INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS
- This paper has two sections A and B
- Answer ALL the questions in section A. In section B answer question 6 and any other TWO questions.
SECTION A
-
- What is mining? (2 mks)
- State three ways in which minerals occur. (3 mks)
-
- Name indigenous soft wood tree species found in the Kenyan forest. (2 mks)
- Give three importance of agro forestry. (3 mks)
-
- Distinguish between horticulture and market gardening. (2 mks)
- Give three characteristics of horticultural farming in Kenya. (3 mks)
-
- Name two major swamp areas that have been reclaimed in Kenya. (2 mks)
- State three physical factors that influenced the location of Perkera irrigation scheme. (3 mks)
-
- Identify two types of tourism. (2 mks)
- State three problems facing tourism in Kenya. (3 mks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any two questions in this section
- The table below shows the number of Zebu cattle in different countries in Kenya in 2014.
County Number of Zebu cattle Isiolo 42500 Wajir 22600 Marsabit 20300 Mandera 15400 - Draw a divided rectangle 15 cm long to represent the data above.(7 mks)
- Calculate the range of the above data. (2 mks)
- Give three advantages of using divided rectangle to represent data. (3 mks)
-
- Give three reasons why nomadic pastoralists keep large herds of animals.(3 mks)
- Name two nomadic communities involved in beef cattle rearing in Kenya. (2 mks)
- Explain four ways in which the government of Kenya assist nomadic pastoralists to improve the quality of their livestock. (8 mks)
-
-
- Name two major categories of minerals. (2 mks)
- Identify four factors that influence the occurrence of minerals. (4 mks)
-
- Apart from shaft mining name three other methods of mining. (3 mks)
- Describe how shaft mining method is carried out. (6 mks)
-
- Name two areas in South Africa where diamond is mined. (2 mks)
- Explain four ways in which diamond mining contributed to the economy of South Africa. (8 mks)
-
-
-
- Define re-afforestation. (2 mks)
- State four reasons why afforestation is encouraged in Kenya. (4 mks)
-
- Name three provinces in Canada where forestry is practiced on a large scale. (3 mks)
- State four factors favouring exploitation of forest in Canada. (4 mks)
-
- Explain three factors that favour the growth of natural forest on the slopes of Mount Kenya.
(6 mks) - Explain three problems which hinder the Kenyan government efforts to manage and conserve forest in Kenya. (6 mks)
- Explain three factors that favour the growth of natural forest on the slopes of Mount Kenya.
-
-
-
- Differentiate between land reclamation and land rehabilitation. (2 mks)
- Give four problems facing Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme. (4 mks)
-
- Explain three ways in which land is being rehabilitated in Kenya. (6 mks)
- Name two projects in Netherlands which were aimed at reclaiming land from the sea. (2 mks)
- Describe the steps followed in reclaiming land for agricultural use in Netherlands. (6 mks)
- State five benefits which Kenya derives from irrigation farming. (5 mks)
-
- The diagram below shows a fishing in the pacific ocean.
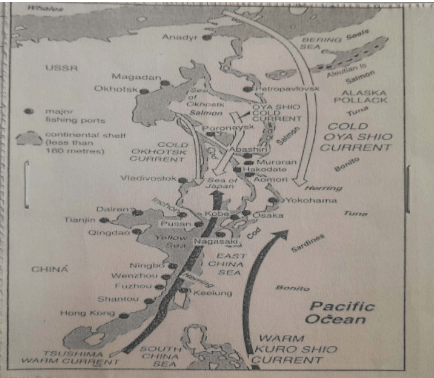
-
- Identify the fishing ground shown above. (1 mk)
- Name three types of fish species found in the fishing ground above. (3 mks)
-
- Differentiate between fishing and fisheries. (2 mks)
- Name two inland types of fisheries in Kenya. (2 mks)
-
- Describe the long lining fishing method. (5 mks)
- Explain four physical factors that influenced development of fishing in Japan. (8 mks)
- State four problems facing marine fishing in Kenya.
-
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
-
- What is mining? (2 mks)
- The process of extracting valuable minerals that occur on or below earth’s crust,
- State three ways in which minerals occur. (3 mks)
- Some occur in veins and lodes
- Some occur in seams and beds or layers.
- Some as alluvial deposits on rivetr valleys or lowlands
- Some occur as weathered rock products.
- What is mining? (2 mks)
-
- Name indigenous soft wood tree species found in the Kenyan forest. (2 mks)
- Podo
- Kenya cedar or red or white cedar.
- Juniper
- Bamboo
- Give three importance of agro forestry. (3 mks)
- To maximize land use as farm products are a source of income to farmers.
- To conserve the land and protect it from erosion or increase water retention on land.
- To provide raw materials for industries.
- To sustain wood fuel supply and conserve forests.
- To produce crops, trees, logs and timber which are sold for income.
- Lead litter decomposes and adds humus to the soil.
- Livestock waste is used as manure.
- Trees modify climate
- Some trees have medicinal value.
- Trees provide beauty or aesthetic value.
- To conserve the soil
- To provide fruits as food.
- Some trees provide fodder
- Trees act as wind breakers.
- Name indigenous soft wood tree species found in the Kenyan forest. (2 mks)
-
- Distinguish between horticulture and market gardening. (2 mks)
- Horticulture is the intensive cultivation of vegetables fruits, flowers and ornamental plants for commercial purposes or it is export market oriented while market gardening is the intensive cultivation of vegetables and fruits for sale in the nearest urban markets or local market oriented.
- Give three characteristics of horticultural farming in Kenya. (3 mks)
- Farms are generally small in size.
- Intensive use of land for maximum production
- Mostly done under green houses especially for flowers
- Use of irrigation water or controlled water supply
- Labour intensive
- Capital intensive
- It is export market oriented and little sold in the domestic market.
- Uses selected seeds and inputs for high production.
- Involves advanced research
- Located in areas with good and valuable transport network
- Highly specialized.
- Owned by rich individuals or foreign companies.
- Distinguish between horticulture and market gardening. (2 mks)
-
- Name two major swamp areas that have been reclaimed in Kenya. (2 mks)
- Yala swamp along river yala
- Bunyula swamp along river Nzoia
- State three physical factors that influenced the location of Perkera irrigation scheme. (3 mks)
- Extensive land that is sparsely populated which allows expansion of the sche,me.
- Gentle sloping land allows mechanization and easy flow of irrigation water by gravity.
- Availability of irrigation water supplied from River perkera for continuous growth of crops.
- Presence of deep fertile soil, loams or alluvial soils suitable for growth of a variety of crops.
- Semi-arid or unreliable or low rainfall causing dry conditions making it necessary to irrigate the area.
- Name two major swamp areas that have been reclaimed in Kenya. (2 mks)
-
- Identify two types of tourism. (2 mks)
- Domestic tourism
- International tourism
- State three problems facing tourism in Kenya. (3 mks)
- Insecurity
- Poaching
- Terrorism
- Demand for land
- Environmental pollution
- Poor transport and communication.
- Identify two types of tourism. (2 mks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any two questions in this section
- The table below shows the number of Zebu cattle in different countries in Kenya in
- Draw a divided rectangle 15 cm long to represent the data above.(7 mks)
Calculations
Isiolo 42500 x 15 = 6.3cm
100800
WajIr 22600 x 15 = 3.4 cm
100800
Marsabit 20300 x 15 = 3.0 cm
100800
Mandera 15400 x 15 = 2.3cm
100800
Divided rectangle showing the number of Zebu cattles in four different counties in Kenya.
KEY Isiolo
Isiolo Wajir
Wajir Marsabit
Marsabit Mandera
Mandera
Calculations 2 mks
Title -1 mk
Rectangle 2 mk
Measurement 1 mks - Calculate the range of the above data. (2 mks)
42500 – 15 400 = 27, 100 - Give three advantages of using divided rectangle to represent data. (3 mks)
- Easy to draw and construct
- Easy to compare components
- Gives clear visual impression
- Takes less space to represent data
- Easy to read./interpret
-
- Give three reasons why nomadic pastoralists keep large herds of animals.(3 mks)
- It’s a form of insurance against natural calamities, diseases and drought that kill many animals.
- t’s a sign of wealth/prestige/social status
- Animals kept are used to pay dowry.
- Animals are used as a source of food, milk meat or blood.
- Source of income from sold animals.
- Name two nomadic communities involved in beef cattle rearing in Kenya. (2 mks)
- Maasai
- Turkana
- Samburu
- Explain four ways in which the government of Kenya assist nomadic pastoralists to improve the quality of their livestock. (8 mks)
- Setting up demonstraytion ranches to educate pastoralsit or beef farming on better ways of keeping livestock/new trends of livestock management.
- Cattle dips are constructed to control ticks and treat pests.
- Provision of extension or vetenary services to adbvice farmers /treat animals hence improving quality of beef animals.
- Construction of roads for easier ytransportation of animals to markets and for easier access of services to farmers.
- Conducts research/encourages cross breeding of traditional cattle breeds with exotic ones. To improve their quality /resistence to drought and diseases.
- Encourage group ranching/formation of cooperations for easier provision of services marketing and for pastoralists to view livestock keeping as a commercial activity.
- Encourages the replacement of coarse grass with nutritious pastures to feed and improve quality of animals.
- The government has revived Kenya meat commission (KMC) that buys animals from the farmers for slaughter and is in process of constructing new abattoirs in livestock rearing areas eg West Pokot and North-Eastern Kenya.
- Give three reasons why nomadic pastoralists keep large herds of animals.(3 mks)
- Draw a divided rectangle 15 cm long to represent the data above.(7 mks)
-
-
- Name two major categories of minerals. (2 mks)
- Non-metallic minerals
- Energy minerals
- Identify four factors that influence the occurrence of minerals. (4 mks)
- Evaporation
- Vulcanicity
- Metamorphism
- Weathering
- Erosion and deposition
- Name two major categories of minerals. (2 mks)
-
- Apart from shaft mining name three other methods of mining. (3 mks)
- Adit/slope mining/horizontal/funnel
- Drilling
- Alluvial
- Open cast mining
- Describe how shaft mining method is carried out. (6 mks)
- A vertical tunnel is dug or a shaft is sunk underground.
- Horizontal tunnels are dug to reach the mineral deposit or one.
- Metal or concrete props are constructed to support the roofs of the funnels.
- Light railways trucks are constructed in the horizontal funnels to join the vertical tunnel.
- The mineral ore is blasted or drilled and dug outside using powerful machines.
- The broken particle are transported on the light tracks or on conveyor belts to the bottom of the shaft.
- Cranes with cages are used to lift the mineral one to the surface of smelting.
- cages also transport workers with their equipment to and from the underground mines.
- Apart from shaft mining name three other methods of mining. (3 mks)
-
- Name two areas in South Africa where diamond is mined. (2 mks)
- Kimberley
- Jaggersfonteir
- Firnsch
- Cullinan
- Pretoria
- Koffiefontein
- Bloemfontein
- Explain four ways in which diamond mining contributed to the economy of South Africa. (8 mks)
- Highly priced diamonds are exported to earn foreign exchange used to improve other sectors of the economy.
- Diamond is a raw material for making jewellery promoting industrial expansion.
- Diamond mining has created employment opportunities which has raised the living standards of the people.
- Mining activities have led to development of towns in raid and orange free state which creates a large market for agricultural products.
- Diamond mining has lead to expansion of transport and communication networks for cheaper and faster movement of people /goods /services.
- Money generated from mining of diamonds has led to development and provision of many social amenities with goods services.
- Mining activities have led to the development of technical industrial and mining skills that are useful in order sectors of the economy.
- Name two areas in South Africa where diamond is mined. (2 mks)
-
-
-
- Define re-afforestation. (2 mks)
- This is the planting of trees in areas where trees have been v=cut down/forest have been cleared/deforestation has taken place.
- State four reasons why afforestation is encouraged in Kenya. (4 mks)
- To ensure continuous supply of wood fuel /timber/ herbal medicine/raw materials for pare making.
- To protect water catchment area/create micro climate to maintain hydrological cycle.
- To create scenic beauty aesthetic value.
- To expand the habitat for wildlife/conservation of wildlife.
- To create employment opportunists
- To reduce importation of forests products.
- Define re-afforestation. (2 mks)
-
- Name three provinces in Canada where forestry is practiced on a large scale. (3 mks)
- British Columbia
- Quebec
- New Brunswick
- Ontanio
- Edward island
- Newfold land.
- State four factors favouring exploitation of forest in Canada. (4 mks)
- Mild winters which facilitate transportation of logs throughout the year.
- Availability of water from rivers for pulp and paper industries.
- Availability of cheap and efficient transport system of ferrying logs to factories.
- Availability of ready market in Canada and USA for the forest products.
- Availability of a lot of HEP harnessed from many rivers with waterfalls to provide power for paper industries.
- Valley bottoms along the Coast provide good sites for the paper mills and there is clay which is used is smoothening the paper.
- Name three provinces in Canada where forestry is practiced on a large scale. (3 mks)
-
- Explain three factors that favour the growth of natural forest on the slopes of Mount Kenya.
(6 mks)- Coal climates in the Kenya highlands favour the growth of trees.
- High rainfall 1000-2000mm favour growth of trees.
- Rugged landscape in some area which discourage settlements and agriculture leaving growing of trees as the only alternative.
- Varied altitude which favours the growth of different types of trees due to varied temperatures and rainfall.
- Creation of forest reserves which enables the forest to develop without interference from humans.
- Fertile volcanic soils within the Kenyan highlands favour growth of trees.
- Explain three problems which hinder the Kenyan government efforts to manage and conserve forest in Kenya. (6 mks)
- Prolonged drought leads to drying up of some trees.
- Some wild animals damage trees through uprooting
- Rapid increase in population has led to encroachment into forest land hence destruction of trees/high demand for fuel.
- Occurrence of forest trees which have led to destruction of large areas under forest.
- Illegal logging/indiscriminate cutting of trees thereby reducing depleting indigenous species.
- Attacks by aphids/locusts lead to destruction of trees.
- Explain three factors that favour the growth of natural forest on the slopes of Mount Kenya.
-
-
-
- Differentiate between land reclamation and land rehabilitation. (2 mks)
- Land reclamation is the process of converting less productive or waste land into a more productive state for agricultural and settlement purposes while land rehabilitation is the process of restoring degraded or damaged land back into a useful state.
- Give four problems facing Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme. (4 mks)
- Low prices of rice
- Fluctuating water levels in the irrigation canals.
- Water borne dieases
- Land tenure conflicts
- Pests and weeds
- Differentiate between land reclamation and land rehabilitation. (2 mks)
-
- Explain three ways in which land is being rehabilitated in Kenya. (6 mks)
- Re-afforetstaion/planting/grass strips on degraded land thus protecting it against soil erosion.
- By constructing gabions so as to hold/trap thesoil carried by running water.
- Construction of terracces thus reducing the speed of surface run-off/to control soil erosion.
- Filling open pits so that it can be used for farming/ settlement.
- Constructing dykes along river banks/dams so as to control floods during the high rainfall season.
- Applying manure on degraded land so as to restore its fertility.
- land/bush fallowing to allow land to regain fertility.
- Mulching of land/planting cover crops so as to retain soil moisture and to add manure.
- Controlling grazing to allow regeneration of pasture/control soil erosion.
- Name two projects in Netherlands which were aimed at reclaiming land from the sea. (2 mks)
- The Zuiderzee project.
- The delta plan project
- Explain three ways in which land is being rehabilitated in Kenya. (6 mks)
- Describe the steps followed in reclaiming land for agricultural use in Netherlands. (6 mks)
- Protective dykes/walls are constructed to enclose the part of the sea to be reclaimed.
- Ring canals are constructed to lead water into the pumping stations and todrain pumped water to the sea.
- Pumping stations are installed to pump out the sea water from the enclosed area.
- Water is pumped out of the enclosed area to the sea using wild mills/electric pumps.
- Reeds are planted to help dry out the soil in the reclaimed area.
- Drainage ditches/canals are made on the land being reclaimed to drain away excess water.
- Drainage pipes are laid below the soil to drain excess water from reclaimed land.
- The soil is then treated with chemicals to reduce salinity.
- Fresh water is pumped/flushed into the enclosed land to remove excess salts from the soil and reduce salinity.
- Deep ploughing is done to mix up the leached nutrient in the soil
- Oats ./rye/sugar beets are planted to improve the soil pH and reduce water in the soil
- State five benefits which Kenya derives from irrigation farming. (5 mks)
- Provides farmers with steady income through sale of crops thus improving their living standards.
- Irrigation activities have created employment opportunities raising the living standards of many people.
- Wastelands/unproductive marginal lands are reclaimed increasing land under agriculture and settlements which helps to curb desertification.
- has facilitated the development of infrastructure and social amenities for better services and improved living standards.
- It he led to increased food production making the country self sufficient in food supply this saving foreign exchange that would have been used to import food.
- Some crops grown under irrigation are exported which earns foreign exchange for the country.
- Some crops grown under irrigation provide raw materials for agro-based industries thus promoting industrialization.
- Irrigation schemes have promoted the development of urban centres which has opened up remote areas.
-
- The diagram below shows a fishing in the pacific ocean.
-
- Identify the fishing ground shown above. (1 mk)
- North west pacific fishing ground
- Name three types of fish species found in the fishing ground above. (3 mks)
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Tuna bonito
- Sardine
- Cod
- Allaska pollack
- Identify the fishing ground shown above. (1 mk)
- '
- Differentiate between fishing and fisheries. (2 mks)
- Fishing is the extraction /exploitation of aquatic animals/fish while fisheries is a water body where aquatic animals /fish are found or reared and exploited for food and commercial purposes.
- Name two inland types of fisheries in Kenya. (2 mks)
- Lakes
- Rivers/streams
- Swamps
- ponds
- Differentiate between fishing and fisheries. (2 mks)
-
- Describe the long lining fishing method. (5 mks)
- Long lining fishing method.
- Long lines with many balted hooks are used to catch fish on rough sea bed
- The lines have floats on each and to suspend them on water.
- The lines are attached to a large boat (dory)
- The line is pulled by the boat along the water near the sea bed.
- Fish are caught by the hooks along the line as they eat the bait.
- The lines are then pulled into the boat and the fish is unhooked by fishermen.
- The fish are put in refrigerated containers and the ;line put back into the water.
- Explain four physical factors that influenced development of fishing in Japan.(8 mks)
- Cool waters ideal for fish breeding and abundant supply of planktons as fish food thus throwing of numerous fish species.
- Coast with many offshore islands which provide sheltered water inlets for establishment of fishing ports and villages.
- Indented coastline which provide secure breeding grounds for fish.
- The meeting of warm Kurosiwo and cold Oya siwo current results in upwelling of sea water bringing minerals to the surface for growth of planktons as fish food.
- The mountains /rugged nature of the country restrict agriculture hence fishing is an alternative economic activity.
- The shallow continental shelf allow sunlight to penetrate to the sea bed for growth of planktons which is fish food.
- Describe the long lining fishing method. (5 mks)
- State four problems facing marine fishing in Kenya. (4 mks
- The narrow continental shelf with deep waters is unsuitable for growth of planktons and fish breeding limiting fish species.
- Sea water is too warm for fish breeding
- Poor transport connections between fisheries and market discouraged fishermen.
- Early straight/regular coastline are unsuitable for fish breeding.
- Inadequate skills and technology lead to use of poor equipment and poor storagen discovering deep sea fishing.
- Inadequate capital to buy modern fishing vessels and preservation facilities limit fishing.
- Low demand or salt water fish discourage marine fishing.
- Competition in deep sea fishing and poaching in territorial waters by advanced countriies discourage local fishermen.
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Chogoria Murugi Zone Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
