INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- You are supposed to spend the first 15 minutes to read the whole paper carefully before commencing your
work.
- You are provided with solution labelled L, a piece of visking tubing, some string, four,test tubes, a beaker a white tile and these reagents iodine solution and Benedict’s solution.
- Using the appropriate reagents, carry out food tests to identify the food substances contained in L. Outline procedure used and record your observation and conclusions in the table below. (6 marks)
Securely tie one end of the visking tubing with the string and place solution L into it until it is about ¾ full. Ensure that it is not leaking and tie up the other end securely.Food substance Procedure Observations Conclusion
Wash away all traces of solution L from the outside of the visking tubing. Place the visking tubing in the beaker and submerge in distilled water. Note the time and allow the set up to stand for at least 30 minutes. After 30 minutes take some of the water from the beaker and carry out similar food tests on it. - Record your observation and conclusions in table below. (4mks)
Food substance Procedure Observations Conclusion - Account for the results obtained (a) and (b) (3 marks)
- What physiological process is demonstrated by this experiment? (1 mark)
-
- Name one part of the body where a similar process takes place. (1 mark)
- What is the process you have named in e(i) above called? (1 mark)
- Using the appropriate reagents, carry out food tests to identify the food substances contained in L. Outline procedure used and record your observation and conclusions in the table below. (6 marks)
- You are provided with photographs of specimens labeled K and L. examine them and answer the questions that follow.
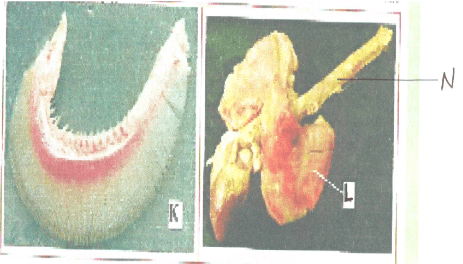
- Identify each specimen and name the class of the organism from which they were obtained. (2mks)
Specimen Identity Class K L - Label all the parts of specimen K, on the photograph. (3mks)
- State the functions of each of the parts you have labeled in (b) above. (3mks)
- State two ways in which the part labeled L is adapted to its functions. (2mks)
- State the functional relationship between
- Specimen K and L (1mk)
- State two adaptations of the part labeled N to its function. (2mks)
- Identify each specimen and name the class of the organism from which they were obtained. (2mks)
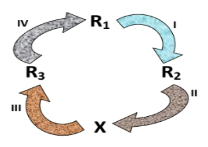
- You are provided with specimens labeled R1, R2 and R3 representing different stages of plant development. Study the specimens carefully and answer questions related to them.
- The chart below shows relationship between the specimens
- Identify process 1 (1mark)
- state one internal and one external condition necessary for the process identified in (1) above (2 marks)
- Name the: (2 marks)
- Stage of development R2
- Process immediately before R3 in process (III)
- Dissect specimen R3 logitudinally and open it out
- Make a drawing section and labeled it (4 marks)
- Explain two adaptations of the specimen to its function (2marks)
- The chart below shows relationship between the specimens
CONFIDENTIAL
- Solution L – Mixture of starch and glucose.
NB: Glucose to be concentrated. - Visking tubing one per student.
- Strings.
- Four Test tubes
- Beaker
- Iodine solution.
- Benedict’s solution.
- Source of heat.
- Distilled water.
- Bean seeds one per student labelled as R1
- whole atleast one week old bean seedling(one per student) labelled R2
- a bean pod (one per student) labelled R3
- Stop watch
- scalpel
- white tile
MARKING SCHEME
- You are provided with solution labelled L, a piece of visking tubing, some string, four,test tubes, a beaker a white tile and these reagents iodine solution and Benedict’s solution.
- Using the appropriate reagents, carry out food tests to identify the food substances contained in L. Outline procedure used and record your observation and conclusions in the table below. (6 marks)
Securely tie one end of the visking tubing with the string and place solution L into it until it is about ¾ full. Ensure that it is not leaking and tie up the other end securely.Food substance Procedure Observations Conclusion Starch Put 2cm3 of solution L in a test-tube
Add two drop of iodine solutionColour changes from brown/ yellow to blue-black Starch present Reducing sugars Put 2cm3 of solution l in a test-tube
Add equal amount of Benedict's solution
Heat to boilColour changes from blue to green to yellow to orange/brown Reducing sugar present
Wash away all traces of solution L from the outside of the visking tubing. Place the visking tubing in the beaker and submerge in distilled water. Note the time and allow the set up to stand for at least 30 minutes. After 30 minutes take some of the water from the beaker and carry out similar food tests on it. - Record your observation and conclusions in table below. (4mks)
Food substance Procedure Observations Conclusion Starch Put 2cm3 of water from the beaker in a test-tube
Add two drops of iodine solutionYellow/Brown colour Starch absent Reducing sugars Put 2cm3 of water from the beaker in a test-tube
Add equal amount of Benedict's solution
Heat to boilColour changes from blue to green to yellow to orange/brown Reducing sugars present - Account for the results obtained (a) and (b) (3 marks)
- Visking tubing is semi-permeable; selectively permeable allowing small molecules of reducing sugar to pass through but not large molecules of starch.
- What physiological process is demonstrated by this experiment? (1 mark)
- Diffusion
-
- Name one part of the body where a similar process takes place. (1 mark)
- Lungs/Alvelous
- Ileum/Villus
- proximal convoluted tubule
- What is the process you have named in e(i) above called? (1 mark)
- Gaseous exchange, Absorption, Selective Reabsorption
- Name one part of the body where a similar process takes place. (1 mark)
- Using the appropriate reagents, carry out food tests to identify the food substances contained in L. Outline procedure used and record your observation and conclusions in the table below. (6 marks)
- You are provided with photographs of specimens labeled K and L. examine them and answer the questions that follow.

- Identify each specimen and name the class of the organism from which they were obtained. (2mks)
Specimen Identity Class K Gill Pisces L Lung mammalia, amphibia, reptilia. aves - Label all the parts of specimen K, on the photograph. (3mks)
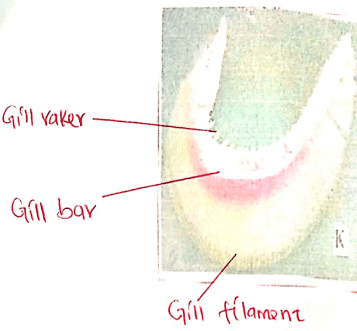
- State the functions of each of the parts you have labeled in (b) above. (3mks)
- Gil bar- supports gill filaments & gill rakers/attachment of gill filaments & gill rakers
- Gill raker - prevent entry of solid particles into the gill filament.
- Gill filament - Site for exchange of respiratory gases.
- State two ways in which the part labeled L is adapted to its functions. (2mks)
- Elastic to accomodate varied volume of air.
- Numerous alveoli to increase S.A for gaseous exchange.
- State the functional relationship between
- Specimen K and L (1mk)
- Both are used for gaseous exchange
- State two adaptations of the part labeled N to its function. (2mks)
- Has cilia to waft mucus containing dust particles away from lungs
- Rings of cartilage to keep trachea open/ to prevent it from collapsing
- Specimen K and L (1mk)
- Identify each specimen and name the class of the organism from which they were obtained. (2mks)
- You are provided with specimens labeled R1, R2 and R3 representing different stages of plant development. Study the specimens carefully and answer questions related to them.
- The chart below shows relationship between the specimens
- Identify process 1 (1mark)
- Germination
- state one internal and one external condition necessary for the process identified in (1) above (2 marks)
- Internally: Embryo maturity, sufficient hormone & enzymes/viability
- Externally: optimum temperature/ water/ oxygen
- Name the: (2 marks)
- Stage of development R2
- seedlings
- Process immediately before R3 in process (III)
- Double fertilisation
- Stage of development R2
- Identify process 1 (1mark)
- Dissect specimen R3 logitudinally and open it out
- Make a drawing section and labeled it (4 marks)
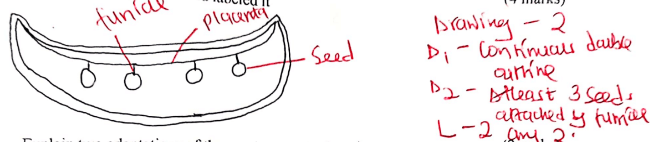
- Explain two adaptations of the specimen to its function (2marks)
- Seeds: dispersed for propagation of the plants
- Pericarp: protection of immature seeds
- Lines of weakness/ sutures opens up when R3 matures and dries up.
- Make a drawing section and labeled it (4 marks)
- The chart below shows relationship between the specimens
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Paper 3 Questions and Answers - Sukellemo Joint Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students