SECTION A : 40MKS
- The following are branches of physics. Elaborate what each one of them entails.
- Thermodynamics (1mk)
- Atomic physics (1mk)
- State how
- Physics is related to Religion (1mk)
- Physics is related to Homescience (1mk)
- Define a laboratory (1mk)
- State the first aid measures you would undertake if any of the following calamities befall you:
- Cuts (1mk)
- Eye damage due to chemicals (1mk)
- Define length stating its SI units (2mk)
- A 240 cm long rod when standing perpendicular to the ground cast its shadow 160 cm long on the ground. If a tree casts its shadow 990cm long on the ground at the same time, determine the height of the tree (3mks)
- The diameter of the bore of capillary tube is 2.0mm. Calculate the cross section area of the bore in cm2. (take π=3.142) (3mks)
-
- Define density of substance. (1mk)
- A cylindrical glass of mass 770 grams has a radius of 7cm and height 20cm. Calculate its density in g/cm3 (3mks)
- The mass of a density bottle is 20g when empty and 45g when full of water. When full of mercury, its mass is 360g. Determine the density of mercury (take density of water to be 1gm/cm3)
Calculate- Mass of water (1mk)
- Volume of water (1mks)
- Volume of mercury (1mk)
- Density of mercury (2mks)
-
- Define a force stating its SI units (2mk)
- A form 1 student has a mass of 60kg. Determine his weight (g = 10N/kg) (2mks)
- The figures below shows a free spring and stretched spring. Indicate with arrows the tension forces in fig (ii) (1mk)
-
- Name two situations where friction is applied (2mks)
- A body weighs 30N in air and 26 N when immersed in water. Determine the upthrust force experienced by the body while inside water (3mks)
-
- State how the following factors affect surface tension in a liquid (2mks)
- Presence of impurities
- Rise in temperature
- Explain;
Why the meniscus of water curves upwards as shown below (2mks)
- State how the following factors affect surface tension in a liquid (2mks)
- Trucks which carry heavy loads have many wheels. Explain (2mks)
SECTION B: 60 MKS
- State three (3) differences between MASS and WEIGHT (3mks)
MASS WEIGHT - A diver is 8m below the surface of water in a dam. If the density of water is 1000kg/m3 determine the pressure due to the water on the diver (take g = 10N/kg) (3mks)
-
- State the principle of transmission of pressure in liquids (1mk)
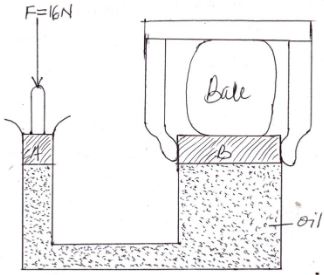
- The figure below shows a simple hydraulic press used to compress a bale. The cross section areas of A and B are 0.002m2 and 0.30m2 respectively.
Determine- Pressure exerted on the oil by the force 16N applied at A (2mks)
- Force produced on B compressing the bale. (hint: pressure on B = pressure on A) (3mks)
-
- Define ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE. (1mk)
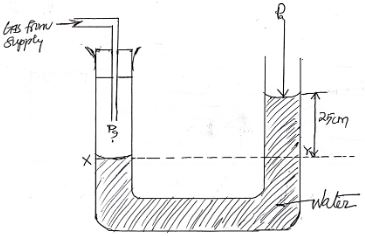
- The following diagram shows one limb of a manometer connected to a gas supply. And due to the pressure of the gas Pg the water level in the other limb has risen a height as shown.
Pg = gas pressure
Pa = atmospheric pressure
Determine pressure of the gas, Pg given that atmospheric pressure = 103000N/M2, density of water = 1000Kg/m3 and g = 10N/kg (3mks)
- A lift pump is used to raise water from wells. Why is the pump unable to raise water the theoretical height of 10m (2mks)
-
- State the kinetic theory of matter state (1mk)
- How does temperature affect Brownian motion (1mk)
- Give two reasons why it is possible to compress gases but not solids or liquids (2mks)
-
- What is diffusion (1mk)
- State two (2) factors on which diffusion of a gas depends on: (2mks)
-
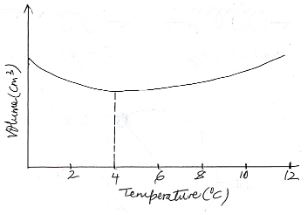
- What is anomalous expansion of water (1mk)
- Draw a graph of volume of water against its temperature as it is heated and its temperature is raised from 0°C to 15°C (3mks)
- State two effects of anomalous expansion of water (1mk)
-
- Draw a well labelled diagram of a liquid in glass thermometer (3mks)
- state the functions of the main features of the thermometer you’ve drawn above (3mks)
- Draw a well labelled diagram of a liquid in glass thermometer (3mks)
- State three (3) differences between alcohol and mercury as thermometric liquids (3mks)
Alcohol mercury -
- Differentiate between heat and temperature (2mks)
-
- State the three factors affecting thermal conductivity of a material (3mks)
-
- Define convection (1mk)
- State two types of convections (2mks)
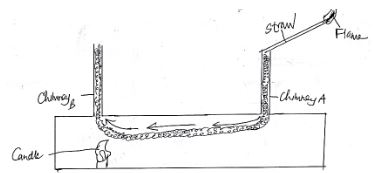
- In an experiment to demonstrate convection currents in gases, in which a candle was lighted underneath chimney B and a burning straw attached to chimney A as shown below. Show on the diagram what happens to the smoke that is produced by the burning straw (2mks)
- Give an explanation of what you have indicated in the diagram in 27 (b) (3mks)
-
- Define thermal radiation (1mk)
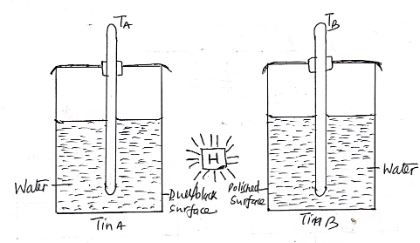
- In an experiment to compare absorption of heat by different surfaces, the following setup was used and temperatures by thermometers TA and TB were recorded after 2 minutes. Water in tins A and B was cold at the same temperature at the beginning of the experiment and the source of heat, H placed equal distant from tins A and B.
- Which of the two thermometers recorded the higher reading (1mk)
- Give a reason for your answer in (i) above (2mks)
- What conclusion can you draw from the graph you have drawn (1mks)
- State which feature in the thermos flask (vacuum flask) reduces heat loss through
- conduction and convention (1mks)
- radiation (1mk)
- Evaporation (1mk)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A: 40MKS
- The following are branches of physics. Elaborate what each one of them entails.
- Thermodynamics (1mk)
- It is the study of the transformation of heat to and from other forms of energy
- Atomic physics (1mk)
- It involves the study of the behaviour of particles constituting the nucleus and the accompanying energy changes
- Thermodynamics (1mk)
- State how
- Physics is related to Religion (1mk)
- Systems in the universe reveal great orderliness which can be traced back to the creator
- Physics is related to Homescience (1mk)
- Physics knowledge has been applied in the design and manufacture of kitchen equipments.
- Physics is related to Religion (1mk)
- Define a laboratory (1mk)
- It is a room designed and equipped for the conducting of experiments and practical work in the course of the studying science subjects.
- State the first aid measures you would undertake if any of the following calamities befall you:
- Cuts (1mk)
- Seek assistance to stop bleeding and for immediate dressing up of the wound
- Eye damage due to chemicals (1mk)
- Wash with a lot of water then seek treatment.
- Cuts (1mk)
-
- Define length stating its SI units (2mk)
- Length is a measure of distance between two points expressed in meters
- A 240 cm long rod when standing perpendicular to the ground cast its shadow 160 cm long on the ground. If a tree casts its shadow 990cm long on the ground at the same time, determine the height of the tree (3mks)
height of tree = lenght of the shadow of the tree
height of rod length of the shadow of the rod
h = 990 cm
240cm 160 cm
H = 990 x 240
160
= 1485cm
- Define length stating its SI units (2mk)
- The diameter of the bore of capillary tube is 2.0mm. Calculate the cross section area of the bore in cm2. (take π=3.142) (3mks)
Cross section area = πr2
= 3.142 x (2/2)2
100
= 3.142 x1
100
= 0.0142cm2 -
- Define density of substance. (1mk)
- Density is mass per unit volume expressed in kilogram per cubic meter
- A cylindrical glass of mass 770 grams has a radius of 7cm and height 20cm. Calculate its density in g/cm3 (3mks)
Density = mass
volume
= 770
22/7 x 7 x 7 x 20
= 770
22x7x20
= 0.25 g/cm3 - The mass of a density bottle is 20g when empty and 45g when full of water. When full of mercury, its mass is 360g. Determine the density of mercury (take density of water to be 1gm/cm3) Calculate
- Mass of water (1mk)
Mass of water =45 – 20 = 25g - Volume of water (1 mks)
= 25cm3
1 g/cm3
= 25cm3 - Volume of mercury (1mk)
Volume of mercury = volume of density bottle
= 25cm3 - Density of mercury (2mks)
Density of mercury = mass of hg
volume of hg
= 3400
25
= 13.6 g/cm3
- Mass of water (1mk)
- Define density of substance. (1mk)
-
- Define a force stating its SI units (2mk)
- It is a push or a pull, expressed in newtons
- A form 1 student has a mass of 60kg. Determine his weight (g = 10N/kg) (2mks)
Weight = mass x gravitational field intensity
W = mg
W = 60 x 10
= 600 N - The figures below shows a free spring and stretched spring. Indicate with arrows the tension forces in fig (ii) (1mk)
- Define a force stating its SI units (2mk)
-
- Name two situations where friction is applied (2mks)
- Walking
- braking
- A body weighs 30N in air and 26 N when immersed in water. Determine the upthrust force experienced by the body while inside water (3mks)
upthrust = weight in water – weight in air
= 30 – 26
= 4N
- Name two situations where friction is applied (2mks)
-
- State how the following factors affect surface tension in a liquid (2mks)
- Presence of impurities
- Presence of impurities in a liquid reduce surface tension
- Rise in temperature
- Rise in temperature lowers surface tension
Or - Drop in temperature raise surface tension.
- Rise in temperature lowers surface tension
- Presence of impurities
- Explain;
Why the meniscus of water curves upwards as shown below (2mks)- Adhesive force between water and glass molecules is greater than the cohesive force between the water – water molecules hence water rises up the tube so that more water molecules can be in contact with the glass.
- State how the following factors affect surface tension in a liquid (2mks)
- Trucks which carry heavy loads have many wheels. Explain (2mks)
- Many wheels offer a larger area upon which heavy loads on trucks acts. Hence exerting minimum pressure (less penetration) on the ground / road.
SECTION B: 60 MKS
-
- State three (3) differences between MASS and WEIGHT (3mks)
MASS WEIGHT It is quantity of matter in a body
It is measured in kilogram
It is the same everywhere
It is measured using a beam balance
Has magnitude onlyIt is the pull of gravity in a body
It is measured in newton
It changes from place to place
It is measured using a spring balance
Has both magnittude and direction
- State three (3) differences between MASS and WEIGHT (3mks)
- A diver is 8m below the surface of water in a dam. If the density of water is 1000kg/m3 determine the pressure due to the water on the diver (take g = 10N/kg) (3mks)
Pressure on driver = density of water x depth x gravitational field/ intensity
= dhg
= 1000 x 8 x 10
= 80000 N/m2 -
- State the principle of transmission of pressure in liquids (1mk)
The principal states that:- Pressure applied at one part in the liquid is transmitted equally to all other parts of the enclosed liquid.
- The figure below shows a simple hydraulic press used to compress a bale. The cross section areas of A and B are 0.002m2 and 0.30m2 respectively
Determine- Pressure exerted on the oil by the force 16N applied at A (2mks)
Pressure = force
area
= 1600
0.002
= 80, 000 N/m2 - Force produced on B compressing the bale. (hint: pressure on B = pressure on A) (3mks)
Pressure on B = pressure on A - force = 80,000
area
Force = 80,000 x 0.30
= 24, 000 N
- Pressure exerted on the oil by the force 16N applied at A (2mks)
- State the principle of transmission of pressure in liquids (1mk)
-
- Define atmospheric pressure. (1mk)
- It is the pressure exerted on the surface of the earth by the weight of the air column.
- The following diagram shows one limb of a manometer connected to a gas supply. And due to the pressure of the gas Pg the water level in the other limb has risen a height as shown.
Pg = gas pressure
Pa = atmospheric pressure
Determine pressure of the gas, Pg given that atmospheric pressure = 103000N/M2, density of water = 1000Kg/m3 and g = 10N/kg (3mks)
Pressure at Y = atmospheric pressure + pressure due to the column of the water
= 103000 + shg
= 103000 + 1000x 10 x 25
100
= 105, 500 N/m2
- Define atmospheric pressure. (1mk)
- A lift pump is used to raise water from wells. Why is the pump unable to raise water the theoritical height of 10m (2mks)
- Low atmospheric pressure in places high above the sea level
- Leakages at the valves and pistons
-
- state the kinetic theory of matter state (1mk)
- Matter is made up of very small particles which are in constant random motion
- How does temperature affect Brownian motion (1mk)
- Rise in temperature makes the particles of a substance to increase their random movement
- Give two reasons why it is possible to compress gases but not solids or liquids (2mks)
- Particles in gases are further apart in solids and gases/ inter particle distances are largest
- Particles in gases lose their energy easily
- state the kinetic theory of matter state (1mk)
-
- What is diffusion (1mk)
- It is the process by which particles spread from regions of high concentration to those of low concentration
- State two (2) factors on which diffusion of a gas depends on: (2mks)
- Density
- Temperature
- What is diffusion (1mk)
-
- What is anomalous expansion of water (1mk)
- It is expansion of water as its temperature is lowered from 4°C to 0°C
- Contraction of water as its temperature is raised from 0°C to 4°C
- Draw a graph of volume of water against its temperature as it is heated and its temperature is raised from 0°C to 15°C (3mks)
- State two effects of anomalous expansion of water (1mk)
- Water pipes burst when the water flowing through the pipes freeze.
- Weathering of rocks: expansion of water in cracks of rocks breaks the rocks in small pieces as water freezes
- What is anomalous expansion of water (1mk)
-
- Draw a well labelled diagram of a liquid in glass thermometer (3mks)
- State the functions of the main features of the thermometer you’ve drawn above (3mks)
- The bulb: its thin glass wall transmits heat effectively between the liquid inside and the body whose temperature is to be taken
- Capillary bore- the liquid expands and contracts along the capillary bore
- Glass stem – it serves as magnifying glass for easy reading of the scale.
- Draw a well labelled diagram of a liquid in glass thermometer (3mks)
- State three (3) differences between alcohol and mercury as thermometric liquids (3mks)
Alcohol mercury Low boiling point 78°C
Low melting point, -115°C
Expansion slightly irregular
Wets glass
TransparentHigh boiling point 357°C
Relatively higher melting point , -39°C
Expands regularly
Does not wet glass
Opaque and silvery -
- Differentiate between heat and temperature (2mks)
- Heat is energy while temperature is degree of hotness or coldness
- Heat is expressed in joules while temperature is expressed in degrees Celsius or kelvin
- Differentiate between heat and temperature (2mks)
-
- State the three factors affecting thermal conductivity of a material (3mks)
- Temperature difference between the ends of the conductor
- The length of conductor
- The cross section area of the conductor
- The nature of the material
- State the three factors affecting thermal conductivity of a material (3mks)
-
- Define convection (1mk)
- It is the process by which heat is transferred through fluids (liquids and gases)
- State two types of convections (2mks)
- Force convection
- Natural convection
- In an experiment to demonstrate convection currents in gases, in which a candle was lighted underneath chimney B and a burning straw attached to chimney A as shown below. Show on the diagram what happens to the smoke that is produced by the burning straw (2mks)
- Give an explanation of what you have indicated in the diagram in 27 (b) (3mks)
- The candle heats up the air above it which expand and rises up because of lower density
- Cold more denser air is drawn in through chimney A carrying along the smoke which replaces the air that is escaping through chimney B
- Define convection (1mk)
-
- Define thermal radiation (1mk)
- Heat transfer through a vacuum
OR - Flow of heat from one place to another by means of electromagnetic waves
- Heat transfer through a vacuum
- In an experiment to compare absorption of heat by different surfaces, the following setup was used and temperatures by thermometers TA and TB were recorded after 2 minutes. Water in tins A and B was cold at the same temperature at the beginning of the experiment and the source of heat, H placed equal distant from tins A and B.
- Which of the two thermometers recorded the higher reading (1mk)
- Ta
- Give a reason for your answer in (i) above (2mks)
- A dull and black surface is a better emitter / radiator of heat than a polished surface
- What conclusion can you draw from the graph you have drawn (1mks)
- Black and dull surfaces are better absorbers of radiant heat than polished surfaces.
- Which of the two thermometers recorded the higher reading (1mk)
- State which feature in the thermos flask (vacuum flask) reduces heat loss through
- conduction and convention (1mks)
- Vacuum
- radiation (1mk)
- Silvery coating/ surface
- Evaporation (1mk)
- Well - fitting cork
- conduction and convention (1mks)
- Define thermal radiation (1mk)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Physics Questions and Answers - Form 1 Term 3 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students