacted with bromine to form 2,3 – dibromobutane. Draw the structural formula of K. (1mks)
- Name substances
- Starting with copper metal describe how a solid sample of copper (II) carbonate can be prepared. ( 3 marks )
- Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
Select the element which isElement
Electrical conductivity
Ductility
Action of water
A
Good
Good
No reaction
B
Good
Poor
No reaction
C
Good
Good
Reacts
- Likely to be in group II of the periodic table. ( ½ mark )
- Could be used to make electric cables. ( ½mark )
- Likely to be graphite. ( ½ mark )
- In an investigation, sulphur (IV) oxide gas was bubbled through acidified bromine water. This was followed by drops of barium nitrate solution.
- State the property of sulphur (IV) oxide under investigation. (½ mark)
-
- State the observation that were made on addition on sulphur (IV) oxide into the bromine water. (1mk)
- Explain the observation. (1mk)
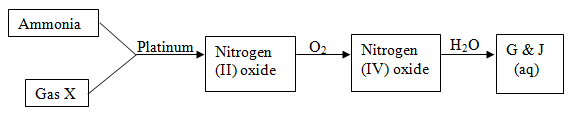
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
- Identify gas X (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction between ammonia and gas X (1mk)
- Write an equation to show the formation of G and J. (1 mk)
-
- Define pollution. ( 1 mark )
- Mention one pollutant that is
- A Particle ( ½ mark )
- Gaseous (½ mark)
- Hydrogen gas was burnt in air to form a colourless liquid.
- Describe a chemical test to identify the colourless liquid. (2mk)
- State how the purity of the colourless liquid can be determined. (1mk)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Period 3
- Y3-
- Ionic radius is large because incoming electrons are repelled by the electrons already in energy levels.
-
- SO42-√1mk
- Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
 BaSO4(s) √1mk
BaSO4(s) √1mk
-
- K and M √1mk one stated no mark
- K√ ½ mk and M√ ½ mk Aluminium hydroxide is amphoteric √1mk (i.e. reacts with both acids and bases)
-
- States that rate of diffusion of a gas is inversly proportional to the square root of its density at constant temperature and pressure
- ti/t2 = √m1/m2 = 50/t2 = √32/64
50/t2 = 0.707
t2 =70.72
-
- Zinc oxide
- Zn2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq)
 Zn(OH)2(s)
Zn(OH)2(s) - [Zn (NH3)4]2+
-
- flammable
- barium and sulfur
both elements must be present for the mark. allow Ba and S
reject sulfide/sulfate reject if any other elements included - experiment involving handling H2S should be done in fume cupboard do not inhale the gas
-
- 69 − 31 = 38
- R.A.M of R = (61.3 x 69) + (38.7 x 71)
100
= 69.774
-
- covalent bond
-
-
- KNO3(s)
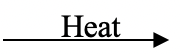 KNO2(s) + O2(g) ✓1
KNO2(s) + O2(g) ✓1 - (NH4)2 CO3(s)
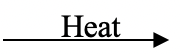 NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) ✓1
NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) ✓1
- KNO3(s)
- A bee sting produces an acidic ✓1 substance application of sodium hydrogen ✓1 carbonate, a base neutralizes the acid from the bee sting ✓1.
-
- Na2O has a giant ionic structure with strong ionic or electrovalent bonds which need large amounts of heat to break hence high melting points. P4O10 has covalent bond with simple molecular structure1
-
- Alkali
Al2O3(s) + 2NaOH(aq) + 3H2O(l) 2Na Al(OH)4 ✓1
2Na Al(OH)4 ✓1 - Acid
Al2O3(s) + 3H2SO4(aq)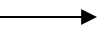 Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2O(l) ✓1
Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2O(l) ✓1
- Alkali
- Butane
-
- ionization energy-minimum energy required to remove an electron form the outermost energy level in the gaseous state
- Electron affinity-energy released when an atom gains an electron in the gaseous state.
Na2CO3(aq) + MgSO4(aq)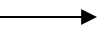 MgCO3(s) + Na2SO4(aq)
MgCO3(s) + Na2SO4(aq)
CO32-(aq) + Mg 2+(aq)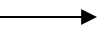 MgCO3(s) ✓1
MgCO3(s) ✓1
( MgSO4 / CaSO4)
-
- HCl acid
- 760 x V = 722 X 7
298 455
= 4.4dm3
24dm3 - Mol
4.4dm3
4.4 = 0.18mol
24
Mass = 0.18 x 64 = 11.52g -
- Z
- Y
- X
- Monomer
✓ ½
RMM of monomer = 36 + 3 + 14 = 53 ✓½
No of monomers = 5194 ✓ ½ = 98 ✓ ½
53 -
-
- Potassium
- chlorine gas
-
- cathode 2K+(l) +2e¯
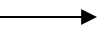 2K(s)
2K(s) - Anode 2Cl¯ (l)
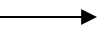 Cl2(g) + 2e¯
Cl2(g) + 2e¯
- cathode 2K+(l) +2e¯
-
-
- its less dense than air
- Its unreactive
-
- closure of air hole leads to insufficient supply of air hence incomplete combustion of gas.
- incomplete combustion of gas produces tiny carbon particles which glow yellow when heated
-
- level of water in boiling tube reduces/Gas is collected in boiling tube
Chloric (I) acid present in chorine water decomposes in sunlight producing oxygen gas and HCl acid. -
- No gas wil be collected in the boiling tube.
- Chlorine dissolves in tetrachloromethane but remains in molecular form thus no chloric (I) acid is formed.
- level of water in boiling tube reduces/Gas is collected in boiling tube
-
-
- W – Sodalime / NaOH
- Y - Sodium carbonate Na2CO3 √1mk
-
-
- Add excess Cu to HNO3 ✓1, filter the mixture, add excess soluble carbonate filter ✓ rinse residue with water and dry residue between filter papers
//
Heat copper metal in excess air. Add excess CuO to H2SO4 and warm ✓, filter ✓ ½ then add soluble carbonate ✓1, filter ✓ ½ . rinse residue with water and dry residue between filter papers -
- C ✓1
- A ✓1
- B ✓1
-
- reducing property/reduction
-
- Yellow/red-brown colour of bromine water is decolourised
- SO2 reduces bromine water to colourless hydrobromic acid while itself is oxidized to sulphuric (VI) acid.
-
- Oxygen;
- 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g)
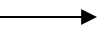 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
4NO(g) + 6H2O(g) - 2NO2(g) + H2O(l)
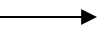 HNO2(aq) + HNO3(aq)
HNO2(aq) + HNO3(aq)
-
- Pollution is the presence of harmful substances in the atmosphere ✓1
-
- Particles – particulate carbon✓ ½ / lead ✓ ½ / dust
- SO2 ✓ ½ , H2S ✓ ½ , NO2, CO
-
-
- add the liquid to anhydrous copper (ii) sulphate.
- Anhydrous copper (ii) sulphate changes from white to blue hydrated copper (ii) sulphate
-
- freeze the liquid. Freezes at 0°C
- boil the liquid. Boils at 100°C at sea level
-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Chogoria Murugi Zone Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students