GEOGRAPHY
FORM 1
MID TERM 2
INSTRUCTIONS:
- Answer all the questions
QUESTIONS
-
-
- What is Geography? (2 mks)
- Give the two Greek words from which the term Geography is derived. (2 mks)
-
- Define the term environment. (2 mks)
- Identify two type of environment. (2 mks)
-
-
- State any three areas of study in practical geography. (3 mks)
- Explain any four importance of studying geography. (8 mks)
-
- For each of the following statements, identify the subject which is applied.
- Identifying the types of rocks in the earth’s crust. (1 mk)
- Studying atmospheric conditions of an area. (1 mk)
- Study of solar energy. (1 mk)
- Calculation of areas, distance and densities in geography. (1 mk)
-
- What is orbit? (1 mk)
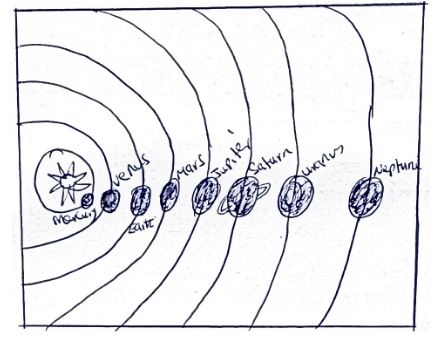
- With the aid of a diagram show the order of the planets based on their distance from the sun. (8 mks)
- For each of the following statements, identify the subject which is applied.
-
-
- Give the specific shape of the earth. (1 mk)
- Name three forces responsible for the shape of the earth. (3 mks)
- State four reasons why the earth is believed to be spherical in shape. (4mks)
-
-
- One of the theories used to explain the origin of the solar system is the passing star theory. Give three weaknesses of this theory. (3 mks)
- List down three effects of the earth’s revolution. (3 mks)
-
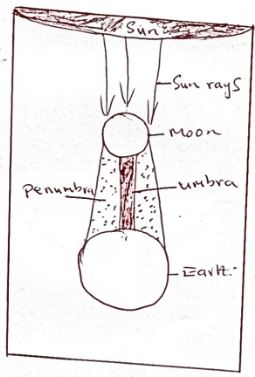
- With the aid of a well labeled diagram, describe the occurrence of a solar eclipse. (6 mks)
- Give two differences between solar eclipse and lunar eclipse. (4 mks)
-
- Give the specific dates of the year when overhead position of the midday sun is on the following latitudes.
- Tropic of cancer (1 mk)
- Tropic of Capricorn (1 mk)
- Equator (1 mk)
- If the local time in Sydney (600W) is 7.30 a.m. What time is it at Wajir (400E)? (4 mks)
- Give the specific dates of the year when overhead position of the midday sun is on the following latitudes.
-
- Name three minerals that makes up the earth’s crust. (3 mks)
- State three characteristics of the mantle. (3 mks)
-
- List down any four elements of weather. (4 mks)
- State four factors that determine the amount of solar radiation reaching the earth’s surface. (4 mks)
-
- Give the purpose for each of the following items in a weather station.
- Stevenson screen (1 mk)
- Hygrometer (1 mk)
- Barometer (1mk)
- Name four main zones/layers of the atmosphere. (4 mks)
- Give the purpose for each of the following items in a weather station.
-
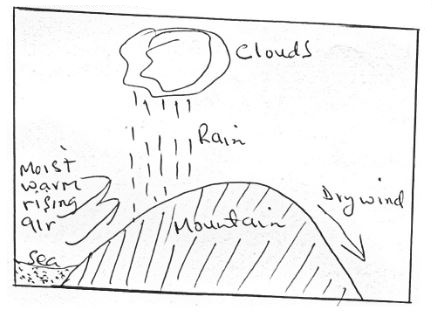
- With the aid of a well labeled diagram describe the formation of relief rainfall. (7 mks)
-
- Name three high clouds. (3 mks)
- Highlight four significance of weather forecasting. (4 mks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- What is Geography?
- Study of the earth as a home of humankind/man. (2 mks)
- Two Greek words from which the term Geography is derived.
- Geo
- Graphein(2 x 1 = 2 mks)
- What is Geography?
-
- Define the term environment.
- Refers to all external conditions surrounding an organism/plant or an animal. (2 mks)
- Types of environment.
- Physical environment
- Human/social environment
(2 x 1 = 2 mks)
- Define the term environment.
-
-
- Areas of study in practical geography.
- Fieldwork
- Mapwork
- Photograph work
- Statistical methods
(Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks)
- Importance of studying geography.
- The learner is able to learn and explain the origin of the earth, the solar system and the internal structure of the earth.
- Geography helps the learner to develop the skills of observing, reading, analyzing and interpreting maps, photographs, charts, diagrams and statistical data.
- Geography enables the learner to understand and appreciate different environmental influences at work on different societies.
- Study of geography encourages international awareness, interaction and co-operation.
- Geography teaches the learner how to manage time properly by drawing time schedule and adhering to it.
- Geography is a career subject.
- Geography creates awareness in the people on significance of management and conservation of the environment.
- Geography enables the learner to acquire basic skills and knowledge which contributes to local, regional and national development.
(Any 4 x 2 = 8 mks)
- Areas of study in practical geography.
-
-
- Identify the types of rocks in the earth’s crust.
- Geology (1 mk)
- Studying atmospheric conditions of an area
- Meteorology(1 mk)
- Study of solar energy.
- Physics(1 mk)
- Calculation of areas, distances and densities in geography.
- Mathematics(1 mk)
- Identify the types of rocks in the earth’s crust.
-
- Orbit.
- The path that the planet follows as they move round the sun.(1 mk)
-
- Orbit.
-
-
-
- Specific shape of the earth.
- Geoid/Oblate Spheroid(1 mk)
- Forces responsible for the shape of the earth.
- Centrifugal force
- Centripetal force
- Force of gravity/Gravitational force
(3 x 1 = 3 mks)
- Specific shape of the earth.
- Reasons why the earth is believed to be spherical in shape.
- Circumnavigation: it is possible to fly or sail round the earth following one direction and coming back to the same point of origin.
- When a ship is approaching a port, an observer standing on a cliff or any raised ground will first see the smoke and then the other parts of the ship will appear gradually/two ships following each other at a given distance, the nearest will be seen first while the one behind will be seen later.
- During the eclipse of the moon, the shadow of the earth casted onto the moon appears spherical.
- The earth’s horizon is always circular.
- Since all other planets, the moon and the sun are round when viewed through a telescope, it follows the earth being one of the planets must also be round.
- Photographs taken by satellite at great distance away from the earth shows that the earth is round.
- The earth rotates from west to east. Therefore the sun appears earlier in the east than in the west.
(Any 4 x 1 = 4 mks)
-
-
- Weaknesses of the passing star theory.
- The origin of the passing star and the sun is not mentioned.
- The high temperature material drawn from the sun would disperse rather than condense.
- The chances of another star approaching the sun is minimal.
- The gaseous materials drawn from the sun would continue following the star since it had greater gravitational pull.
- The effects of the star would have stopped by now but the planets are still in motion.
(Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks)
- Effects of the earth’s revolution.
- It causes lunar eclipse
- It causes the four seasons
- It causes varying lengths of day and nights
- It causes changes in the position of the midday sun at different times of the year
(Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks)
- Weaknesses of the passing star theory.
-
- Occurrence of solar eclipse.
- Solar eclipse occurs when the moon lies between the sun and the earth
- The moon’s shadow is casted onto the earth
Text – 2
Diag – 4
- Differences between solar eclipse and lunar eclipse.
(Any 2 x 2 = 4 mks)Solar eclipse Lunar eclipse Occurs during the day Occurs at night Moon’s shadow is casted on the earth The earth’s shadow is casted onto the moon Occurs when the moon has between the sun and the earth Occurs when earth lies between the sun and the moon
- Occurrence of solar eclipse.
-
- Specific dates of the year when the overhead position of the midday sun is on the following latitudes.
- Tropic of cancer - 21st June (1 mk)
- Tropic of Capricorn- 22nd December (1 mk)
- Equator - 21st March/23rd September (1 mk)
-
- 60º + 40º = 100 √(1)
100 x 4 = 400 minutes √ (1)
400/60 = 6hr 40 min √ (1)
7.30
+6.40
2.10 p.m. √(1)
- 60º + 40º = 100 √(1)
- Specific dates of the year when the overhead position of the midday sun is on the following latitudes.
-
- Minerals that makes up the earth’s crust.
- Silica
- Magnesium
- Aluminium
(3 x 1 = 3 mks)
- Characteristics of the mantle.
- It is made up of two parts, the upper mantle and the lower mantle
- It is composed of silicate rocks
- The dominant mineral is olivine
- Upper mantle is made up of semi-solid rocks
- Lower/inner mantle is made up of liquid rocks
- Mantle has a density ranging from 3.0 – 3.3 gm/cc
- Mantle has a thickness of 2900km
- Mantle lies between the crust and the core
- Mantle has a temperature of about 5000oc
(Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks)
- Minerals that makes up the earth’s crust.
-
- Elements of weather.
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Precipitation
- Wind
- Sunshine
- Cloud cover
(Any 4 x 1 = 4 mks)
- Factors that determine the amount of solar radiation reaching the earth’s surface.
- Intensity of the sun’s radiation in the space
- Transparency of the atmosphere
- Position of the earth on its orbit
- Inclination/angle of the surface on which the sun’s rays fall
- Nature of the surface on which the sun’s rays fall
(Any 4 x 1 = 4 mks)
- Elements of weather.
-
- The purpose of the following items in a weather station.
- Stevenson screen - For keeping weather recording instruments (1 mk)
- Hygrometer - Used for measuring humidity (1 mk)
- Barometer - Used for measuring atmospheric pressure (1 mk)
- Main zones of the atmosphere.
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere/Ionosphere
(4 x 1 = 4 mks)
- The purpose of the following items in a weather station.
-
- Formation of relief rainfall.
- Moist air rises over hill or mountain
- The moist air expands, cools and condense to form clouds
- Eventually, this leads to rain falling on the windward slope
- The rain bearing winds lose their moisture on the windward slopes
- On crossing the relief barrier, they become dry descending cold winds
Text – 3
Diag – 4
-
- High clouds.
- Cirrus
- Cirro – stratus
- Cirro – cumulus
(3 x 1 = 3 mks)
- Significance of weather forecasting.
- It helps to determine the farmers calendar
- It helps to determine suitable clothing for the day
- It influences the fishing habitats
- It helps to determine the time for air and sea travels
- It determines the military activities
- It determine suitable housing
(Any 4 x 1 = 4 mks)
- High clouds.
- Formation of relief rainfall.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Geography Questions and Answers - Form 1 Mid Term 2 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students