INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- You are required to spend 15 minutes of the 2¼hrs reading through the paper and make sure you have all the apparatus and chemicals needed for the practical.
- Answer all the questions
- Electronic calculators and mathematical tables may be used
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- For Examiners Use Only
1. You are provided with the following
- An acid labeled solution H
- 2.0M sodium hydroxide solution labelled solution J
- Solution K containing 25 g per litre of an alkanoic acid
You are required to - Prepare a dilute solution of sodium hydroxide solution J
- Determine the:
- Molar mass of alkanoic acid, solution K.
- Reaction ratio between sodium hydroxide and acid H
Procedure 1:
Using a pipette and pipette filler, place 25 cm3 of solution J into a 250 ml volumetric flask. Add about 150 cm3 of distilled water and shake well. Add more distilled water to make up to the mark. Label this as solution L. Retain the remaining solution J for use in procedure 2.
Fill the burette with solution K. Using clean pipette and pipette filler, place 25 cm3 of solution L in to a 250 ml conical flask. Add 2 drops of phenolphthalein indicator and titrate with solution K. Record your results in the table I. Repeat the titration two more times and complete the table.
Table I (4 marks)
| I | II | III | |
| Final Burette Reading (cm3) | |||
| Initial Burette Reading (cm3) | |||
| Volume Of Solution K (cm3) |
- Calculate:
- The average volume of solution K used. (1 mark)
- Concentration of solution L in moles per litre. (1mark)
- Concentration of the alkanoic acid solution K in moles per litre. (1 mole of the acid reacts with 3 moles of the base.) (1mark)
- Molar mass of the alkanoic acid (1mark)
PROCEDURE 2
Fill a clean burette with solution H. Place 5 cm3 of solution H in 100 ml plastic beaker. Measure the initial temperature of solution H in the beaker and record it in the table II. Using a 50 ml measuring cylinder, measure 25 ml of solution J. add it to solution H in the beaker and immediately stir the mixture with the thermometer. Record the maximum temperature reached in table II. Repeat the experiment with other sets of volumes of solutions H and J and complete the table 2 below
Table 2. (6 marks)
| Volume of solution H(cm3) | 5 | 9 | 13 | 17 | 21 | 25 |
| Volume of solution J (cm3) | 25 | 21 | 17 | 13 | 9 | 5 |
| Maximum temperature (°C) | ||||||
| Initial temperature (°C) | ||||||
| Change in temperature (°C) |
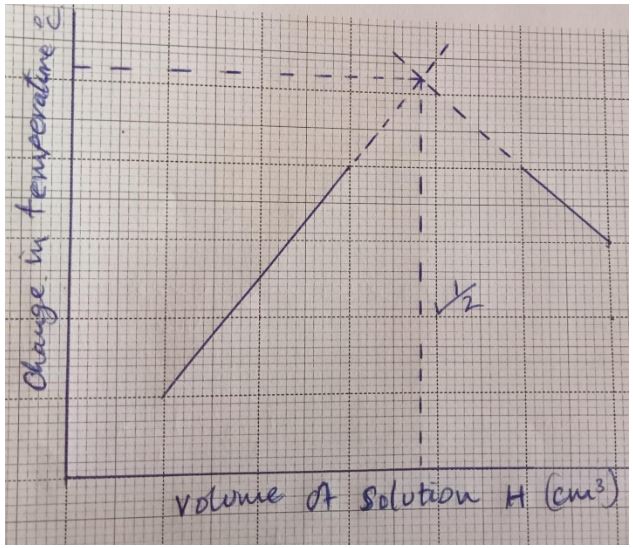
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of change in temperature against the volume of solution H. (3 marks
- From the graph, determine the volume of solution H that was needed for complete neutralization. (1 mark)
- Calculate the volume of solution J that fully reacted with the solution H stated in (b) above. (1 mark)
- Calculate the:
- Ratio between the volumes of solutions H and J that neutralized one another. (1 mark)
- Concentration in moles per litre of the acid in solution H. (Assume that the volume ratio is the same as mole ratio). (1 mark)
- Calculate the molar heat of neutralization of sodium hydroxide solution in kJmol-1 given that the specific heat capacity for water is 4.2J/g/K and the density for water is 1g/cm3. (2marks)
2. You are provided with solid P. Carry out the following tests and write your observation and inferences in the spaces provided.
- Place all of the solid P in a boiling tube. Add about 10 cm³ of distilled water and shake well. Divide the mixture into five portions.
Observation Inferences 1mark 1 mark - To the first portion of solution in a test tube, add 2 - 3 drops of aqueous potassium iodide solution.
Observation Inferences 1mark 1 mark - To the second portion of the solution in a test tube, add 2M sodium hydroxide solution drop wise until in excess.
Observation Inferences 1mark 1 mark - To the third portion of the solution in a test tube, add 2M ammonia solution drop wise until in excess.
Observation Inferences 1mark ½mark - To the fourth portion of the solution in a test tube, add 2 - 3 drops of barium nitrate solution.
Observation Inferences ½mark 1 mark - To fifth portion of the solution in a test tube, add 2 - 3 drops of lead (II) nitrate solution.
Observation Inferences ½mark ½ mark
3. You are provided with substance U. You are required to
- Carry out tests on the substance U
- Record all observations and inferences accordingly.
- Scoop half a spatula end full of substance U and ignite it using a non-luminous flame.
Observation Inferences ½mark ½mark - Place the remaining substance U in a boiling tube, add about 8 cm3 distilled water and shake the mixture well. Divide the mixture into three portions.
Observation Inferences 1mark ½mark - To the first portion in a test-tube, Add ½ spatula end full of solid sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Observation Inferences ½mark ½ mark - To the second portion of U in a test tube, add acidified potassium manganate (VII).
Observation Inferences 1mark ½mark - To the third portion of U in a test tube, add acidified potassium dichromate (VI) and warm the mixture.
- Scoop half a spatula end full of substance U and ignite it using a non-luminous flame.
CONFIDENTIAL
INSTRUCTION TO SCHOOLS
The information contained in this paper is to enable the head of the school and the teacher in charge of chemistry to make adequate preparations for this year’s chemistry practical Joint examination. NO ONE ELSE should have access to this paper or acquire knowledge of its contents. Great care must be taken to ensure that the information herein does not reach the candidates either directly or indirectly. Chemistry teachers SHOULD NOT perform any of the experiments in the same room as the candidates or make the results of the experiments available to the candidates or give any other information related to the experiments.
In addition to the equipment, apparatus and chemicals in an ordinary Laboratory, each candidate require:
- About 150cm3 of solution H.
- About 150cm3 solution J
- About 80cm3 solution K
- Burette
- Pipette 25 ml
- 1 pipette filler
- 2 Conical flask
- Means of labelling
- 250ml volumetric flask
- White tile
- 250ml plastic beaker
- tissue paper
- Thermometer (-10-110oc)
- 50ml measuring cylinder
- 500 ml Distilled water in a wash bottle
- 2 boiling tubes
- Filter funnel
- Test tube holder
- 5 clean dry test tubes
- 100 ml plastic beaker
- Metallic spatula
- About 0.5g solid U in a stoppered container.
- About 0.5g Solid P in a stoppered container.
- 1 label
- About 0.5g of sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Access solutions
- 2M sodium hydroxide supplied with a dropper.
- 2M ammonia solution supplied with a dropper.
- 0.1M Lead (II) nitrate supplied with a dropper.
- 0.1M barium nitrate solution.
- 0.2M Potassium iodide.
- Acidified potassium manganate (VII)
- Acidified potassium dichromate (VI)
- Phenolphthalein indicator supplied with a dropper.
- Source of heat.
NOTES
- 2M sodium hydroxide is prepared by dissolving 80g of sodium hydroxide pellets in about 200 cm3 of distilled water and topping up to 1 litre of solution
- 2M ammonia solution is prepared by diluting 112 ml of concentrated ammonia solution in about 200 cm3 of distilled water and top up to 1 litre.
- 0.1 M lead (II) nitrate is prepared by dissolving 33.0 g of solid lead (II) nitrate in about 400 ml of distilled water and top up to 1 litre of solution.
- 0.1 M barium nitrate is prepared by dissolving 26 g of solid lead (II) nitrate in about 400 cm3 of distilled water and top up to 1 litre of solution.
- 0.2M Potassium iodide is prepared by dissolving 33g in about 400cm3 of water and dilute to one litre of solution.
- Solid U is maleic acid.
- Solid P is Zinc chloride.
- Solution H is prepared by dissolving 55 ml of concentrated Sulphuric (VI) acid in about 600cm3 of distilled water and dilute to 1 litre of solution.
- Solution J is prepared by dissolving 80g of sodium hydroxide in 400cm3 of distilled water and top up to one litre of solution using distilled water.
- Solution K is prepared by dissolving 25g of citric acid C3H5O(COOH)3 RFM = 192 in about 400cm3 and dilute to 1 litre of solution. (0.13M Citric acid)
- Acidified potassium manganate (VII) is prepared by dissolving 3.12g of potassium manganate (VII) in 200cm3 of 2M sulphuric (VI) acid and making it to one litre.
- Acidified potassium dichromate (VI) is prepared by dissolving 25g of potassium dichromate (VI) in 400cm3 of 2M sulphuric (VI) acid and making it to one litre.
MARKING SCHEME
Q 1: Table 1 (5mks)
The marks are distributed as follows
- Complete table (1mk)
- Complete table with 3 titration done. (1mk)
- Incomplete table with 2 titration done. (½mk)
- Incomplete table with 1 titration done. (0mk)
Penalties- Wrong arithmetic (subtraction of the initial from final burette readings)
- Inverted table
- Burette reading beyond 50cm3 unless explained e.g. 50.0cm3 + 12.0cm3 = 62.0cm3
- Unrealistic titre values i.e. hundred or below 1.0
Note
Penalize ½ mk for each to a maximum of ½ mk. i.e. penalize ½mk once
- Use of decimals (1mk)
- Accept only 1 or 2 decimal places used consistently otherwise penalize FULLY. i.e award 0 mk
- If 2 decimal places are used, the second decimal place must be either a “0” or “5” otherwise penalize FULLY.
- Accept inconsistency in the use of zeros as initial burette readings e.g 0, 0.0, 0.00
- Accuracy (1mk)
Compare the candidate’s titre values with school value (SV) and tick (✔) the chosen value if it earns a mark.
CONDITIONS- If at least one value is within + 0.10cm3 of the S.V award 1mark.
- If no value is within + 0.10cm3 of the school value, but at least one value is within + 0.20cm3 of the S.V award ½ mark
- If no value is within + 0.20cm3 of the S.V award 0 mark
Note:
If there is arithmetic error in the table, compare the S.V with worked out correct value and award accordingly.
- Principles of averaging (1mk)
Values averaged MUST be shown and MUST be within + 0.20 of each other.
CONDITIONS:- If 3 titration are done and consistent and averaged (1mk)
- If 3 titrations are done and only two are consistent and averaged. (1mk)
- If only two titrations are done and consistent are averaged. (1mk)
- If 3 titrations are possible but only 2 are averaged (0mk)
- If only 2 titration done are inconsistent and are averaged. (0mk)
- If only 1 titration done. (0mk)
PENALTIES- Penalize ½mk for wrong arithmetic in average titre if error is outside ±2 units in the 2nd decimal place.
- Penalize ½mk if no working is shown but answer given is correct
- Penalize FULLY if no working and answer given is wrong
- Accept rounding off answer (average titre) to 2 decimal places e.g 12.6666 to 12.66 or 12.67, 21.3333 to 21.33. Otherwise penalize mk for rounding off to 1dp or a whole number.
Note:- Accept answer (average titre) to 1dp or a whole if it works out exactly and credit FULLY.
- Question 1 a (i) MUST be marked before the marking for averaging is awarded in table (1)
- FINAL ANSWER (1mk)
(Tied to correct average titre)
Compare the candidates CORRECT AVERAGE TITRE in S.V. and- If within + 0.010 of the S.V (1mk)
- If NOT within + 0.10 of the S.V but within + 0.20 then award ½mk
- If beyond ± 0.20 of the S.V. (0mk)
Note:- Where there are 2 possible pairs of titres(can be averaged, use the pair that is closed to the S.V. and credit accordingly e.g if S.V = 24.0 and the titres are 23.8, 23.6 and the candidate averages 23.8 +23.6
2
Pick 23.8 + 23.9 = 23.85 so as to credit ½mk of the candidates titre which would score 0 mk .
2
Also if a candidates titre were 23.9, 24.3, 24.1 and the same S.V = 24.0 and the candidate average
24.3 + 24.1 = 24.2
2
Pick 24.1 + 23.9 = 24.0cm3 to credit 1mk
2
Instead of ½ mk, if the candidates averaging titre is used.
If wrong values are averaged pick the correct values (if any) following the principles of averaging, average then award according.-
- V1 +V2 + V3 = CORRECT ANSWER
3 - (2 X 25)✔½
250
= 0,2M. ✔½ - Mole ratio 1:3
0.2 X 25 X 1✔½
Ave vol X 3
= ✔½ - (25 x1) ✔½ = correct Ans. ✔½
Ans. In iii
- V1 +V2 + V3 = CORRECT ANSWER
-
- Where there are 2 possible pairs of titres(can be averaged, use the pair that is closed to the S.V. and credit accordingly e.g if S.V = 24.0 and the titres are 23.8, 23.6 and the candidate averages 23.8 +23.6
PROCEDURE 2
-
- Award s a follows:
- Complete table (1mk)
- Decimal (accept whole numbers or 1 d.c.p. where decimal place is 5 or 0) for (1mk)
- Accuracy (1mk) - within + 2 of school value) for 1 mk otherwise award (0mrk)
- Trends (1mk) - (change in temperature must be positive with continuous rise followed by a constant then continuous drop)
- Calculation of temperature change (2mks)
- correct showing on the graph✔½ correct reading from the graph ✔½ (1mk)
- 30 – answer in (b) above (1mk)
-
- Ratio of volumes = Large volume/small volume = ans
- Use mole ratio in d (i) and moles of J to get the molality of H.
- ∆H = mc∆T = correct ans
Use correct ans to get heat change for 1 mole.
Final ans in kJmol-.
- Award s a follows:
-
observation inferences ✔½ ✔½
Solid dissolve to form a colourless solutionSoluble salt ½ mk Fe2+ Fe 3+ Cu2+ absent ½ mk
observation inferences No yellow ppt ✔1
Reject: - No ppt
- No observable changePb2+ absent ✔½
observation inferences White ppt ½
Soluble in excess ½Al3+✔½, Zn2+✔½, 1mk
All 2 mentioned . . . . .1 mark
Penalise ½ mark for any other contradicting ion to a maximum of 1 mark-
observation inferences White ppt ½
Soluble in excess ½Zn2+ ✔½
-Penalise fully if not correctly infered in 2(b) above.
-Penalise fully for any contradictory ion. -
Observation inferences No white ppt ✔1
Reject : - No ppt
- Observable changeSO2-4, SO2-3, CO2-3 absent 1
3 mentioned - 1 mark
2 mentioned - ½ mark
1 mentioned - 0 mark -
Observation inferences White ppt ✔½ Cl- present ✔½
Reject Cl- if mentioned as absent in (d) above.
-
Observation inferences U Burns with a blue flame✔ ½
absent ✔ ½
or long chain organic compund ✔ ½
Penalize fully for long chain hydrocarbon-
Observation inferences ✔½ ✔½
Solid dissolves to form a colourless solutionPolar compound✔ ½ -
Observation inferences Bubbles/effervescence ½ mark R-COOH present ½ mark
Observation inferences Purple potassium manganate (VII) changes to colourless. (1 mark)
R-OH present ½ mark
Observation inferences Orange acidified potassium dichromate (VI) does not change to green (1 mark) R-OH Absent
(1 mark)
Download Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and Answers with Confidential - Lainaku 1 Joint PreMock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students